1.3 Chemical Calculations
1/30
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is the relative isotopic mass?
The mass of an atom of an isotope relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
e.g. 35Cl has a relative isotopic mass of 35
What is the relative atomic mass (Ar)?
The average mass of one atom of the element relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
What is the relative formula mass (Mr)?
The average mass of a molecule relative to one-twelfth the mass of one atom of carbon-12.
What is a mole?
One mole is the amount of substance that contains the same number of particles as there are atoms of carbon in exactly 12g of carbon-12.
Mass =
Mr x moles
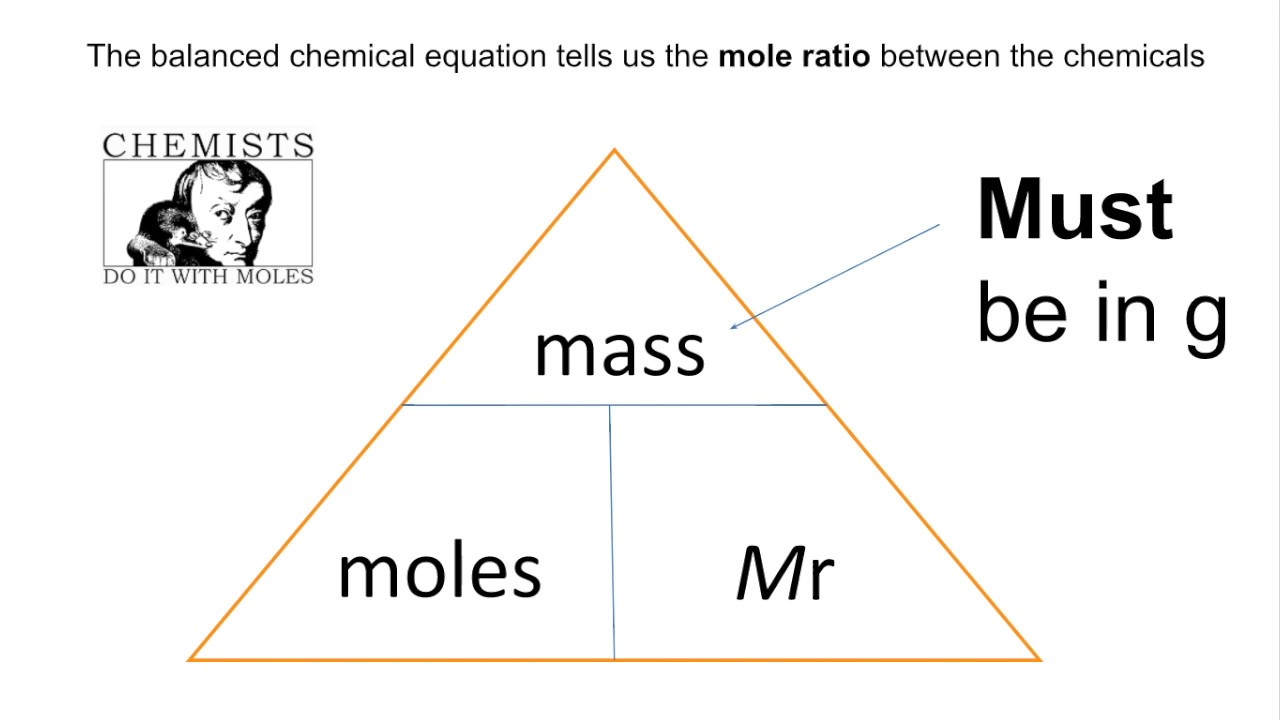
What is the molar mass?
One mole of any substance has a mass equivalent to the Mr of that substance in grams (gmol-1).
e.g. MgCl2 - Mr=95.3, molar mass = 95.3 gmol-1
What is the empirical formula?
