FCM Labor and Delivery
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What is normal labor?
Presence of regular and painful uterine contractions resulting in cervical dilation or effacement or both
Regular contractions that cause cervical change
What are contractions?
Rhythmic tightening and releasing of the muscles in the uterus, usually every 3 to 5 minutes
Peaks when you can feel the contraction at the fundus
What is an external tocometer?
Monitor that measures how frequent contractions are, when they start and end
What is cervical dilation?
How open the internal os of the cervix is (measured by sterile vaginal exam)
What is cervical effacement?
Cervix stretches and gets thinner --> described in % from 0 to 100, measured by sterile vaginal exam
What is false labor?
Uterine contraction without cervical change
Can include Braxton-Hicks contractions
What are Braxton-Hicks contractions?
Irregular, infrequent contractions that do not cause cervical change (dilation and/or effacement)
Resolve spontaneously (can see resolution with ambulation or change in activity)
Cervical dilatation in the absence of uterine contraction suggests:
Cervical insufficiency
What are the keys of success for a vaginal delivery?
Synergistic interactions of uterine activity, fetus, and maternal pelvis
Three P's:
- Power (uterine contractions, frequency x strength)
- Passenger (fetal lie, fetal presentation, fetal size)
- Passage (maternal pelvis, shape)
Only way to determine adequacy is trial of labor
What are the different pelvic shapes in women?
- Gynecoid (m/c shape, 50% of women, associated with most successful chance of vaginal delivery)
- Platypelloid
- Android
- Anthropoid
What are the different stages of labor?
- First stage (onset of labor until 10 cm dilated, latent and active phases)
- Second stage (fully dilated to delivery of infant)
- Third stage (delivery of placenta, normally should occur within 30 min of delivery of infant)
- Fourth stage (postpartum/puerperium)
What are the two phases of the first stage of labor?
- Latent phase: onset of labor to 6cm dilated
- Active phase: 6cm to 10 cm (fully dilated)
What is Naegele's rule?
Estimation of gestational age/estimated date of delivery
Formula:
(First day of LMP) - 3 months + 7 days + 1 year
What is the most accurate method to establish or confirm gestational age?
Ultrasound measurement of the embryo or fetus in the 1st trimester
**Always check if consistent with LMP --> both together serve as most accurate measurement
How do we determine estimated date of delivery if a pregnancy resulted from assisted reproductive technology?
Go by age of the embryo and the date of the transfer
What is pre-viable, pre-term, early term, full term, late term, and post-term?
- Pre-viable: before 24 weeks
- Preterm: 24 weeks to 36 weeks 6 days
- Early term: 37 weeks to 38 weeks 6 days
- Full term: 39 weeks to 40 weeks 6 days
- Late term: 41 weeks to 41 weeks 6 days
- Post term: 42 weeks+
How does rupture of membranes present?
- "Sudden gush of fluid"
- Colorless, odorless, large amount of fluid
What can we see on speculum exam of a patient with rupture of membranes?
- Pooling of fluid
- Can sometimes see cervical dilation
What are some diagnostic tests done for rupture of membranes?
Commercial tests: ROM Plus, Amnisure, Actim PROM
Ferning
- Noted on microscopic evaluation of dried vaginal fluid, also called arborization
Nitrazine test
- Dark blue for pH > 6.5
- Amniotic fluid has pH of 7.1-7.3
- False-positive may occur with blood, semen, lubricants, BV
At this point, check GBS status
Ultrasound:
- Check amniotic fluid
- Oligohydramnios (low amniotic fluid <5cm) --> ROM
What is the disposition of rupture of membranes?
Based on whether ROM is confirmed, presence of labor, and gestational age
If ROM ruled out --> safe to discharge patient home
If SROM --> admit patient for labor management, possible augmentation
If PROM --> admit patient for induction
What is SROM?
Spontaneous rupture of membranes
Membranes ruptured AND presence of labor
What is PROM?
Pre-labor rupture of membranes
Membranes ruptured but before onset of labor, patient is >37 weeks
What is PPROM?
Preterm, premature rupture of membranes
Before onset of labor and before 37 weeks
What is augmentation of labor?
Used for patients who present in their own labor
Done to stimulate uterine contractions if adequate cervical changes are not occurring
Usually uses pitocin (synthetic oxytocin), can also have mechanical agents
What do we use to determine if the cervix is favorable?
