bio 1AL- lab 8 bioinformatics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
complementation group
strains that fail to complement (they are mutated in the same gene)
all streaks which fail to grow are in one complementation group
streaks that grow could be one group but we don’t know unless they are crossed
cDNA
complementary DNA- it is complementary to the mRNA, used during sequencing
reverse transcription
process of getting cDNA from mRNA
carried out by reverse transcriptase
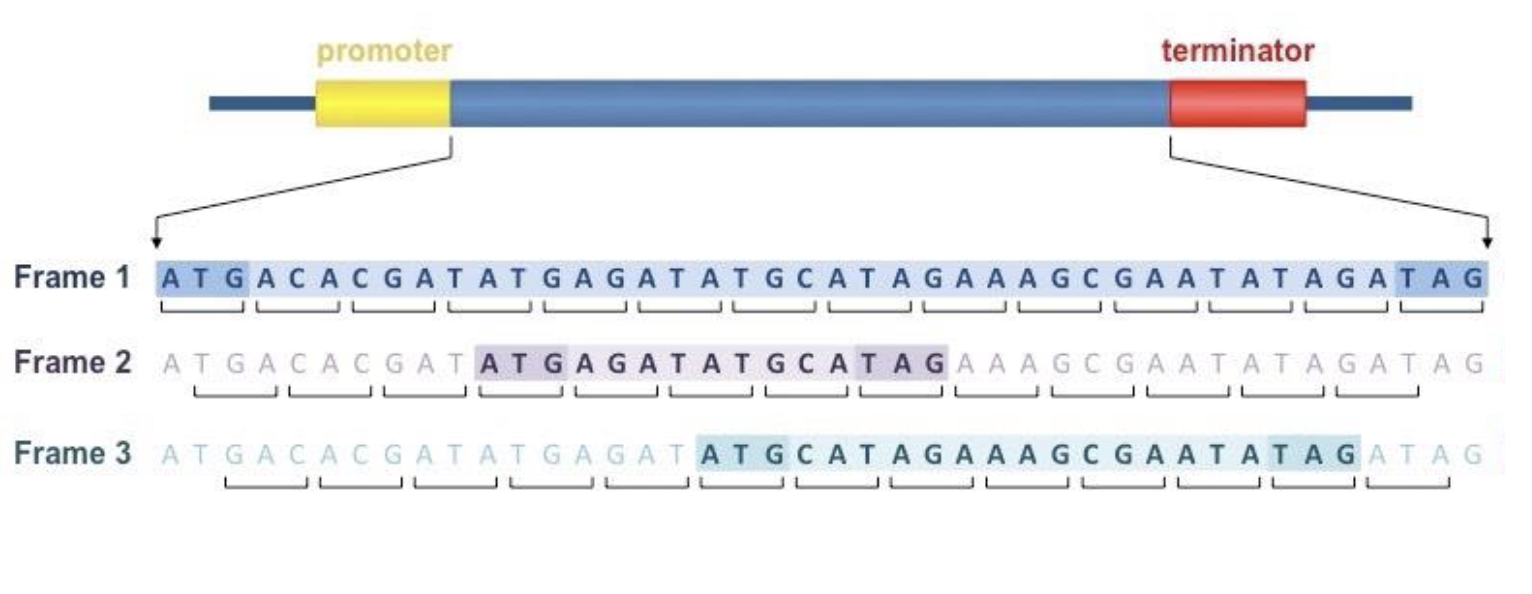
