OptoPrep Part 1 - Contact Lenses
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
A soft contact lens with a power of -7.00 D states on the package that it has a Dk/t of 35. However, given your knowledge of Dk/t, you know that the lens actually possesses which of the following characteristics?
Because the lens is what in power, The lens' center/periphery has what Dk/t?
Because the lens is minus in power; the periphery of the lens has a Dk/t lower than that stated on the package
Increasing silicone content and decreasing water content will have what effect on the oxygen transmissibility of soft contact lenses?
The oxygen transmissibility will increase
A new patient to your office presents wearing rigid gas-permeable contact lenses. You begin to analyze the lenses with a lensometer and notice that both lenses have a toric prescription and prism. Which of the following type of lenses does the patient MOST likely currently wear?
Front Surface (F1) Toric
(They are the only lenses that have a prism ballast design)
When analyzing a rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens, you measure base curves of 7.30mm (46.25D) and 7.54mm (44.75D) with a radiuscope, and powers of -3.75D and -6.00D on lensometry. What type of toric RGP contact lens design do you have?
Toric Base Curve
46.25 (steep) -6.00 (most minus)
44.75 (flat) -3.75 (most plus)
Difference in BC: 46.25-44.75 = 1.50D
Difference in CL Power: -6.00 - (-3.75) = -2.25D
Test with the 3/2 x base curve difference test: 3/2 x 1.50 = 2.25D
Confirmed Toric Base Curve
When analyzing a gas permeable (GP) contact lens, you measure base curves of 7.58mm and 7.84mm with a radiuscope, and powers of -1.00D and -2.50D on lensometry. What type of toric GP lens design do you have?
Spherical power effect (SPE) bitoric
BC1 = 7.58mm = 337.5/7.58 = 44.50D
BC2 = 7.84mm = 337.5/7.84 = 43.00D
Change in BC = 1.50D
CLP1 = -1.00D
CLP2 = -2.50D
Change in CLP = 1.50 D
The differences in base curves and contact lens powers for the above GP contact lens are equal (both 1.50 D), indicating that the design of the lens is a spherical power effect (SPE) bitoric.
If the difference in base curve is equal to the difference in contact lens power,
spherical power effect (SPE) bitoric lens
If the difference in base curve is not equivalent to the difference in CL power, and 3/2 x the difference in base curve is also not equal to the difference in CL power,
cylinder power effect (CPE) bitoric lens
Your 54-year-old female patient wishes to wear soft contact lenses as monovision. She currently wears distance contact lenses for both eyes, is right eye dominant, and requires a +2.00 add power. Based on the following data, which contact lenses would you prescribe for each eye?
Current distance CL Rx: OD: -2.50 OS: -1.00
Distance over-refraction: OD: plano OS: +0.25 -0.50 x 180
OD: -2.50 OS: +1.00
Your 22-year-old patient with a manifest refraction of OD: +2.00 -2.00 x 086 and OS: +2.50 -1.75 x 092 wishes to try soft contact lenses. After discussion, you decide to try Air Optix Toric monthly lenses. Which of the following prescriptions would you try first for her right eye?
+2.00 -1.75 x 090
Hypoxia associated with hydrophilic (soft) contact lens wear is MOST likely to result in what ocular signs?
Corneal swelling
A patient walks into your office and would like to be fit with soft contact lenses. Your subjective refraction reveals: OD: +5.50 DS, OS: +4.75 DS. If the phoropter was placed 13 mm from the corneal plane, which of the following contact lens prescriptions would likely be the BEST choice for the right eye of this patient?
+6.00
(+5.50)/(1-(0.013)(5.50) = 5.92 = 6.00
In addition to flattening the base curve, which alteration will help to loosen a tightly-fitting gas permeable (GP) contact lens?
Reduce the size of the optic zone
Your rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens patient presents with dimple veiling of the cornea. What modification can be made to the contact lens in order to decrease the occurrence of this finding?
Decrease the optic zone diameter
What is the equivalent base curve in millimeters of a rigid gas-permeable (RGP) contact lens with a spherical base curve of 49.75D?
6.78 mm
(337.5/49.75) = 6.78 mm
Modern corneal rigid gas-permeable (GP) contact lenses are usually fit to adhere with which of the following parameters?
