the eye
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
fovea
center of the retina
only cone cells (no rods) which are less sensitive to light
high visual acuity
optic disc
blind spot
exit of the optic nerve and vessels
retina: direct pathway
photoreceptors
bipolar cells
ganglion cells (send axon projections to the forebrain)
retina: lateral connections
horizontal and amacrine cells
which cells are directly light sensitive?
photoreceptors
which cell type provides output from the retina?
ganglion cells
which cell type can fire action potentials?
ganglion cells
organization of the retina
ganglion cell layer
inner nuclear layer (bipolar cells, amacrine and horizontal cells)
outer nuclear layer (photoreceptors)
photoreceptors
converts light into neutral signals (change in Vm)
rods and cones
contains photopigment proteins that sense light
rods
used during night time or low light levels
contains rhodopsin (photopigment)
1000x more sensitive to light
can’t see low/dark colors
cones
used during day time or high light levels
L, M, and S opsins
L opsins
views mainly red
M opsins
views mainly green
S opsins
views mainly blue
trichromacy
3 cones
dichromacy
2 cones
monochromacy
1 cone
colorblindness
most individuals are anomalous trichromats
shifts of cones among the wavelengths makes it harder to distinguish between colors
why does the fovea have high visual acuity?
there are no cells in the inner layer meaning less scattering and there is less averaging
peripheral retina
more rods than cones
more sensitive to light
what is phototransduction?
light energy causing changes in membrane potential (Vm)
are photoreceptors typical neurons?
no!
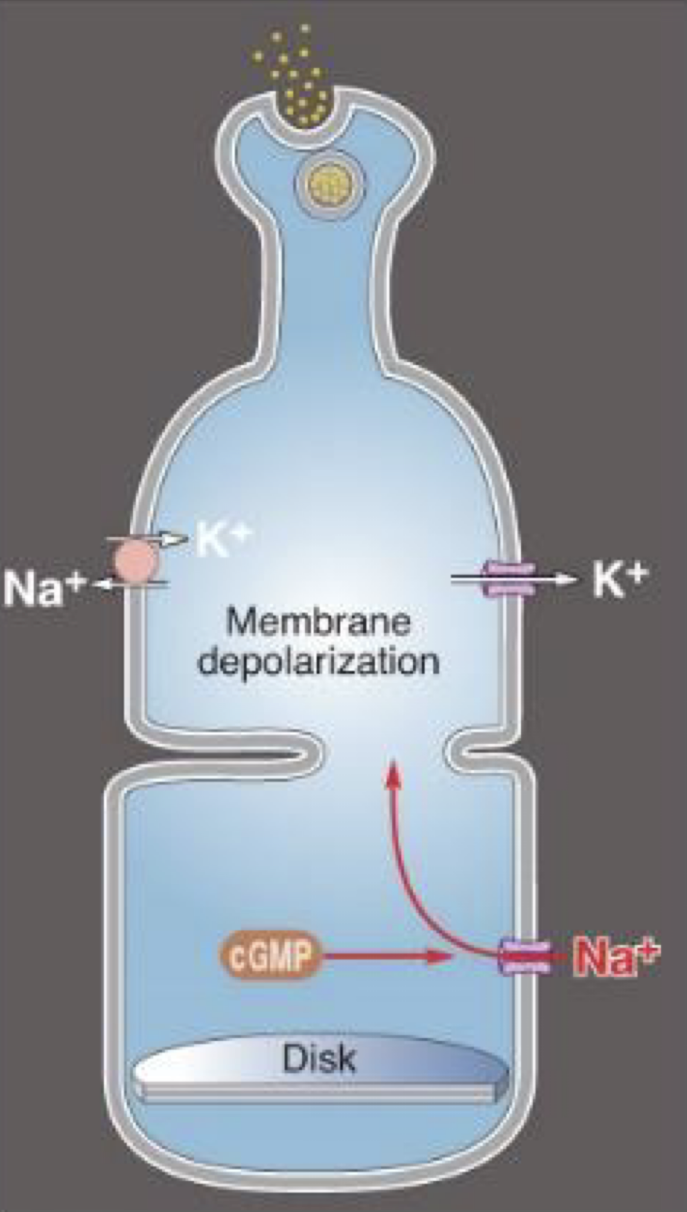
photoreceptors without light..
