Key concepts in chemistry- ionic and covalent bonding, types of substanc
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
negative ion
anion
positive ion
cation
define ionic bond
the electrostatic force of attraction beween positive and negative ions
(between a metal and a non metal)
how are ionic bonds formed?
transfer of electrons between atoms to produce cations and anions
dot and cross diagrams
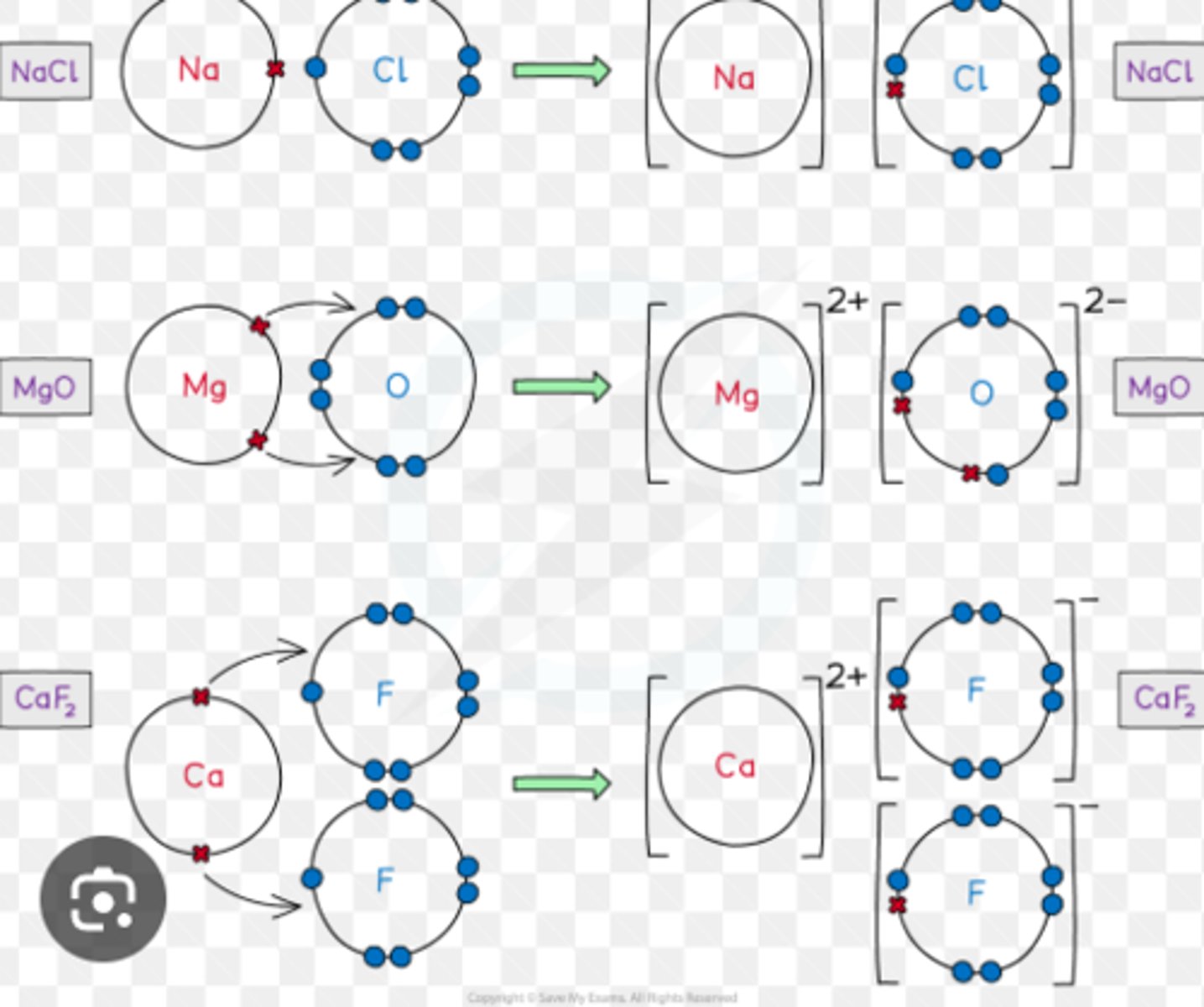
number of protons in an ion
atomic number
number of electrons in an ion
The atomic number - the charge
number of neutrons in an ion
mass number - atomic number
explain the formation of ions in groups 1, 2, 6 and 7
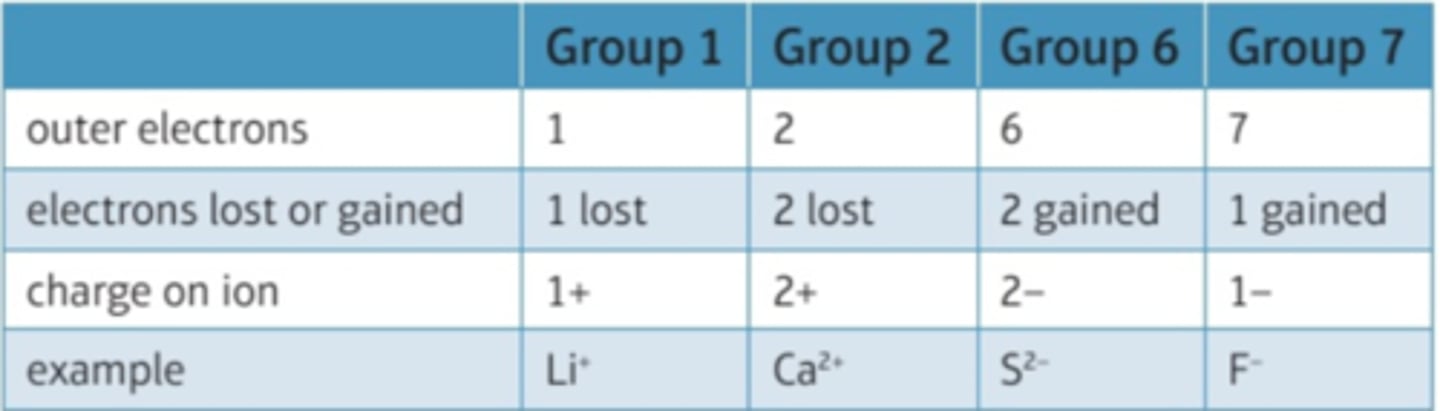
what happens to the name of 2 substances when they become an ionic compound?
the non-metal substance's ending goes to -ide
e.g. sodium + chlorine = sodium chloride
when happens to the name of 3 or more substances when they become an ionic compound?
end of polyatomic ions change to -ate
e.g. sulfate
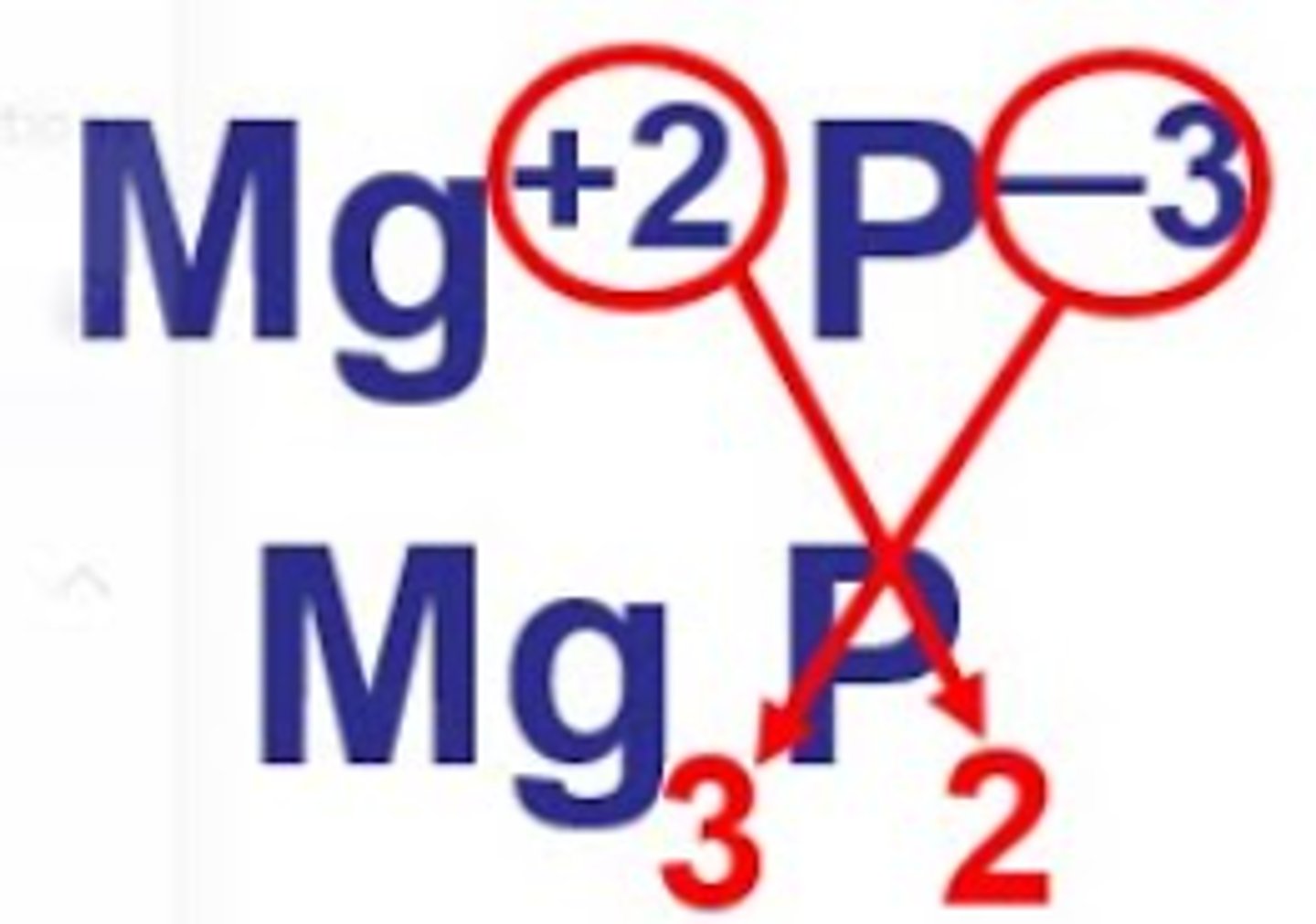
deduce the formulae of ionic compounds
criss-cross method
structure of ionic compound
1. lattice structure
2. consisting of a regular arrangement of ions
3. held together by strong electrostatic forces between oppositely charged ions
covalent bond definition
the electrostatic force of attraction between a shared pair of electrons and positive nuclei