(They must align to what surface and also maintain something.)
Align with the anterior corneal surface and maintain tear exchange
Which 2 of the following statements are TRUE in regards to the center thickness of rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses? (Select 2)
As the overall diameter of the contact lens increases, what happens to the thickness?
As the base curve of the contact lens becomes steeper, what happens to the thickness?
As the overall diameter of the contact lens increases, the center thickness of the contact should increase
As the base curve of the contact lens becomes steeper, the center thickness of the contact lens should increase
What is the power of the tear lens created by a gas permeable (GP) contact lens with a base curve of 42.87D that is placed on a cornea with a spherical curvature of 43.25D? (Round to the nearest 0.12D)
-0.37D
Tear lens (TL) = base curve (BC) - keratometry (K)
TL = 42.87 - 43.25
TL = -0.37 D
The Dk/t value of a contact lens is referred to as which of the following terms?
Oxygen transmissibility
When designing a rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens, which type of edge contour is MOST desirable in order to achieve maximal comfort for the patient?
A plus edge
A round edge is also acceptable
Which of the following non-silicone hydrogel contact lens types tend to absorb the LEAST amount of protein?
Low/High Water, Ionic/non-ionic polymers (What group number?)
Low water, non ionic polymers (Group 1)
A 53-year-old female is seen at your office reporting symptoms of dry eyes while wearing her contact lenses. Her current medications include anti-hypertensive medications and blood thinners. Which dry eye treatments should NOT be recommended to her?
Omega III fish oil capsules
While it is acceptable, Omega III fish oil can cause an increase in blood clotting time, which can be dangerous when used in combination with blood thinners.
What can occur to a cl's base curve when a soft contact lens dehydrates?
The base curve steepens
An aphakic patient is seen at your office and wishes to be fit with contact lenses. Of the following parameters, which is the MOST important to be considered in this patient's care?
Ultraviolet (UV) inhibitor
You are fitting the left eye of your patient with a toric soft contact lens. The patient's manifest refraction is +3.00 -1.00 x 050. You apply a +3.00 -0.75 x 060 diagnostic toric soft contact lens. It fits well, but the horizontal lens markings are consistently located at the 4 o'clock and 10 o'clock positions. What axis should you order?
080 degrees
Every hour on the clock dial would translate to 30 degrees of rotation. Rotates to the doctor's left by 1 hour. 30 + Manifest refraction axis (050) = 080
You are fitting your patient's right eye with a toric soft contact lens. The patient's manifest refraction is -2.00 -1.50 x 095. You apply a -1.75 -1.25 x 085 diagnostic toric soft contact lens. It fits well, but the prism base down marking consistently locates halfway between the 6 o'clock and 7 o'clock positions. What axis should you order?
110 degrees
15 degrees (between the 6 and 7 o'clock)
15 + Manifest refraction axis (095) = 110 degrees
When fitting a scleral contact lens, how much clearance over the steepest area of the cornea is considered ideal?
100-300 microns
Your gas permeable (GP) contact lens patient has an apical alignment fluorescein pattern with a 9.0 mm overall diameter / 7.5 mm optic zone diameter lens in place. However, the patient experiences symptoms of flare with this design. If he is refit to a 9.5 mm overall diameter / 7.5 mm optic zone diameter design, what base curve change is necessary to maintain the apical alignment fluorescein pattern?
Flatten the base curve by 0.25 D
one must change the base curve by 0.25 D for every 0.5 mm change in optic zone or overall diameter.
You obtain the following data during your gas permeable (GP) contact lens evaluation:
OD Diagnostic CL: 43.37 / -2.87
OD Distance OR: -0.50-0.25 x 90
OD Fluorescein Pattern: Alignment
OS Diagnostic CL: 42.87 / -3.25
OS Distance OR: -0.75 DS
OS Fluorescein Pattern: Flat by 0.37 D
It is decided that monovision is the best option for this 51-year-old patient who requires a +1.75 D add. Testing reveals that the right eye is dominant. You prescribe GP contact lenses to fit alignment for both eyes. What contact lens powers would you order?
