COMP 155: Object Oriented Programming Concepts
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
Inheritance
Class obtains variables and methods from another class.
Subclass
Derived class that specializes behavior of superclass.
Superclass
Base class from which subclasses are derived.

Code Reuse
Using existing code to avoid duplication.

Class Hierarchy
Structure showing relationships between classes.
Transitive Inheritance
Subclass instances are also superclass instances.

extends keyword
Keyword used to inherit from another class.
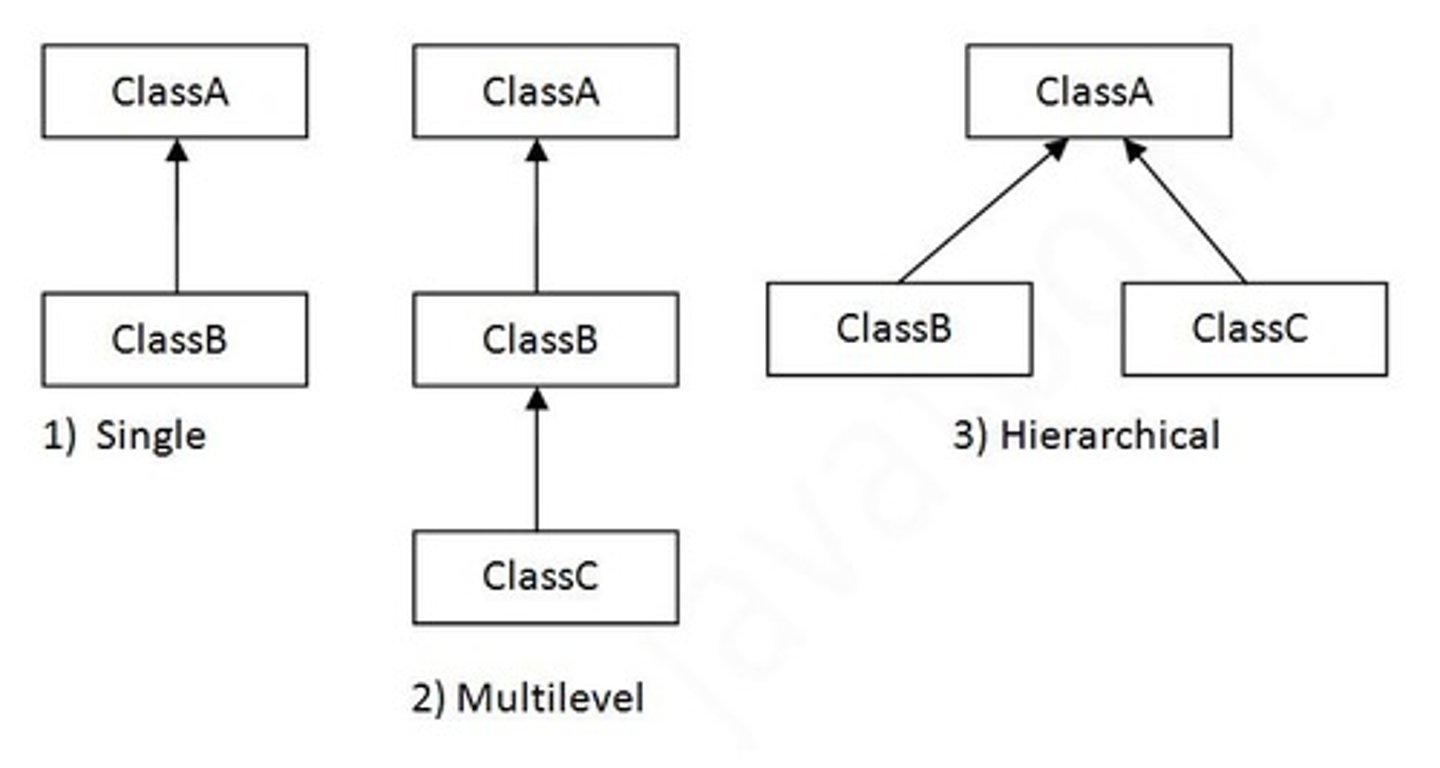
Single Inheritance
One subclass extends one superclass.
