Physics IGCSE Edexcel- Forces and Motion
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Velocity
Speed in a given direction
Acceleration
The rate at which velocity changes
change in velocity can be...
To change speed, change direction or both.
unit for acceleration
m/s^2
Distance-time graphs
gradient= at any point gives the speed
flat line= object stopped/stationary
curve getting steeper= acceleration
curve levelling off= deceleration (slowing down)
Straight line= steady speed
line going back down= object going back to starting point
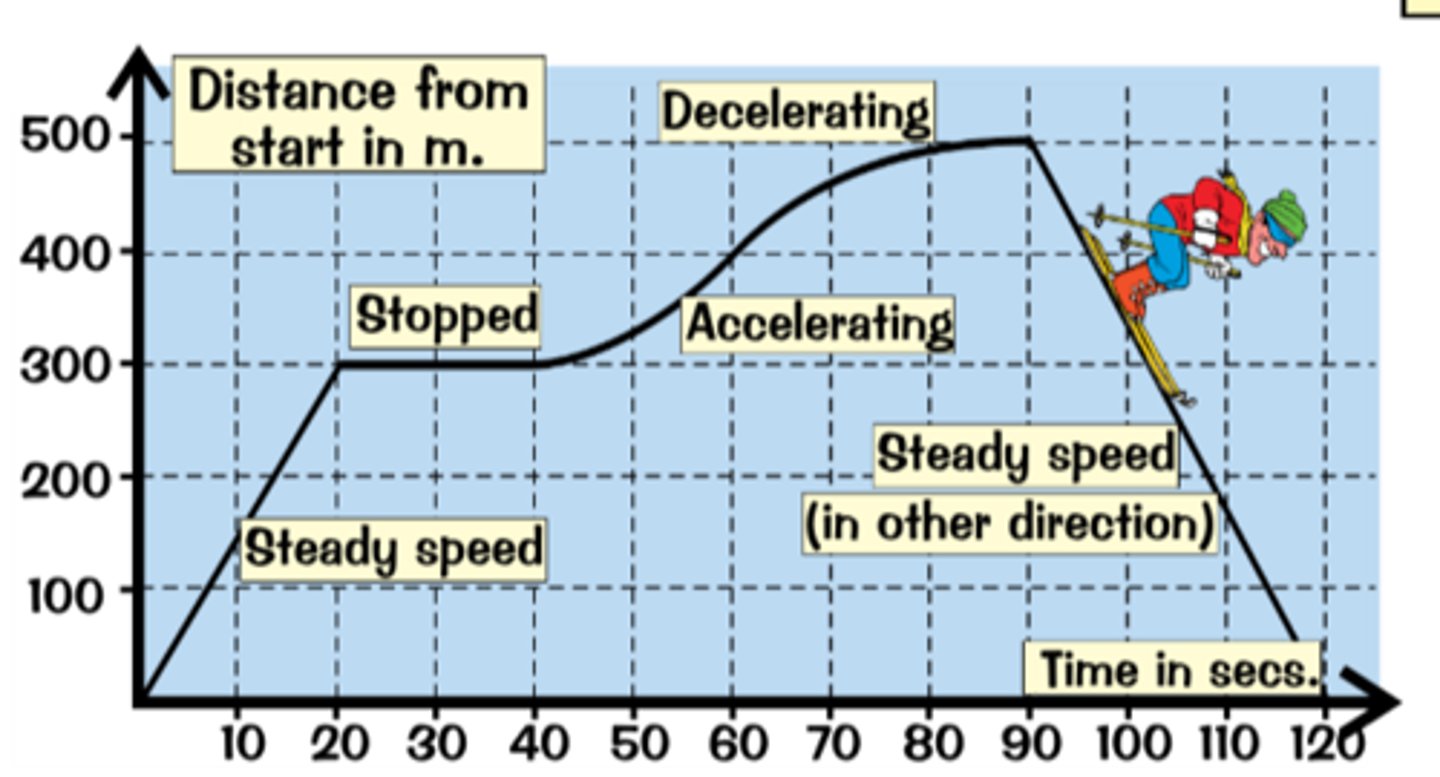
finding speed on a distance-time graph
speed = gradient = vertical/horizontal
finding average speed on a distance-time graph
average speed = total distance/total time
velocity-time graph
gradient= acceleration
flat line= steady speed
steeper line going up or down= greater acceleration or deceleration
uphill sections= acceleration
downhill line= deceleration
area under line= distance travelled in that time interval
curved line= changing acceleration
Acceleration on a velocity-time graph
acceleration = gradient = vertical/horizontal
gravity is...
the force of attraction between all masses
weight
Mass x gravitational field strength (10 on earth)
different types of forces
- gravity or weight
- reaction force
- electrostatic force
- thrust
- drag, air resistance or friction
- lift
- tension
Friction occurs in three main ways:
- static friction - between solid surfaces which are gripping
- sliding friction - between solid surfaces which are sliding past each other
- resistance or "drag" from fluids
The three laws of motion
1. balanced forces mean no change in velocity
2. a resultant force means acceleration
3. reaction forces
First law
Balanced forces mean no change in velocity, this means if an object is not moving then it will stay still, but if an object is already moving then it will carry on at the same velocity
Second law
A resultant force force means acceleration, if there is an unbalanced force (resultant force), then the object will accelerate in that direction.
equation for force
Force = mass x acceleration
Third law
reaction force, if object A exerts a force on object B then object B exerts an equal and opposite force on object A
vectors
quantities that have both a magnitude and a direction
scalars
quantities that have only a magnitude (do not include direction)
vector quantities
force, velocity, acceleration, momentum
scalar quantities
Mass, temperature, time, length
terminal velocity
the constant velocity of a falling object when the force of air resistance is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force of gravity
terminal velocity of an object is dependent on...
the drag of an object. the drag depends on the shape and area
Hooke's Law
Extension is directly proportional to force until the spring reaches it's elastic limit
Hooke's law stops when...
the force becomes great enough. When you get to that point it is called the 'elastic limit', if you increase the force past the elastic limit the material will be permanently stretched
the two main factors affecting stopping distance
- thinking distance
- braking distance
Thinking distance is affected by...
-the speed you're going
-your reaction time (affected by age, drugs, tiredness etc)
Braking distance is affected by...
-how fast you're going (faster=further)
-the mass of the vehicle (bigger mass=longer to stop=go further)
-what condition you're brakes are in
-how good the grip is (depends on road surface, weather conditions, and tyres)
momentum equation
momentum=mass x velocity
momentum conservation
momentum before = momentum after
force and momentum equation
Force = change in momentum / time taken
larger force =
a faster change in momentum
moment equation
Moment = force x distance from pivot
a moment is...
the turning affect of a force
centre of gravity
The point where the entire weight of an object appears to act.
swinging with a centre of gravity
a freely suspended object will swing until its centre of gravity is vertically below the point of suspension
principle of moments - equal
total anticlockwise moments = total clockwise moments
principle of moments - unequal
If the total anticlockwise moments do not equal the total clockwise moments, there will be a resultant moment