OD: -3.50 D; OS: -2.62 D
For the left eye, adding the trial lens power (-3.25 D) to the OR (-0.75DS) results in a power of -4.00 D. You would order this power if you were prescribing a 42.87 D base curve for distance viewing. However, you desire to prescribe a 43.25 D base curve to achieve an alignment fitting relationship. To compensate for the steeper base curve, you will need to adjust the power by -0.37 D, resulting in a distance correcting power of -4.37 D (SAM-FAP). To prescribe a near monovision lens for the left (non-dominant) eye, you also need to add the patient's add power (+1.75 D) to the -4.37 D value. The final contact lens power for the left eye will be -2.62 D.
You place a diagnostic rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens on your patient's right eye with a base curve of 46.50D and a power of -3.00D. Analysis of the fit shows that the lens is apical touch by 1.50D, and an over-refraction reveals -4.50DS. If you desire an apical alignment lens fit and plano over-refraction, which contact lenses would you order that would MOST likely provide this?
48.00 / -8.75
In order to find the power of the contact lens, one would add the diagnostic contact lens power to the equivalent spherical value of the over-refraction. Remember though, if the over-refraction is greater than 4.00D, this must be vertexed. Therefore, in this case, one would add the contact lens power of -3.00 to the vertexed over-refraction of -4.25, which equals -7.25. If there was no need to alter the base curve of the contact lens, this would be the power that would provide a plano over-refraction. However; in this case, the base curve needs to be adjusted to provide an apical alignment fit. Because the diagnostic contact lens shows apical touch by 1.50D, the base curve needs to be steepened by 1.50D (to 48.00D). When a base curve is steepened, the tear lens becomes more plus (or less minus), thus an equal amount of additional minus must be added to the contact lens power to adjust for this. Therefore, adding -1.50D to -7.25D means that the new contact lens will require a power of -8.75 in order to provide a plano over-refraction.
You place a diagnostic rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens on your patient's right eye with a base curve of 44.75D and a power of -3.00D. Analysis of the fit shows that the lens is apical touch by 0.75D, and an over-refraction reveals -1.25 -0.50 x 170. If you desire an apical alignment lens fit and plano equivalent spherical over-refraction, which of the following contact lenses would you order that would MOST likely provide this?
45.50 / -5.25
What is the most effective "procedure" for removing lipid deposits from an existing soft contact lens?
Rub with surfactant cleaner
Your 26-year-old patient wears rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses with the following base curves and powers:
OD: 44.37D / -1.00DS and OS: 44.00D / -1.50DS
He reports that after he put his contacts on this morning, his vision was blurred at distance, especially out of the left eye. You suspect that he may have accidentally switched the lenses. If this were the case, what would you expect the over-refraction (OR) to be for each eye? (Assuming that the over-refraction is plano and fit is apical alignment with the proper lenses on each eye)
OD: +0.87DS OS: -0.87DS
the 0.50 difference and then the additional 0.37 of the BC.
Which of the following rigid gas permeable (RGP) lens designs is MOST appropriate for a patient presenting with corneal toricity of 0.50D at axis 090, and 1.75D of residual cylinder axis 090 on over-refraction (when a spherical RGP diagnostic lens is placed on the eye)?
Front Surface (F1) Toric
Your patient undergoes pre-testing and reports that she was wearing her +5.00D soft contact lenses while non-contact tonometry (NCT) was performed. How would you expect this finding to alter the test results?
The measured intraocular pressure will be
Which of the following BEST describes the proper method of measuring the contact lens "sag" on your soft contact lens-wearing patient?
Have the patient move from primary gaze to superior gaze; measure the amount the soft contact lens drops
Regarding gas-permeable contact lenses, what happens to the following parameters as the oxygen permeability (Dk) of these lenses is increased?
