Etruscan and Roman Art and Architecture
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and concepts related to Etruscan and Roman art, architecture, and funerary practices.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
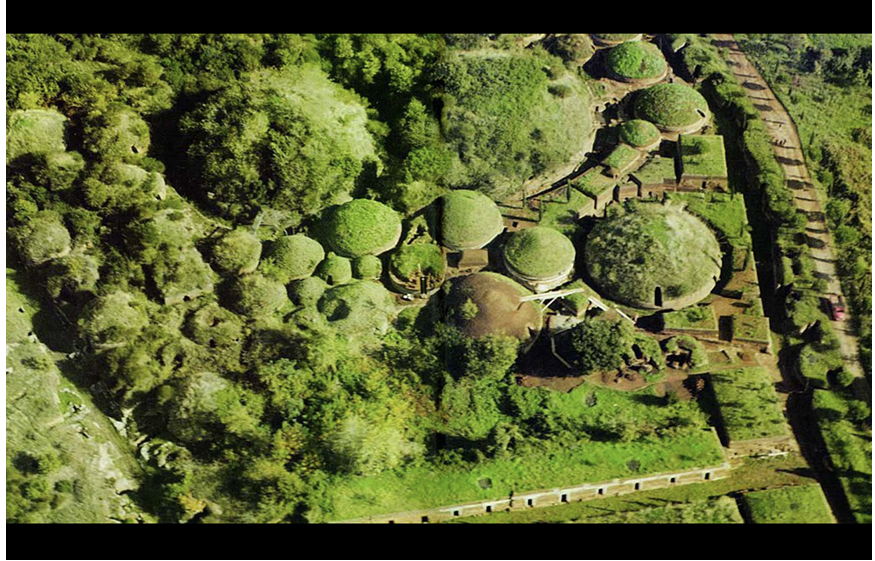

Banditaccia Necropolis at Cerveteri
Tumuli: burial mounds signifying:
Wealth accumulation via trade
Cross-cultural interaction
Emphasis on family lineage (used for generations)
Visible in landscapes, signs of conscious consumption
Made of tufa (volcanic rock)
Transitioned to cube tombs over time
Cube Tombs in Cerveteri
Carved into hillsides
Reflected economic advancement, social stratification
Indicated population growth and urban expansion
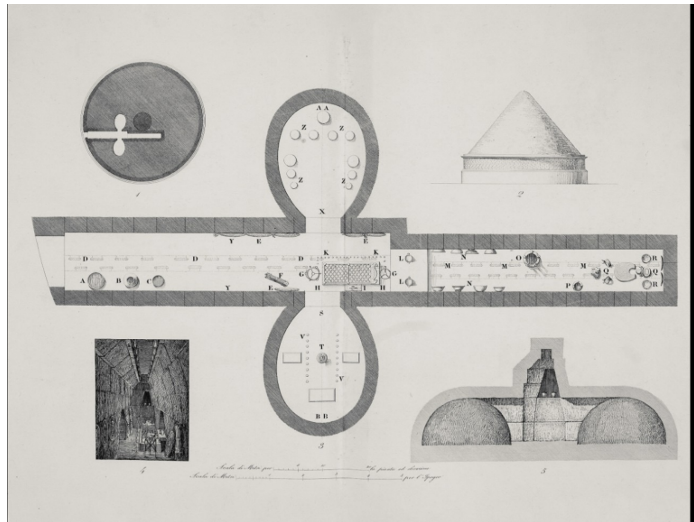
Regolini-Galassi Tomb (700–600 BCE)
Reflects early Etruscan expansion
Features: dromos, vaulted ceilings, house-like design
Inhumation and cremation
Rich grave goods: bronze beds, chariot (ekphora), silver bowls, gold fibula
Advanced metalworking: granulation, filigree, Egyptian & Eastern motifs (lions, birds, water symbols)
Women buried with jewelry, honored in death → status of women
Cross-cultural exchange evident in imported grave goods
Illustrates belief in afterlife and family reputation
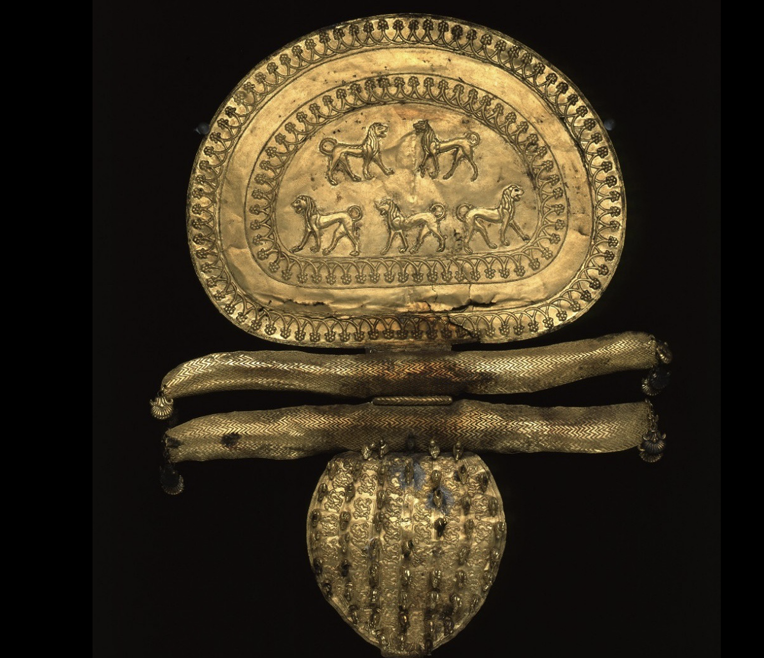

Regolini-Galassi Tomb Fibula
Featured a gold fibula, a pin used to hold garnet.
Craftsmanship Techniques:
Repousse: technique involving pounding metal to create a design.
Filigree: use of delicate threads of gold for decorative purposes.
Granulation: creation of small bead-like pieces of gold.