depolarize at -30 mV
cGMP gated channels (permeable to Na+) are opened
dark Na+ current in the dark
photoreceptors with light..
hyperpolarize at -60 mV
light reduces cGMP to GMP
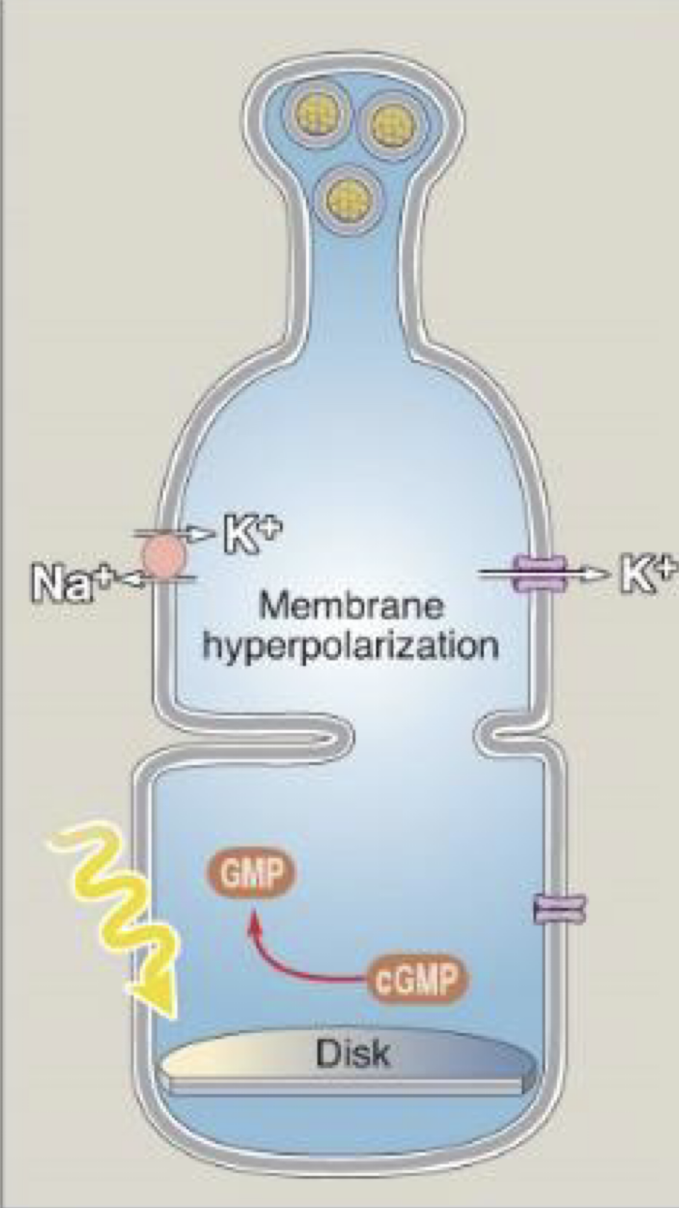
can photoreceptors release neurotransmitters?
yes, but they decrease with light
phototransduction in rods
rhodopsin is activated with light
G protein (transducin) is activated and activates phosphodiesterase (PDE)
PDE reduces cGMP to GMP
Decrease in cGMP causes a cGMP gated Na+ channels to close causing hyperpolarization
photobleaching
when light hits rhodopsin (receptor), 11-cis retinal ligand (inactive form) undergoes conformational changed to all-trans retinal (active form)
rhodopsin activation requires…
11-cis retinal bound to receptor
light
what is the retinoid cycle?