Bishop score
Takes into account position, consistency, effacement, dilation, and station
What is cervical ripening?
Prior to spontaneous labor, the cervix first begins to soften over time, and then before contractions ensue, the connective tissue components of the cervix are extensively remodeled
What are ripening agents we can use to induce labor?
- Synthethic prostaglandins (Cytotec, Cervidil)
- Pitocin
What are mechanical agents we can use to induce labor?
Cervical balloon or foley
Physically open the cervix
What are some reasons for why we induce labor?
- Pre-labor rupture of membranes
- Post-term induction
- Fetal conditions (oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios, abnormal dopplers, multiple gestation)
- Maternal conditions (chronic HTN, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (gestational hypertension, preeclampsia), gestational diabetes, HIV, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy)
What are the different types of delivery?
- NSVD: normal spontaneous vaginal delivery
- VBAC: vaginal birth after cesarean
- Operative vaginal delivery: forceps-assisted or vaccuum-assisted
>> Decision made during the labor process, not pre-determined
- Cesarean delivery: described based on nature of delivery – scheduled, unscheduled, urgent, STAT
>> Type of incision: low transverse (pfannenstiel), classical (vertical)
What is the normal baseline fetal heart rate?
110-160 bpm
What is considered fetal bradycardia and fetal tachycardia?
Fetal bradycardia: <110 bpm
Fetal tachycardia: >160 bpm
How do we determine fetal oxygen status? What can fetal hypoxia be caused by and lead to?
Fetal surveillance
Strong uterine contractions can interrupt uteroplacental blood flow and transfer of oxygen from mother to fetus
- Fetuses can tolerate transient hypoxemia
- Prolonged hypoxia can lead to metabolic acidosis, tissue damage
What are the two types of fetal surveillance during labor?
- External fetal monitoring
- Fetal scalp electrode
What is fetal position?
Refers to the presenting part relative to the maternal pelvis
What is the mnemonic to remember the FHR pattern and its causes?
VEAL CHOP
FHR pattern (VEAL):
- Variable decels
- Early decels
- Accels
- Late decels
Cause (CHOP):
- Cord compression
- Head compression
- Okay!
- Placental insufficiency
What is fetal station?
Defined as the number of centimeters of the bony presenting part above or below the level of the ischial spines
0 station is the bony part at the level of the ischial spines
What are the cardinal movements of labor?
- Engagement
- Descent
- Flexion
- Internal rotation
- Extension
- External rotation
- Expulsion
What are the different delivery maneuvers done when delivering a baby?
- Protect perineum
- Hand cupping the head
- Allow for restitution
- Check for nuchal cord once head is out
- Apply downward traction to deliver shoulder below pubic bone
- Then upward to deliver other shoulder
- Hold body and place on maternal abdomen or hand off to pediatrics
- Doubly clamp and cut umbilical cord
- Massage fundus and apply traction on remaining portion of umbilical cord until placenta spontaneously delivers
- Inspect perineum/vagina/cervix for lacerations
What are the benefits of delayed cord clamping?
Increases hemoglobin levels and iron stores, associated with lower incidence of necrotizing enterocolitis and intraventricular hemorrhage
What is an episiotomy?
Surgical extension of the vaginal opening into the perineum during labor
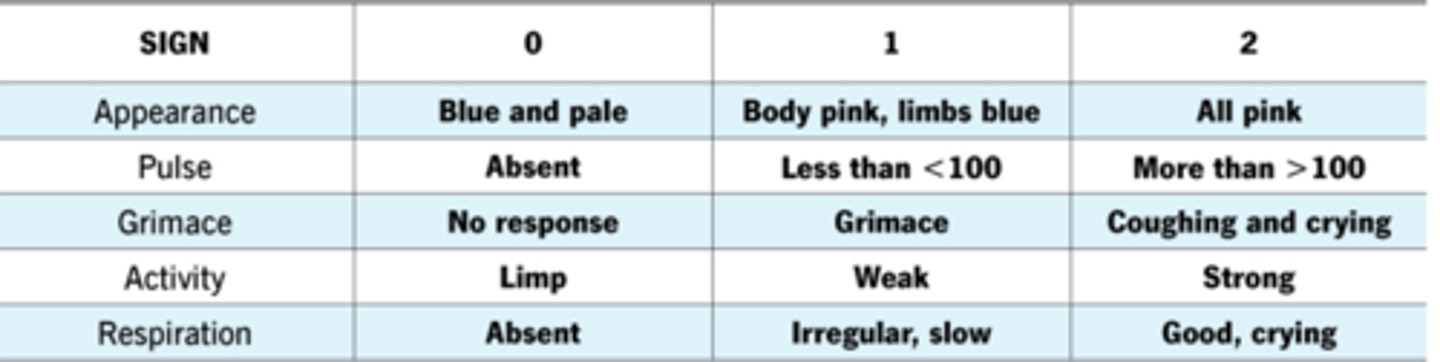
When are APGAR scores measured?
