Unit 6 & 7 - African Civilizations and Industrialization
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
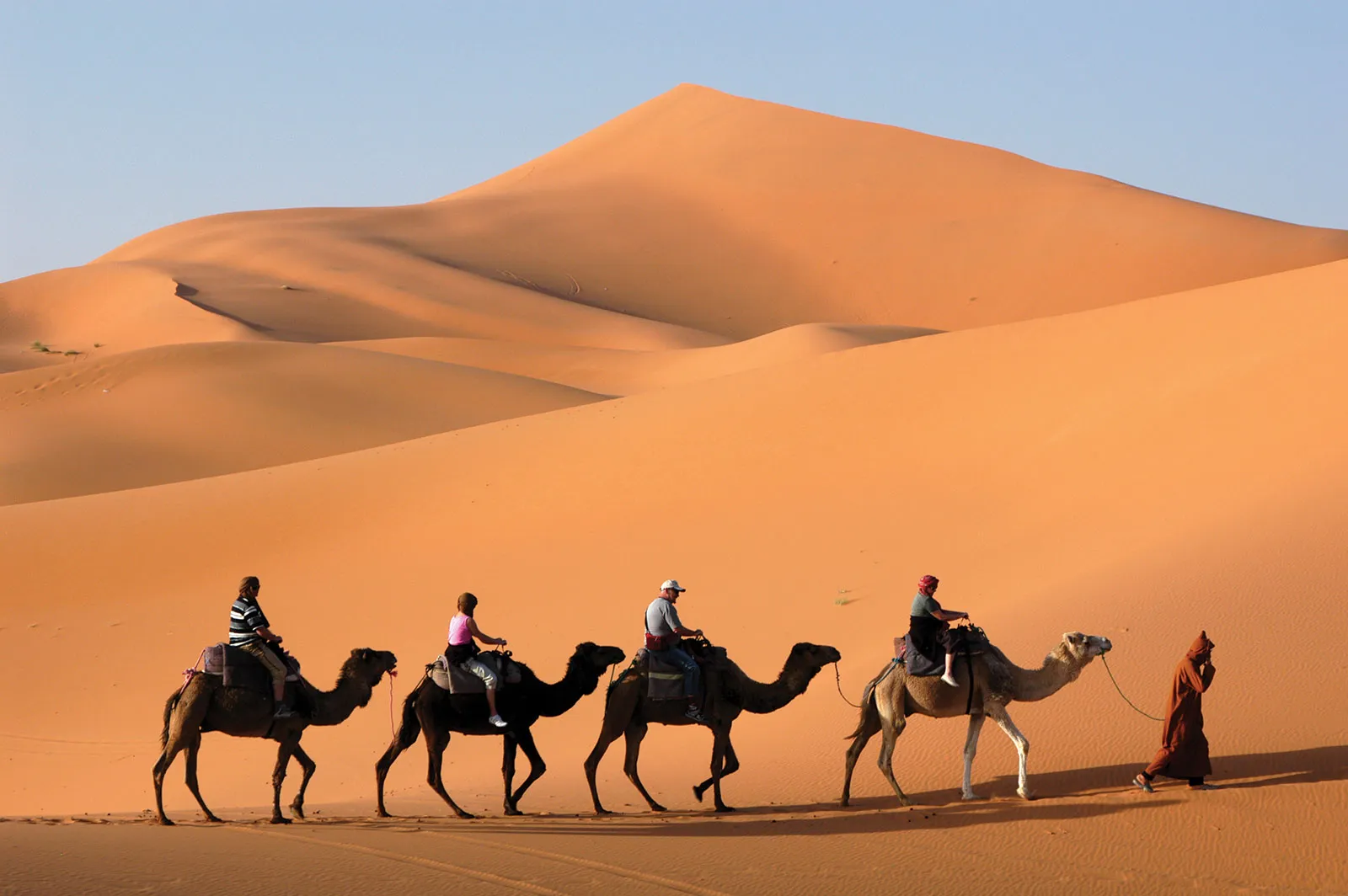

Caravan
A cooperative group of people traveling together across a desert
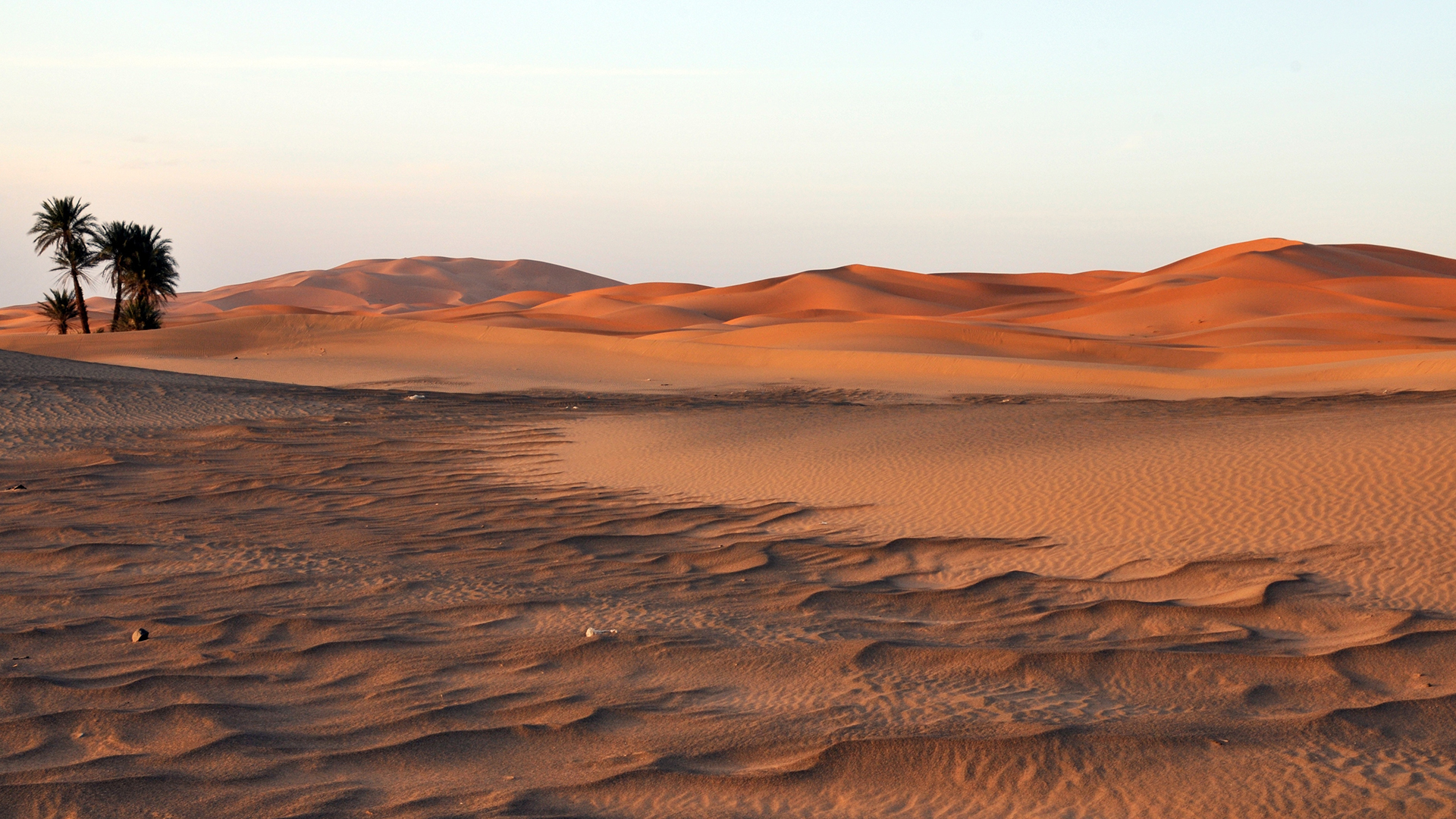

Sahara Desert
Desert stretching across the northern region of Africa across which important trade routes stretched

Sundiata Keita