Multi-level Inheritance
Subclass extends another subclass.
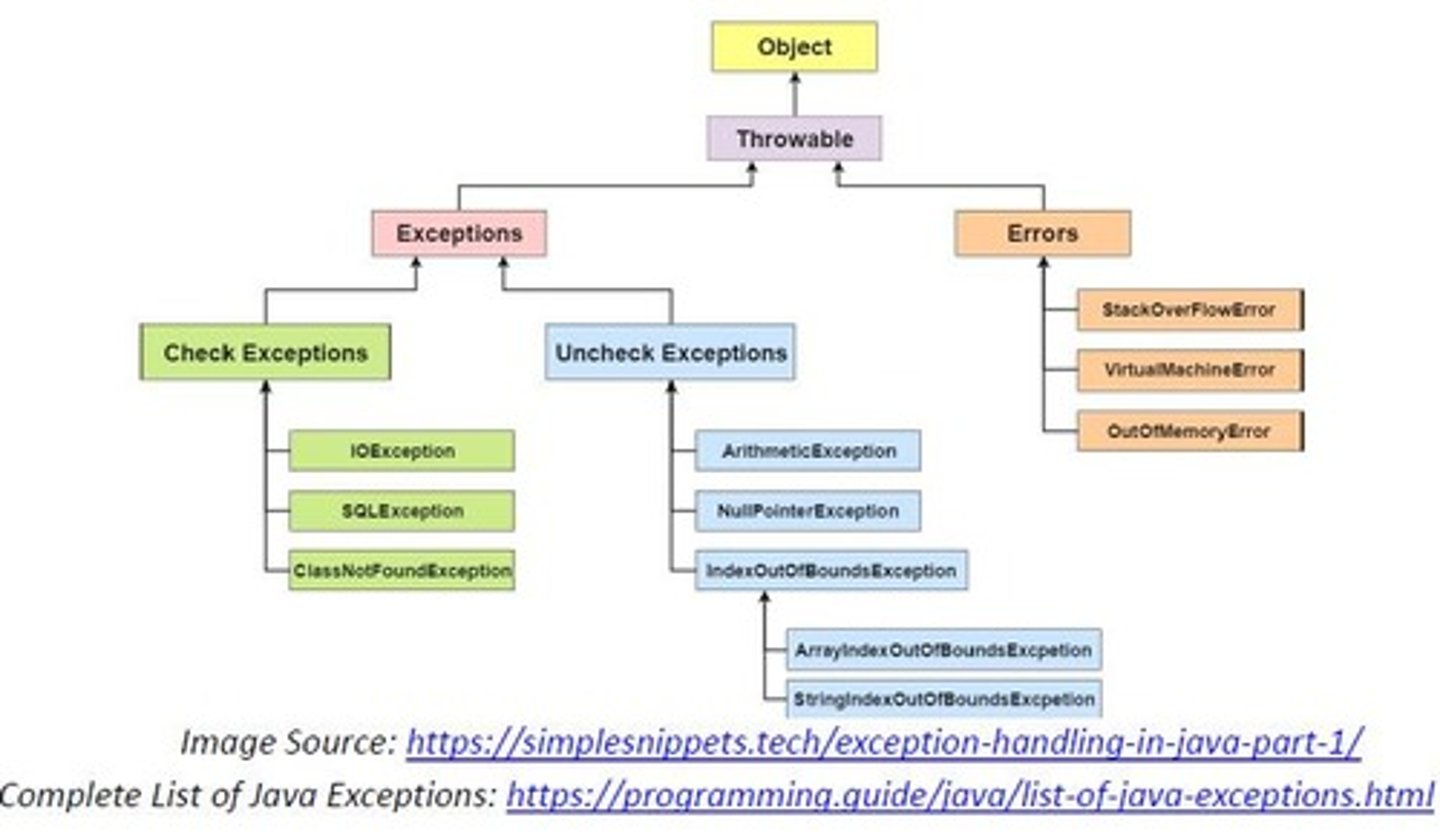
Hierarchical Inheritance
Multiple subclasses extend a single superclass.