Simplest formula of a substance
symbol of elements
% or mass
Ar
moles
divide by smallest mole
ratio
How to calculate reacting masses?
balanced equation
moles of one
ratio for moles of what we need
mass=mrxmoles
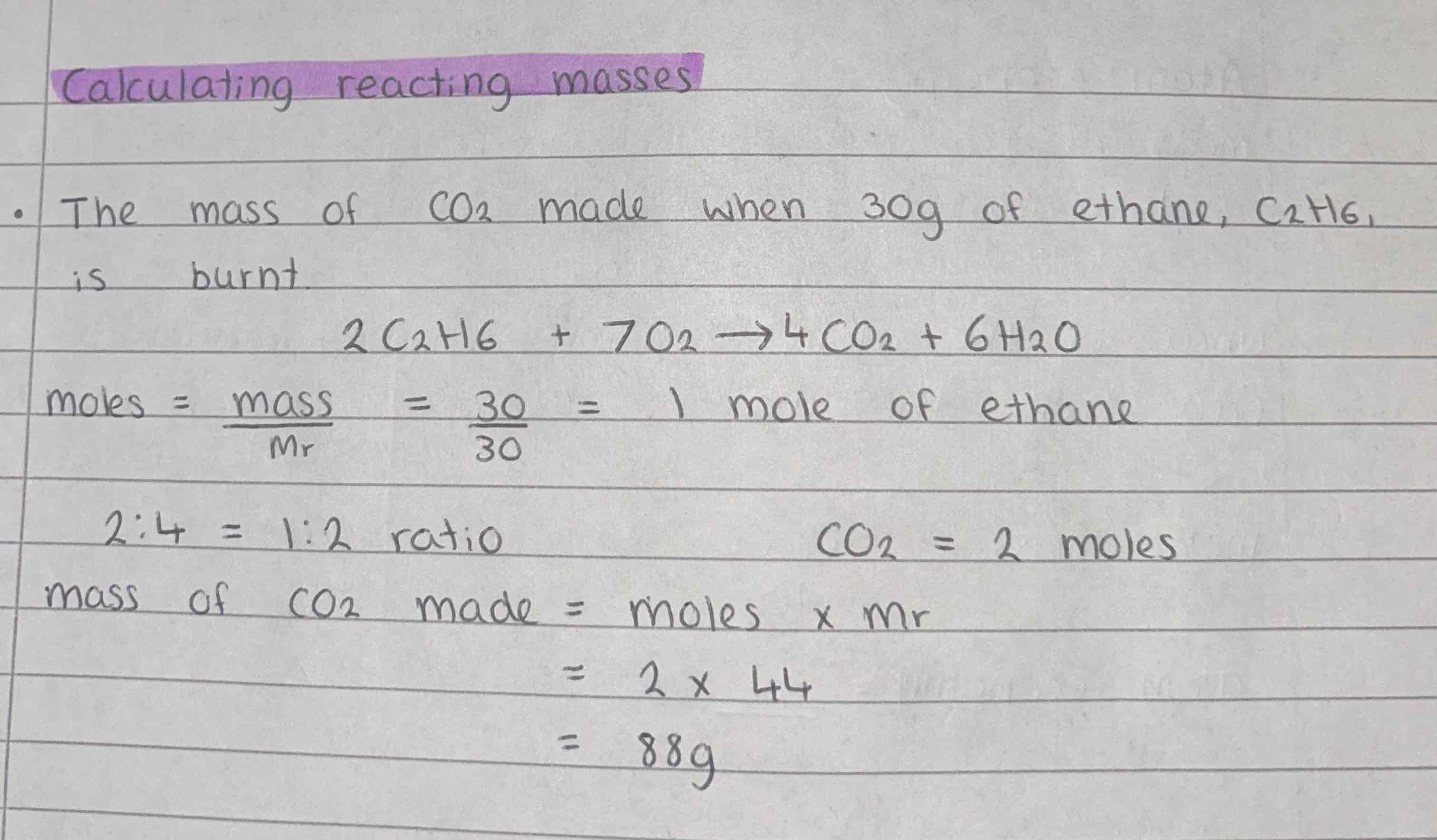
Percentage yield =
mass of product obtained / maximum theoretical mass x 100
Why will percentage yield always be less than 100%?