The wettability _________, the durability _____________, the lens flexes/warps ________ easily, and the ability of the lens to resist scratches ________________
The wettability decreases, the durability decreases, the lens flexes/warps more easily, and the ability of the lens to resist scratches decreases
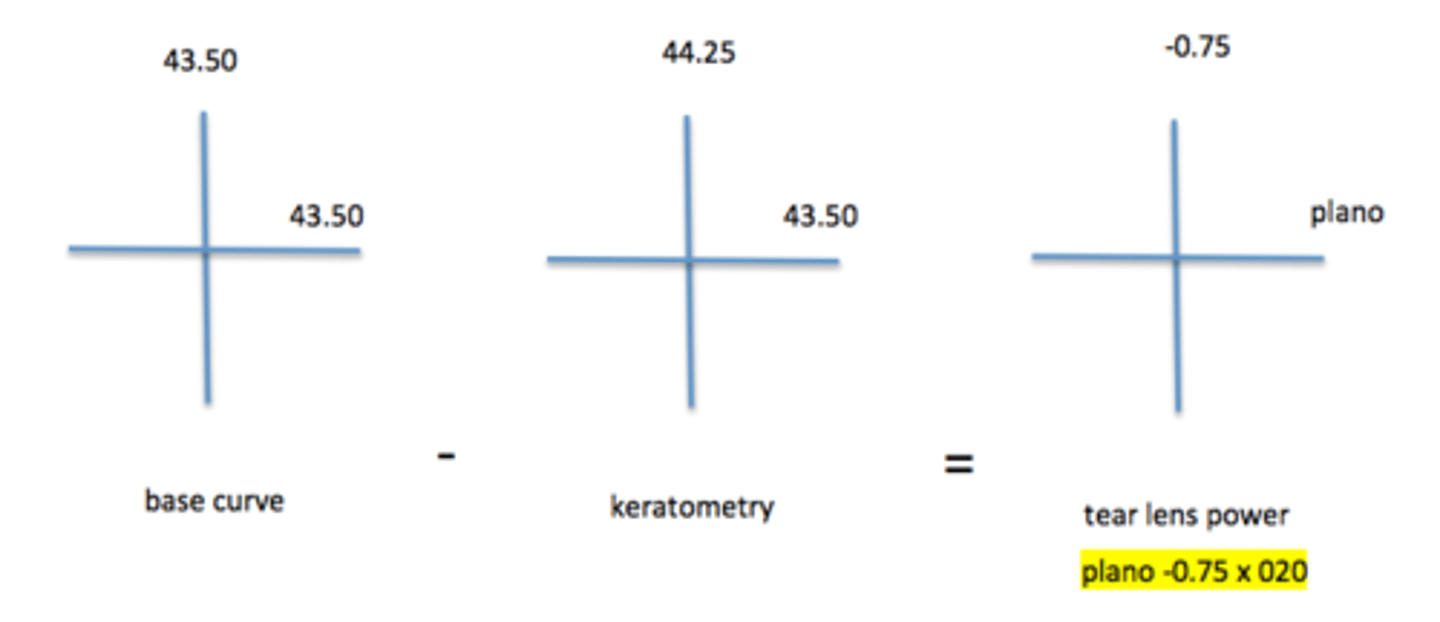
What is the power of the tear lens created by a gas permeable (GP) contact lens with a base curve of 43.50D that is placed on a cornea with a keratometry reading of 44.25 x 43.50 @ 020?
plano -0.75 x 020
Tear lens (TL) = base curve (BC) - keratometry
Ultraviolet (UV) protection is very important for people who wear contact lenses. What is a drawback to adding UV protection to a rigid gas-permeable contact lens?
It can interfere with the interpretation of the sodium fluorescein pattern
Given the following parameters, what is the power of the tear lens formed by a rigid gas-permeable lens with a base curve of 42.00 D and a power of +3.00 DS that is placed upon a cornea with a keratometry reading of 43.25 DS?
-1.25 DS
42.00-43.25 = -1.25
It's Only asking for the tear lens, not the complete refraction.
You are recording the parameters of your patient's rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses into his record that you have obtained from a prescription from his prior optometrist. The overall diameter (OAD) is noted to be 9.0 mm, the optic zone (OZ) is 7.4 mm, and the tertiary curve width (TCw) is 0.2 mm. The secondary curve width (SCw) is not available; however, based on the above information you calculate it to be which of the following values?