Founder and first ruler of the Mali Empire
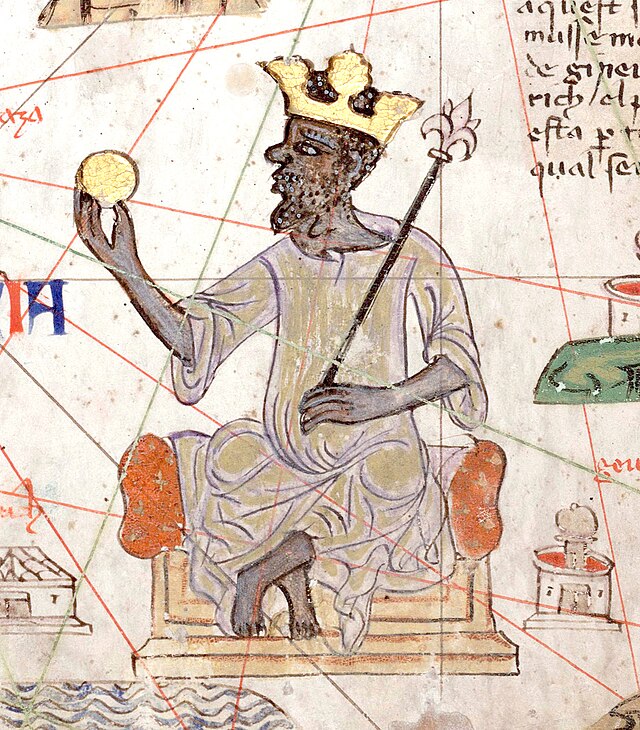

Mansa Musa
King of the Mali Empire who is commonly referred to as the richest person to have ever lived
Mali Empire
West African empire lasting from the 11th-17th centuries known for its prolific trade networks, rich gold mines, and for spreading Islam in West Africa

Tributary Princes
A ruler of a state that pays tribute to a more powerful state
