Polymers, Lipids, Fats, Phospholipids, and Sterols
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
topic 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is a polymer?
Multiple monomers held together by covalent bonds.
What is dehydration synthesis?
The synthesis of a polymer where covalent bonds form between monomers, resulting in the loss of H2O (dehydration).
NRG + enzymes required (nucleic acids are the exception for NRG)
how lipids are formed
What is hydrolysis?
The breakdown of polymers by adding H2O (hydration), which breaks covalent bonds between monomers
Releases NRG
Requires enzymes
What are lipids?
Fats that provide half the answers to how life evolves
Creates distinct, separate internal environment
Eg. Phospholipid Bilayer (example of amphipathic)
What cells are lipids in?
Fats, hydrogenated oils, steroids
Are fats part of cell membranes?
No, they are not part of the membrane (unlike some other lipids).
What is the basic structure of a fat (triglyceride)?
Made up of 1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acids, joined by dehydration synthesis.
What factors determine the type of fatty acid?
Length of the hydrocarbon (HC) chain and the number/location of double bonds.
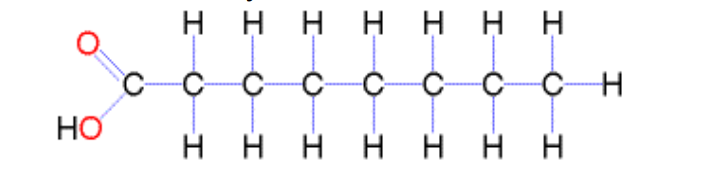
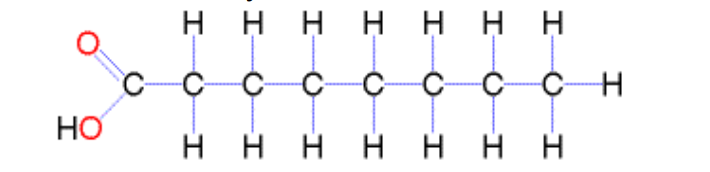
What are saturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with no double bonds; straight molecules that pack closely together, solid at room temperature (e.g. red meat, butter).
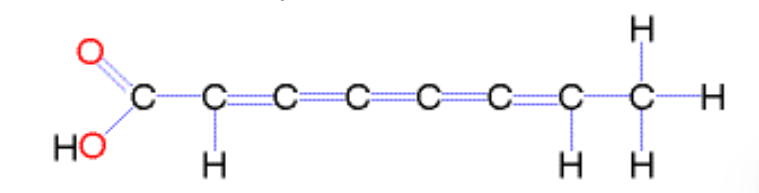
What are unsaturated fatty acids?
Fatty acids with one or more double bonds; bend at double bonds, can't pack closely, liquid at room temperature (e.g. oils, fish, and plants)
There are two types = Cis and trans
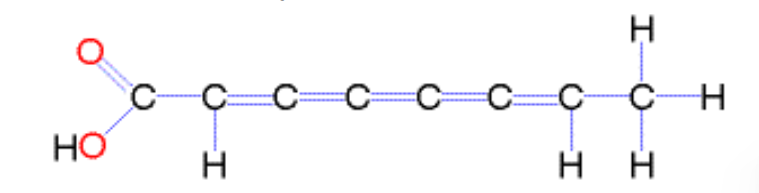
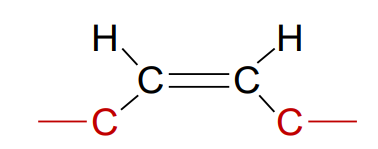
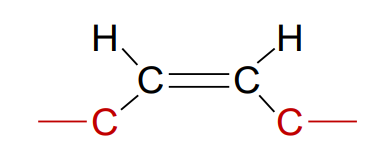
What is a cis fatty acid?
Unsaturated fatty acid where the chains are on the same side of the double bond; naturally occurring, and its fatty acid tail is bent
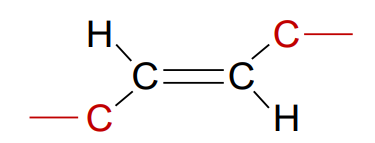
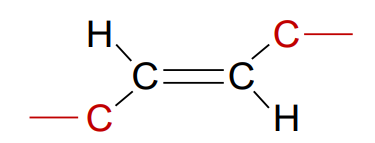
What is a trans fatty acid?
Unsaturated fatty acid where the chains are on opposite sides of the double bond; unnaturally occurring, its fatty acid tails are straight, and can turn an unsaturated fatty acid tail into a saturated one
What are hydrogenated oils?
Makes the unsaturated fat like a saturated fat by synthetically adding hydrgen to the unsaturated fat and remove its double bonds
Why are oils hydrogenated?
Makes them less perishable, remains more solid at room temp, doesn’t separate compared to animal fat
What are the characteristics of lipids?
Amphipathic (part hydrophobic/part hydrophilic) but doesn’t have to be
Lots of non-polar bonds
Low water solubility
NOT polymers but STILL macromolecules
What are the function of fats?
NRG source, insulation, and protection
What are the characteristics of fats?
Almost entirely hydrophobic molecules
NOT part of the membrane
made up of 1 glycerol + 3 fatty acids = triacyglycerol
fatty acids are stuck via attached ester linkage
formed by dehydration synthesis
Why do variations in fatty acids occur?
It all depends on the length of the HC chain, and its location of the double bond
What are the three types of fatty acids?
Saturated
Unsaturated
Trans
What is the problem with trans fatty acids?
Unnatural, doesn’t digest well, clogs arteries, causes inflammatory response
What is the main function of phospholipids?
A major component of cell membranes due to their amphipathic nature.
What is the structure of a phospholipid?
2 fatty acid tails (hydrophilic head/hydrophobic tail)
the 3rd carbon of glycerol is attached to the phosphate group
held by ester bonds
How are the parts of a phospholipid held together?
Ester bonds.
What is the basic structure of sterols?
A carbon skeleton with four fused rings
The subtype of steroids
non-polar
What are the functions of sterols?
Signalling molecules, important part of the membrane due to its amphipathic nature, precursor for steroids
How does variation occur in sterols?
From attachment of different functional groups to the carbon skeleton.
What is an example of a key sterol?
Cholesterol.
What is cholesterol's role?
Component of animal cell membranes
precursor to all other steroids
What are the negative health effects associated with cholesterol?
Can clog your artieres
Can there be multiple types of phospholipids?
Yes, it just depends on what’s added to the phosphate group
Can cholesterol be good for you?
Yes, but ONLY if its in the membrane