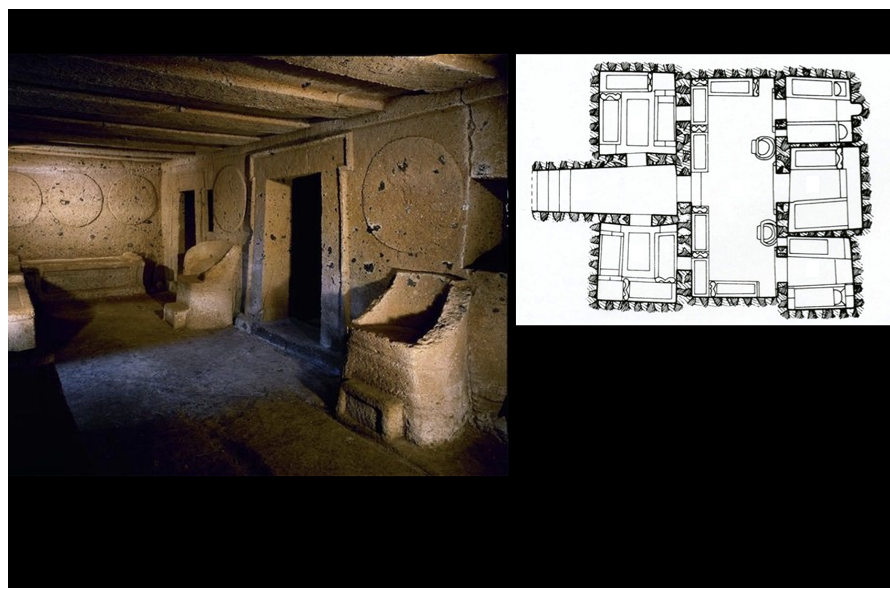
Tomb of the Shields and Chairs
Represents transition from tumuli to house-like tombs
Roof beams carved to mimic homes
Terracotta statues show ancestor veneration, funerary dining
Merges living and dead, ritualized remembrance
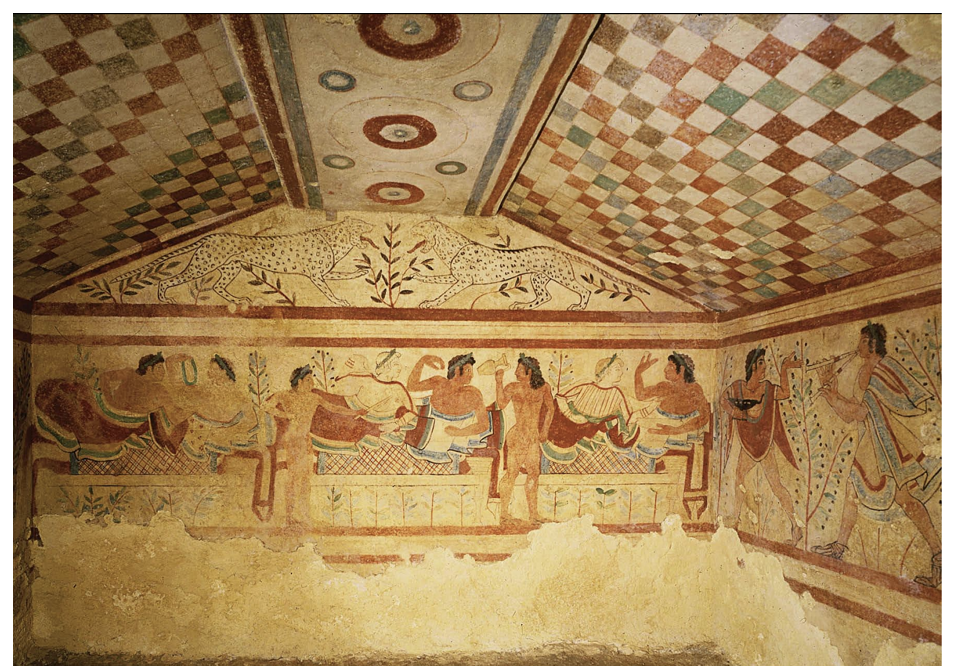

Tomb of Leopards, Tarquinia (c. 480 BCE)
Also shows a symposium
Symbol of rebirth and fertility (egg)
Women shown with light skin tone; participating → high female status
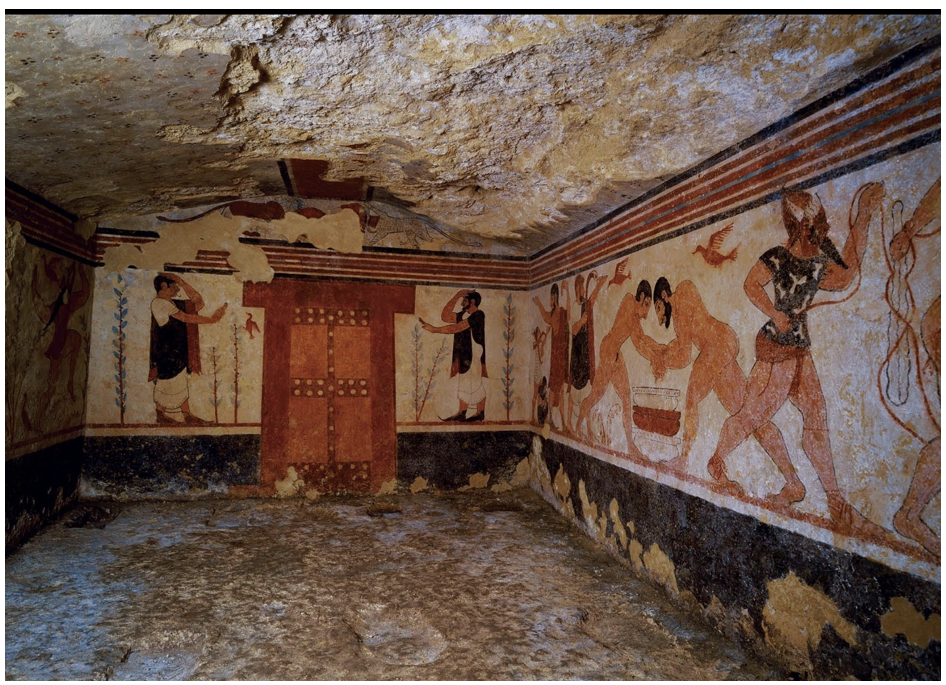

Tomb of Augurs, Tarquinia (c. 520 BCE)
Scenes depicting augury, the practice of interpreting bird behavior to predict the future.
Features elements of funerary games in honor of the deceased:
Wrestling competitions presided over by a gamesmaster with a staff known as a lituus, a symbol of command.
Phersu, a masked character, possibly indicating a bloodsport involving gladiatorial competition; often involved prisoner-of-war participants.
