Chapter 6: Memory strategies and metacognition
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pdf pages: 134- 151
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
What happens when you use a memory strategy?
You perform mental activities that can help to improve encoding and retrieval.
Generally, when do you recall information more accurately?
When you process it at a deeper level instead of a shallow level
What should you do if you want to emphasize elaboration?
Concentrate on the specific meaning of a particular concept and try to relate it to prior knowledge and concepts you have already mastered.
What will happen if you use simple rehearsal?
You are less likely to be able to accurately retrieve knowledge that you stored shallowly later.
What does deep process increase?
Distinctiveness.
What is distinctiveness?
When one memory trace should be different from all other memory traces in order to help recall.
How does the self-reference effect work?
You can enhance long-term memory by relating the material to your own experiences.
What is the encoding-specificity principle?
Recall will be better if the context at the time of encoding will match the context at the time when your retrieval will be tested.
What is the total-time hypothesis?
The amount of information that you learn depends on the total time you devote to learning.
What happens during the distributed-practice effect?
If you space out your learning, then you were more likely to remember materials. You will remember a lot more than if you tried cramming, or doing massed learning.
What is one reason that distributed practice is helpful for long-term recall?
It introduces desirable difficulties, which is a learning situation that is somewhat challenging, but not too difficult (allowing yourself time to forget means you have to work to remember, allowing yourself to remember it for longer periods of time).
What is the testing effect?
When you are being tested on material, your memory of that material will also go up.
What was the result of the Study, study and Study, test experiment (or Repeated study vs Testing)?
That students who had 2 study sessions originally did just as well as those who only studied once, but those who studied once and then did a test recalled more than their peers when asked to recall everything that they had learned after a set period of time. (basically, testing really helps with recall)
What did Cassady find out about testing anxiety?
That participants who were more anxious would do worse on a reading-comprehension test, and those who were very anxious would have poorer study skills.
What happens if people are highly anxious about taking tests?
They are more likely to experience interference from high levels of worry.
What is a mnemonic?
A mental strategy designed to improve memory.
What are the two different types of mnemonics?
Mnemonics using mental imagery and mnemonics using organization.
When is imagery especially effective?
When items that must be recalled are shown to be interacting with each other.
What is the keyword method?
A way to learn new words, possibly from a different language, and identifying an English word that sounds similar to the new word that you want to learn, and create an image that links the keyword with the meaning of the new word.
What is the loci placement method?
When you have a series of familiar locations, and then create a mental image of the item you want to remember, placing an item in each of those locations.
What are the mnemonic methods that fall under using mental imagery?
The keyword method and the loci placement method.
How does the mnemonic method of organization work?
When you want to remember a list of things, you’ll try to bring systematic order to the material you want to learn.
What kind of processing does organization use?
It uses deep processing due to the participant needing to sort the items into categories, and it helps retrieval efficiency increase.
What is chunking?
It is an organization method mnemonic, and it is when you combine several small units into larger units (ex: recalling YMC AJF KFB ISA TNB CTV or AMA PHD GPS VCR CIA CBS. The second is easier bc they look like actual words to us).
What is the hierarchy technique?
It is an organizational mnemonic where you arrange the items in a series of classes, from most general to most specific.
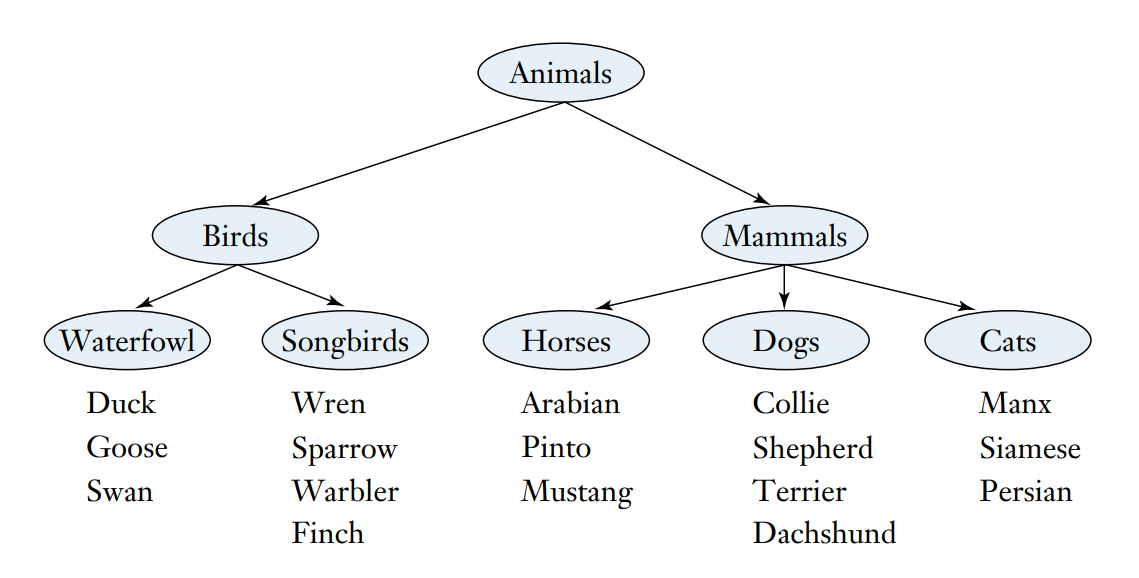
What is an examples of a hierarchy?