Object Class
Default class at the top of hierarchy.
Method Overriding
Subclass provides its own implementation of superclass method.

Access Modifiers
Control visibility of class members (e.g., private).

Instance
Object created from a class.

Polymorphism
Ability to treat objects of different classes uniformly.
Encapsulation
Bundling data and methods that operate on data.
Abstract Class
Class that cannot be instantiated, may contain abstract methods.
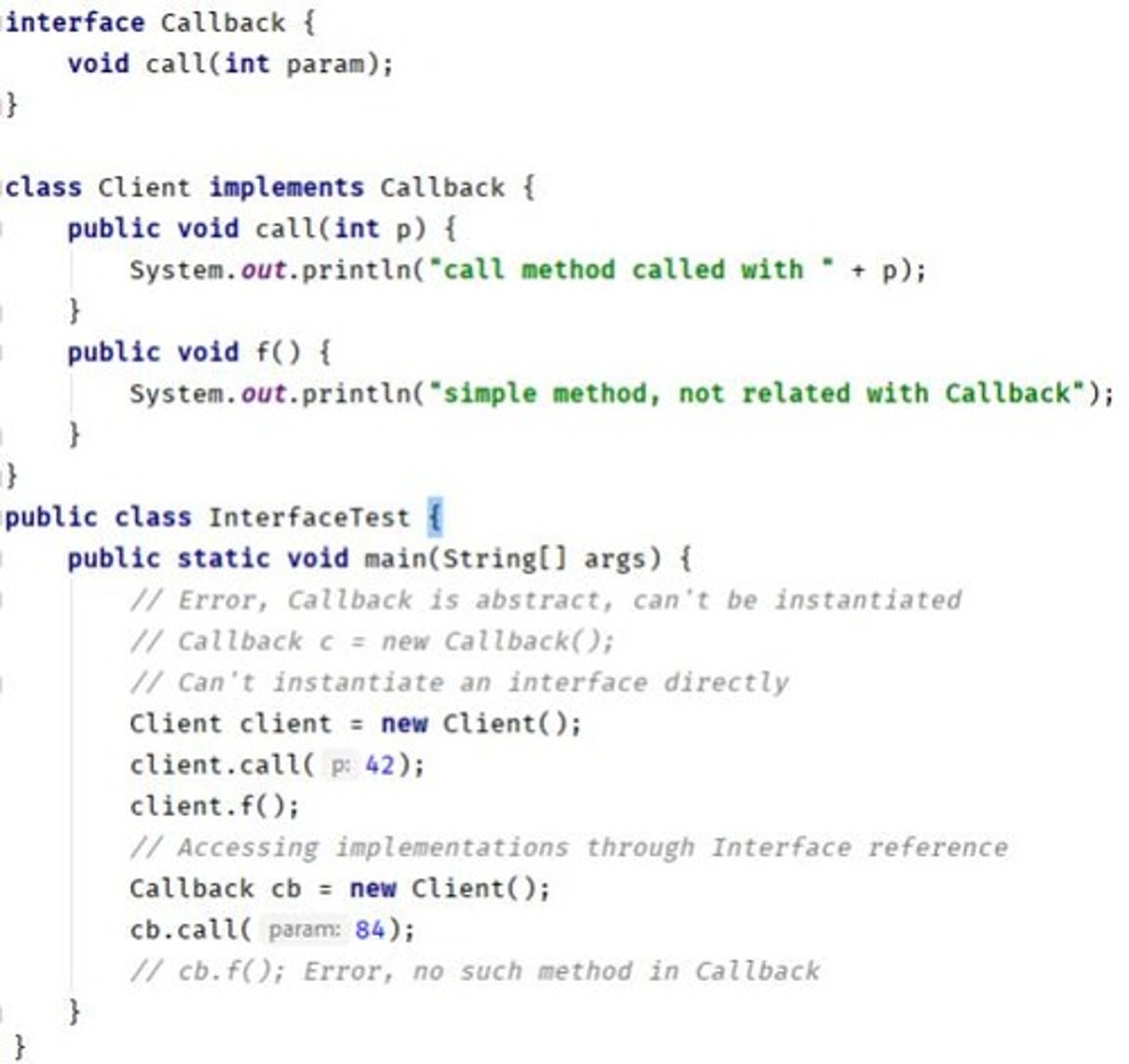
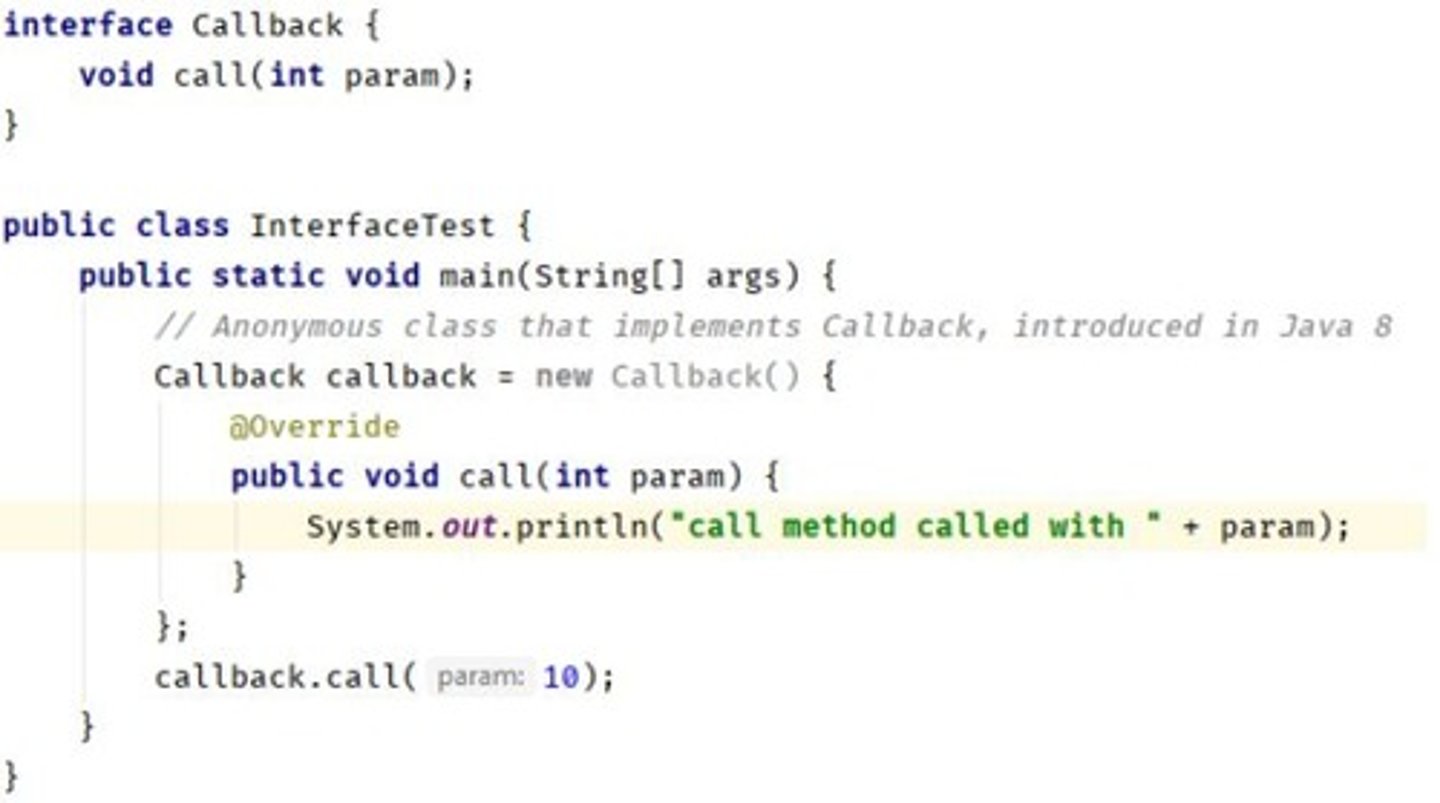
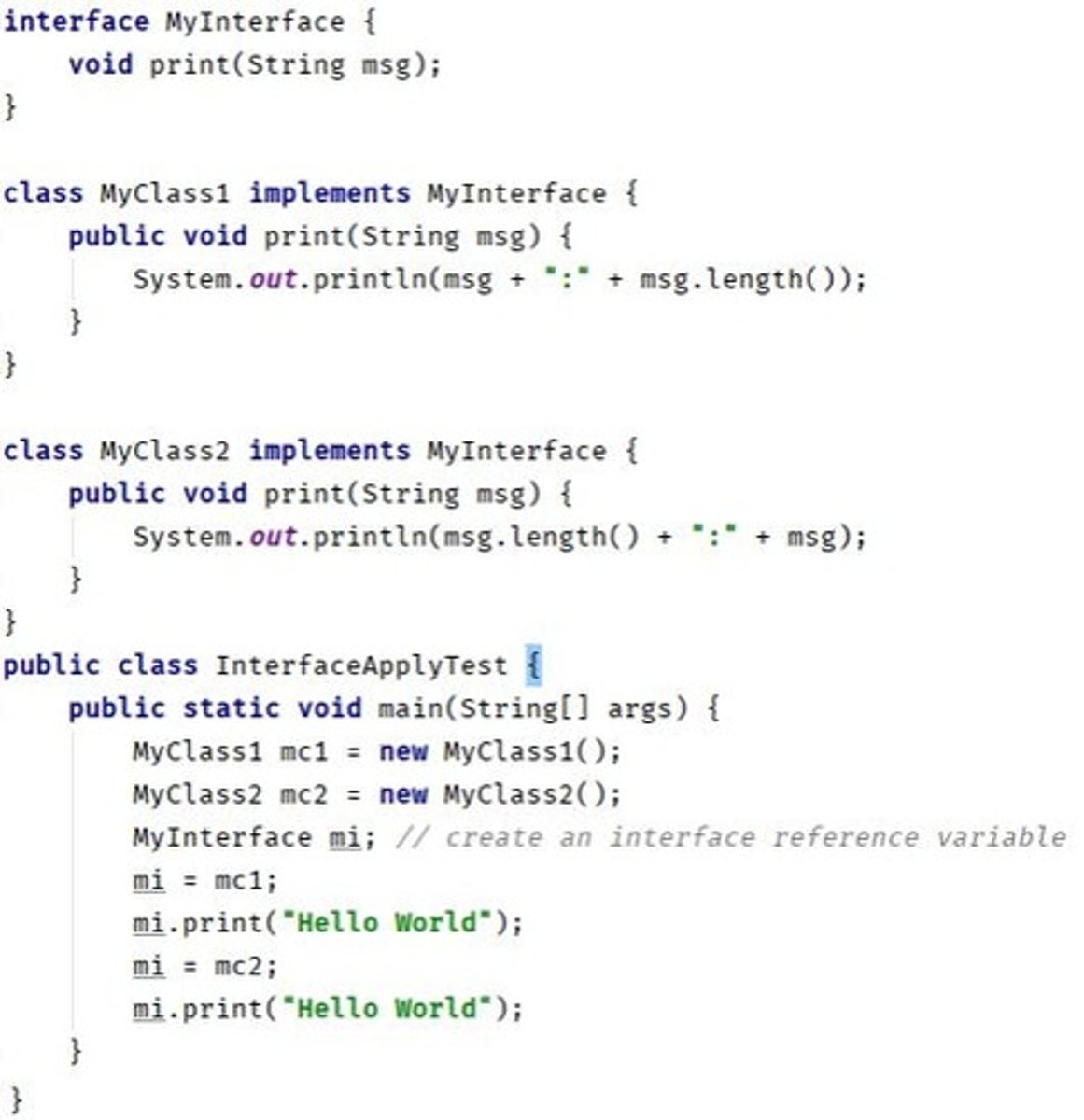
Interface
Contract that classes can implement, defining methods.
Method Signature
Combination of method name and parameter types.
Constructor
Special method called when an object is instantiated.
Overloading
Defining multiple methods with the same name but different parameters.