the process of restoring retinal to a form capable of signaling photon capture
all-trans retinal is transported to the pigment epithelium to be converted back to 11-cis retinal
dark adaptation
the transition from all-cone daytime vision to all rod nighttime vision
regeneration of unbleached rhodopsin (opsin and 11 cis retinal)
do rods function during daytime?
no, almost all rods are photobleached and cannot respond to light due to saturation
regeneration of unbleached rhodopsin
retinoid cycle needs to occur
process is slow usually minutes to an hour
light sensitive is higher compared to day time
phototransduction in cones
similar to rods except of the type of opsins
less sensitive to light and more energy is required to photobleaching
what is the receptive field?
the area within which a stimulus changes the avidity of neuron (changes in AP firing on Vm)
where in the visual system are receptive fields found?
retina
bipolar cell receptive field
no dark currents
2 types of bipolar cells that respond to light in the receptive field center: ON bipolar and OFF bipolar cells
ON (center) bipolar cells
cell is depolarized in response to light in the receptive field center
less glutamate is released from photoreceptors which leads to less mGluR6 receptor activation
light in the receptive field surround causes hyperpolarization due to horizontal cells counteracting the light in the center
OFF (center) bipolar cells
cell is hyperpolarized in response to light in the center
less glutamate is released from photoreceptors which leads to less activation of AMPA and kainate receptors
cell is depolarized in the receptive field surround when activated with light
ganglion cell receptive field
ON and OFF center ganglion cells with ligand-gated glutamate channels
the response to stimulation of the center is cancelled by stimulation of the surround
responds to differences in illumination that occur within their receptive field
ON center ganglion cells
input from ON bipolar cells via excitatory synapse
depolarized by light in the center
hyperpolarized by light in the surround
allows us to see edge with high light in center (light increment)
OFF center ganglion cells
input from OFF bipolar cells via excitatory synapse
hyperpolarized by light in the center
depolarized by light in the surround
allows us to see edge with low light in center (dark increment)
why do we need both ON and OFF center ganglion cells?
to allow us to effectively perceive light and dark increments which is contrast
the visual field
binocular visual field
visual hemifields
partial decussation
retina divided into nasal and temporal retina by vertical line passing through the fovea
visual hemifield
left visual hemifield is viewed by right hemisphere
right visual hemifield is viewed by left hemisphere
partial decussation
only fibers from the nasal retina cross
targets of the optic tract
lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) in thalamus to the primary visual cortex (90%)
(10%) midbrain: superior colliculus and pretectum
hypothalamus
superior colliculus
orients the eyes to stimuli (visual grasp)
pretectum
reflect control of the pupil and lens
hypothalamus
controls circadian rhythm
lateral geniculate nucleus
found in dorsal thalamus
major target of optic tract
is input from the two eyes kept separate?
yes
primary visual cortex (striate cortex)
contains 6 layers
layer 4C (=IVC) receives most of LGN inputs
ocular dominance columns
stripes of neurons in the V1 that respond preferentially to input from one eye or the other
layer 4C
each neuron receives input from only one eye
project to layer 4B and 3
layer 4B and 3
integrates information from both eyes
response is still dominated by one eye though they are binocular
binocularity receptive fields
most neurons in layer 2 and layer 3 in the striate cortex are binocular
binocular disparity
difference in the location of a feature between the right eye’s and left eye’s image
basis for the sensation of depth
orientation selectivity
neurons in V1 present the greatest response to a bar with a particular orientation
not a spot of light in the receptive field center
analysis of object shape
direction selectivity
subset of neurons in V1 show direction-selective response to a moving stimulus
analysis of object motion
extrastriate areas
V2, V3, V4, and MT (V5)
dorsal stream
towards parietal lobe
processing of object motion
ventral stream
toward temporal lobe
process stimuli other than motion, such as color and form
critical for facial recognition