0.60 mm
OAD = OZ + 2(SCw) + 2(TCw)
9 = 7.4 + 2(x) + 2(0.2)
x = 0.60mm
Which 3 things typically occur when the oxygen permeability (Dk) of a rigid gas permeable (RGP) lens increases? (Select 3)
Lenses are more likely to scratch
Wettability of the lens decreases
Lenses are less likely to warp/flex
Durability of the lens increases
Less resistant to protein deposits on the
Lenses are more likely to scratch
Wettability of the lens decreases
Less resistant to protein deposits on the
You place a soft toric contact lens on your patient's right eye. You let the lens settle for several minutes and then assess the fit with the slit-lamp. You note that coverage is full and the lens is centered, but the inferior laser lens marking is rotated so that it sits at the 7 o'clock position. Which of the following BEST describes the amount of rotation of this contact lens (in degrees)?
30 degrees
Which parameter contributes the MOST to the vision achieved through a soft toric contact lens?
Overall stability
You are designing a rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens for your patient who presents with a keratometry reading of 44.25 x 41.00 @ 180, and manifest refraction of -2.50 -3.00 x 180. With a spherical RGP diagnostic lens placed on the eye, the over-refraction is +0.50 -0.25 x 180. Which of the following RGP lens designs is MOST appropriate for this patient?
Spherical Power Effect (SPE) Bitoric
Turn this question over and do the exercise, the next flashcard will have the answer
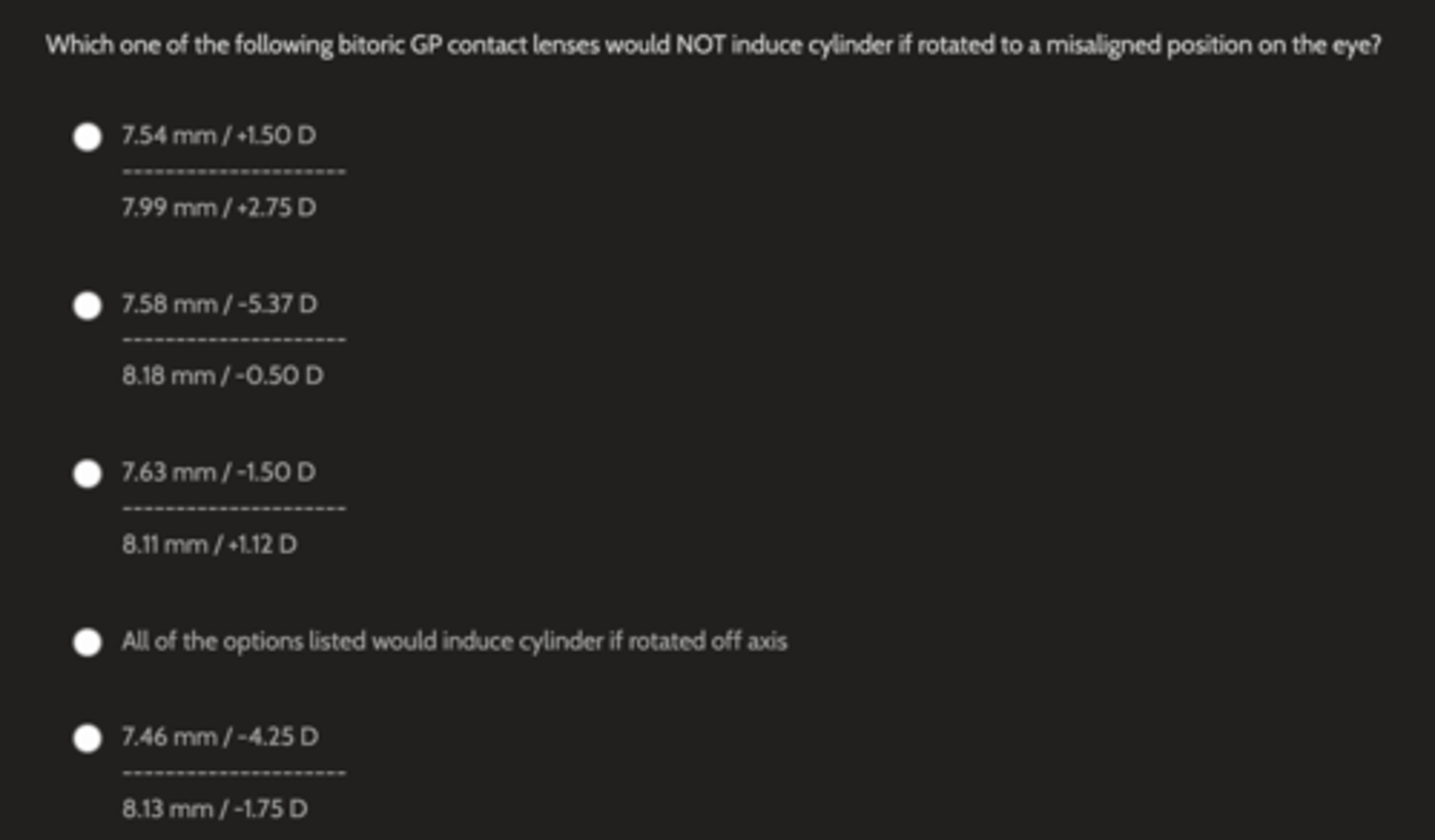
Which one of the following bitoric GP contact lenses would NOT induce cylinder if rotated to a misaligned position on the eye?
