Hollistic Health, content for midterm 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
types of skin cancer
basal cell, squamous cell, malignant melanoma
basal cell
most common (90%), caused by long term sunlight exposure, easily treated, starts at lowest level of epidermis and grows very slowly (rarely metastasizes)
squamous cell
second most common type, easily treated when detected early, epidermis appears crusted and scaly- can metastasize, appears as persistent thick and rough patches that may bleed, can look like warts or open sores with raised border and crusted surface
malignant melanoma
from pre existing mole that changes or new irregular spot, from pigment producing melanocytes, most lethal, metastasize to lymph and internal organs, cured if diagnosed and removed early
health teaching: skin cancer
check skin once a month, use ABCDE rule, have someone search areas you cant see, wear high spf sunscreen and protective clothing
epidermal wound healing
superficial wounds, new skin cant regenerate if injury destroys large area of stratum basale- that requires skin graft
deep wound healing
when wound extends to dermis and subcutaneous layer, 4 phases- Inflammatory, Migratory, Proliferative, Maturation
Inflammatory phase
blood clot unites wound edges, epithelial cells migrate across wound, vasodilation, phagocytes and fibroblasts
Migratory phase
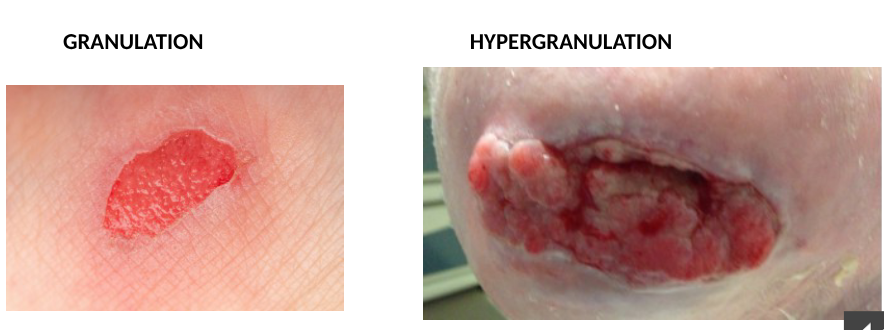
repair the wound- epithelial cells bridge wound, fibroblasts make scar tissue, damaged blood vessels regrow, tissue in wounds called granulation tissue
proliferative phase
migratory phase intensifies
maturation phase
scab sloughs off epidermis- returns to normal size, collagen organised, fibroblasts disappear, blood vessls return to normal
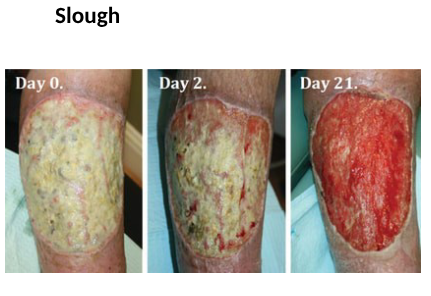
examining wound: slough
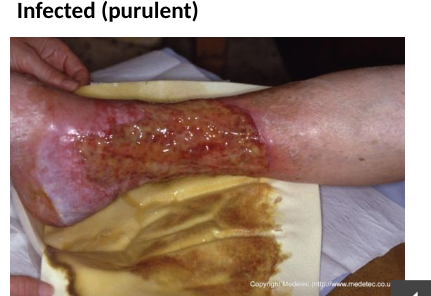
examining wound: infected (purulent)
examining wound bed: granulation vs hypergranulation
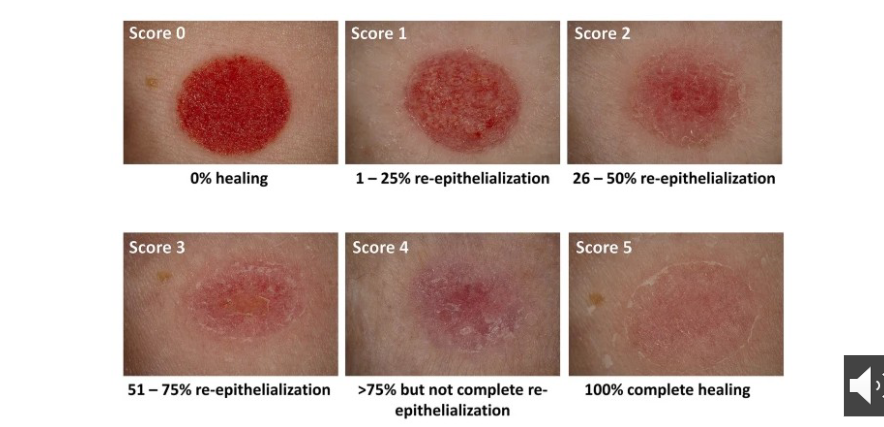
re-epithelialisation and percentage
what is fibrosis
scar formation
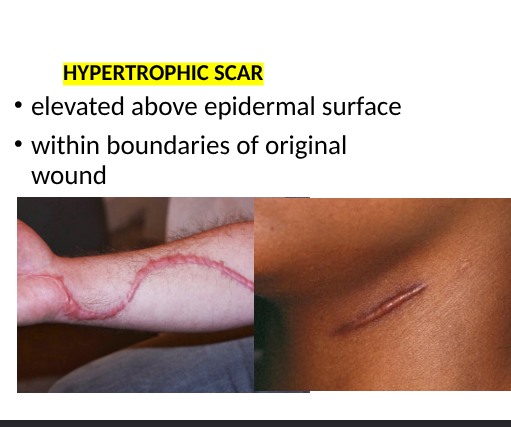
hypertrophic scar
elevated above epidermal surface, within boundries of original wound
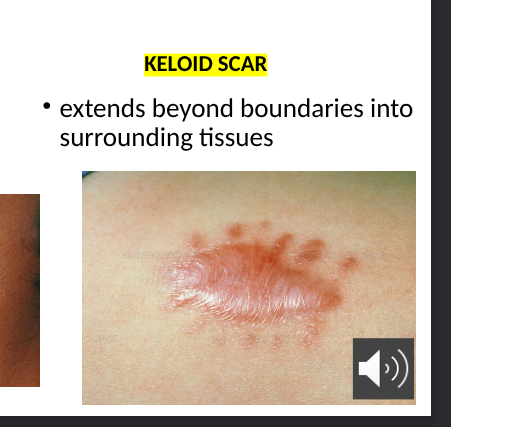
keloid scar
extends beyond boundries into surrounding tissues
initial components of cardiac assessment
wash hands, privacy, introduce, ask them to introduce and check id bracelet, ask reason for seeking care and demographics
risk factors for hypertension - demographics that impact cardiac disease
smoking, dislipidemia, diabetes mellitus, older age (over 60), sex (men and post menopausal women), family history, poor diet, obesity, excess alcohol consumption (modifiable or non modifiable)
subjective data for cardiac assessment
