Y10T2 Test 2 Science - Physics
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Scalar Quantity
A quantity which only measures magnitude/amount, like grams being the amount of mass, and metres being amount of distance
Vector Quantity
A quantity which measures both magnitude, and distance, like displacement being amount of distance and direction from starting point
V
The symbol for velocity, or final velocity, in equations
s
The symbol for distance/displacement in equations
Displacement
The distance and direction from a starting point (like if you moved 5 metres north, your displacement would be 5m N). Goes by the symbol s
Velocity
The average rate and distance you move away from a starting point per second. Moving 5m north in a second would give a velocity of 5m/s N. Running in one circle would make your velocity 0m/s as you do not move from your starting point
t
The symbol for time in equations
Acceleration
Uses the symbol a, and is the rate of change of speed over time, using the unit ms-2 -(or m/s/s). Can be a negative if something slows down
Formula for Acceleration
a = (v-u)/t, where v=final velocity, u=initial velocity, and t=time
Displacement-Time Graph
A graph that shows the distance of someone/thing from an initial starting point. A flat area shows them standing still
How velocity, distance, displacement, and avg. speed can be calculated from a Displacement-Time Graph
Velocity: Using rise/run
Distance: Add up lengths of the line itself
Displacement: Final point displacement - First point displacement
Avg. Speed: Distance/time in between edges of distance (e.g if one edge is at 1 second, and another is at 5 seconds, then divide by 4)
How to convert between km/h and m/s
If going from km/h TO m/s, then divide by 3.6
If going from m/s to km/h, then multiply by 3.6
Force
A push, pull, or twist, which causes an object to change in some way, and is measured in Newtons (N)
Can make it start/stop moving, speed up, slow down, change direction, or change shape
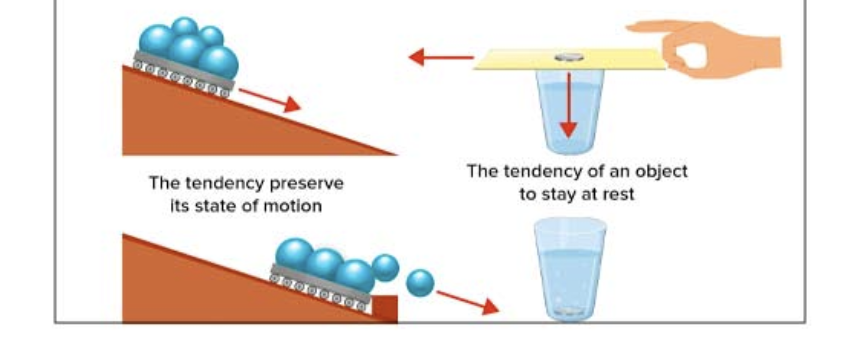
Newton’s First Law
An object which is in motion will remain moving until opposed, and an object at rest will stay at rest until moved. Can be seen in examples like a magician pulling a tablecloth, or a ball on a skateboard
Also known as the law of inertia
Inertia
The tendency of an object to not change their motion in any way (whether it be slowing down, speeding up, or changing direction)
Net Force
The total amount of force acting on an object in opposing directions. Is the larger - the smaller force, and a non-zero answer means an object is in movement
e.g., a ball has 200N pushing it left, and 300N pushing it right, the total is 100N pushing it to the right
Newton’s Second Law
Force is equal to mass times acceleration, meaning that more accelerations is more force, and more mass requires more force to accelerate
Can be simplified as “F=ma”, where F=force, m=mass in kgs, and a=acceleration
Weight
A force, which can be measured in Newtons. Is equal to an object’s mass multiplied by the acceleration of gravity, which on Earth is 9.8ms-2
Newton’s Third Law
For every action, there is an equal opposite reaction
Means that each force applied causes another force to react to it (referred to as applied forces and reaction forces)
Examples of Newtons 3rd Law
When a tennis racquet hits a ball, the net of the racquet tries to spring the ball back
When anything with weight is on the ground, the ground pushes against it with a normal force
When a gun is shot, the acceleration of the bullet pushes the gun back
Velocity-Time Graph
A graph that shows the velocity of an object over time. A flat point shows an object moving at a constant speed, and a point of 0 velocity means an object is stationery. If velocity goes below 0, an object is moving backwards
The 3 Aspects to Add to an Answer
All knowns (e.g., acceleration = 3ms-2, mass = 2kg)
Relevant formula + substituted values (e.g., f = ma, f = 2×3)
Answer (e.g., f = 6N)