7.63 mm / -1.50 D
---------------------
8.11 mm / +1.12 D
Your patient has a spectacle prescription of +10.00 DS OU. Which 2 of the following changes will occur to his visual system when changing from spectacles to contact lens wear? (Select 2)
accomodative demand and convenrgence demand
Accommodative demand decreases
Convergence demand decreases
Your 50-year-old patient currently wears soft contact lenses as monovision with the right eye for distance and left eye for near. Manifest refraction is OD: -2.00 -0.50 x 180 and OS: -2.25 -0.50 x 180. If the patient requires a +1.75D add, what would you expect the over-refraction to be if spherical soft lenses were placed on the eyes to allow for this type of vision?
OD: +0.25 -0.50 x 180
OS: -1.50 -0.50 x 180
You do the plano equivalent sphere (EDS), which would be +0.25 for OD and then use the -1.75 add for the EDS of the left eye and add + 0.25 to that and you get the OS.
Your 32-year-old patient wearing rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses comes in to your office complaining of mild redness and irritation with his current set of contact lenses. On slit-lamp examination you notice moderate peripheral cornea desiccation (3-9 staining). Which 2 of the following adjustments could you make to the contact lens parameters in order to minimize his signs and symptoms? (Select 2)
Base curve and Peripheral curves
Steepen the base curve
Steepen the peripheral curve
Your 29 year-old rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens patient requests a new prescription as she lost her current contacts. Her keratometry reading is 44.62 @ 180 / 43.12 @ 90 and refraction is +2.75 -1.00 x 095 for her right eye. Given this data, which of the following diagnostic rigid contact lenses would provide a predicted fluorescein pattern of apical alignment and predicted spherical over-refraction of plano, respectively? (Assume that overall diameter of the lens is 9.0mm, and optic zone is 7.4mm)
43.12, +2.75
Average K= (44.62 + 43.12) / 2 = 43.87
Average K -0.75D = 43.87 - 0.75 = 43.12
Because it's ON K, the power will be equal to the manifest refraction
Your 23-year-old rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens wearer returns to your office for a contact lens follow-up after wearing his new lenses for about 2 weeks. During slit-lamp evaluation you notice several circular, well-demarcated indentations of the central cornea that pool with fluorescein. What is the name of this finding?
Dimple veiling
Which of the following toric gas permeable (GP) lens designs is MOST appropriate for a patient with keratometry values of 43.50 @ 100 / 43.00 @ 010 and subjective refraction data of -2.00 -2.50 x 095?
Prism ballast front surface (F1) toric
Which of the following ophthalmic instruments is MOST commonly used to evaluate the edge profile of a rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens?
Shadowscope
A 24-year-old female wears soft contact lenses with a Dk/t of 175. She admits to sleeping in her lenses and states that she is very satisfied with both the comfort and the vision with her contacts. Biomicroscopy reveals mucin balls under her lenses that leave impressions in her central corneas upon removal of her contacts. Which of the following actions would BEST help to eliminate the formation of mucin balls?
Maintaining the same lens material but changing to a steeper base curve
A back surface toric (spherical front surface) gas-permeable (GP) contact lens is ordered with base curve radii of 7.85 mm (43.00 D) and 8.44 mm (40.00 D). When verifying this lens with a lensometer you would expect to find approximately how many diopters of "total cylinder"?
