Functional Groups - Orgo 1
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Alykl
a carbon and hydrogen group. Common example is CH4
Alcohol Generic Structure
R-OH
R=Alkyl
Alcohol
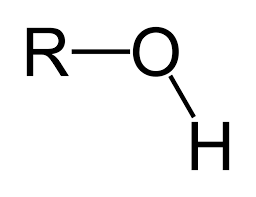
Primary Alcohol (1())
Carbon is directly connected to oxygen, as well as one additional carbon
Secondary Alcohol (2())
Carbon is directly connected to oxygen, as well as two additional carbons
Tertiary Alcohol (3())
Carbon is directly connected to oxygen, as well as three additional carbons
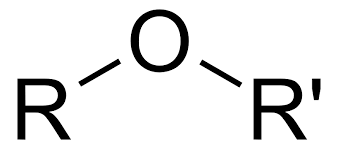
Ether Generic Structure
R-O-R
R= alkyl, cannot be a hydrogen
Ether
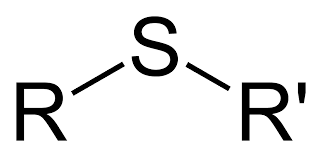
Sulfide Generic Structure
R-S-R
R=alkyl
Sulfide
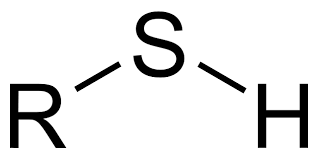
Thiol Generic Structure
R-SH
R=Alkyl
Thiol
Aromatics
Typically in a ring structure. Benzene included
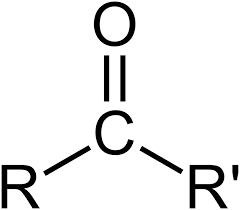
Ketone Generic Structure
O
| |
/ \
R R
R=alkyl
Ketone
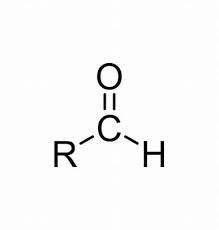
Aldehyde General Structure
O
| |
/ \
H R
R=H, Alkyl
Aldehyde
Carbonyl
one carbon double bonded to an oxygen
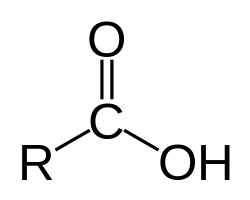
Carboxylic acid
has a carbonyl in it, but is not an aldehyde or a ketone
Carboxylic acid structure
Acyl Halide general structure
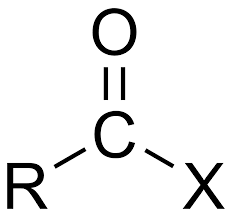
X= halogen
R= Alkyl
Anhydride generic structure
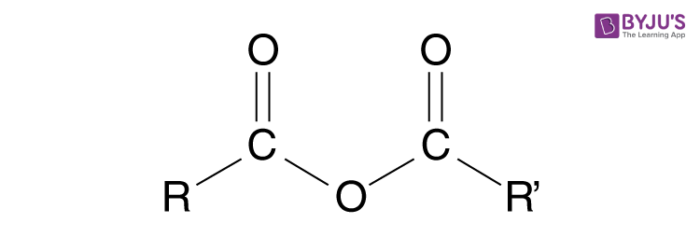
R= H, Alkyl
Ester generic structure
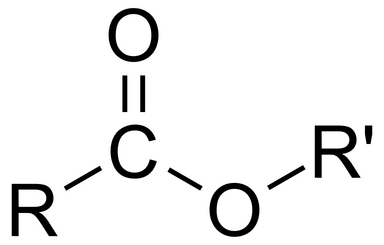
R= alkyl, not H
R’=alkyl
Amine General Structure
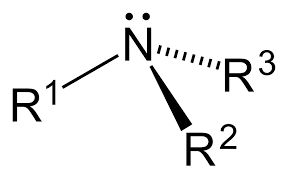
R= H or alkyl
no carbonal
the degree of the amine is based on
how many carbons are directly attached to the N molecule
Amide General Structure
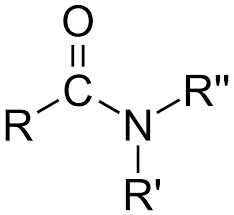
R=H or alkyl
includes carbonyl