midterm 2 reaction reagents
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
irreversible nucleophiles we’ve learned
H-, -CH3
describe the steps of the e1cb mechanism
○ First deprotonate alpha carbon
○ Enolate formed
○ Kick off OH
reagents for amide to aldehyde
1.) DIBAL 2.) H3O+
reagents for amide to amine via double addition of H
1.) LiAlH4
2.) H3O+
reagents for amide hydrolysis in basic conditions (aka amide to deprotonated carboxylic acid)
-OH and H2O solvent
reagents for amide hydrolysis in acidic conditions (aka amide to carboxylic acid)
H+ and H2O solvent
why does ester hydrolysis occur in acidic conditions and not occur in neutral conditions
bc water is the reagent and it’s a relatively weak nucleophile. it only becomes more reactive due to the increased positive charge on the carbonyl carbon after protonation (which can only occur under acidic conditions)
reagents for base promoted ester hydrolysis (aka ester to deprotonated carboxylic acid)
excess NaOH and H2O solvent
reagents for base promoted transesterification
excess NaOR (where R is desired new ester) and HOR solvent
reagent to go from carboxylic acid to acyl chloride
PCl3 or SOCl2
reagent for nucleophilic addition exception to carboxylic acid under basic conditions (aka reagents for carboxylic acid to primary alcohol)
1.) LiAlH4 2.) H3O+ workup
order of relative electrophilicity
acyl halide, anhydride, aldehyde, ketone, ester/carboxylic acid, amide, carboxylate ion
steps of imine formation mechanism with trace acid