what does covalent bonding form?
molecules
why are the bonds between molecules easy to overcome but covalent bonds are strong?
because the bonds between molecules are weak
but the bonds within molecules (the covalent bonds) are strong
order of magnitude of atoms and small molecules
atoms are smaller than molecules
(atoms are joined together covalently to make molecules)
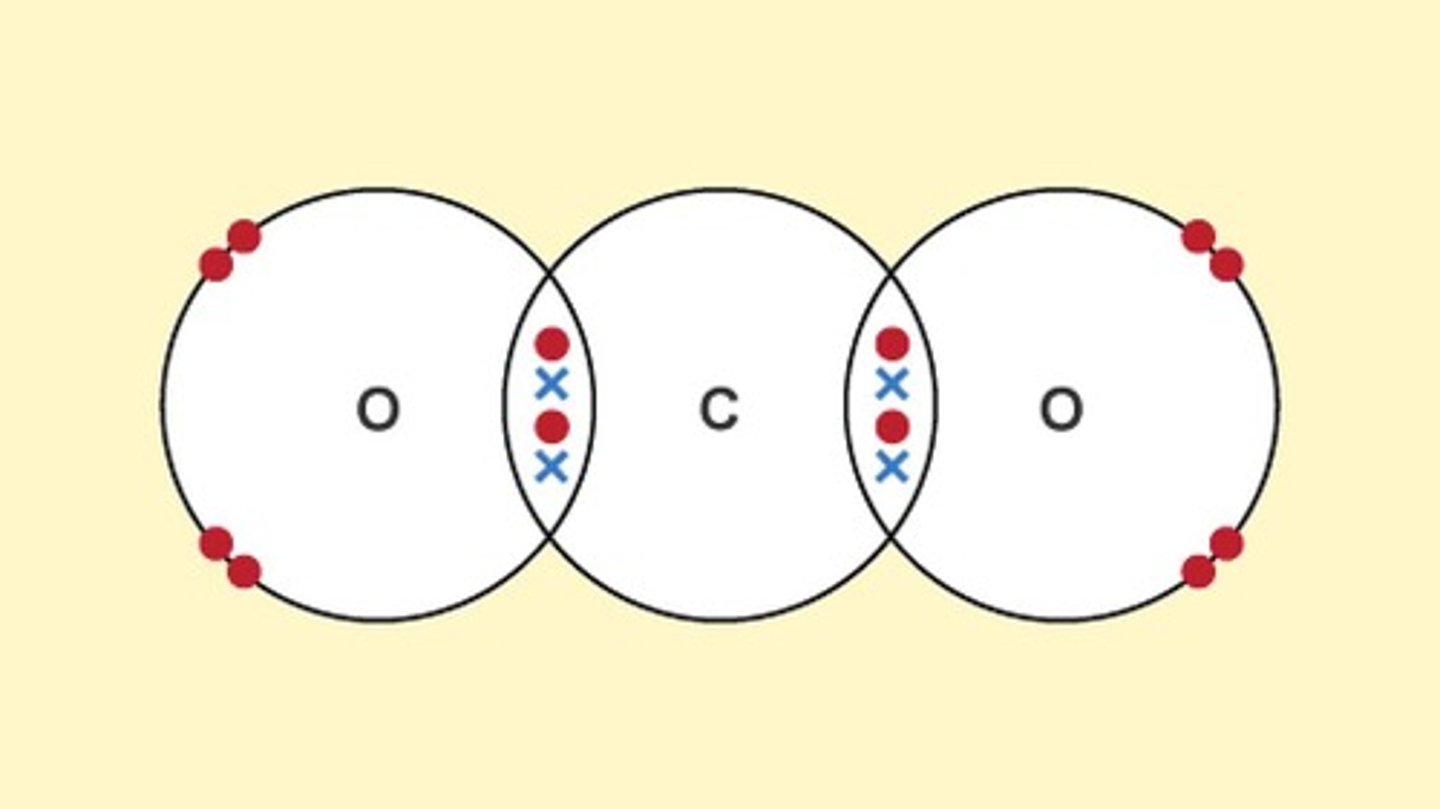
dot and cross diagram for carbon dioxide
ionic compounds are made up of...
metals and non metals
ionic compounds properties
- high MPs and BPs
- Many are soluble in water
- conduct electricity when molten or in a solution
simple molecular substances are made up of...
non metals
simple molecular substances properties
- low MPs and BPs
- a few are soluble in water
- don't conduct electricity
giant covalent compounds are made up of...
non metals
giant covalent properties
- high mps and bps
- insoluble in water
- don't conduct electricity (except graphite)
metals are made up of...
metals
metallic bond definition
the electrostatic force of attraction between positive metal ions and negative delocalised electrons
metallic structure
regular lattice structure of positive metal ions in a 'sea' of delocalised electrons
metallic bonds properties
- High MPs and BPs
- Insoluble in water
- Conducts electricity
