Physics: Unit 13 Radioactivity
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
What is the mass number on a periodic table?
number of protons and neutrons
What is the atomic number on a periodic table?
Number of protons
What is an isotope?
an atom of the same element with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons.
What is an ion?
A charged atom (can be positive or negative)
What is ionisation?
The loss or gain of an electron to create an ion
What is ionising radiation?
Isotopes can be unstable and emit energy from their nuclei. We say that these isotopes are radioactive.
What is this process of isotopes being radioactive known as?
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is a….
random process
What are the four main types of radiation?
Alpha, Beta, Gamma, neutron emission
What is the symbol, nature, and range in air of alpha particles?
α, It is a particle that is made of 2 protons and 2 neutrons. Few millimeters.
What is the symbol, nature, and range in air of beta particles?
β, It is a particle made of electron from the nucleus. 10cm-1m
What is the symbol, nature, and range in air of gamma particles?
γ, It is a electromagnetic wave. meters or even km.
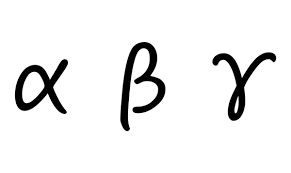
What is alpha stopped by, penetrative power and ionising ability?
Paper or skin, least penetrative power, most ionising ability (dangerous)
Why is alpha the most dangerous?
because it damages DNA/cells → mutation → can lead to cancer (if duplicates). However this is only an issue if ingested as cannot penetrate the skin.
What is beta stopped by, penetrative power and ionising ability?
Thin foil, middle penetrative power, middle ionising ability
What is gamma stopped by, penetrative power and ionising ability?
Thick concrete or lead, most penetrative power, least ionising ability
What is Bequerels (Bq) used for?
The “activity” of a material. How many decays happen per second (how many nuclei ‘kick out ‘ can alpha, beta or gamma each second)
What is sievert (Sv) used for?
Radiation dose (how much alpha beta or gamma something is hit with/recieved)
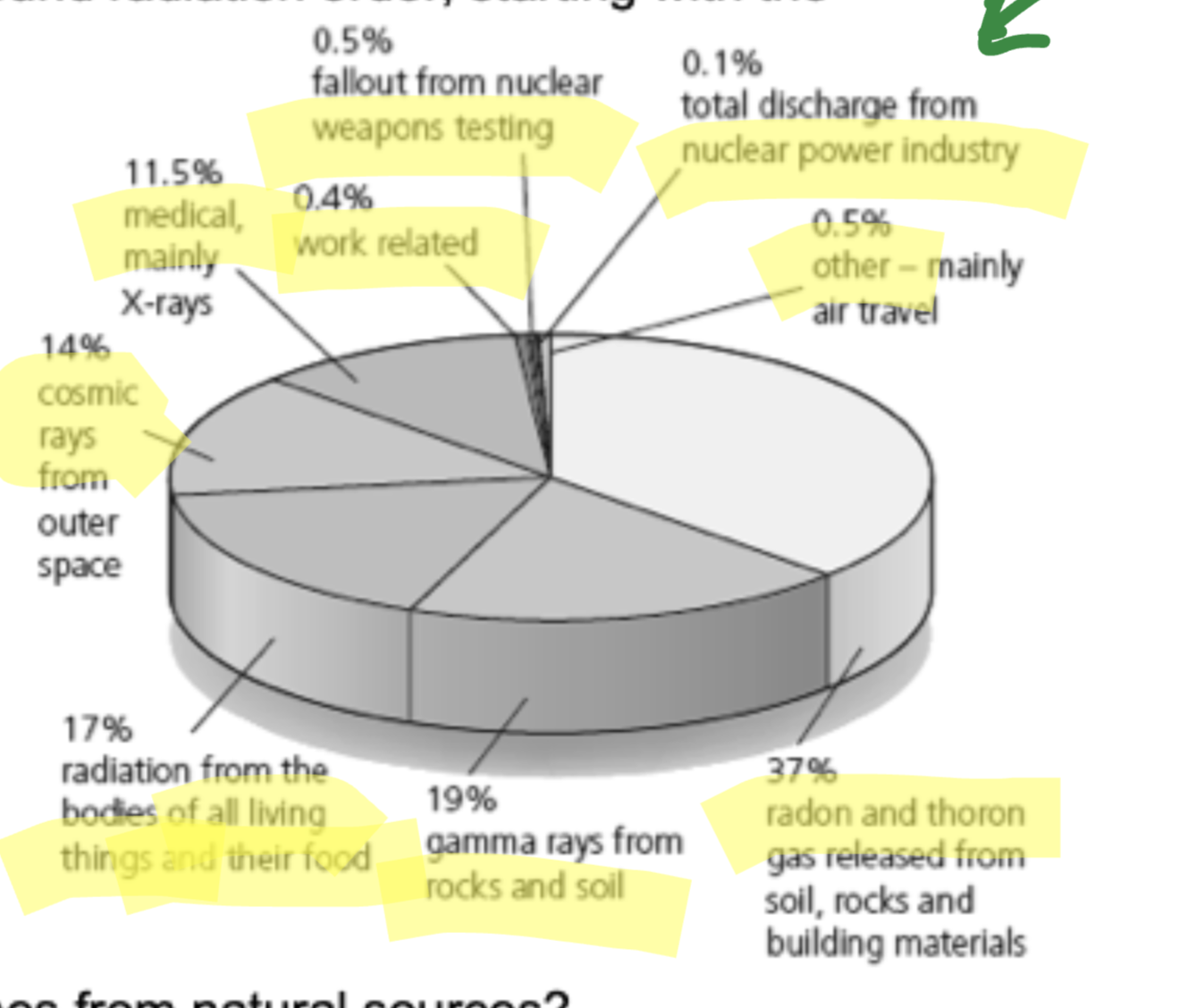
What is background radiation?