1.) primary amine attacks carbonyl carbon and forms neg charge on oxygen
2.) proton transfer to take one H from amine and move to neg charged oxygen
3.) base protonates OH to make water, LP from amine move down to form pi bond and kick off h2o LG too
4.) base deprotonates nitrogen to restore neutral charge and imine is formed
steps of enamine formation w trace acid
1.) secondary amine attacks carbonyl carbon and pi bond e move up to form neg charge on oxygen; attached amine also has pos formal charge on nitrogen
2.) proton transfer to move the H from nitrogen to neg oxygen
3.) protonate OH to make water LG, push LP from N down to kick off LG
4.) deprotonate beta hydrogen to push e onto molecule to form double bond, pi bond e move up to restore neutral charge on nitrogen
steps of inamine/enamine hydrolysis
PADPED
protonation of imine/enamine, addition of water, deprotonation of oxygen, protonation of nitrogen, elimination of amine, deprotonation
purpose of hofmann rearrangement
convert a primary amide to a primary amine with one fewer carbon atoms
reagent for methyl benzene to carboxylic acid
H2CrO4
reagents for amide to carboxylic acid
HCl, H2O
reversible nucleophiles we’ve learned
-C≡N, NH3, -OH, H2O, CH3OH, CH3NH2
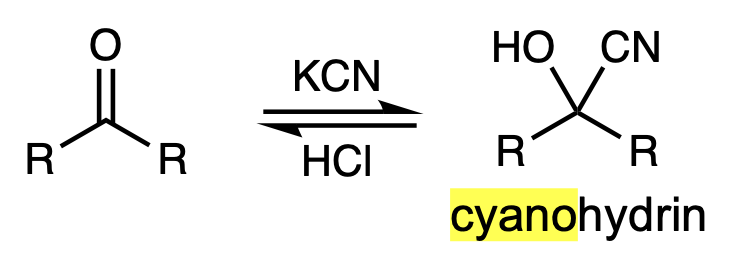
reagents for nucleophilic addition to convert ketone into a cyanohydrin
KCN and HCl
reagents for nucleophilic addition to convert ketone into a hydrate
H2O, catalyst (H+ or HO-)
reagents for nucleophilic addition elimination to convert ketone into an acetal (with hemiacetal intermediate)
