The European Middle Ages
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
Earn XP
Last updated 10:24 PM on 6/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
1
New cards
DARK AGES
410 CE to 1066 CE, __early middle ages,__ **Rise of Barbarians,** Monasteries became centers of education, __Romanesque Architectural Style__
2
New cards
MIDDLE AGES
1066 CE to 1453 CE, Marked by the **Crusades, Feudalism and the Plague,** Lasting Political Ideas- the Magna Carta and Parliament, __Gothic Architecture Style__
3
New cards
Political, economic, spiritual, and cultural force
The Christian Church became an important ___, ____, _____, and ____ ____ in Europe.
4
New cards
Pope and Patriarch
Leading officials were
5
New cards
1054
Great Schism occurred in
6
New cards
small kingdoms developed across Europe
The Roman Empire dissolved then,
7
New cards
Franks
**controlled** the largest and strongest **kingdom in the former Roman province of Gaul**
8
New cards
Clovis
Franks’ first Christian king was _____
invaded and conquered of parts modern France, northwest Germany, and low countries
asked the bishops for support to govern the land by converting to Christianity
invaded and conquered of parts modern France, northwest Germany, and low countries
asked the bishops for support to govern the land by converting to Christianity
9
New cards
he divided the territory among his four sons, which they destroyed its unity by fighting, and the power fell into chief officials
What happened after Clovis died?
10
New cards
Charles Martel
About 200 years after Clovis died, ________ _______ rose to power and established reforms
prevented Muslim takeover in Europe
prevented Muslim takeover in Europe
11
New cards
Pepin the Short
continued reforms and established the Carolingian Dynasty
provided protection to fight off the Lombards in exchange the pope made him king, he and his heirs had more authority in Europe
provided protection to fight off the Lombards in exchange the pope made him king, he and his heirs had more authority in Europe
12
New cards
Papal states
The Roman Church called the new lands
13
New cards
CAROLINGIAN DYNASTY
dynasty formed to protect the papacy and establish that the pope and bishops make kings
14
New cards
Charlemagne
After his brothers’ death, ____________ quickly seized control of the entire kingdom
15
New cards
CHARLEMAGNE
Named **Holy Roman Emperor** by Pope Leo III in __**800 CE**__ **on Christmas**
__First Ruler of the (Holy Roman Empire) HRE__
Imposed order throughout the Church and the state
Ordered standardization throughout the empire
**marked the revival of arts and education in Europe**
__First Ruler of the (Holy Roman Empire) HRE__
Imposed order throughout the Church and the state
Ordered standardization throughout the empire
**marked the revival of arts and education in Europe**
16
New cards
united Germanic Kingdoms
converted Germanic people to Christianity through military campaigns and alliance with the Church of Rome
Doubled the size of the empire and led his army and conquered near by territories
converted Germanic people to Christianity through military campaigns and alliance with the Church of Rome
Doubled the size of the empire and led his army and conquered near by territories
What did Charlemagne do for the Germanic kingdoms?
17
New cards
Charlemagne being crowned by the pope showed that church and state were combined- Pope had religious and political power
Why was Charlemagne being crowed the pope significant?
18
New cards
divided the Charlemagne empire into 3 parts- west, east, and middle
Treaty of Verdum
19
New cards
Charlemagne had a great push on available education, more people could read and write, preserve Greek and Roman Philosophy.
How did Charlemagne reshape European society (education)?
20
New cards
Carolingian Dynasty declined after his death, his provisions did not last because his heirs were not good rulers, in the early 800s and **feudalism became important**
What happened to the Carolingian dynasty after Charlemagne died? (hint: what was now important)
21
New cards
ANGLES
a tribe that had invaded England
22
New cards
“land of the Angles”
Alfred the Great and his successors united England- called English Shores
23
New cards
heir
In 1042, King Edward the Confessor took the throne but died without an _____, struggle for the throne began and led to one last invasion
24
New cards
William the Conqueror from Normandy
Invader of the English Shores and where they were from
25
New cards
NORMANDY
region in France
26
New cards
William
King Edward’s cousin, _________ claimed the English crown and invaded England with his Norman army
27
New cards
Harold Godwinson
the Anglo-Saxon claiming the throne
28
New cards
Battle of the Hastings
the battle fought in Oct of 1066 by the Normans and Saxons that changed the course of English history; **the Normans/William the Conqueror won**
29
New cards
marked end of early middle ages + start of feudalism in Europe
Battle of the Hastings importance
30
New cards
Feudalism
system __based on rights and obligations__
**In exchange for military protection, a lord granted land to a vassal**
**In exchange for military protection, a lord granted land to a vassal**
31
New cards
Vikings
Carolingian Dynasty was destroyed by invaders such as the
32
New cards
s: narrative, legend, or myth telling of a hero’s deeds
d: saga is from Scandinavia, epic is from Rome
d: saga is from Scandinavia, epic is from Rome
similarities between epic and saga
33
New cards
Norsemen
Vikings set sail from __Scandinavia,__ known as Northmen or __________
34
New cards
800s
Vikings came to Europe in the
35
New cards
Helmets, swords, and heavy shields would strike quickly in towns and then leave as fast as they could
Viking armor and tactic
36
New cards
DRAKKEN
ships used by vikings to raid and plunder villages; could hold lots of men
37
New cards
FJORD
long, narrow, deep inlet of the sea
38
New cards
traders, farmers, and explorers
**Vikings were also**
39
New cards
Vikings gradually accepted Christianity and stopped raiding monasteries, better farming in Scandinavia, fewer men adopted sea life of vikings
Why did Vikings begin to fade in Europe?
