ANSC 300 Water Balance
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
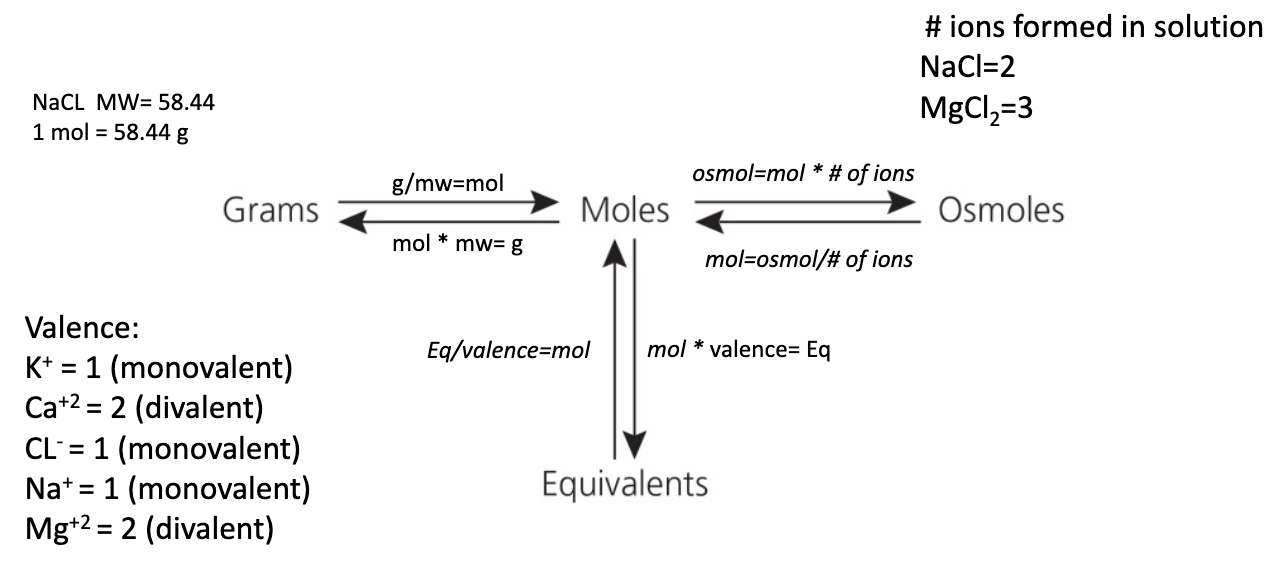
Ways to Express Mass of Solutes
g (grams) / mw (molecular weight) = mols
mols * mw = g
osmol = mol * # of ions
mol = osmol / # of ions
eq (equivalent) / valence = mol
mol * valence = eq
Ways to Express Concentration of Solutes
osmolarity = osm / kg of fluid
osmolarity = osm / L of fluid
molarity = mol / L of fluid
g / L
Solute Concentration Inside vs Outside the Cell
more sodium, calcium, and chloride outside the cell
285-290 mOsm/kg both inside and outside the cell
concentration gradients for individual ions are important for cell function
concentration gradients maintain membrane electrical potential: difference in net charge between inside and outside the cell (action potential)
Diffusion
molecules are in constant motion
molecules bounce off each other and transfer energy
random trajectory
energy (heat) of molecules is directly related to the temperature
Net Diffusion Rate
depends on concentration, charge, and pressure
higher concentration outside means molecules cross the membrane to the inside than the other way
more positive charge inside draws more negatively charged ions from the outside
higher pressure (P1) drives more molecules to cross the membrane
Osmosis
net movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane
movement of water across the membrane equalizes solute concentration on both sides
water moves towards the compartment with lower water concentration
water moves towards the compartment with higher solute concentration
Osmotic Pressure
is the force required to equalize volume on both sides of the membrane
high water concentration on left side
water diffuses through the membrane from compartment 1 to compartment 2
water moves to the right until the opposing pressure gradient is equal to the force of the concentration gradient
Net Movement of Water can Change _____
cell shape
Hypotonic
lowest solute concentration causing water to move into the cells
Isotonic
water movement is in equilibrium
Hypertonic
highest solute concentration causing water to move outside the cell which leads to cell shrinkage
Cell Structure
defines function
interior of a cell is highly structured
different compartments do different things