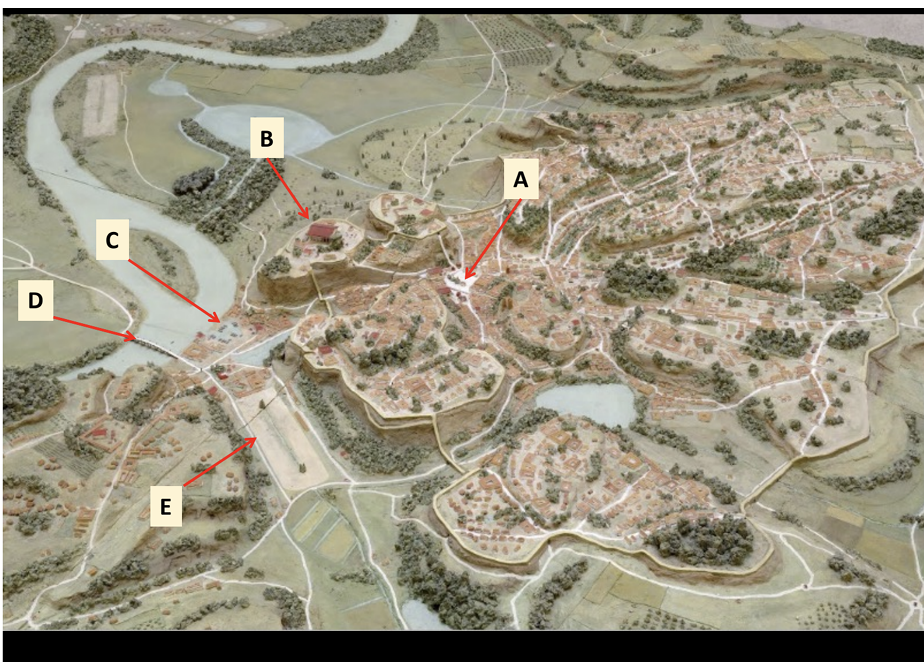
Late Archaic Rome (6th Century BCE)
Key architectural developments include:
The Forum: central public space for civic activities.
Temples of Jupiter Optimus Maximus: significant religious site.
Circus Maximus: arena hosting chariot racing and public spectacles.
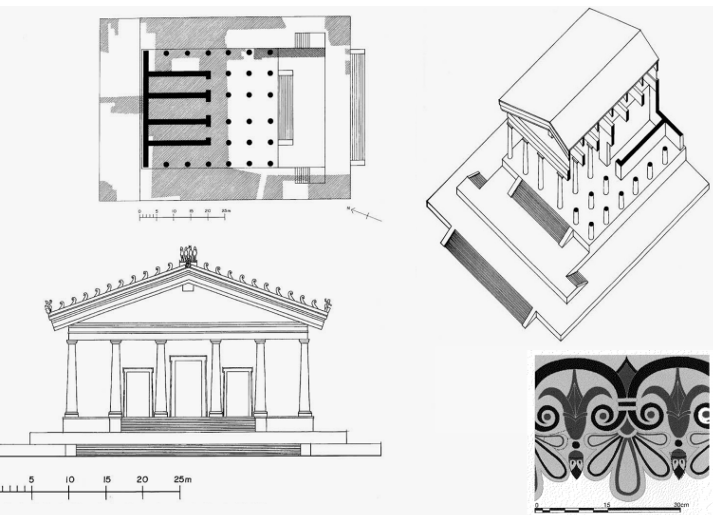
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus (c. 550-500 BCE)
Located on the Capitoline Hill.
Significant features include:
Triple cella dedicated to Juno, Jupiter, and Minerva.
Etruscan style: stairs exclusively in the front, in contrast to earlier architectural forms.
Decorated ridgepole with figures.
Aegean-style terracotta roofing.
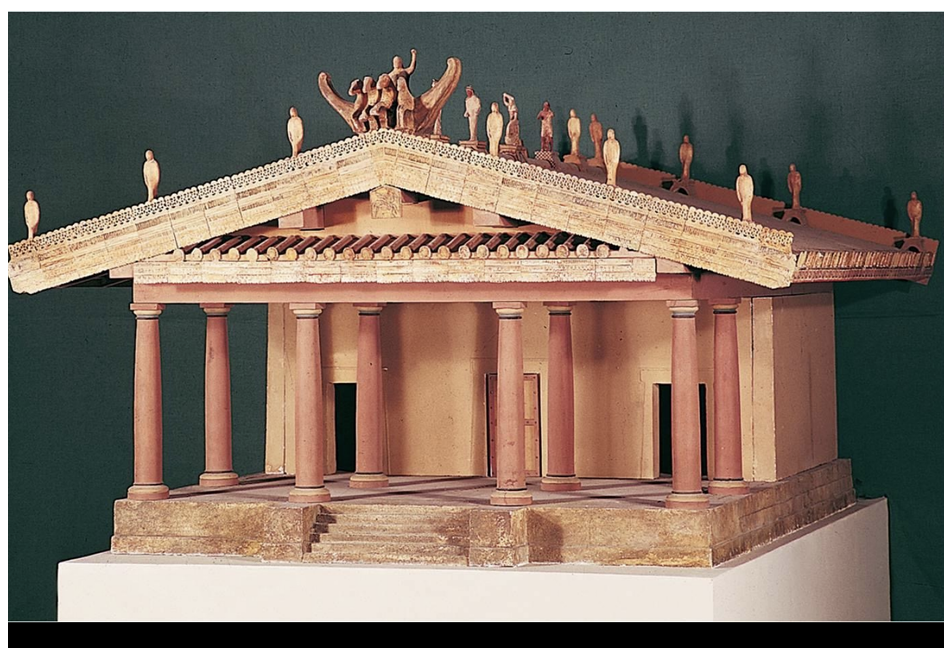
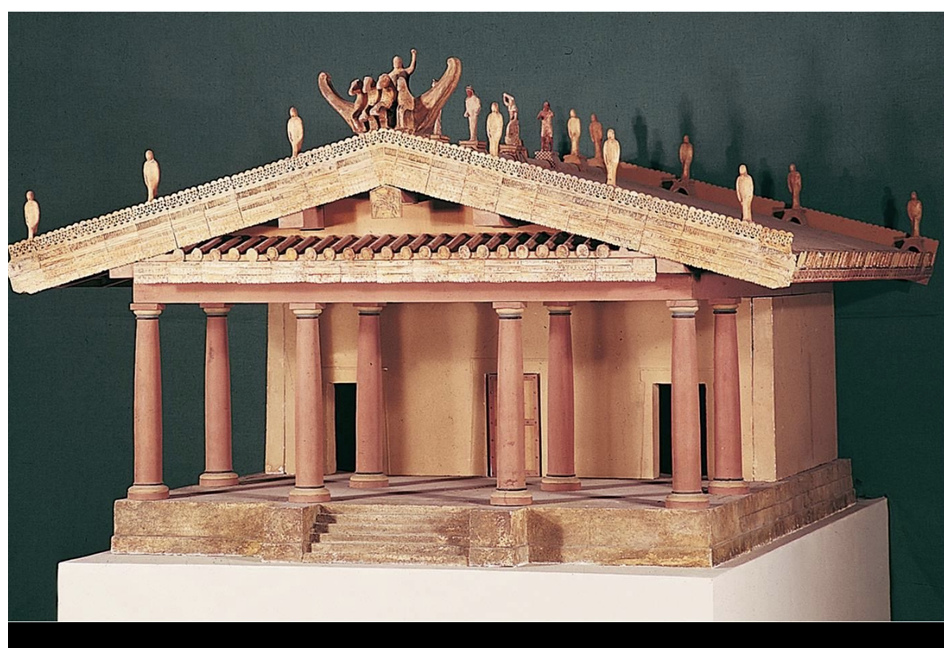


Etruscan Temple (c. 500 BCE)
Influenced by Vitruvius's architectural principles.