Radiation from natural and man-made sources which are exposed to everywhere and at all times.
What is used to measure radiation?
geiger-müller tube / geiger counter
What do the nuclear decay equations measure?
how the unstable nuclei change.
What is alpha’s nuclear decay equation?
The original (parent) nucleus → The new (daughter) element + The alpha particle (2 atomic number, 4 mass number)
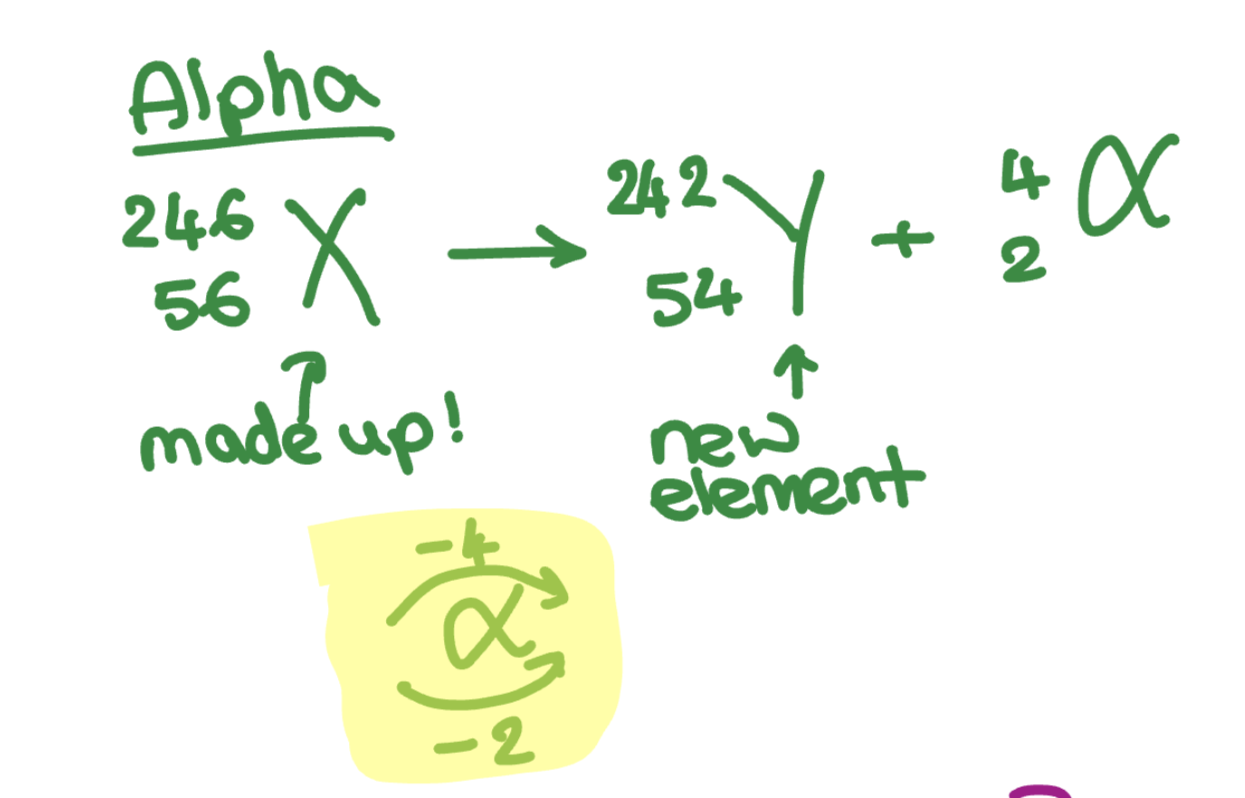
What is beta’s nuclear decay equation?