cells specialize by altering their structure
specialization is called differentiation
Membrane Physiology
selective semi-permeable: water can freely diffuse across the membrane or through protein channels
transporters and channel proteins alter membrane permeability when open
carrier membrane proteins control transport of other molecules:
nutrients
ions
metabolites
allows for separate internal compartments to contain different molecules: Mitochondria (H+), ER (Ca++), Lysosomes (H+)
source of signaling molecules (IP3, DAG)
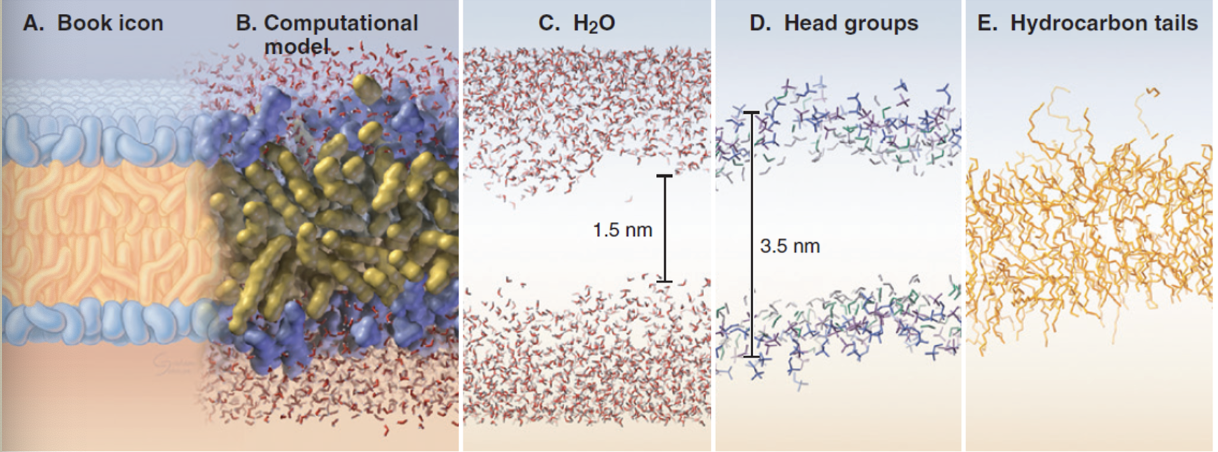
Lipid Bilayer
hydrophobic tails orient away from the aqueous environment. Exclude water
polar heads interact with water molecules
phospholipids move around which makes membrane fluid and flexible
composition of phospholipids alter membrane fluidity and stiffness
Simple diffusion
small molecules that are lipid soluble pass through the membrane, such as oxygen and carbon dioxide
Facilitated Diffusion
molecules move down their energy gradients
requires a carrier protein
binds molecules with high specificity
binding causes a change in shape (conformation) of the carrier protein
no ATP required
Active Transport
molecules move against energy gradients, requires ATP
Energy Gradients
concentration or electrical
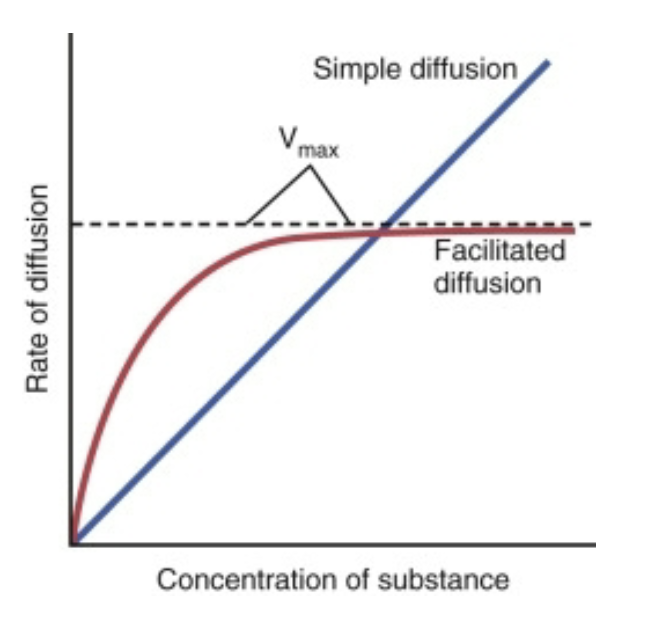
Rate of Diffusion
rate of simple diffusion increases at a constant rate as concentration of the solute increases
rate of diffusion increases more rapidly in facilitated diffusion
facilitated diffusion has a maximum rate at which higher solute concentration will not longer increase the rate of diffusion (Vmax)
Primary Active Transport: Na-K Pump
maintains concentration gradients of Na and K
uses to generate electrochemical gradients for action potentials (neurons and muscle contractions)
requires ATP
important for maintaining isotonic environment of the cell
other pumps move Ca, Cl, and H against concentration gradients
Sodium Electrochemical Gradient
sodium and glucose co-transporter (SLGTs) are important for absorption in Gi and kidney
sodium gradient is used to move calcium and hydrogen ions out of the cell
Heat Tolerance in Camelids
body temp can increase during day ~40 C
cooling at night to ~34 C
tolerate losing up to 25% of body water
can rehydrate without side effects