Distinctive design features:
Statues placed atop the temple to draw the viewer's gaze upward.
A departure from traditional Greek temple structures.
Use of Tuscan columns, showcasing a blend of cultural influences.
Votive offerings typically placed in the temple.
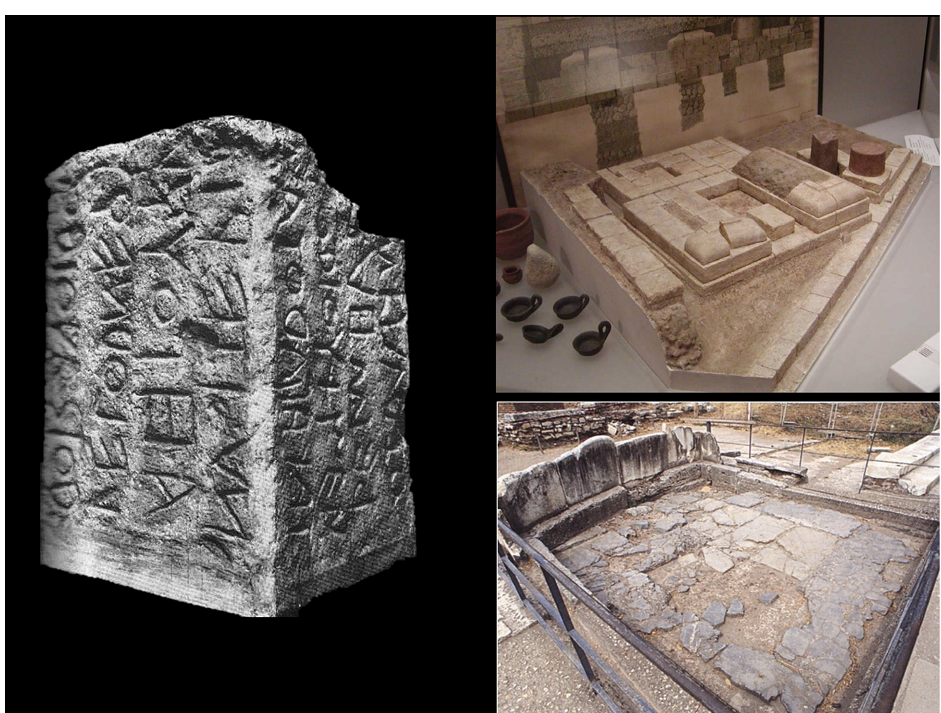

Lapis Niger (6th Century BCE)
Comprising a rectangular stele with inscriptions on all sides.
Served as a monument with ties to royal authority and legitimacy.
Historical significance linked to the kingship transition in Rome:
Covered and preserved, likely due to changing political sentiments.
Brutus and others lead the movement away from monarchy.
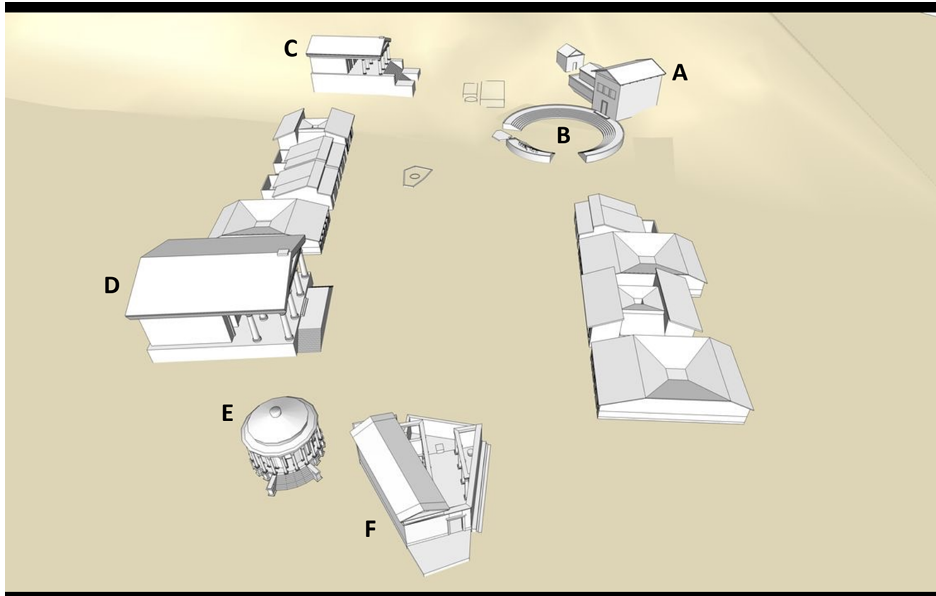
Forum Romanum, Republican Period
Key components:
Curia/Curia: Senate meeting hall.