40
New cards
rights and obligations
Feudal system based on
41
New cards
land, the more land the more power
main part of the Feudal system was
42
New cards
military protection
\
**In exchange for ________ _________, a lord granted land to a vassal**
**In exchange for ________ _________, a lord granted land to a vassal**
43
New cards
LORD
landowner
44
New cards
FIEF
land given by a lord to a vassal
45
New cards
VASSAL
person receiving a fief/given land in return for services
46
New cards
PRIMOGENITURE
inheritance of a fief only by the oldest son
47
New cards
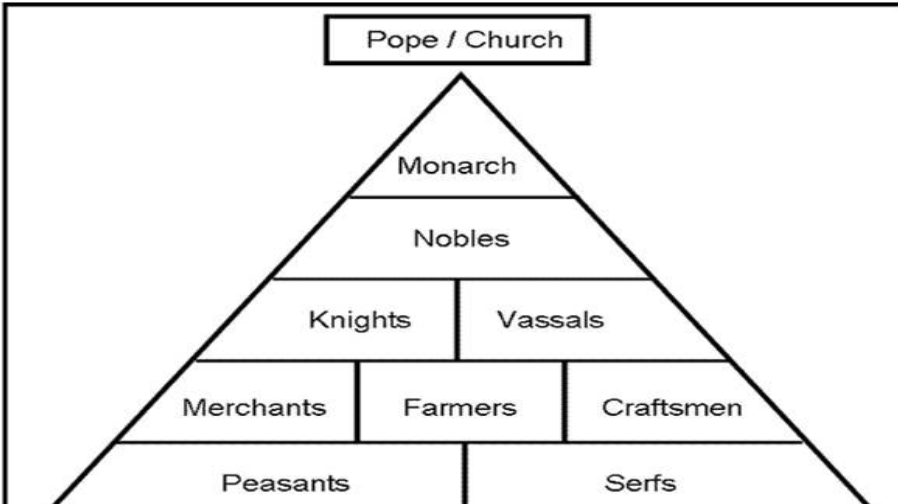
Pope/Church, Monarch, Nobles, Knights, Vassals, Merchants, Framers, Craftsmen, Peasants, Serfs
Feudal Pyramid (highest to lowest position, left to right)
48
New cards
Status determined prestige and power, Social class was inherited, the vast majority of people we peasants, and most peasants were serfs
Aspects of Feudal Social Classes
49
New cards
SERFS
people who could not lawfully leave the place where they were born
50
New cards
slaves
Serfs were not _______ - lords could not sell or buy them
51
New cards
MANOR
lord’s estate
52
New cards
housing, farmland, and protection
Vassals provided serfs with ____, _____, ______, in return, Serfs tended the land and maintain the estate
All peasants- serf or not- owed a lord certain duties
All peasants- serf or not- owed a lord certain duties
53
New cards
land
**The Lord controlled everything that happened on his _____**
54
New cards
manor
Peasants rarely traveled from their own ______
55
New cards
lord, village priest
Peasants paid high taxes to the ______ to live and the __________
56
New cards
TITHE
church tax representing 1/10th of income
57
New cards
35
**Life for serfs was work and more work, so the average life expectancy was __ years(lack of health and hygeine)**
58
New cards
Heresy
Serfs accepted their life as part of the Church’s teachings (if they didn’t obey they would be committing ______ )
59
New cards
HERESY
the denial of an idea that is generally held sacred
60
New cards
INQUISITION
church efforts to eliminate Heresy
61
New cards
INTERDICT
church’s punishment of an entire region by withholding some sacrament
62
New cards
knights
Feudal lords used private armies of _______ to defend their territories
63
New cards
fiefs
Knights received ___( land given by a Vassal), wealth from _____ allowed knights to pay for weapons and armor
64
New cards
**CHIVALRY**
code of the Knights; a complex set of ideals; a knight must be loyal to his lord, brave in battle, courteous and merciful to his enemies, and generous to the poor and helpless
65
New cards
Page, squire, knight
stages of knight hood
66
New cards
**loyal, brave, and courteous**
3 qualities of a ideal knight
67
New cards
fighting local wars
Young knights gained experience in ____ ___ ____ or at tournaments
68
New cards
TOURNAMENT
chivalrous competition or mock battle
69
New cards
TROUBADOURS
traveling poet-musicians at the castles and courts of Europe; wrote poems and songs recounting a hero’s deeds and adventures; became popular
70
New cards
Feudal society believed women were inferior to men, noblewomen had some power, but their lives were limited, Peasant women performed endless labor at home and in fields
Women in Feudal Society
71
New cards
Peasant women's contribution was key for survival, without the agreement to be at the bottom and do the work, the system would collapse
Why were peasant and servent women so important to the society?