2 HOR and H+ catalyst
reagents to convert aldehyde into an imine
primary amine (H2NR) and trace acid
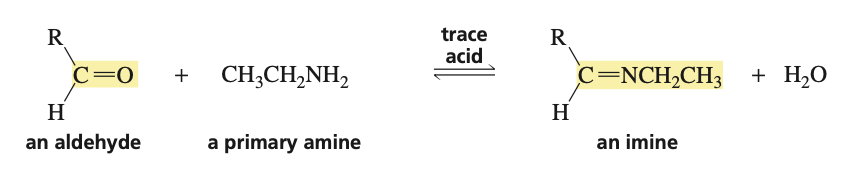
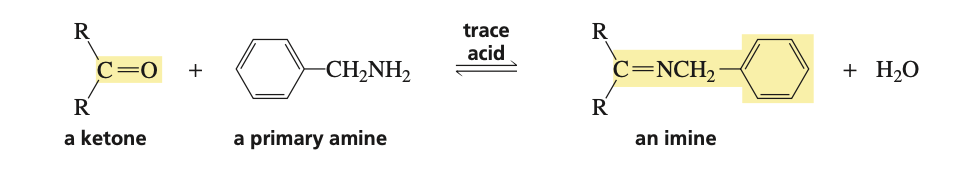
reagents to convert ketone into an imine
primary amine (H2NR) and trace acid
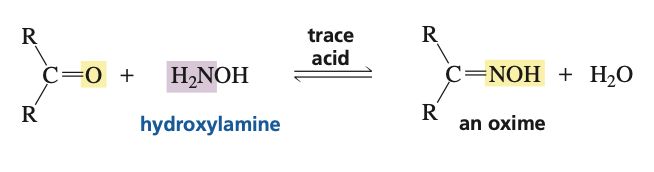
reagents for ketone to oxime (R2C=NOH)
hydroxylamine (H2NOH) and trace acid
reagents for ketone to hydrazone (R2C=NNH2)
hydrazine (H2NNH2) and trace acid
reagents for imine back to carbonyl compound (aka imine hydrolysis)
HCl and H2O
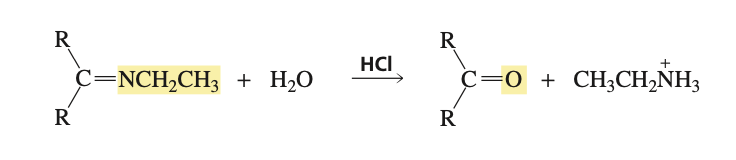
reagents for 2 step reductive amination
1.) primary amine and trace acid (to create imine)
2.) NaBH3CN (to reduce imine to amine)
reagents for 1 step reductive amination
primary amine, acetic acid (AcOH), NaBH3CN, MeOH
what are the possible products you can form with reductive amination (with aldehyde or ketone as starting product)?
shortcut: end product is an amine one degree of saturation higher than the starting reagent
using NH3 —> produces primary imine —> reducing imine creates primary amine
using primary amine —> produces secondary imine —> reducing imine creates secondary amine
using secondary amine —> produces tertiary enamine —> reducing enamine creates tertiary amine
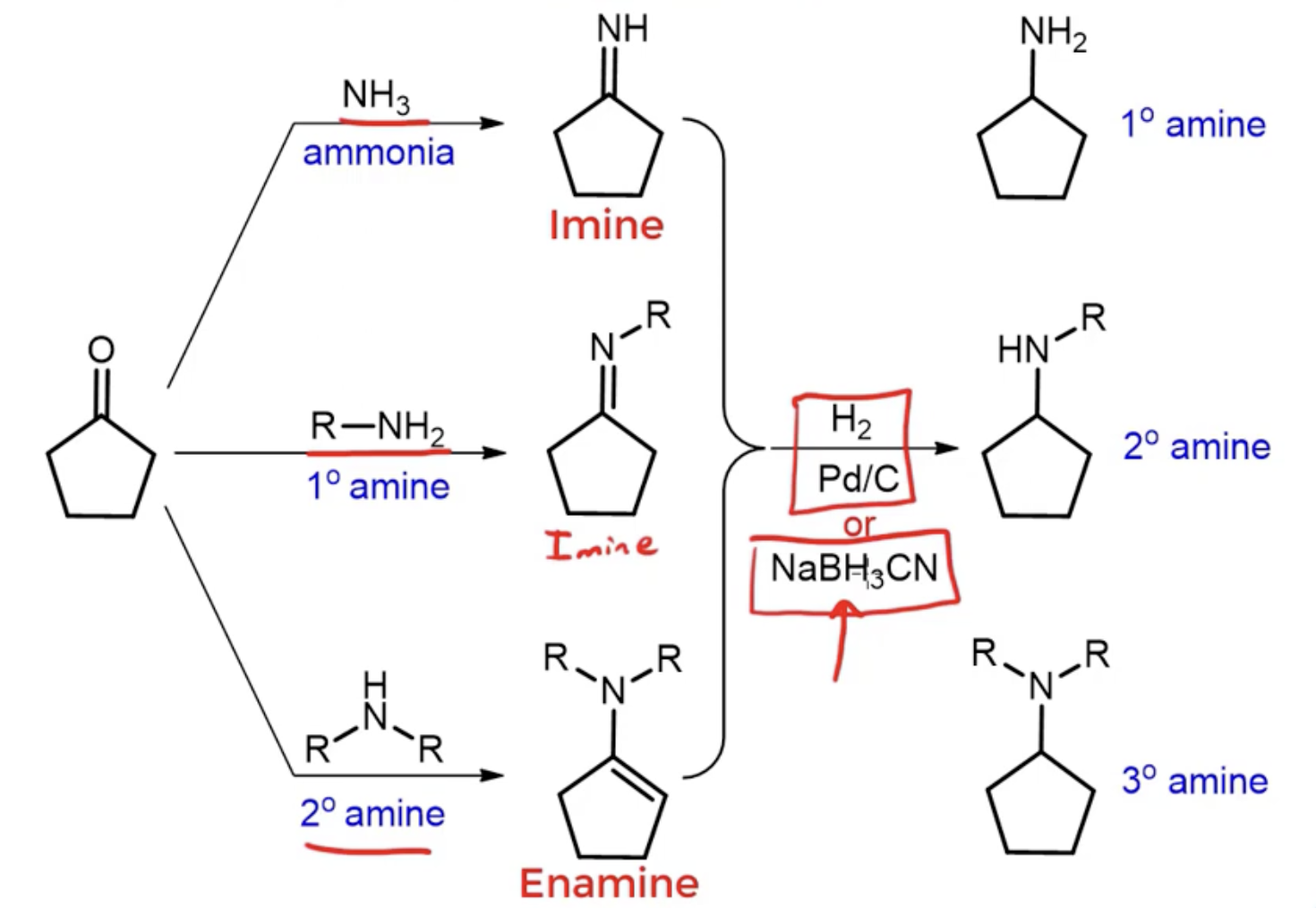
describe the general purpose of reductive amination
create an imine from an aldehyde or a ketone then reduce it with NaBH3CN to make an amine
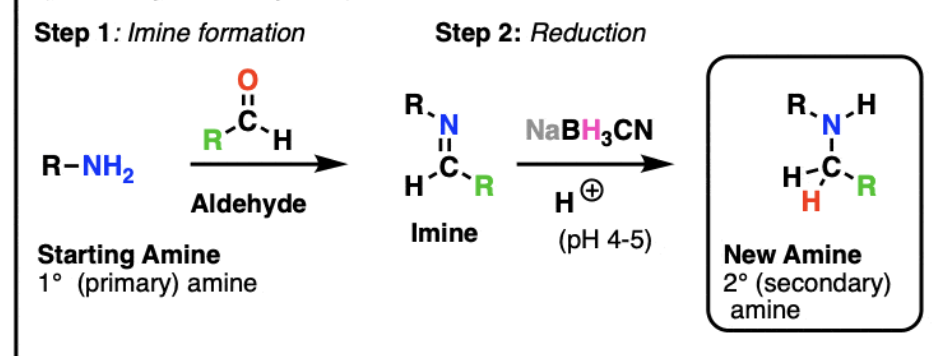