The original (parent) nucleus → New element + Beta particle (atomic number increases 1 mass number stays same)
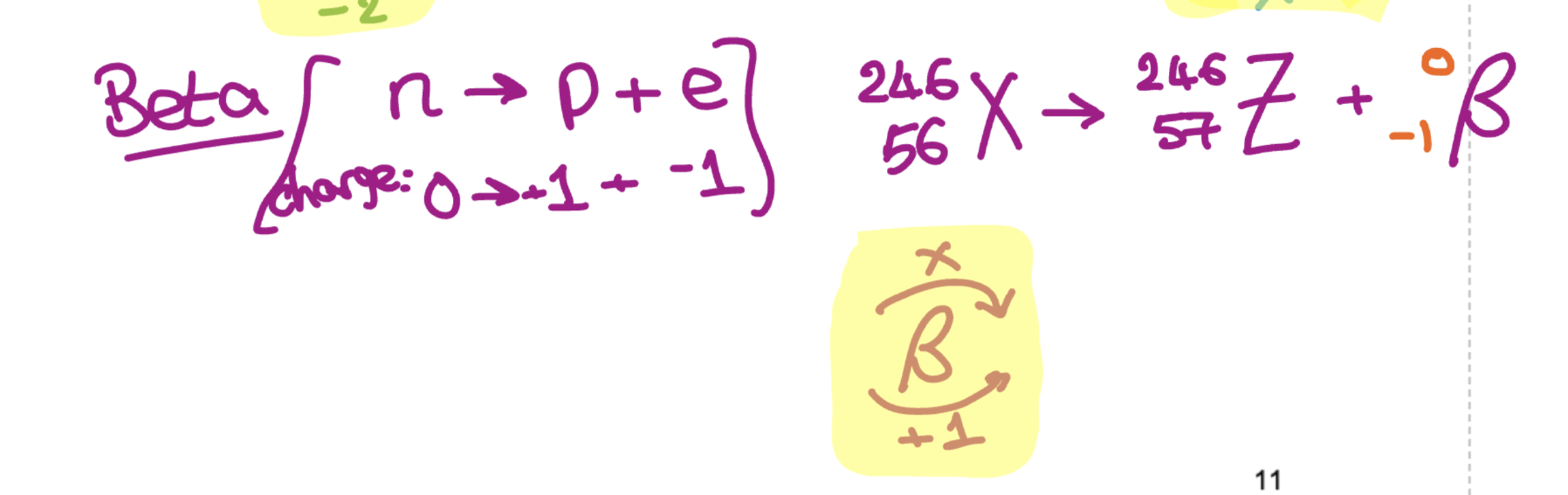
What is neutron’s nuclear decay equation?
The original (parent) nucleus → New element + neutron particle (atomic number stays same mass number decreases 1)

What is half life?
Time for half of the nuclei in a sample to decay.
What will happen to activity in half life?
will decrease over time
What is constant in half life?
“chance” or probability of decay is constant
What do half-life graphs look like?
See diagram
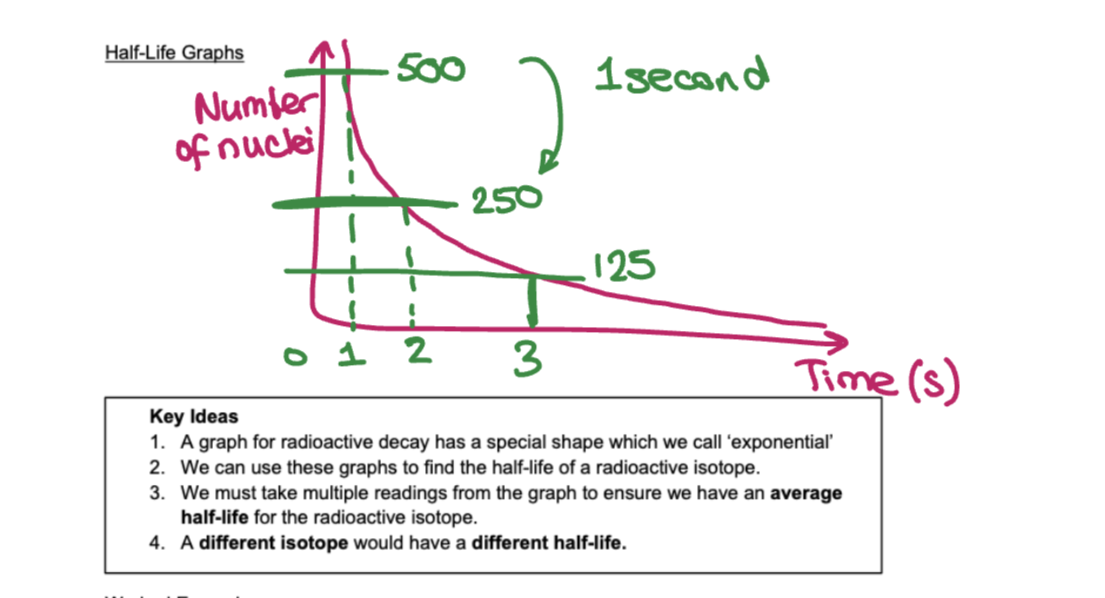
What is contamination?
Contact with the unstable nuclei (constantly being irradiated too)
What is irradiation?
Contact with radiation, but NOT the unstable nuclei.