Due to loss of product during transfer,separation or an incomplete reaction
Atom economy =
mass of required product / total mass of reactants x 100
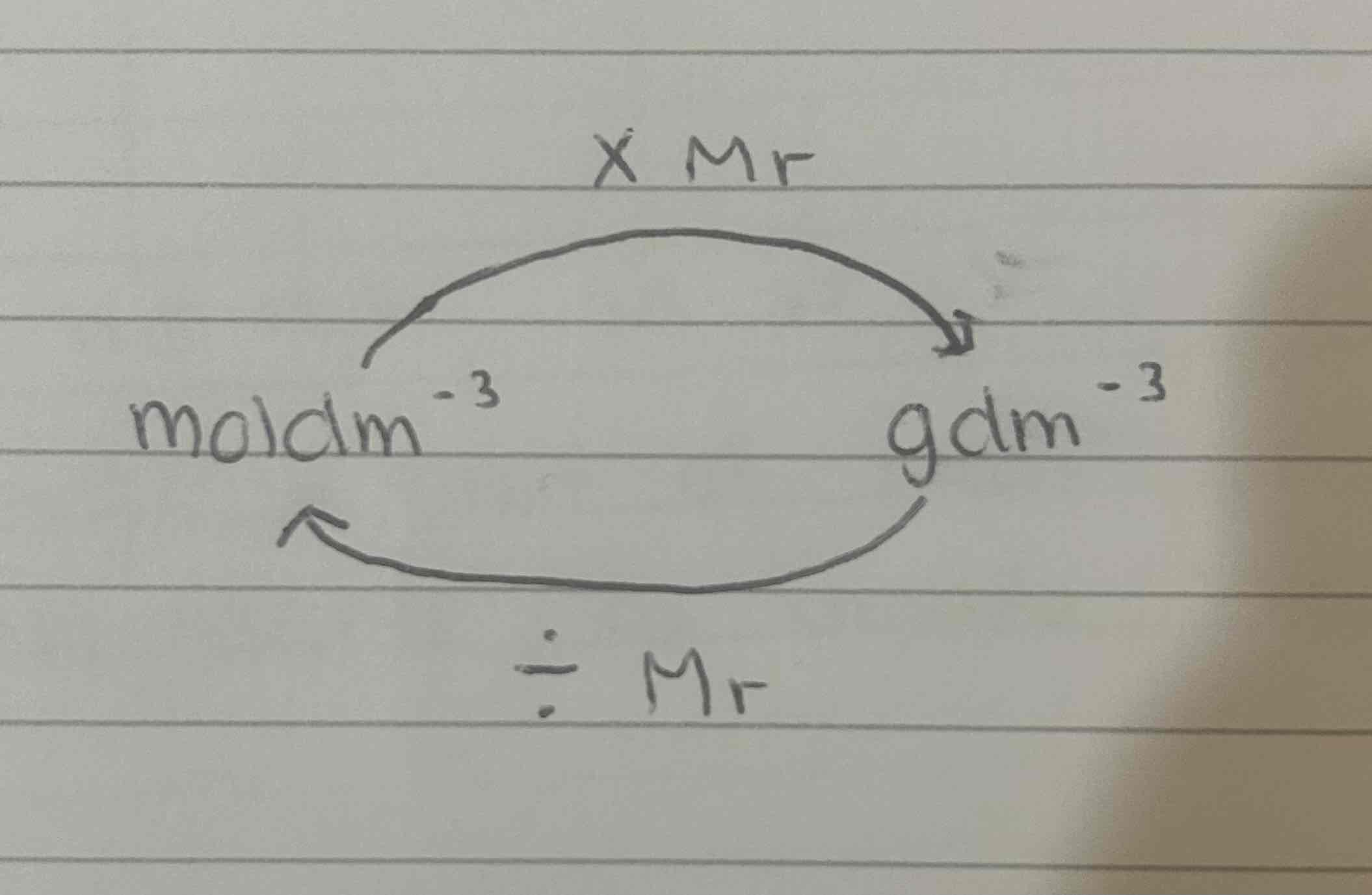
Concentration (moldm-3) =
moles / volume (dm3)
What is neutralisation?