An outline, since it divides the material into general categories and each category is further divided.
What is the first-letter technique?
An organizational mnemonic that uses the first letter of each word that you want to remember, and then you make a word or a sentence from those letters (ex: ROY G BIV or the planets).
What is the narrative technique?
An organizational mnemonic method where you make up stories that link a series of words together.
What is one downside to the narrative technique?
It is only effective if you can generate the narrative easily and reliably, both in learning and in recall.
What are the different organization mnemonics discussed in this chapter?
Narrative technique, the hierarchy method, the first-letter technique and chunking.
What is prospective memory?
Memory that involves tasks for the future.
Which groups are more likely to make prospective memory errors?
Long-term opiate users, individuals with schizophrenia, or older age (when compared to younger participants). Of course, everyone experiences prospective memory errors
What are the two components involving prospective-memory?
You need to establish that you intend on accomplishing a particular task, and then later you need to fulfill your intention.
Prospective memory is typically focused on what?
Action
Retrospective memory is more likely to be focused on remembering what?
Ideas and information.
Which one of the two memories is more likely to emphasize ecological validity?
Prospective memory (eco)
Which region in the brain does both prospective and retrospective memory lay in?
Regions of the frontal lobe.
What kind of situation does the typical prospective-memory task represent?
A divided-attention situation (since you need to focus on what you are currently doing and what you will be doing).
When is absent-minded behavior more likely to happen?
When you attempt to disturb a customary, or regular, activity (ex: you usually aren’t the one to pick up your toddler from daycare, but one day you do after coming home from work, and you forget to take them out of the car since you aren’t used to doing so).
When are prospective-memory errors more likely to occur?
When you are in highly familiar surroundings when performing tasks automatically.
What are some other causes for absentminded behaviors?
When you are preoccupied/distracted, feeling pressured by time, or are feeling stressed.
What is one of the best ways to avoid prospective-memory errors?
Through providing yourself with reminders to complete a task at a certain point of time in the future.
What is an external memory aid?
An external memory aid is defined as any device outside of yourself that facilitates your memory in some way (ex: a shopping list, band around the wrist, ringing of an alarm, etc.).
What is metacognition?
Your knowledge and control of your cognitive processes.
Why is metacognition important?
Because during college, you are learning how to think and how to become a reflective person, and the only way to do that is to consciously think about how you are learning and how to improve.
What is self-knowledge?
What people believe about themselves, including knowledge about your social behavior and your personality.
What is metamemory?
A topic that refers to people’s knowledge, monitoring, and control of their memory.
When is metamemory important?
It is important if you want to improve your memory.
What is foresight bias?
The tendency to be overconfident about performance on a recall task (usually in the case of a test for a class)
What was the result of the Dunning and co’s experiment (Giving a test and then afterwards asking about what percent they think they got)?
Students in the top and second quartile were fairly good at estimating their scores, but students in the third and bottom quartile overestimated their scores, assuming they got a higher score than they actually did.
What is the takeaway of Dunning and co’s experiment (Giving a test and then afterwards asking about what percent they think they got)?
That the student’s who scored low don’t know that they don’t know the material that well.
When is metamemory usually accurate?
When they are predicting which individual item them remember and which one they’ll forget. It is also accurate if you wait a bit after reviewing to see how they think on a test (ex: i will be overconfident if you ask me 5 minutes after i studied, but i will be less confident and more accurate after a day of reviewing the material)
What is the tip-of-the-tongue effect?
It describes your subjective experience of knowing the target word which you are searching for, but can’t recall at the moment.
What is the feeling-of-knowing effect?
It describes your subjective experience of knowing some information but you are unable to recall the information at the moment.
What is the main difference between the tip-of-the-tongue effect and feeling-of-knowing effect?
TOTT is more of an involuntary effect, while FOK is more conscious.
Which part of the brain is important for metacognitive tasks?
The frontal lobe of the brain.
Why are bilinguals more likely to experience TOTT effect than monolinguals?
Because bilinguals have greater words in their semantic memory when compared to monolinguals
What is the tip-of-the-finger effect?
It is similar to the tip-of-the-tongue effect, but it is for the deaf community for when they know they target sign, but the sign is temporarily inaccessible to them.
Which part of the brain is the TOTT effect more likely to be associated with?
The right prefrontal region of the cortex
Which part of the brain is the FOK effect more likely to be associated with?
the left prefrontal cortex.