Details of Lipids
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Lipids
a group of organic compounds (C,H,O) that are generally insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They include fats, oils, waxes, and other related substances.
nonpolar, mostly made of C-H bonds
two types of lipids
Fats
Made of fatty acids and glycerol backbones. Used to store long term energy, insulate the body, synthesizes hormones, and ensures the proper function of cell membranes.
two types of fats
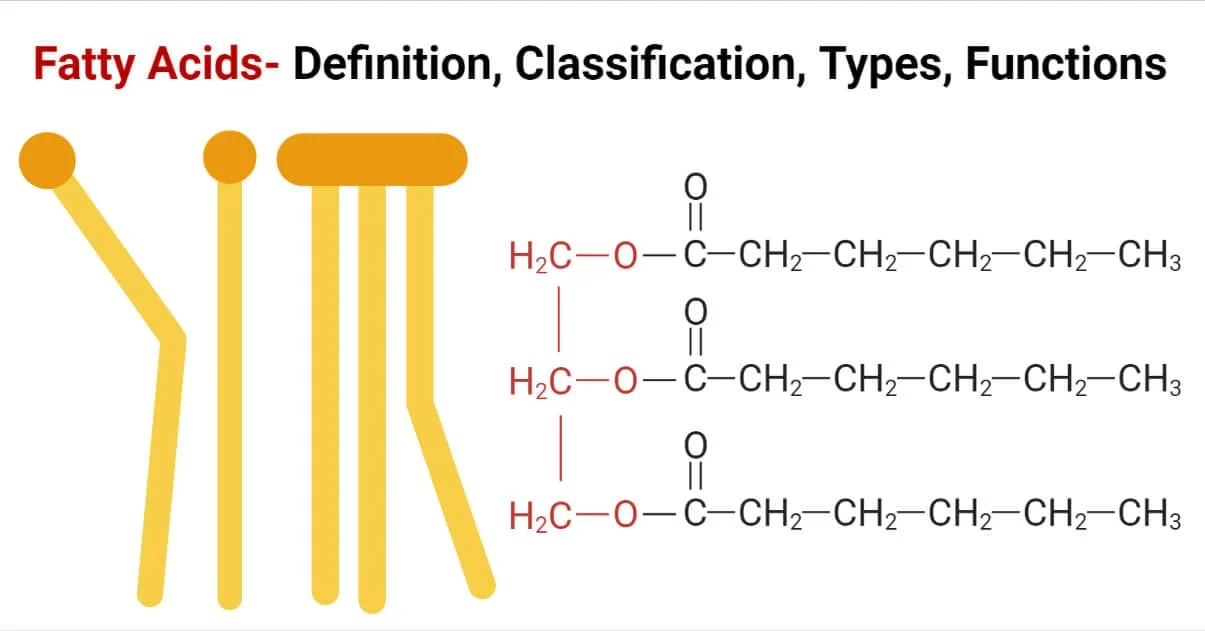
Saturated Fats
a type of lipid (fat) where the fatty acid chains are composed of only single bonds between carbon atoms, making them "saturated" with hydrogen.
no C-C double bonds
more hydrogen
straight hydrocarbon chain; packed together
solid fats found in animals
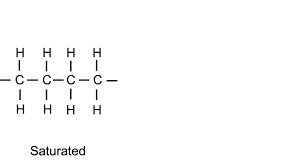
Unsaturated Fats
fatty acids with one or more double bonds between carbon atoms in their hydrocarbon chain.
Has C=C double donds
less hydrogen
bends hydrocarbon chains
liquid fats made of plants
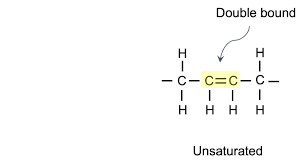
Phospholipids
Phospholipids are a type of lipid (fat) molecule that are the primary components of cell membranes. They consist of a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head, a phosphate group, and two hydrophobic (water-repelling) tails, fatty acids. This structure allows them to form lipid bilayers, which create a barrier that separates the inside of a cell from its external environment called the phospholipid bilayer.
Steroids
Hormones that act as chemical messengers, and are used for communication to coordinate activities in the organism.
made of four fused carbon rings
Cortisol/Cortisone
a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal glands that serves as a vital regulator of the body's stress response, metabolism, and immune function. It essential for survival and helps the body cope with physical and emotional stress.
in a stress response, it hydrolyzes glycogen into glucose
anti-inflammatory; redues swelling
Sex Hormones
steroid hormones, primarily produced by the gonads (ovaries and testes), that regulate sexual development, function, and reproduction in vertebrates.