pt cardiac history- (HTN, CAD/MI, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, congenital heart disease, obesity,) family cardiac history, allergies, medications (vitamins, herbals, prescribed, otcs)
lifestyle and teaching in cardiac
Diet: salt, caffeine, fat (dietary approachs to stop hypertension, Alcohol: abstain or less than 2 drinks per day, Drugs: cocaine, Smoking: reduce or quit, Last Physical exam, Immunisations: flu can cause MI, covid can cause myocarditis and heart complications, Excersize: 30-60 mins moderate excersize, healthy body weight and BMI, Reduce Stress
chest pain OPQRSTUA
o- when did it start? constant or come and go? p- what makes it better or worse? is it triggered by an activity? q- how would you describe it? r- is it localised or does it radiate? s- rate it on a scale of 1-10. does it affect ADLs? t- is there a time of day when it is worse or better? u- what do you think it is? have u had this pain before? a- what other symptoms do you have?
locations off cardiac related chest pain image
FINISH
chest pain associated symptoms
pain, shortness of breath, cough, heavy sweating, fatigue or weakness, light headedness, nausea or vomiting, swelling, urinating during the night FINISH
types of shortness of breath chart insert
FINISH
developmental considerations when pregnant
HR increase by 10-15 bpm, changes in BP (varies w position), apical pulse is higher and more lateral), splitting of S1 and it is louder, S3 has extra blood volume, systolic murmur in 90% of cases, ECG slows slight left axis deviation, mammary souffle (continous murmur because of extra blood being supplied to breast)
developmental considerations for older adults
increased AP diameter of chest (barrel chest), gradual increase of systolic bp, risk of orthostatic hypotension, decreased ability of heart to augment co with excersize, S4 common if heart disease, decreased tolerance for tacharrhythmias, premature ectopic beats more common, systolic murmur common, arrhythmia and heart failure are more common
cultural and social considerations
increased CVD in men and women in Canada, influence of social factors: high bp, smoking, serum cholestrol, access to healthy foods, obesity, diabetes
hypertension canada guidelines important
FINISH
salt intake per day
less than 2 grams
excersize FINISH
FINISH
cardiovascular disease in women
symptoms can be attributed to something else, often ignored, women minimise the significance of symptoms, heart disease is leading cause of death in women older than 55, ovaries decrease production of estrogen- increased low density lipoprotein, b and body fat above the waist, decreased high density lipoprotein, metabolism of sugar affected, HRT helps improve post menopausal symptoms
finish cardiac
FINISH