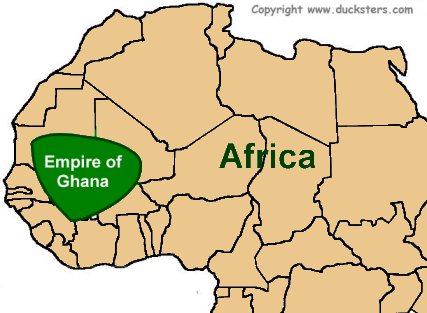
Ghana Empire
The first of the great medieval trading empires of western Africa lasting from the 7th-13th centuries, which gained influence from it's gold and salt trade
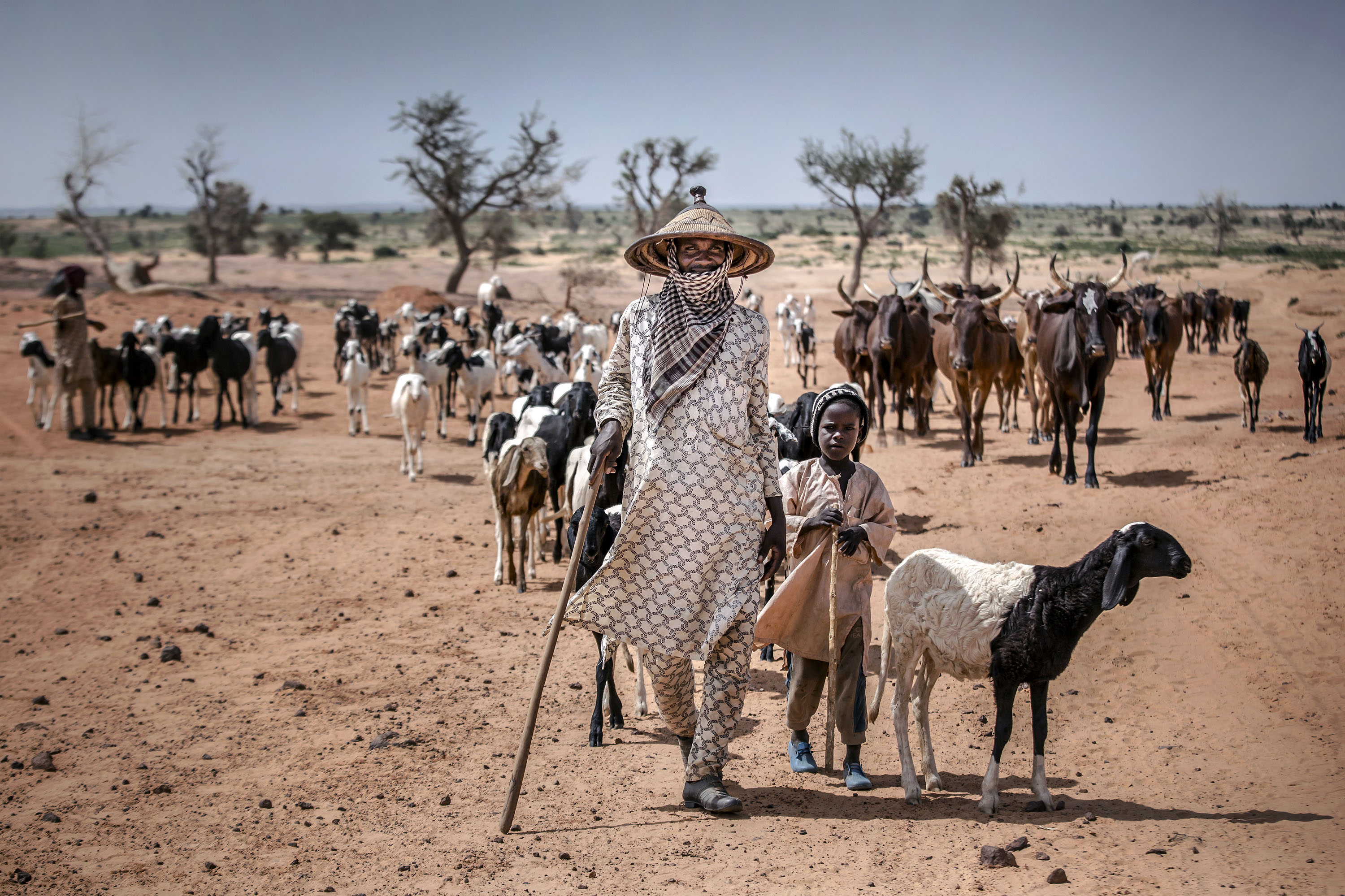

Pastoralism
A way of life and land use system that involves raising domestivated animals on open grassland for subsistence, sale, and social exchange