4.50 D
43-40 = 3
3 x (3/2) = 4.50
Your 38-year-old male patient wears rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses. The following parameters are for his right eye:
Keratometry: 45.50 @ 090 x 44.00 @ 180
Base curve of RGP: 44.00 (apical alignment)
Original over-refraction: +0.50 -1.00 x 180
Which 2 of the following would you expect to occur to the over-refraction if you suspect that his contact lens is warped by 0.50D? (Select 2)
- The equivalent diopter sphere of the over-refraction
- The amount of with-the-rule astigmatism in the over-refraction
The equivalent diopter sphere of the over-refraction will not change
The amount of with-the-rule astigmatism in the over-refraction will increase
Which term describes the Dk value of a contact lens?
Oxygen permeability
A patient walks into your office and would like to be fit with soft contact lenses. Your subjective refraction reveals: OD: -4.50 -2.00 x 180 and OS: -5.00 -3.25 x 180. If the phoropter was placed 13 mm from the corneal plane, which of the following contact lens prescriptions would be the BEST choice for the right eye of this patient?
-4.25 -1.75 x 180
Because of vertex
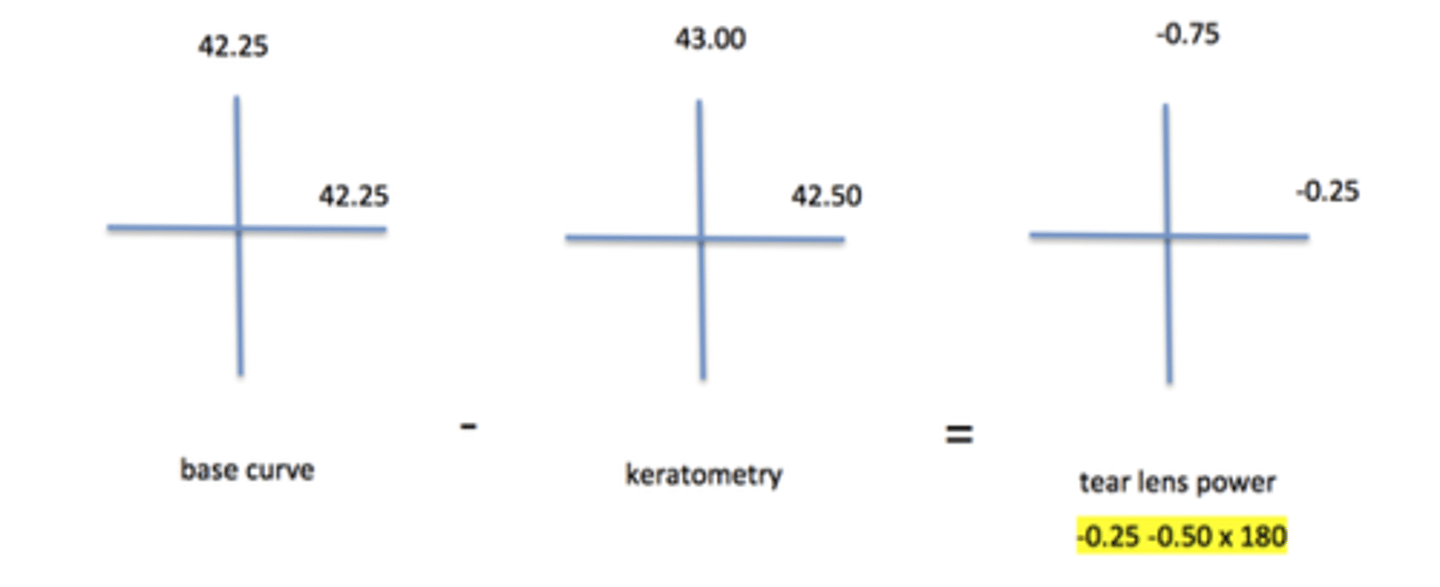
What is the power of the tear lens created by a gas permeable (GP) contact lens with a base curve of 42.25 D placed on a cornea with a keratometry reading of 43.00 x 42.50 @ 180?
-0.25 -0.50 x 180
Which of the following BEST describes the proper method of measuring the contact lens "lag" on your soft contact lens-wearing patient?