Aggregation
Relationship where one class contains references to another.
Visibility Modifiers
Determine accessibility of class members.
Public Modifier
Accessible from outside the class definition.
Private Modifier
Accessible only within the class definition.
Protected Modifier
Accessible in subclasses and same package.
Default Access
Accessible within the current Java package.
Encapsulation
Restricting access to class members.
Super Keyword
Refers to superclass members in subclass.
Constructor Call
Invokes superclass constructor from subclass.
Method Call
Calls superclass method to avoid redundancy.
Variable Hiding
Subclass variables hide superclass variables.
Class A Example
Defines variable 'i' initialized to 1.
Class B Example
Defines variable 'i' initialized to 2.
Show Method
Prints value of variable 'i' in subclass.
Inheritance
Subclassing allows access to superclass members.
Access Control
Regulates member visibility in Java.
Protected vs Public
Protected is less accessible than public.
Protected vs Private
Protected is more accessible than private.
Method Redundancy
Avoids duplicate code by using superclass methods.
Class Member
Variables and methods within a class.
Java Package
Namespace for organizing related classes.
Super
Keyword to access superclass members.
Hiding
Subclass variable obscures superclass variable.
Multi-Level Hierarchy
Inheritance structure with multiple levels of classes.
Box Class
Represents a 3D box with dimensions.
BoxWeight Class
Extends Box to include weight property.
Ship Class
Extends BoxWeight to include shipping cost.
Volume Method
Calculates volume of a box: width height depth.
Constructor
Special method to initialize class objects.
Superclass
Class from which properties are inherited.
Subclass
Class that inherits properties from superclass.
Method Overriding
Subclass method replaces superclass method with same signature.
super Keyword
Used to call superclass constructors or methods.
Child Class
Class that inherits from a parent class.
Parent Class
Class from which child classes derive.
Reference Type
Type of variable that determines which class methods can be called.
Object Creation
Instantiating a class to create an object.
Encapsulation
Hiding class attributes and methods from outside access.
Constructor Overloading
Multiple constructors with different parameters in a class.
Inheritance
Mechanism to acquire properties from another class.
Data Member
Variable defined in a class.
Access Modifier
Defines visibility of class members (e.g., private, public).
Polymorphism
Ability to process objects differently based on their data type.
Overridden Method
Method in sub-class that replaces super-class method.
Sub-class Method
Method that overrides a super-class method.
Super-class Method
Original method hidden by sub-class method.
Hiding
Sub-class method conceals super-class method.
Overriding
Same method name in parent and child classes.
Method Signature
Method name and parameter types combined.
Polymorphism
Objects of different classes respond to same method.
Dynamic Binding
Method call resolved at runtime based on object type.
Polymorphic Reference
Reference that can point to different object types.
Overloading
Multiple methods with same name, different signatures.
Common Interface
Defined by super-class for sub-classes to implement.
Specialized Behavior
Sub-class implementation of inherited method.
Driver Class
Class containing main method to execute code.