finding a reading frame
must start with start codon, and not have a stop codon for a long time
start codon: AUG

missense mutation
point mutation, changes type of protein expressed
nonsense mutation
introduces stop codon (UAG, UAA, UGA)
frameshift mutation
inserts an extra letter, causing everything downstream to change
silent mutation
point mutation that keeps the same protein expressed
reading frame
3 different ways of starting to read, which may be different lengths/different amino codons
the correct one will have a long open reading frame starting with AUG and ending with a stop codon
hemoglobin
2x alpha globin
2x beta globin
homologs
genes related by descent from a common ancestral DNA sequence
classified as paralogs or homologs
paralogs
homologous genes that arose from a gene duplication event within a single genome
Same/related species
encode proteins with different functions
orthologs
homologous genes that arose from a speciation event
different species
encode proteins with same functions
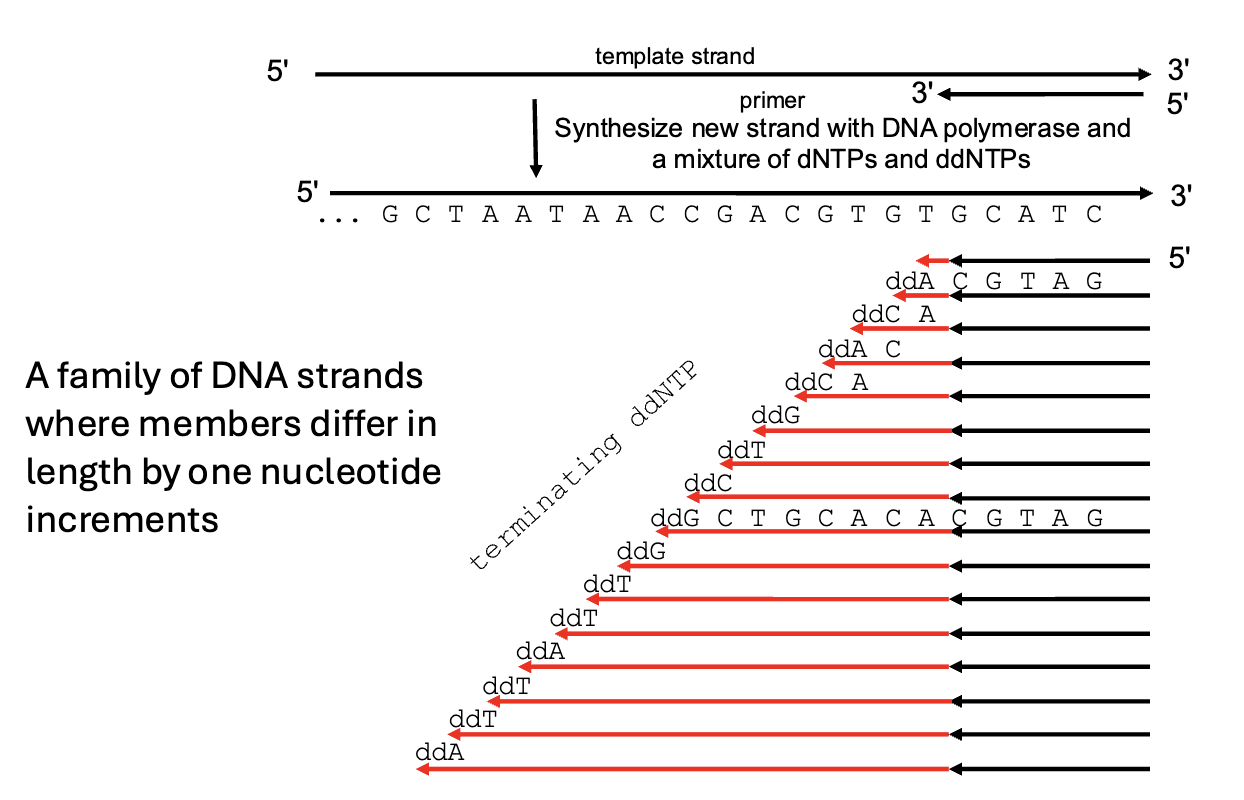
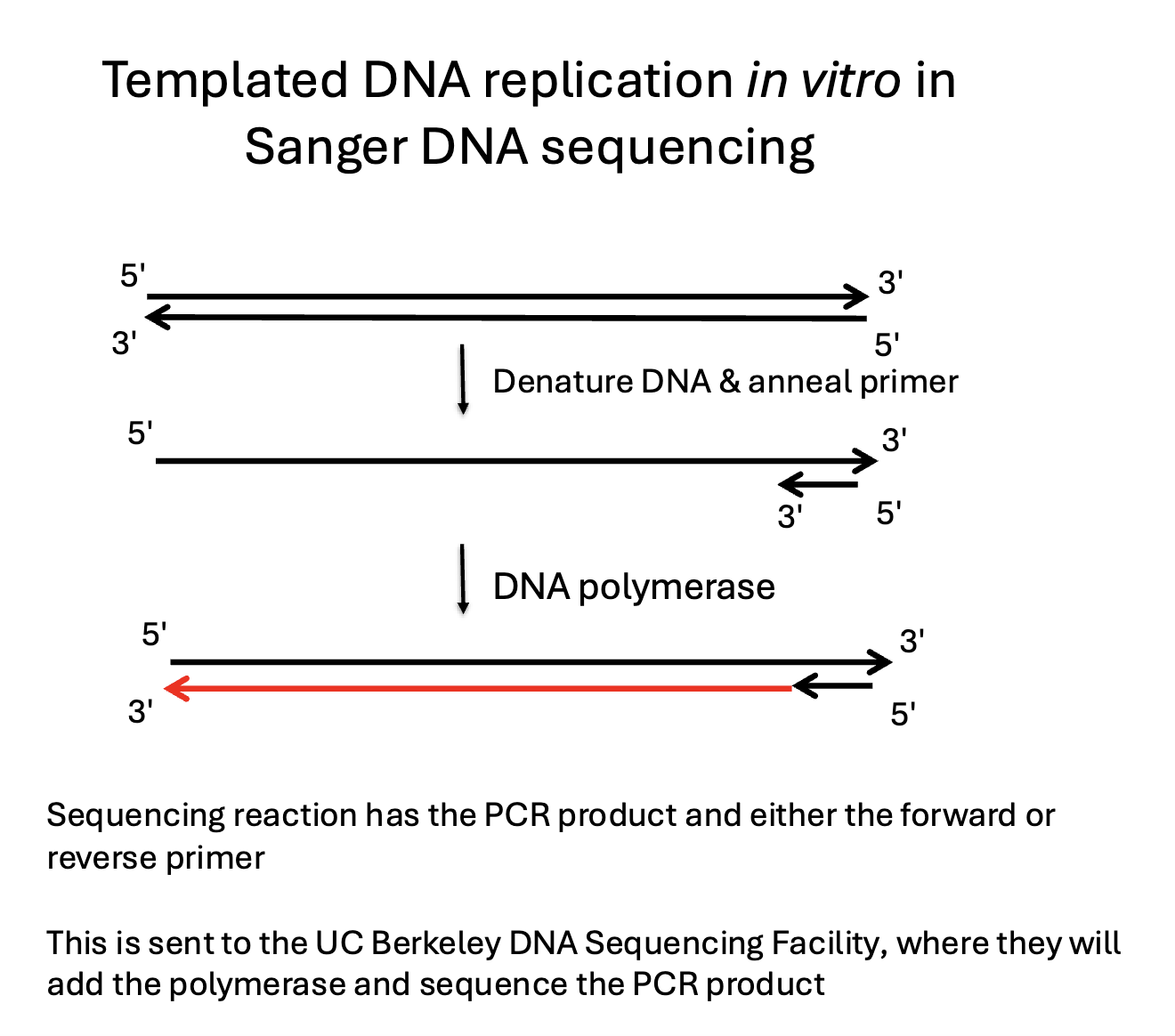