how can substances have high melting points?
if they have many strong bonds which require lots of energy to overcome
how can substances conduct electricity?
if they have charged particles that can freely move
how can a substance not conduct electricity?
if they have no charged particles, or charged particles that cannot freely move
why do ionic compounds have high MPs and BPs?
due to strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
which require a lot of energy to overcome
why can an ionic compound conduct electricity when molten/aqueous, but not when solid?
WHEN SOLID: cannot conduct because the charged particles cannot move
WHEN MOLTEN/AQUEOUS: can conduct because the charged particles are free to move
why do simple molecular structures have low MPs and BPs?
because the weak intermolecular foces between molecules require little energy to overcome
why can't simple molecular structures conduct electricity?
because there are no charged particles or delocalised electrons
allotropes of carbon (3)
1. graphene
2. graphite
3. diamond
4. buckminster fullerene (C60)
what type of substance are the allotropes of carbon?
giant covalent
structure of diamond
- each carbon is joined covalently to 4 other carbon atoms
- this means that there aren't any delocalised electrons so diamond can't conduct electricity
- hard
- very high MP
structure of graphite
- each carbon joined covalently to 3 others, forming layers of hexagonal rings, which have no covalent bonds beween layers
--> the layers can slide over each other due to weak intermolecular foces between layers
--> meaning that graphite is soft and slippery
- 1 electron from each carbon atom is delocalised, meanign that graphite can conduct electricity
what is graphite used for an why?
lubricants:
sheets of carbon atoms (graphene) are held together by weak forces of attraction.
this allows the layers to slide over each other, making graphite soft and slippery, useful as a lubricant
what is diamond used for and why?
cutting tools:
diamond is very hard because of it's tetrahedral arrangement of carbon atoms, held together by strong covalent bonds
this makes diamond useful for tools to cut things, as it will be harder than what needs to be cut.
examples of fullerenes
C⁶⁰ (bucky ball)
graphene
properties of C⁶⁰ and graphene
- both simple covalent structures
- where a carbon atom is bonded to 3 others
- buckminster fullerine has 60 carbons which form a ball
- graphene is a sheet
- fullerenes have low MPs because of weak intermolecular forces between fullerine molecules. this also makes them soft and slippery
- graphene can conduct (delocalised electrons), but bucky ball can't (even though delocalised electron, cannot transfer between molecules)
simple polymers consist of...