When the number of moles of H+ ions from the acid is equal to the number of OH- ions form the alkali
Molar volume =
Volume (dm3) / moles
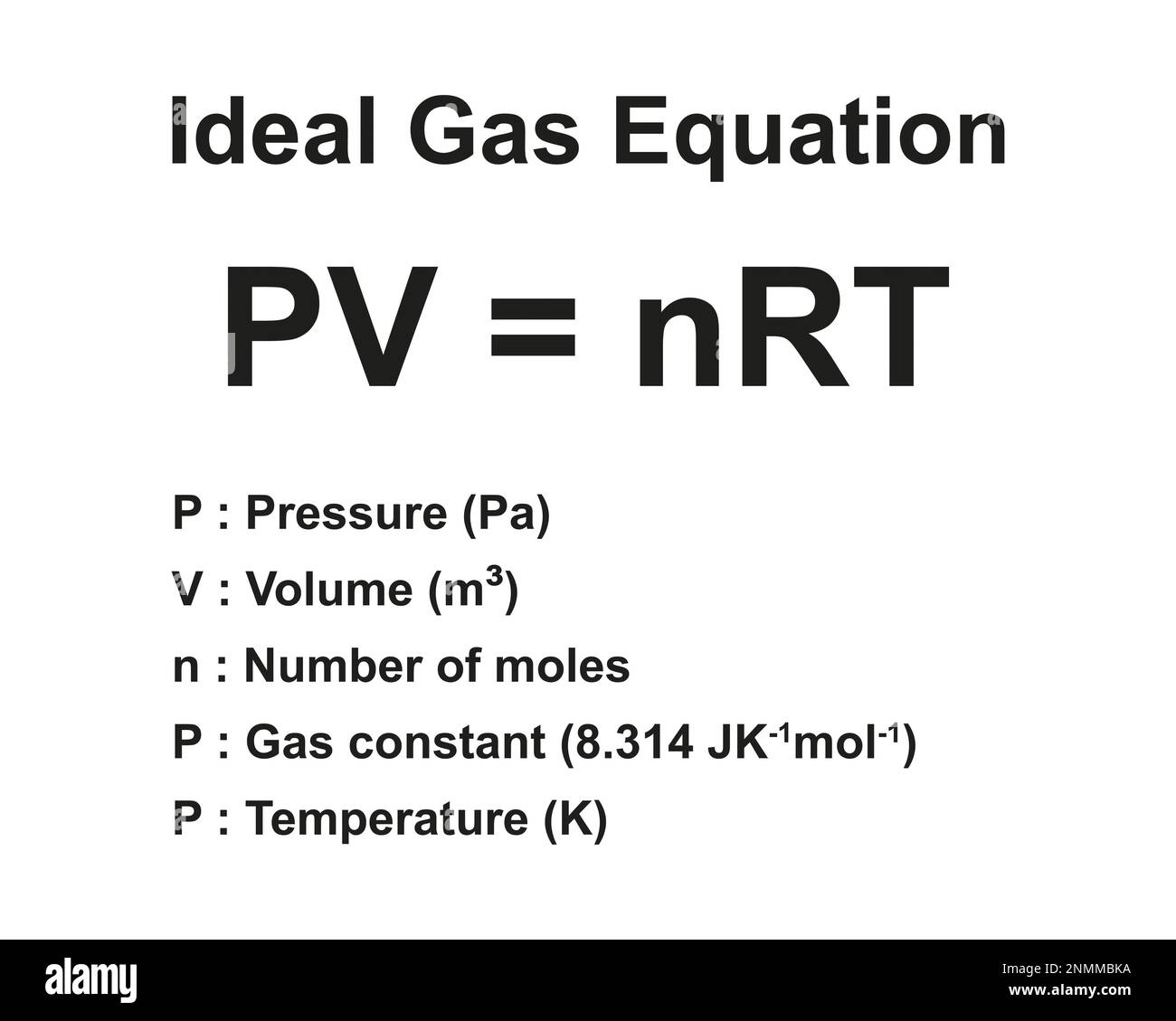
What is the ideal gas equation?
What is the gas equation under changing conditions?
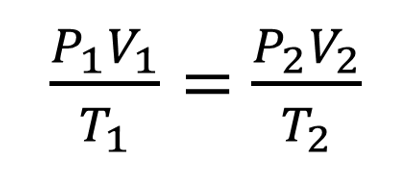
Percentage error =
maximum error / quantity measured x 100
What happens to percentage error on burretes or for temperature change?
Must be doubled
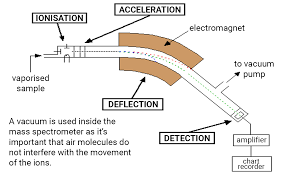
What are the stages of the mass spectrometer?
vaporisation
ionisation
acceleration
deflection
detection
What happens during vaporisation stage of mass spectrometer?
liquid sample is vaporised into a gas
What happens during ionisation stage of mass spectrometer?
beam of electrons knock electrons from atoms or molecules in sample, forming positive ions
What happens during acceleration stage of mass spectrometer?
ions accelerated in electric field so all ions have same kinetic energy
What happens during deflection stage of mass spectrometer?
deflected by electromagnet according to mass and charge
heaver ions are deflected less than light ones
2+ ions are deflected twice as much as 1+ ions
What happens during detection stage of mass spectrometer?
on striking the detector ions accept electrons, lose their charge and create a current
current created is proportional to the abundance of each ion
What are the uses of mass spectrometry?