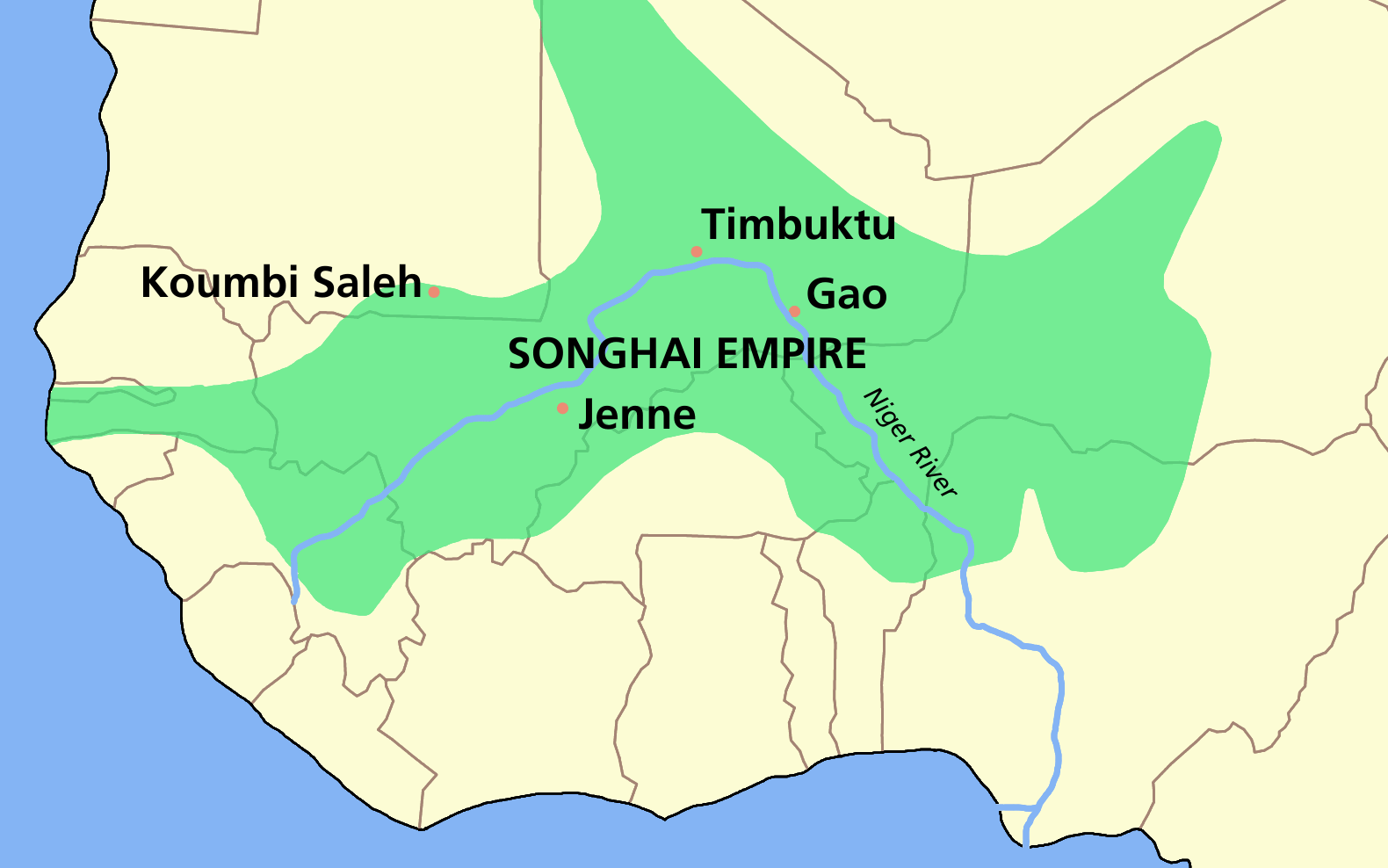
Songhai Empire
Great trading state of West Africa centered around the Niger River and flourished from the 15th-16th centuries.
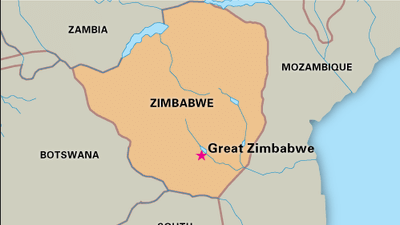
Great Zimbabwe
Capital of the Kingdom of Zimbabwe which lasted from the 11th-15th centuries
Sahara Desert
What physical feature had the largest impact on the development of African civilizations?
Nile River
What is the longest river in Africa?
Congo RIver
Which river formed the basis for the African rainforest?
People traveling together, often using camels
What are caravans?
Current theory humans originated from Africa
Why is Africa known as the “Cradle of Humanity”?
Age of Exploration
Which historic era led to the biggest shift in how Sub-Saharan Africans interacted with non-Africans?