large molecules containing chains of carbon atoms
example of polymer with a long chain of carbon atoms
poly(ethene)
made up of ethene monomers
properties of metals
malleable
can conduct electricity
solids with high mps and bps
shiny
high density
why are metals malleable?
when a metal is hit, the layers of ions slide over each other
the 'sea' of electrons holds the ions together so the metal changes shape instead of breakign
why can metals conduct electricity?
because the delocalised electrons can move randomly in all directions, so can carry a current
properties of non-metals
low melting points
dull
brittle
low density
poor conductors of electricity
dot and cross model
shows how electrons are shared in covalent bonds
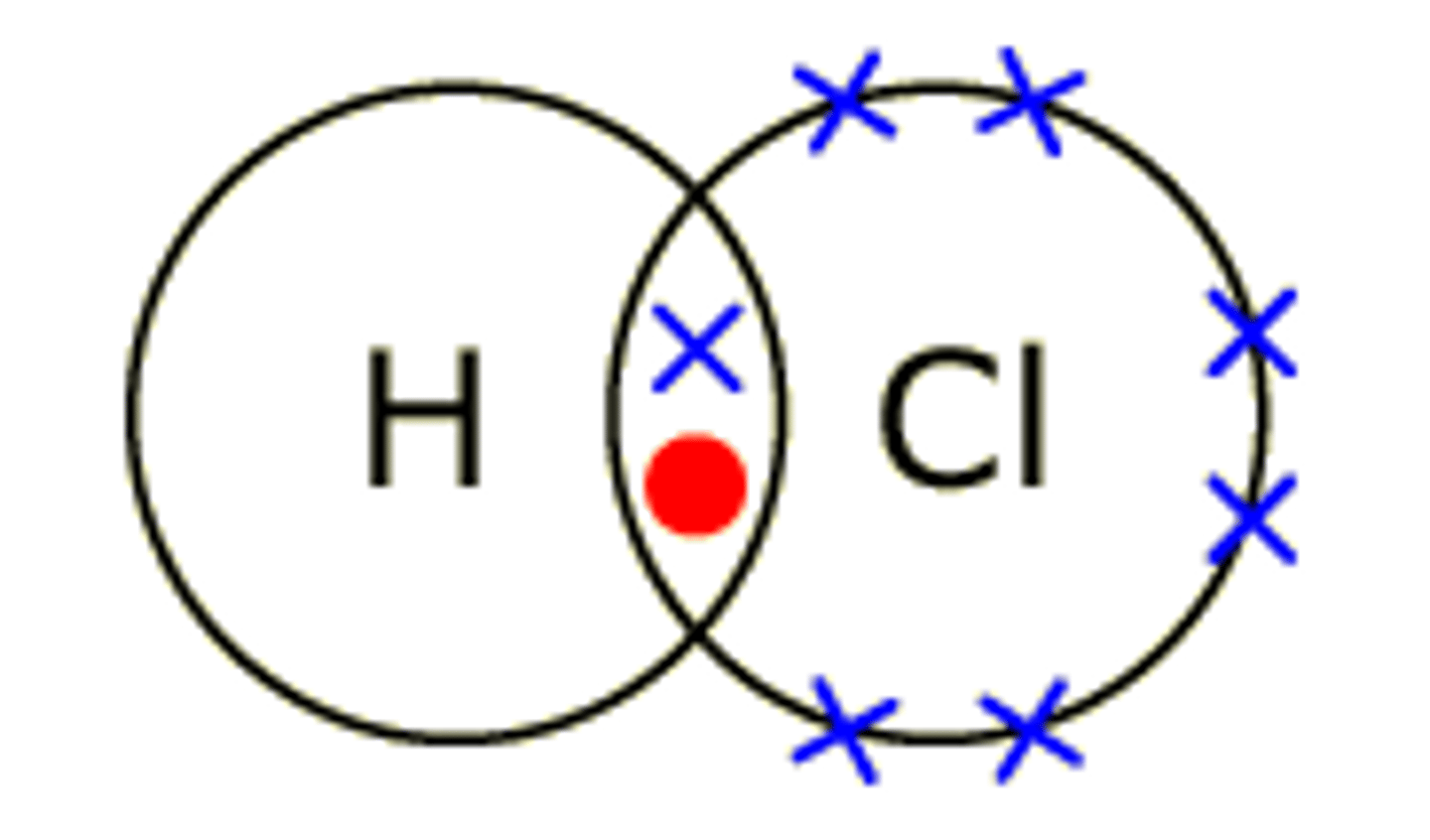
dot and cross model limitations
Doesn't show relative sizes of atoms or intermolecular forces.