Comitium: Open space for popular assemblies.
Temple of Saturn (497 BCE): Public treasury location; father of Jupiter.
Temple of Castor: Dedicated to the twin sons of Jupiter, connected to military tradition.
Temple of Vesta: House for the vestal virgins, maintaining sacred fire.
Regia: Meeting place for high-ranking priests and custodians of religious archives.
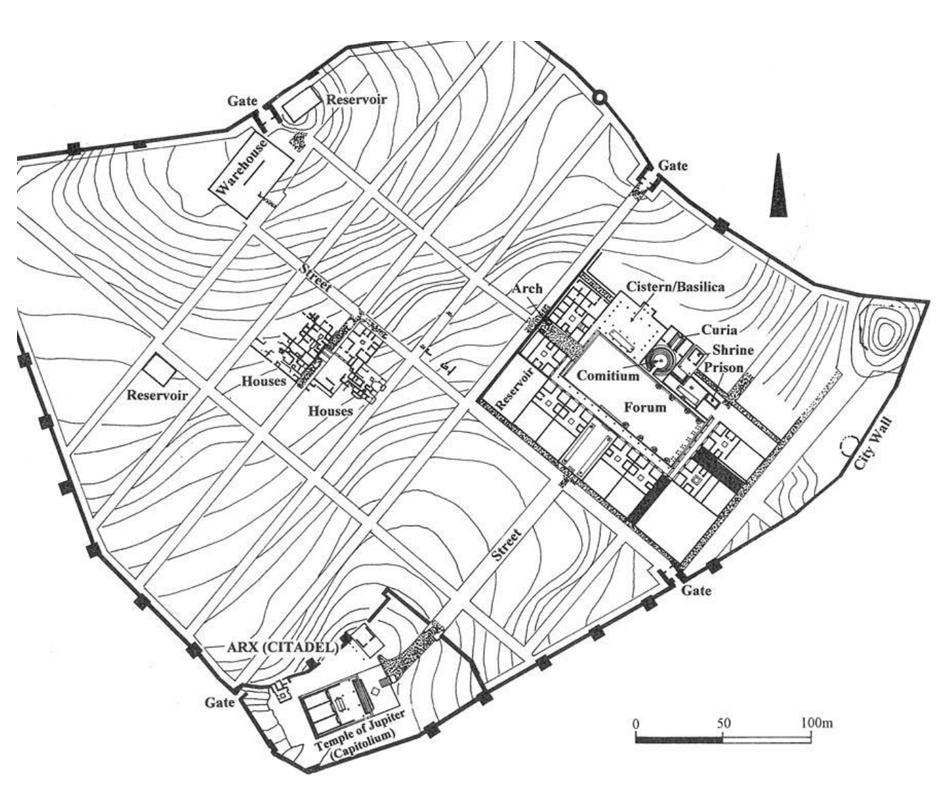
City Plan of Cosa (2nd Century BCE)
Defensive city wall constructed around the perimeter made from cement.
Innovations in building materials leading to stronger, waterproof structures.
Architectural solutions presumably emulating Roman urban design.
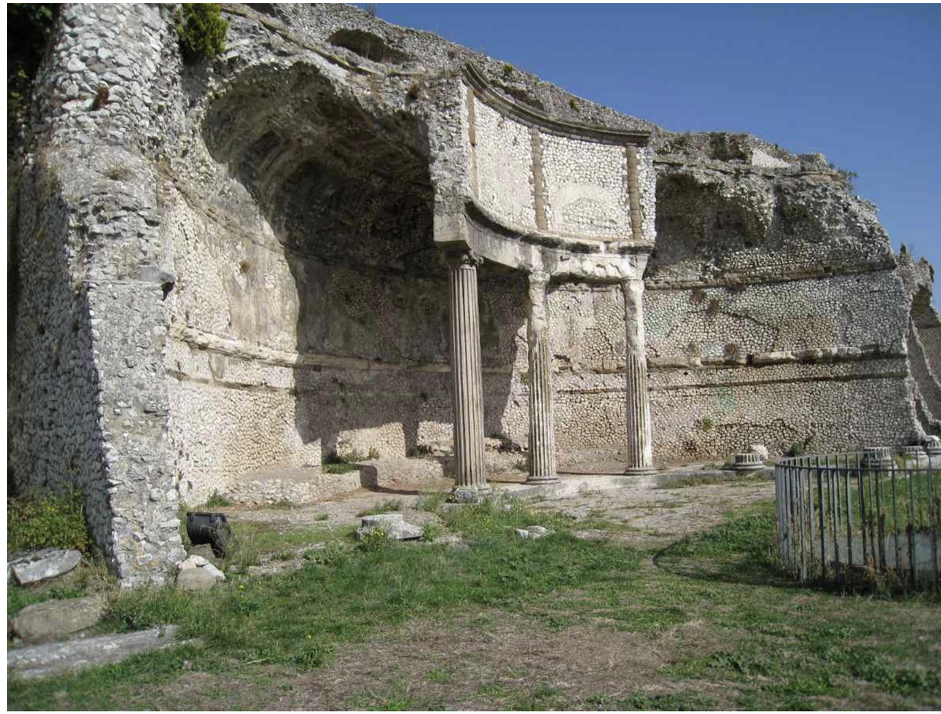
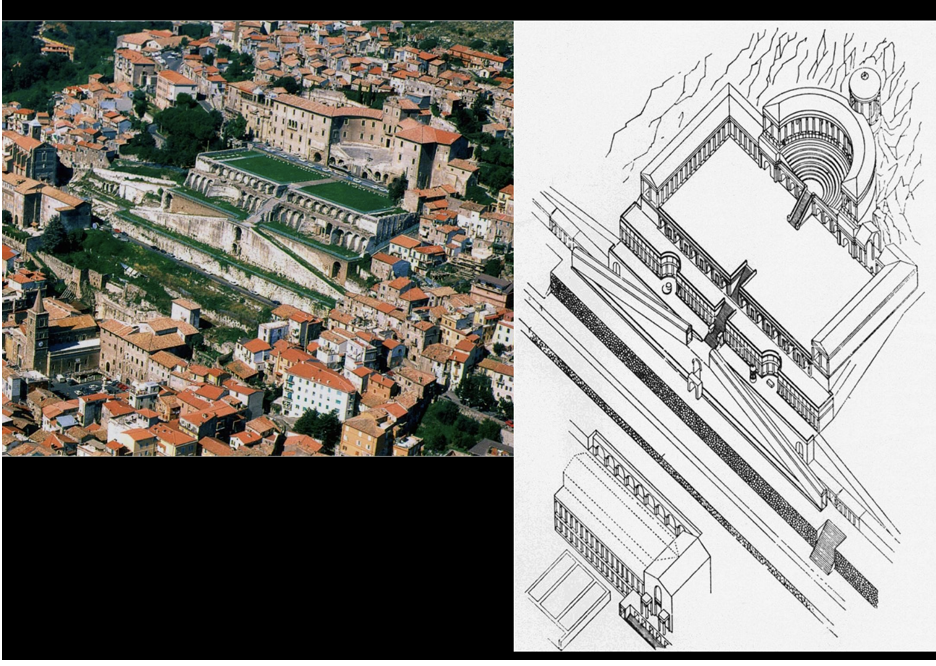

Sanctuary of Fortuna, Praeneste (Late 2nd Century BCE)
Comprises an open courtyard enclosed by structures.