identifying trace compounds in forensic science
identifying unknown compounds e.g. banned substances in athletes
analysing molecules in space
What are the conditions of mass spectrometry?
vacuum so air molecules don’t interfere with moving ions
Double charged ions
greater charge on ion means more deflection
double charge = half mass
smaller abundance as double ionisation is rare
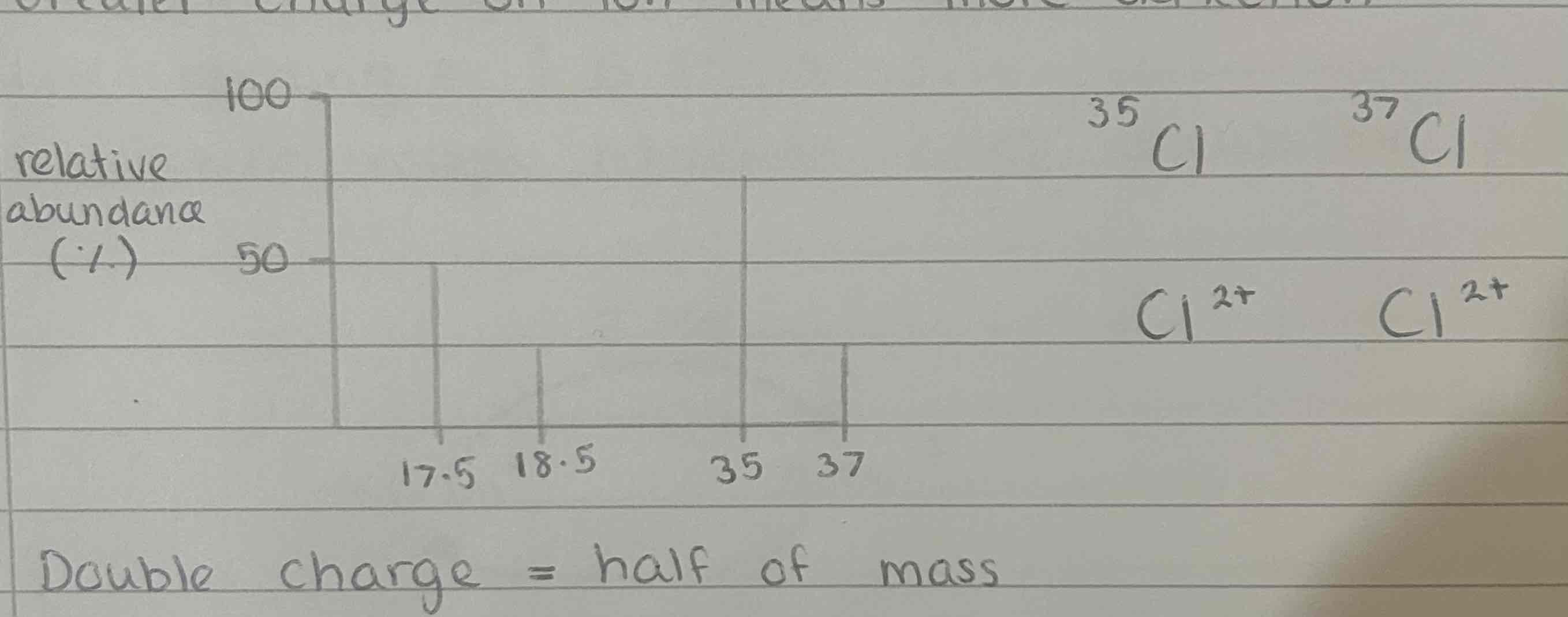
Where are the peaks on the mass spectra of chlorine molecule (Cl2)
at m/z 70 due to 35Cl — 35Cl
at m/z 72 due to 35Cl — 37Cl and 37Cl — 35Cl
at m/z 74 due to 37Cl — 37Cl
Probability of peaks on the mass spectra of chlorine molecule (Cl2)
70 - ¾ x ¾ = 9/16
72 - ¾ x ¼ + ¼ x ¾ = 6/16
74 - ¼ x ¼ = 1/16
How to make a standard solution?
transfer all solid into a beaker, add water until it all dissolves
pour into a volumetric flask through a funnel
fill rest of flask to graduation mark with water
add stopper to flask and shake vigorously
Titration calculations
concordant results = +— 0.20cm3
burette reading = +— 0.05cm3
don’t include rough titration when calculating mean titre