1 and 5 minutes of life
What are the different APGAR scores and signs?
What is uterine atony?
Uterus becomes soft, boggy, poorly contracted (normal = vigorously contracted uterus, hard like a rock)
What are risk factors for uterine atony?
- Prolonged labor
- Prolonged use of oxytocin
- History of many deliveries
How do we treat uterine atony?
First line: bimanual massage
Then, uterotonic agents:
- Oxytocin
- Methylergonovine (methergine)
- Carboprost (Hemabate)
- Misoprostol (cytotec)
In severe cases (when other measures fail), hysterectomy is indicated
What is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage?
Uterine atony
What is chorioamnionitis?
Defined as intra-amniotic infection
Usually an ascending infection from the lower GU tract
What are signs of chorioamnionitis?
- Maternal fever (>100.4 degrees F)
- Fetal tachycardia
How do we treat chorioamnionitis?
IV ampicillin and IV gentamicin
Expedite delivery
What are some other reasons why vaginal delivery might be converted to a C-section?
- Non-reassuring fetal heart tracing (fetal intolerance of labor)
- Rupture of membranes greater than 18 hours
- Arrest of dilation (cervix stops dilating prior to 10 centimeters)
- Too long on pitocin
What is shoulder dystocia?
Failure to deliver the shoulder with gentle downward traction on the fetal head
Cannot be predicted, can happen with any delivery
If there is a history, can counsel on cesarean delivery
What are risk factors for shoulder dystocia?
- Diabetes causing large fetus
- Macrosomia
- Prior shoulder dystocia
What are the different maneuvers to relieve shoulder dystocia?
- McRobert's maneuver: flexing thighs against abdomen
- Suprapubic pressure: combined with McRobert's usually resolves most shoulder dystocias
What are some complications of shoulder dystocia?
- Brachial plexus palsy (Erb-Duchenne, Klumpke)
- Clavicular or humeral fractures
- Maternal 4th degree lacerations or hemorrhage
What is umbilical cord prolapse?
Umbilical cord exits the cervical os before the fetal presenting part
Compression of the umbilical cord can result in:
Vasoconstriction and resultant fetal hypoxia, which can lead to fetal death or disability if not rapidly diagnosed and managed
How do we treat umbilical cord prolapse?
Provider will elevate the presenting part as to prevent cord compression until the patient is transported to OR
Emergent C-section indicated!
How common is Group B streptococcus?
Group B Streptococci (GBS) colonize rectum and vagina in 10-30% of pregnant women
What is the significance of GBS in pregnancy?
Maternal to neonatal transmission is approx 50% and can lead to GBS sepsis in the newborn
All pregnant women need to be screened on or after 36 weeks 0days
How long is GBS result valid for?
5 weeks
How do we treat GBS infection in a pregnant patient?
Intrapartum IV penicillin G
How do we treat pain during labor/delivery?
Always treat per patient request
Do not give NSAIDS!! (can cause premature closure of fetal patent ductus arteriosus)
What are some neuraxial pain relief methods used in labor/delivery?
- Epidural
- Spinal
- Combined spinal-epidural
What is lochia?
Normal shedding of blood and decidua (uterine lining)
Initial red-brown (rubra) which gets lighter each day
Flow is like a period at first, can last up to 6 weeks
What can women expect post-partum?
- Lochia (normal shedding of blood)
- Pain (cramping from uterine involution)
- Monitor CBC due to blood loss from delivery
- Physical exam prior to leaving hospital
- DVT prophylaxis
Why do patients experience pain postpartum?