Features innovative use of concrete, enhancing dramatic effect of the space.
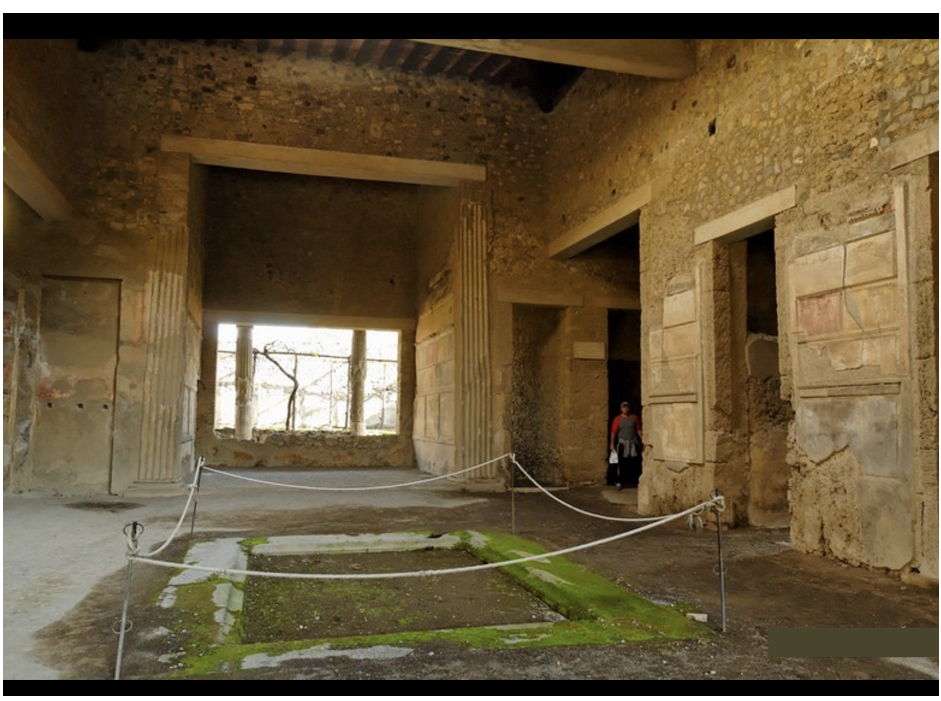

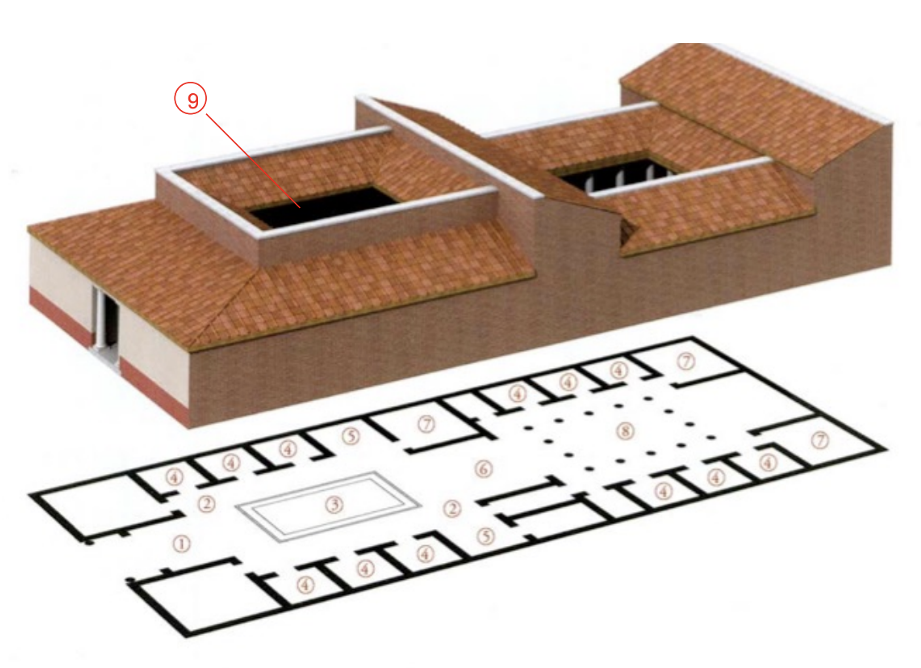
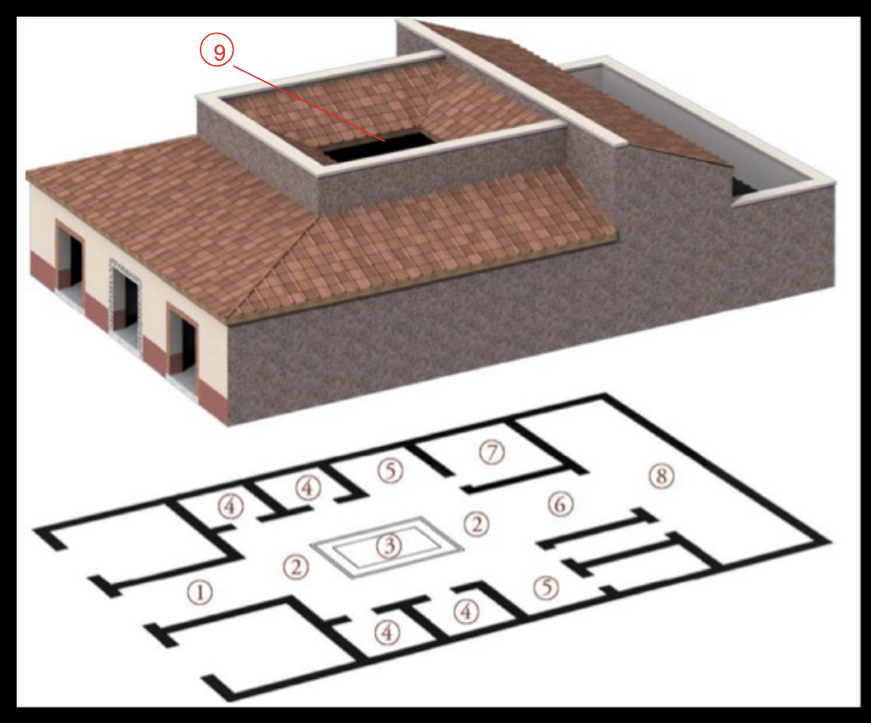
Typical Roman House (3rd Century BCE)
Architectural layout promotes visibility through the atrium, showcasing parts of the house.