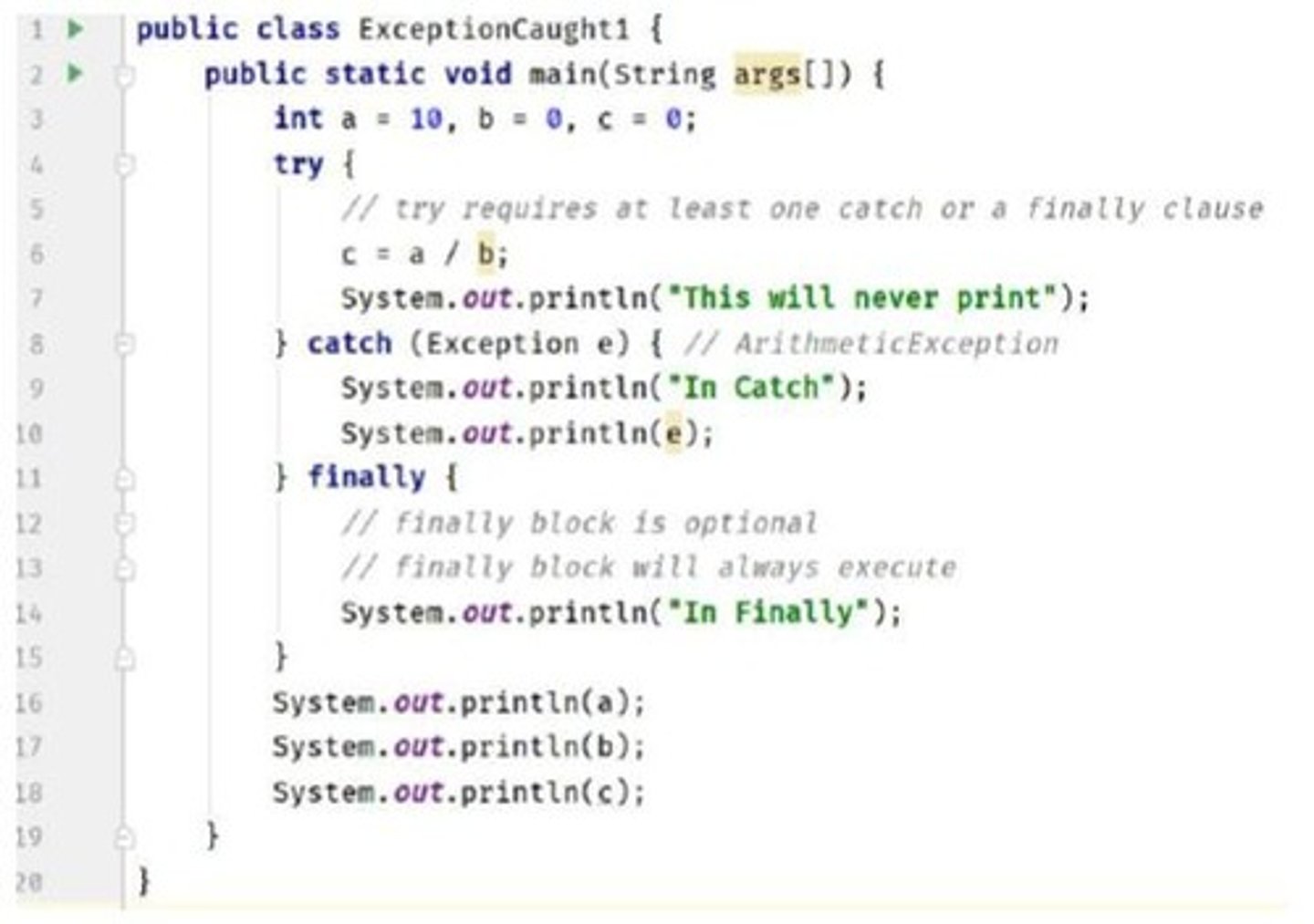
Output of show()
Displays value of k from sub-class B.
Constructor
Method to initialize object attributes.
Inheritance
Mechanism where sub-class inherits properties of super-class.
Object Type
Class type of an instantiated object.
Method Invocation
Calling a method on an object.
Java Reference
Variable that holds the address of an object.
Polymorphic References
References resolved at run-time, not compile-time.
Dynamic Binding
Method invocation determined at run-time.
Dynamic Method Dispatch
Runtime selection of method based on object type.
Animal Class
Base class for animal sound methods.
Pig Class
Subclass of Animal that overrides animalSound.
Dog Class
Subclass of Animal that overrides animalSound.
makeSound() Method
Calls animalSound() based on Animal object.
Superclass Constructor
Called before subclass constructor executes.
Constructor Call Order
Superclass constructors execute before subclass constructors.
Implicit Constructor Call
Default constructor called if no explicit call is made.
Explicit Constructor Call
Use super() to call parameterized superclass constructor.
Base Class Object
All Java classes inherit from Object class.
Object Class Methods
Includes equals(), getClass(), hashCode(), toString().
instanceof Operator
Tests if an object is of a specific type.
Type Comparison Operator
Compares instance type with specified type.
Overriding Methods
Subclass provides specific implementation of superclass method.
Elegant Software Design
Achieved through careful use of polymorphic references.