Sanger DNA sequencing
PCR in vitro
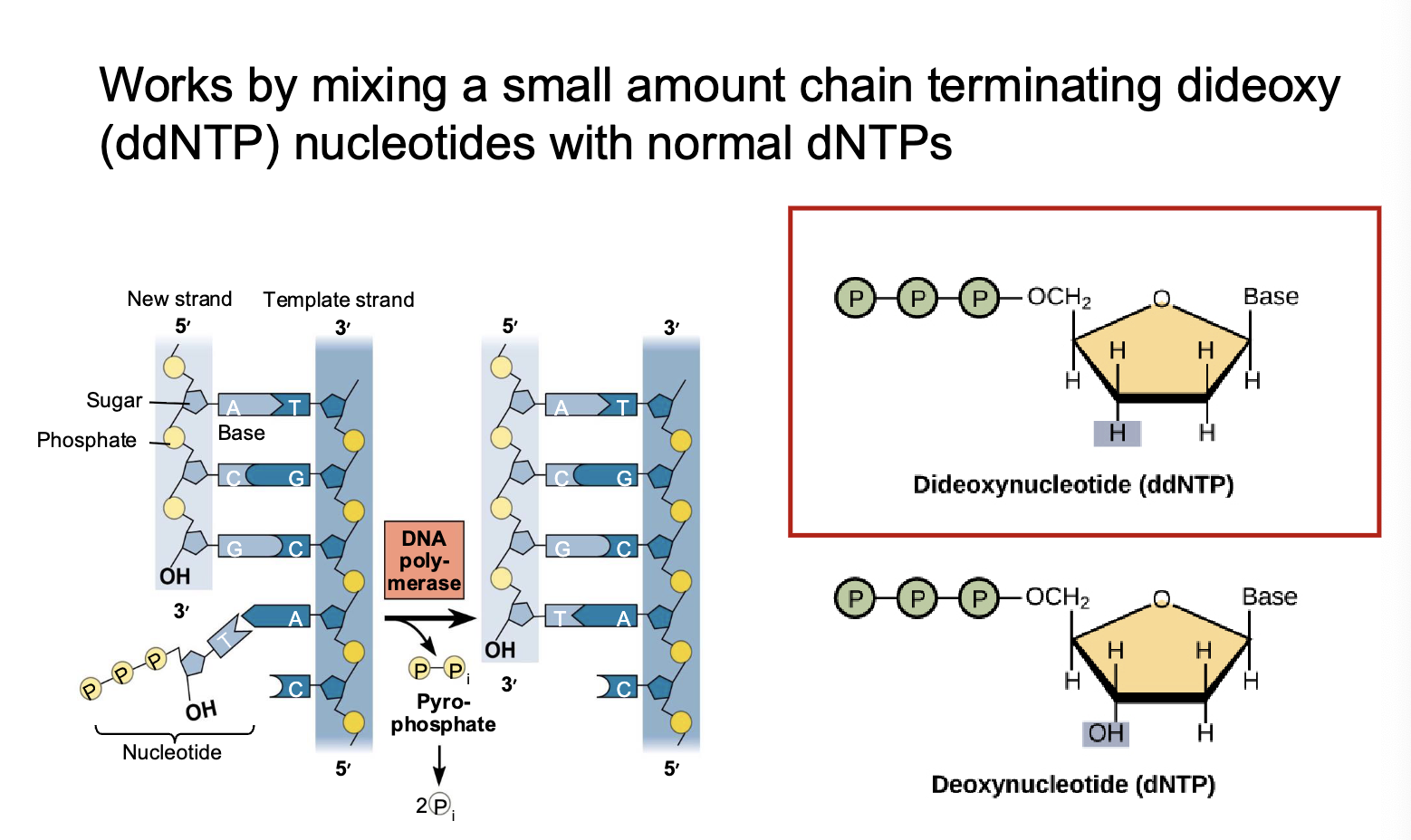
mixes small amount of ddNTP (chain terminating dideoxy nucleotides) with dNTPs
results in different length strands of DNA which are separated by electrophoresis and read by laser excitation (electropherogram)
ddNTP
dideoxynucleotides: nucleotide that terminates DNA extension in Sanger sequencing
four types of ddNTP
ddATP, ddTTP, ddCTP, ddGTP
random chain termination
a mixture of dNTPs and ddNTPs causes chains terminated at each nucleotide termination step