ball and stick model
shows which atoms are joined together and show the shape of structure
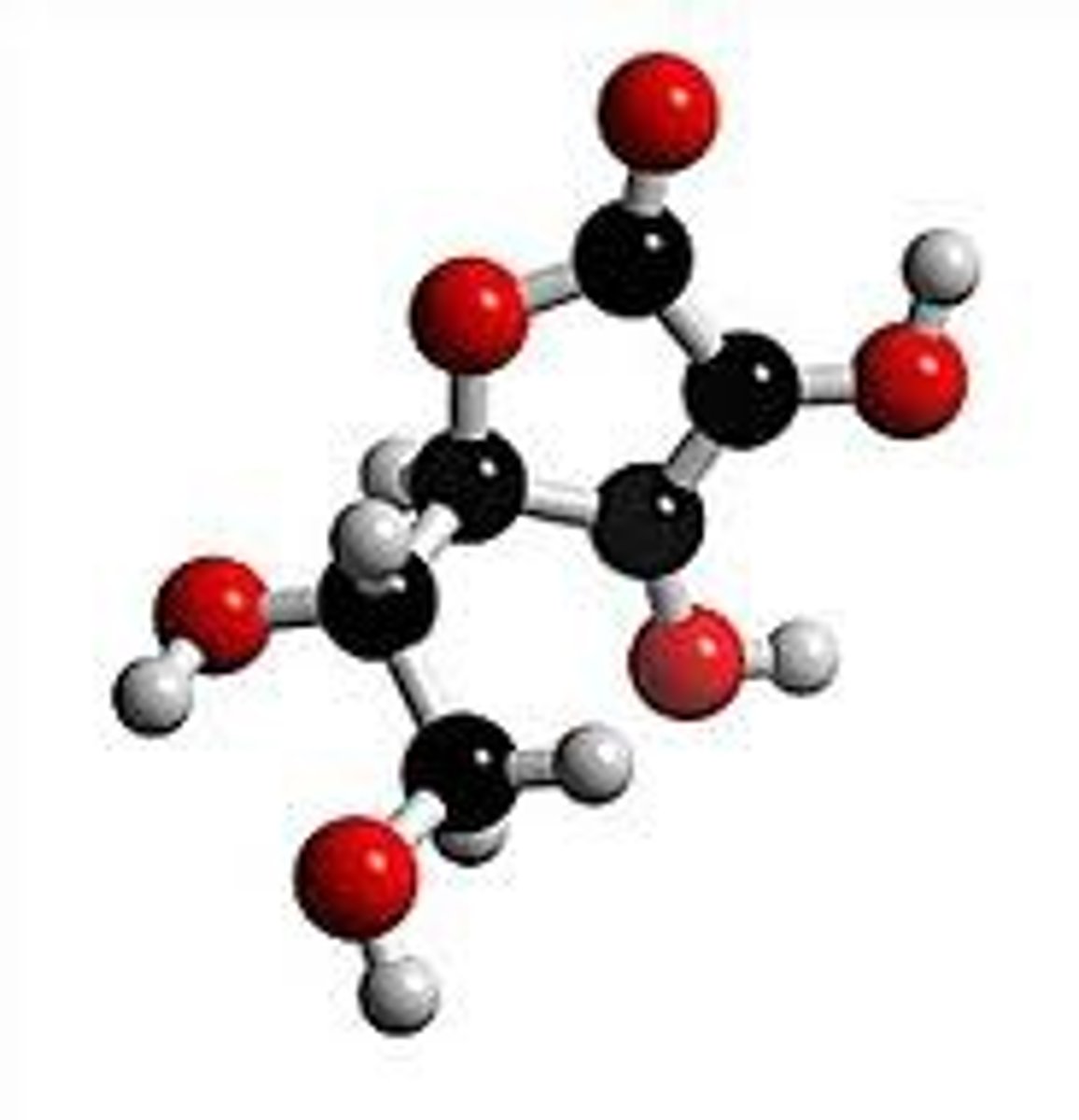
ball and stick model limitations
show atoms too far apart
not really 'sticks holding atoms together'