Economic problems, enlightenment ideals, poor leader
What three things combined to cause the French Revolution?
They attempted to intervene
How did European monarchies react to the French Revolution?
He served as an artillery officer and became a military hero
How did Napoleon Bonaparte gain his early fame?
He no longer needed a “breadbasket” for his slaves and needed cash for wars
Why did Emperor Bonaparte abandon French possessions in the New World?
The Continental System
How did Emperor Bonaparte attempt to counter Great Britain's independence?
The Battle of Waterloo
Which battle was the last defeat of Emperor Bonaparte?
Brought glory to the French, Reforms spread
What positive consequences resulted from Napoleon’s time in power?
Millions of people killed, ended enlightened ideas and democracy in France
What negative consequences resulted from Napoleon’s time in power?
Period of change in farming practices, new crops, breeding techniques
What was the agricultural revolution?
Skilled workforce, technology, demand for goods, government policies
What are the basic requirements for industrialization?
Middle class expanded, higher quality of living
What are positive consequences of industrialization?
Dangerous working conditions, unsafe housing
What are negative consequences of industrialization?
Increase of people and and things in a city
What is urbanization?
More job opportunities
What are positive consequences of urbanization?
Quickly spreading diseases
What are negative consequences of urbanization?
Increase in population, middle class expanded, better quality of living
How did the industrial revolution change the world?
Economic system - factors of production are privately owned and money is invested in business ventures to make a profit
What is capitalism?
A political and economic theory which advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by the state for the benefit of all
What is socialism?
A political and economic theory which advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by a stateless and classless society without private property