reagents for nucleophilic addition elimination to convert ketone or aldehyde into enamine
secondary amine (HNR2) and trace acid
reagents to convert primary or secondary cyclic amine to cyclic enamine
dimethyl ketone (R2C=O) and trace acid
reagents to convert aldehyde or ketone to cyanohydrin
KCN, HCl
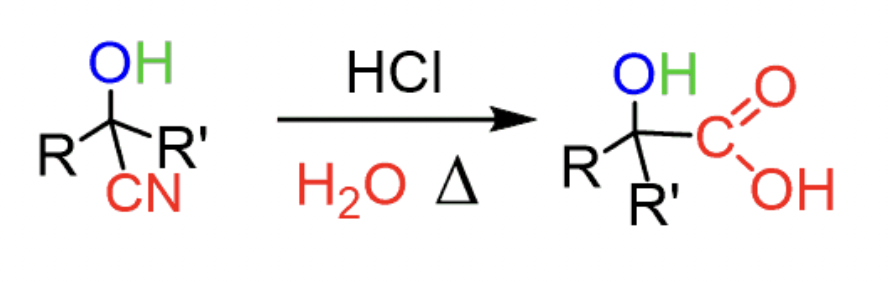
reagents to convert cyanohydrin (with hydroxyl) into carboxylic acid (aka hydrolysis of cyanohydrins)
HCl, H2O
reagents to convert cyanohydrin (with OH) into amine
H2, raney ni
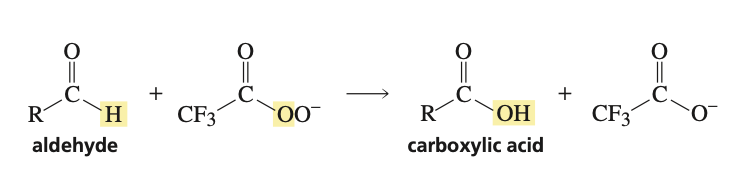
reagents to change aldehydes into carboxylic acid
a peroxyacid is needed, can use -OOC(O)CF3 or mcpba
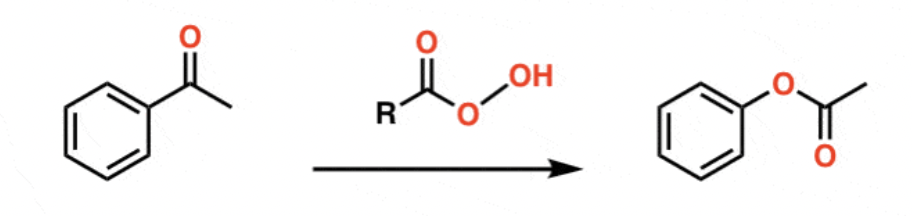
reagents for baeyer villiger (oxidation to change ketone into ester
-OOC(O)CF3
order of migration tendencies for baeyer villiger oxidation
H > tertiary alkyl > secondary alkyl ~ phenyl > primary alkyl > methyl
purpose of wittig reaction
interchanges the doubly bonded oxygen of the carbonyl compound with the doubly bonded carbon group of the phosphonium ylide
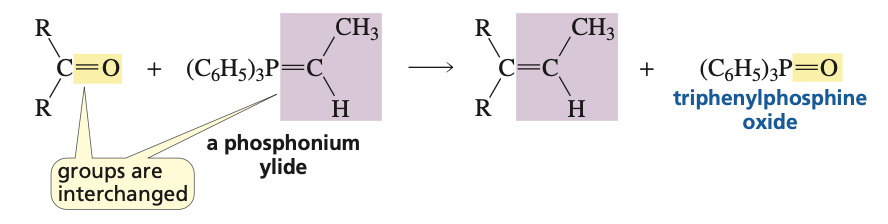
reagents for converting aldehydes and ketones to alkenes via wittig reaction
R=PPh3 (aka phosphonium ylide attached to R group)
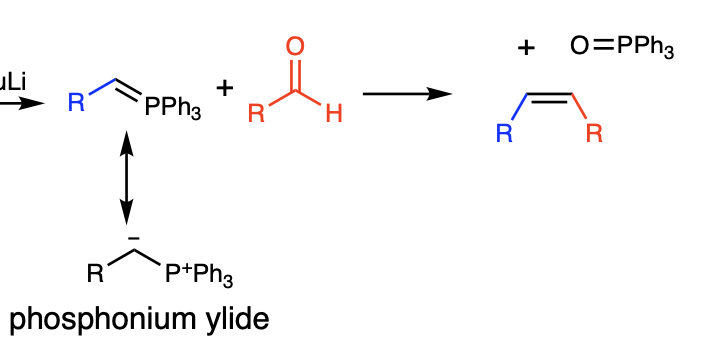
what type of addition do reversible nucleophiles do?
can do BOTH 1,2 (aka kinetic) and 1,4 (aka conjugate) addition
what type of addition do irreversible nucleophiles do?
ALWAYS 1,2 addition (aka kinetic control)
what type of addition do gilman (R2CuLi) reagents do?