72
New cards
the Church emerged as a powerful institution and shaped the lives of people from all social classes. The Church expanded its political role, but people began to question the pope’s authority. Power struggles unfolded between Popes and emperors.
what was the Church’s position in Feudal Europe? what was the view on the Churches political involment?
73
New cards
status
The Church and Monarchs in Europe competed for power and the Church had a power structure that was based on _______
74
New cards
The pope was influenced by the religious devotion and reverence for God shown by new monasteries
Why did the pope reform the Church?
75
New cards
1. **Priests Marrying(they married anyway)**
2. **Simony(bribery for church positions/purchase of church positions)**
3. **Bishop Appointment(lay investure)**
**3 main issues reformed:**
76
New cards
SIMONY
practice of selling Church poistions (bribery)
77
New cards
lay investure
appointment of a bishop by someone **who is not a member of the clergy**
78
New cards
**Francis of Assisi**
founded the **Franciscan** Order of Friars
founder of a preaching order of Monks
founder of a preaching order of Monks
79
New cards
Martyred
killed for your beliefs
80
New cards
Concordat of Worms
compromise reached by Henry V and Pope Calixtus II, allowing the king to invest a bishop with worldly symbols of his office and give him land; **weakened the power of kings to place an ally in an important Church position**
81
New cards
DARK, built between 800 and 1000, round arches and thick walls and pillars, tiny windows, **scare people into believing in God**
Romanesque Style Cathedrals (BEFORE), built, aspects, how people felt?
82
New cards
LIGHT, Came to be in the 1100s, built with pointed roofs as if reaching towards heaven, **stained glass**, **meant to inspire people to believe in God, not intimidate like before**
Gothic Style Cathedrals, built, aspects, how people felt?
83
New cards
dedicate their lives to God
people joined monasteries to…
84
New cards
Secular Clergy
Everyone in the Medieval Church was a member, and Priests, Bishops, and the Pope made up the
85
New cards
MONASTICISM
system of monasteries and convents in which Christians withdrew from the world to lead a life of prayer, fasting, and self denial
86
New cards
Benedictine rule
set of rules created by Benedict to regulate monk lives
87
New cards
ABBOT
head of monastery
88
New cards
Byzantine Emperor
In 1095, the ______ ______ contacted Pope Urban II about a military threat against Constantinople and Muslim control of Jerusalem
89
New cards
Muslim Turks
Pope Urban II called for a crusade against the ____ *_______*
90
New cards
CRUSADE
Holy war
91
New cards
CRUSADER
christian soldier who fought to free the holy land from, Muslim Turks in the Middle Ages. The **word means “carrier of the cross”**
92
New cards
1096
**Spring and summer of ____, armies of Crusaders departed from Western Europe for Constantinople.**
93
New cards
1099
**On July 17, _____, Crusaders captured Jerusalem after a long and costly siege**
94
New cards
Saladin
Christians lost Edessa and Jerusalem to ________; Muslim leader during the Crusades.
95
New cards
Christians believed they were fighting in the name of Jesus to take back the place of his birth from the infidels
\
Perspective of the Crusaders: Christian
Perspective of the Crusaders: Christian
96
New cards
Muslims believe they were defending land that was theirs, from their perspective, Christians were the invaders
Perspective of the Crusaders: Muslim
97
New cards
INFIDEL
a person who follows a religion other than one’s own
98
New cards
moors
Muslims in Spain (_____) were driven out in the Reconquista
99
New cards
RECONQUISTA
long-term effort by the Spanish to drive Muslims out of Spain
100
New cards
**1. Thousands left their homes and traveled**
**2. Women had a chance to manage the affairs at home**
**3. European merchants expanded trade routes**
**4. Failure of later Crusades lessened power of the Pope**
**5. Crusades weakened Feudal nobility**
**6. For Muslims, intolerance and prejudice left behind a legacy of bitterness and hatred**
**2. Women had a chance to manage the affairs at home**
**3. European merchants expanded trade routes**
**4. Failure of later Crusades lessened power of the Pope**
**5. Crusades weakened Feudal nobility**
**6. For Muslims, intolerance and prejudice left behind a legacy of bitterness and hatred**
**6 major effects of the Crusades:**