What is Marxism?
Napoleon Bonaparte
Emperor of France who reformed France’s government and society and waged multiple war around the globe
Congress of Vienna
A series of international diplomatic meetings to reshape the political landscape of Europe in order to bring about a new era of peace in Europe following the Napoleonic Wars
Industrialization
The development of industries in a country or region on a wide scale
Agricultural Revolution
A series of developments in technology and shifts towards industrialization and urbanization that resulted in an unprecedented increase in agricultural production
Factory System
A method of manufacturing using machinery and division of labor
Socialism
A political and economic theory which advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by the state for the benefit of all
Marxism
A political and economic theory which advocates that the means of production, distribution, and exchange should be owned or regulated by a stateless and classless society without private property
Popular Sovereignty
The principal that the authority of a state and its government are created and sustained by the consent of its people
Bourgeoisie
The middle class, typically with reference to its perceived materialistic values or conventional attitudes
Proletariat
Workers or working-class people
Factory System
A method of manufacturing using machinery and division of labor
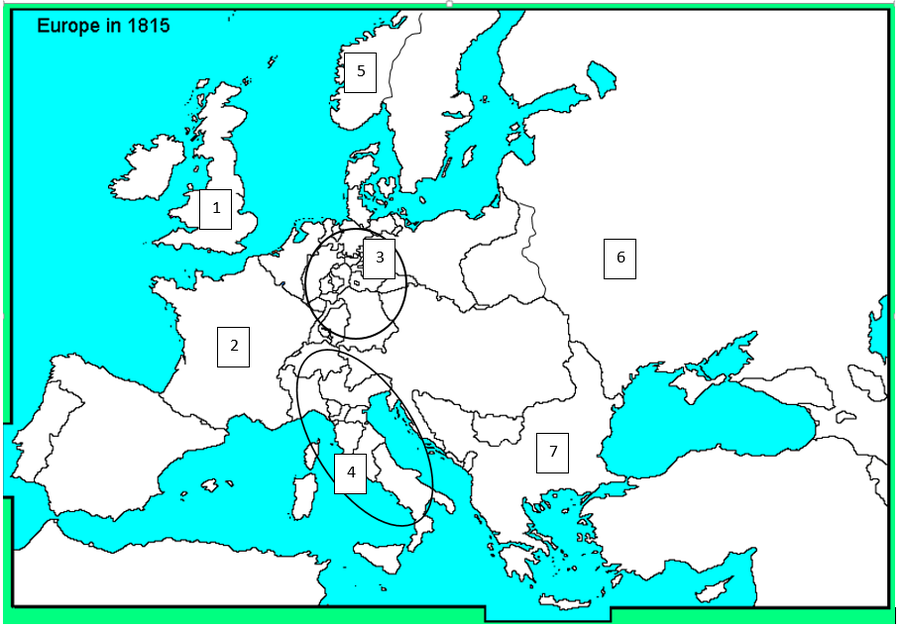
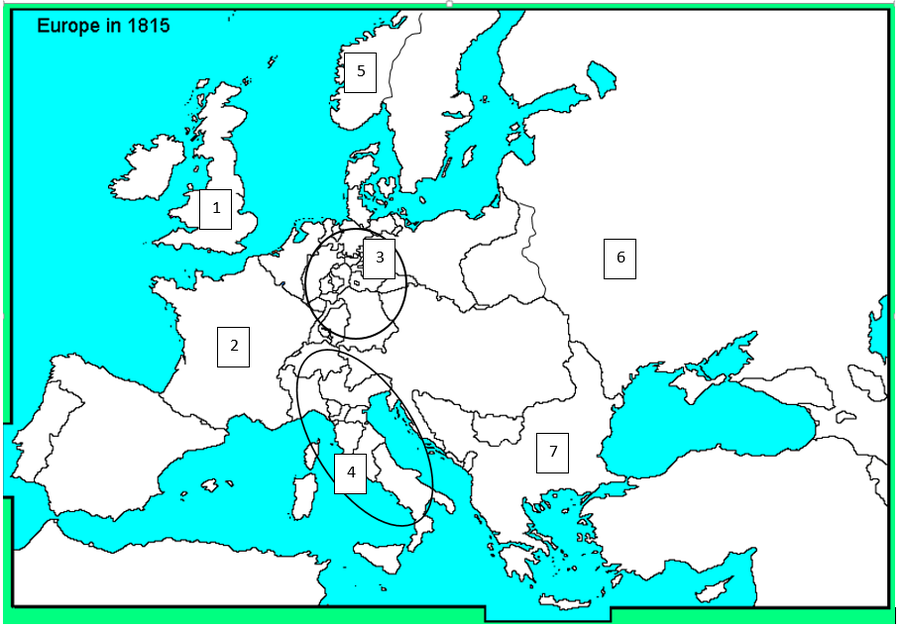
Black Sea
Which body of water best matches the one labeled with a five?
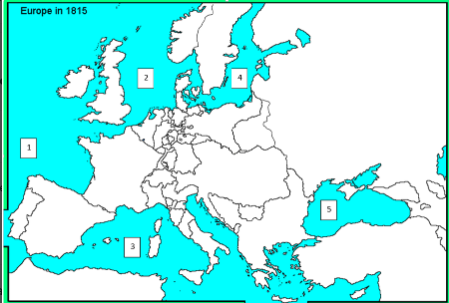
Great Britain
Which nation best matches the one labeled with a one?
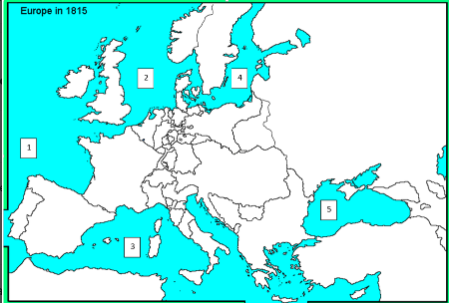
North Sea
Which body of water best matches the one labeled with a two?
Russia
Which country best matches the one labeled with a six?
Ended democracy in France
Which of the following is not a positive consequence of Napolean Bonaparte?
Civil Wars
Which of the following is not a basic requirement of industrialization?
Socialism
Which political and economic theory resulted from laissez-faire policies?