Contains:
Cubiculum: Small private room.
Atrium: Central space where family gathered, adding a sense of passage and proportion.
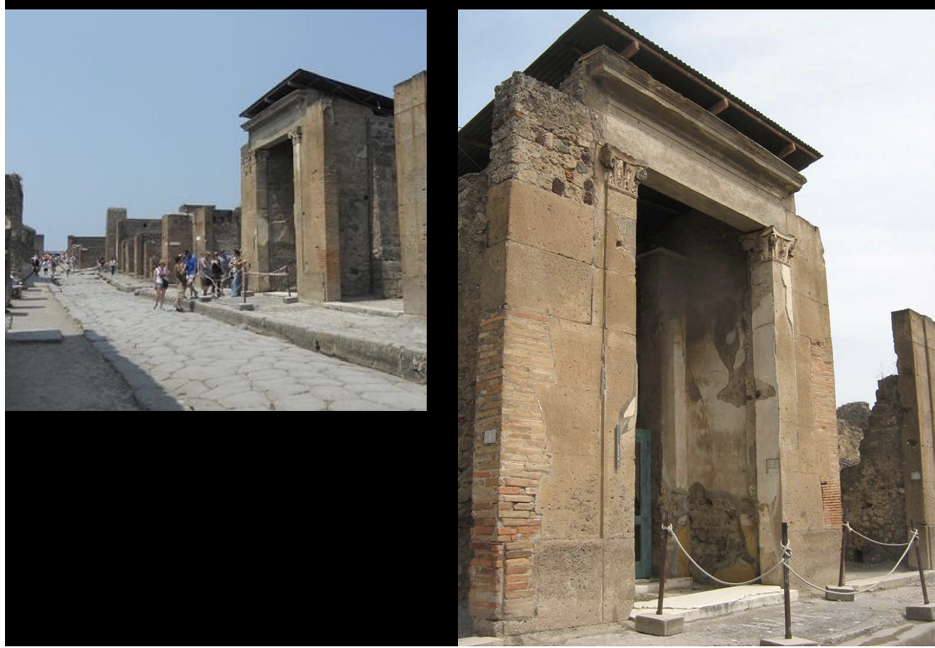
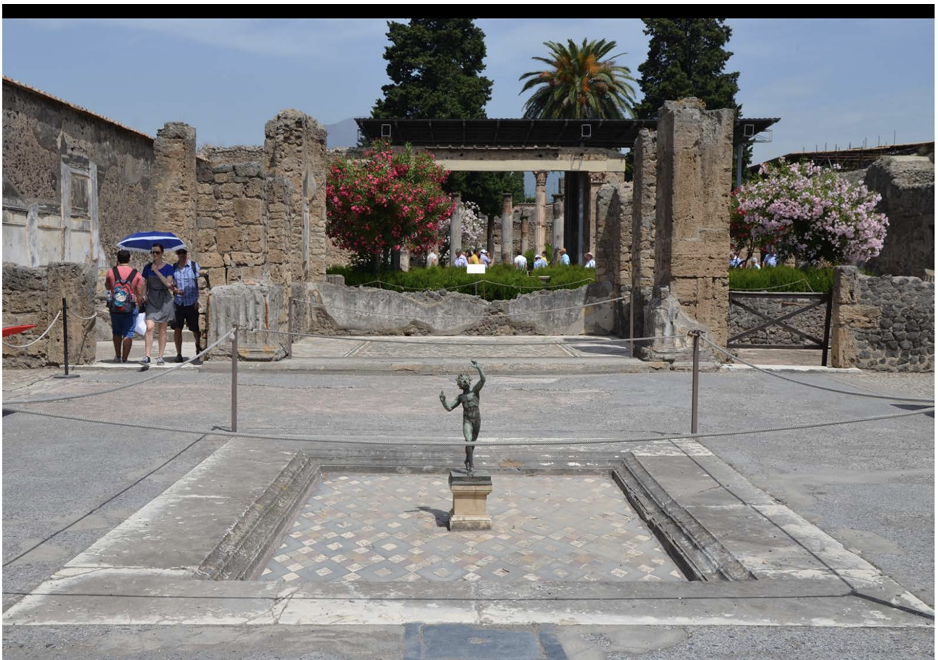


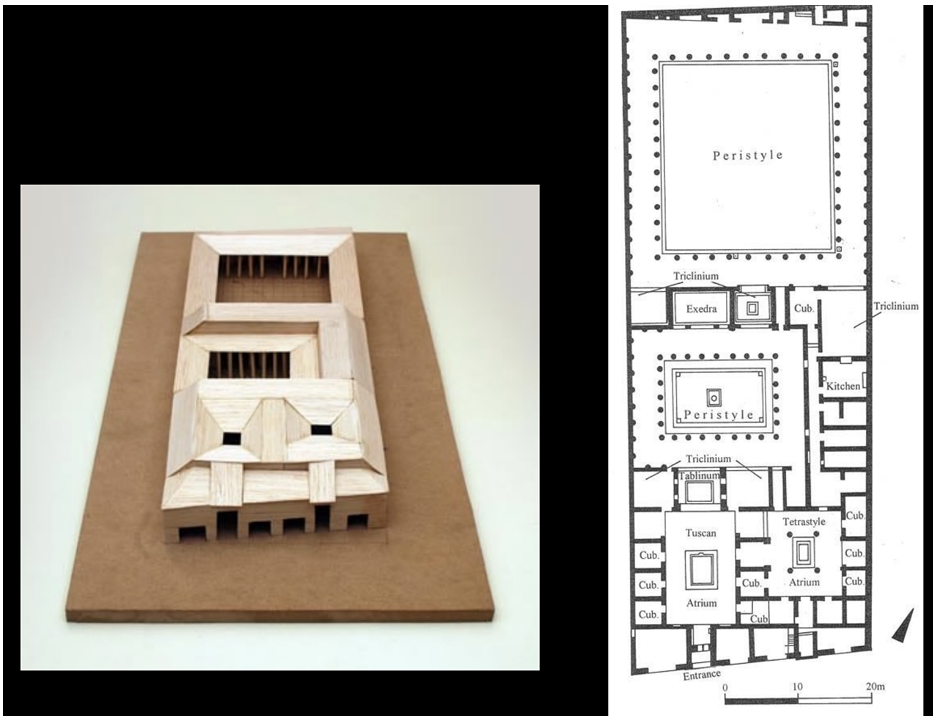
House of the Faun (Early 2nd Century BCE)
Integrated neighboring properties into a large residence.