three types
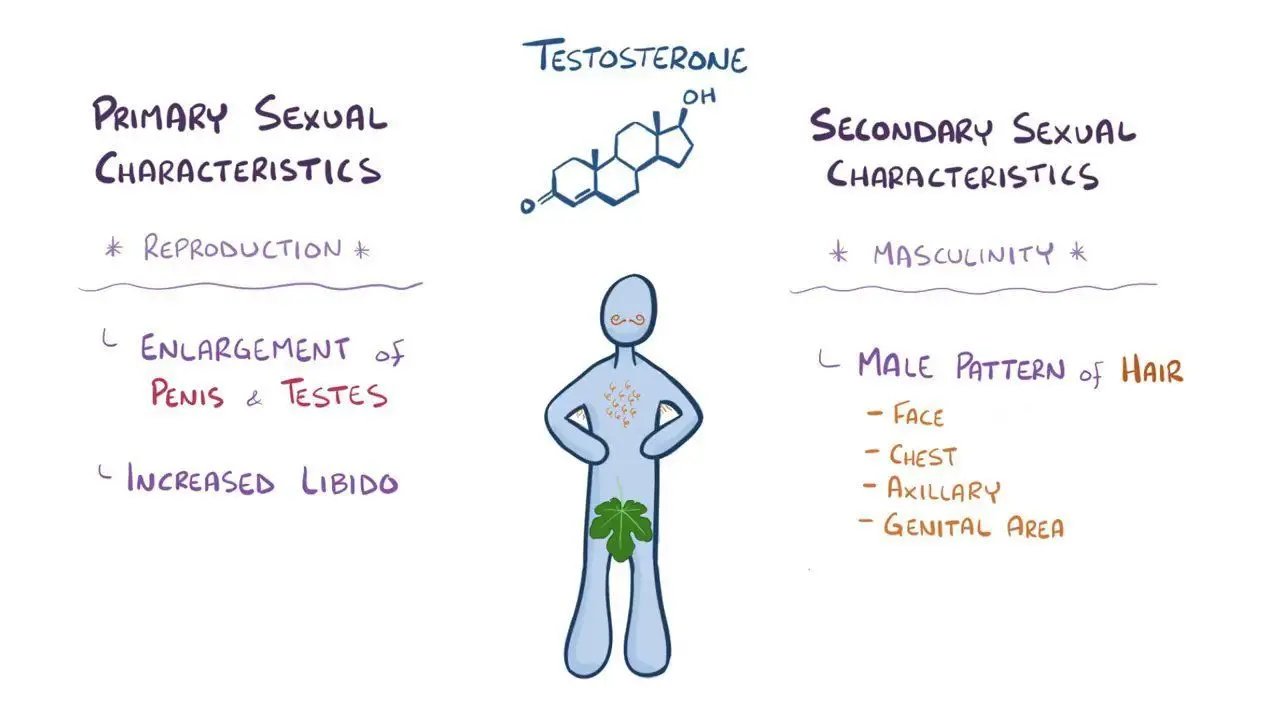
Testosterone
A steroid hormone primarily produced by the testes in males, responsible for developing and maintaining male secondary sex characteristics, such as muscle growth, deep voice, and body hair, and playing a role in reproduction, sperm production, and behavior
produced in smaller amount in women
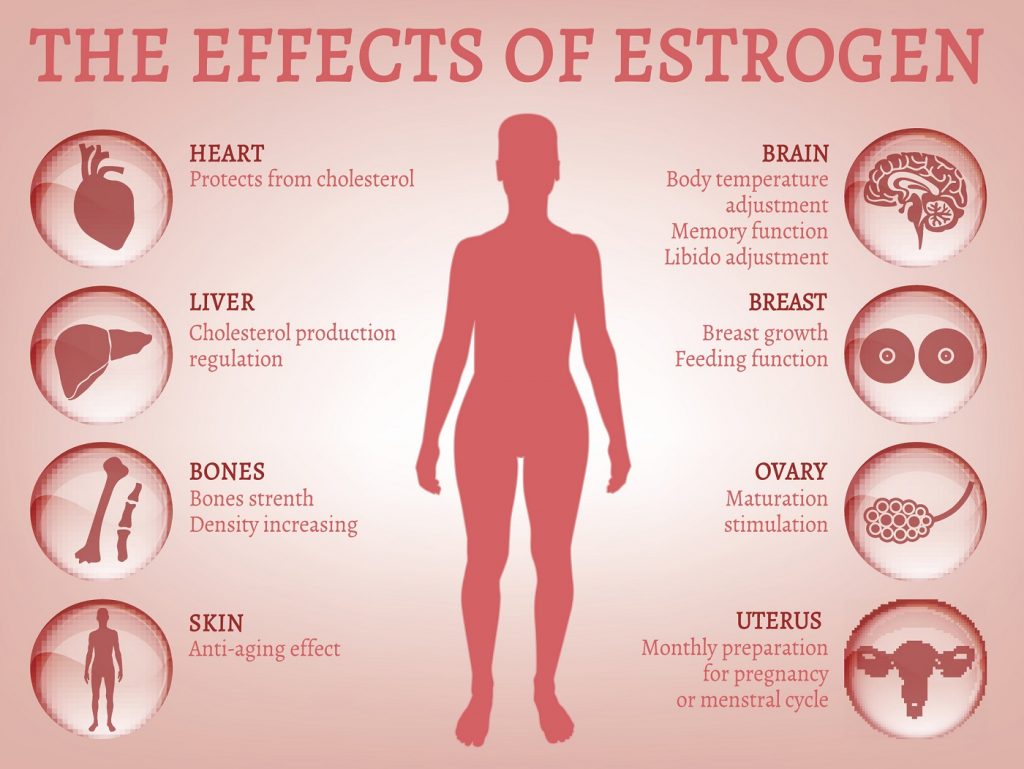
Estrogen
A steroid hormone that is crucial for developing and maintaining female sex characteristics, regulating the menstrual cycle, and promoting bone growth.
increase fat storage, breast development, loosened connective tissue, regulating uterine lining
Progesterone
a steroid hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains it if implantation occurs. It thickens the uterine lining and prevents the shedding of the uterus during a period.
If no fertilization occurs, progesterone levels drop, leading to menstruation. I
f implantation does occur, progesterone levels remain elevated to support the early stages of pregnancy.