Cramping from uterine involution (uterus returning back to normal size)
Will feel period like cramps to contractions, can give NSAIDs or Tylenol
What can we see on physical exam of postpartum patients?
- Fundus: firm, at the level of the umbilicus
- Vulvo vaginal: comment on lochia, vulvar edema (can cover urethra obstructing urinary flow), perineum well approximated
What do we give postpartum patients for DVT prophylaxis?
- Ambulation
- Subcutaneous heparin or LMWH while inpatient
What birth control can we start patients on postpartum?
Progesterone only (pills, Depo-Provera, Nexplanon)
What are some special considerations postpartum for C-section patients?
- Regular post-op care
- Incision care
- Counseling
- Oxycodone PRN
How long do patients stay in the hospital post-partum?
- Vaginal deliveries: 48 hours after delivery
- C-sections: stay until post-op day 2-4
What do we do during a routine 6 week postpartum visit?
- Lochia should stop by this time
- Breastfeeding should be established by this time usually
- Assess psychological well-being (Edinburg postnatal depression scale)
- Resume sexual activity
- Can now start estrogen-containing birth control methods
- Counsel on birth spacing (ideally about 18 months between pregnancies)
What are the different benefits of breastfeeding for the mother?
- Uterine involution
- Weight loss
- Reduced chances of female cancers
What are the different benefits of breastfeeding for the baby?
- Helps with neurodevelopment and glucose regulation
- Decreased risk of SIDS, obesity, and childhood infection
What is lactogenesis stage 1?
Colostrum is available
What is lactogenesis stage 2?
Effective infant sucking builds milk supply
What are contraindications for breastfeeding?
- Infant with galactosemia
- Mothers with HIV
- Human T-cell lymphotropic virus
- Untreated active TB
- Active varicella or herpes on the nipple
How can we verify if medications can be taken with breastfeeding?
LactMed or Hale's medication database, or lactation consultant
How do we know if baby is getting any milk?
- Baby is satisfied
- Sucking sounds
- Not crying
- Voiding and stooling
- Engorgement is relieved
What are some postpartum psychiatric complications?
- Postpartum blues (baby blues)
- Postpartum depression
- Postpartum psychosis
What are postpartum blues (baby blues)?
- Mild and rapid mood swings
- Usually 2-3 days after birth, resolves within 2 weeks
- Supportive care, screening for MDD
What is postpartum depression?
- Depressive episode that starts during pregnancy or in the 4 weeks following delivery
- Commonly occurs 1-3 weeks after delivery
- Patients cannot handle daily tasks due to intense feelings of sadness, anxiety, or despair
What is postpartum psychosis?
Auditory or visual hallucinations
The most common risk factor is hx of bipolar disorder
What are some differential diagnsoes of postpartum fever?
- WIND: atelectasis or pneumonia
- WATER: UTI
- WOUND: C-section incision, episiotomy/laceration infection
- WALKING: DVT/PE (pregnancy and postpartum is a hypercoagulable state)
- WONDER DRUGS: misoprostol (for uterine atony) can cause fever after administration upto 4 hours
- WOMB: endometritis or endomyometritis
- WEANING: breast engorgement or mastitis
What is the most common cause of postpartum fever?
Endometritis or endomyometritis
How does endometritis present?
- Fundal tenderness
- Foul-smelling lochia
What is the most common organism of endometritis?
E. coli (polymicrobial ascending infection from vaginal flora)
How do we treat endometritis?
IV gentamycin and IV clindamycin
What causes mastitis?
S aureus
How do we treat mastitis?
Dicloxacillin
Why does postpartum hemorrhage occur?
4 Ts:
- Tone: uterine atony, most common cause!
- Trauma: lacerations
- Tissue: retained products of conception (placenta, membranes)
- Thrombin: coagulopathies
What is considered to be postpartum hemorrhage?
Greater than 1000mL of blood loss for vaginal or C-section deliveries
How do we treat postpartum hemorrhage?
- Bimanual massage
- Extraction of contents
- Uterotonics
- Take back to the OR for D&C
What is Sheehan syndrome?
Occurs with massive postpartum hemorrhage, necrosis of the pituitary gland