Have the patient move from primary gaze to lateral gaze; measure the amount the soft contact lens moves relative to the cornea
A saucer-shaped depression of the peripheral cornea, usually found adjacent to an area of elevation, is known as which of the following findings?
Dellen
You place a diagnostic rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens on your patient's right eye that has a base curve of 45.25 D and a power of -4.00 D. Analysis of the fit shows that the fitting relationship is apical clearance by 1.00 D, and an over-refraction reveals +0.50 -0.50 x 110. If you desire an apical alignment lens fit and plano equivalent spherical over-refraction, which of the following contact lenses would you order that would MOST likely provide this?
44.25 / -2.75
1) Get the spherical equivalent of the over refraction (0.25)
2) Add that to the -4.00 and it gives you -3.75
3) Subtract the 1.00 from that and you get - 2.75
What may occur if you increase the water content of a soft (non-silicone) hydrogel contact lens?
The patient may report an increase in dry eye symptoms
At the initial dispensing visit, your gas permeable (GP) contact lens patient achieved a visual acuity of 20/15 OU through both her manifest refraction and contact lens over-refraction. At a follow-up visit one year later, the patient's visual acuity is 20/15 OU with a contact lens over-refraction; however, following removal of her contacts, her visual acuity is 20/30 OU through a manifest refraction. What is the MOST likely cause for the reduced visual acuity obtained through the manifest refraction?
Corneal distortion secondary to GP contact lens wear
According to Snyder (1989), a contact lens that is rotated 10 degrees away from its proper axis will result in the manifestation of astigmatism that is equal to roughly:
1/3 of its original power in the over-refraction (located at some oblique angle)
According to Snyder (1989), a contact lens that has rotated 15 degrees away from its axis will display an over-refraction with astigmatism that is equal to:
1/2 of the original power (located at an oblique angle).
According to Snyder (1989), a lens that has rotated 30 degrees away from its proper axis will reveal
the full amount of cylinder power in the over-refraction (at an oblique angle):
Your patient has a vertexed manifest refraction of -2.00 -3.00 x 090 OS. You place a diagnostic soft toric contact lens with a power of -2.00 -3.00 x 090 on her left eye. The over-refraction results reveal +3.00 -1.50 x 135. From the over-refraction results alone (without assessing the fit with a slit lamp), you correctly estimate the lens to manifest what degree of rotation?
15 degrees
According to Snyder (1989), a contact lens that is rotated 10 degrees away from its proper axis will result in the manifestation of astigmatism that is equal to roughly 1/3 of its original power in the over-refraction (located at some oblique angle). A contact lens that has rotated 15 degrees away from its axis will display an over-refraction with astigmatism that is equal to 1/2 of the original power (located at an oblique angle). A lens that has rotated 30 degrees away from its proper axis will reveal the full amount of cylinder power in the over-refraction (at an oblique angle).
Your 18-year-old patient with a manifest refraction of OD: -3.00 -1.50 x 176 and OS: -3.25 -0.75 x 003 wishes to try soft contact lenses. After discussion, you decide to try Biofinity Toric monthly lenses. Which of the following prescriptions would you try first for his right eye?
-3.00 -1.25 x 180
Your 28-year-old female patient wears rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lenses. The following parameters are for her right eye:
Keratometry: 44.50 @ 090 x 43.50 @ 180
Base curve of RGP: 43.25D (apical alignment with 1.00D of with-the-rule toricity)
Which 2 of the following would you expect to occur to the apical relationship if you suspect that her contact lens is warped by 0.50D? (Select 2)
- Apical relationship will
- WTR Toricity will?
The apical relationship will remain the same
The amount of with-the-rule toricity will decrease
When analyzing the fit of a gas permeable (GP) contact lens, you observe pooling of sodium fluorescein under the center of the lens along with minimal peripheral clearance. In order to fix this problem, what parameter of the lens should be adjusted?
The base curve should be flattened
Calculate the center thickness of a rigid gas permeable (RGP) contact lens with a power of +3.50D? (Assume a standard overall diameter of 9.0mm)
0.27mm
center thickness (ct) = 0.023 x contact lens power (CLP) + 0.19mm
ct = 0.023 (+3.50) + 0.19
ct = 0.2705mm
ct = 0.27mm