Divided into:
Public display areas.
Private family quarters, including areas for individual prayer.
Features Corinthian columns and landscaped garden
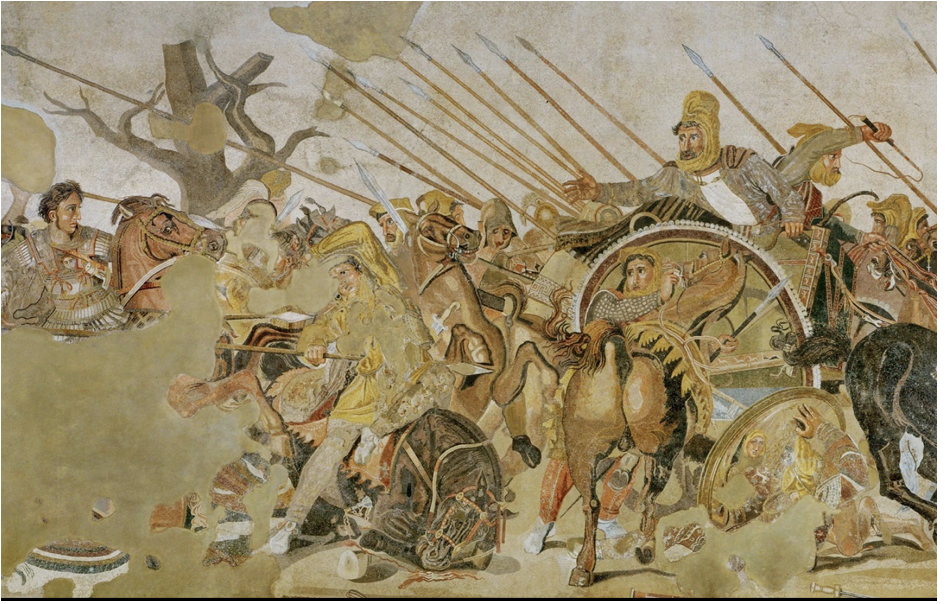

Alexander Mosaic, Pompeii (1st Century BCE)
Illustration of Alexander the Great battling King Darius of Persia.
Epic narrative: Alexander refuses the king's offer for peace through marriage.
Mosaic construction involved meticulous color-matching and placement of individual pieces.
Reflects Roman values: pride, heroism, and strength.

Second Pompeian Style Wall Painting (c. 50-40 BCE)
Exemplifies luxury influenced by Greek culture.
Use of illusionistic techniques to enhance depth and spatial perception.
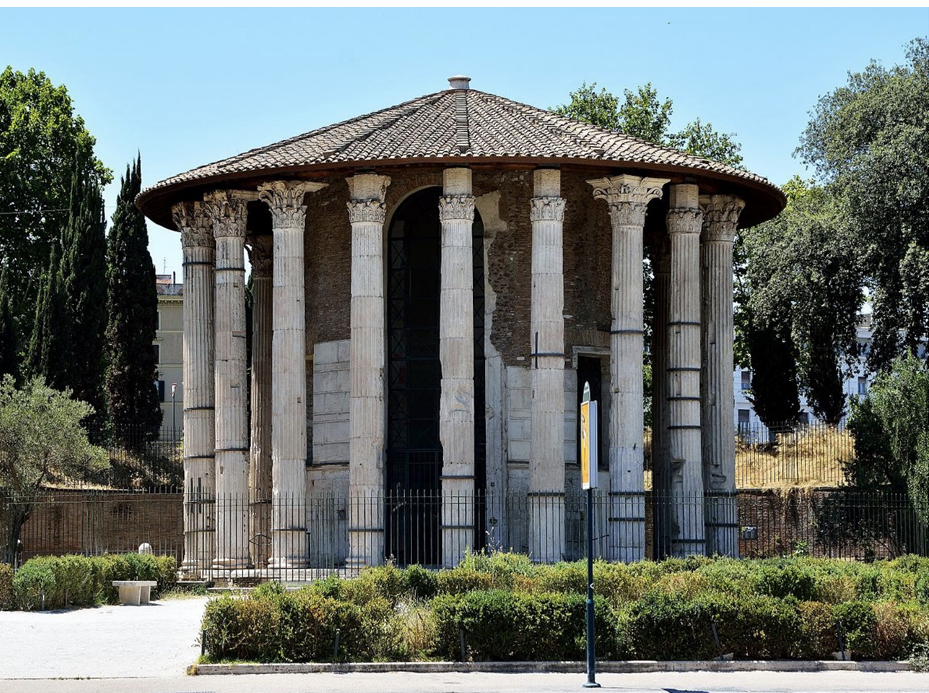

Temple of Vesta, Rome (Mid-2nd Century BCE)
Symbolized success and communal remembrance of victories.
Implemented Corinthian column architecture and imported Greek marbles, indicative of cultural appropriation and conquest.
Such architectural grandeur emphasized Rome's ambitious imperial identity and