ONLY ever 1,4 (conjugate addition)
what type of addition do grignard reagents do
form direct addition products
what type of addition do aldehydes usually do?
mostly direct 1,2 addition
what are the conditions for a carboxylic derivatives to undergo nuc acyl substitution
the new group added to the carboxylic acid’s tetrahedral intermediate MUST NOT be a weaker base than the group previously attached to the acyl group (because the weaker base is eliminated from the tetrahedral intermediate)
why does the substituent need to be a weak base
weak bases cause the carbonyl carbon to be more electrophilic and more reactive towards nucleophiles
relative basicities of LG
weakest base = Cl- < -OR = -OH < -NH2 = strongest base
relative reactivities of carboxylic acid derivatives
acyl chloride > ester > carboxylic acid > amide
reagents for acyl chloride to ester
CH3OH (or any alcohol)
reagent for acyl chloride to carboxylic acid
H2O
reagent for acyl chloride to amide (aka aminolysis)
2 eq of RNH2 (aka 2 eq of amine)
why do you need 2 eq of amine or 2 eq of ammonia when reacting with an acyl chloride
once the first eq acts as a base, it can’t react with the rest of the acyl chloride anymore. 2nd eq is needed to complete the rest of the reaction
reagents for ester to carboxylic acid and alcohol byproduct (aka ester hydrolysis rxn)
H2O and HCl catalyst
reagents for one ester to a different ester (transesterification rxn)
excess ROH and HCl catalyst
reagents for ester to amide (aka aminolysis rxn)
1 eq of an amine (RNH2) and heat
why are different equivalent amounts needed for aminolysis with acyl chlorides vs with esters
aminolysis of an ester requires only one equivalent of amine, unlike the aminolysis of an acyl halide, which requires two equivalents because the leaving group of an ester (RO-) is more basic than the amine, so the alkoxide ion—rather than unreacted amine—picks up the proton generated in the reaction.
what is the main rule for evaluating reactivity ?
the weaker the basicity of the group attached to the acyl group, the easier for the rxn to take place
____ charged species are not formed in basic solutions
positively
____ charged species are not formed in acidic solutions
negatively
reagents for carboxylic acid to ester via nuc acyl substitution
HCl and excess ROH (where R is the new desired ester)
do carboxylic acids undergo nuc acyl substitution with amines
no because having a carboxylic acid react with an amine would just protonate the carboxylic acid and make it an unreactive acyl substitution
why don’t amides (RC(O)NHR) react with halide ions, alcohols, and water?
bc the incoming nucleophile is a weaker base than the LG of the amide
what is the product if an amide is reacted with Cl-, CH3OH, and H20
no reaction
under what conditions do amides react with water
under acidic or strongly basic conditions
under what conditions do amides react with alcohols
under acidic conditions
amides react with ___ to form carboxylic acids with which reagents?
water, HCl and heat
amides react with ___ to form esters with which reagents?
alcohols, HCl and heat
reagents for amides to be hydrolyzed under basic conditions
H2O, HO-
reagents for nitrile (RC≡N) to carboxylic acid
HCl, H2O, and heat
reagents for SN2 rxn to turn alkyl bromide to carboxylic acid
1.) - C≡N, DMF 2.) HCl, H2O, heat
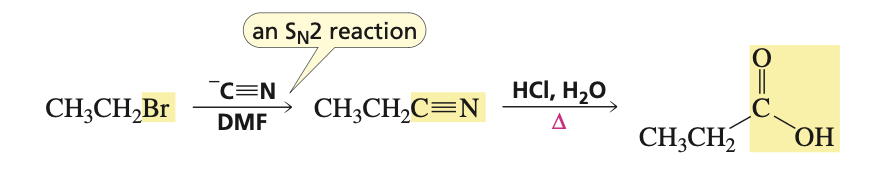
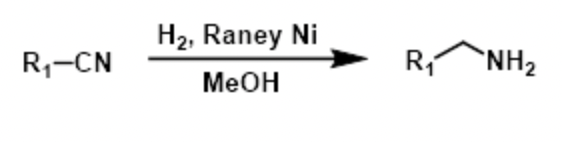
reagents for nitrile to primary amine (aka catalytic hydrogenation)
H2 raney nickel
reagents for amide (NH2) to nitrile (RC≡N) via dehydration
SOCl2
reagents for anhydride to become ester and carboxylic acid
ROH (aka any alcohol)
reagents for anhydride to form 2 eq of carboxylic acid
H2O
reagents for anhydride to form an amide and a carboxylate ion
2RNH2 (aka 2 eq of an amine)
reagent for aldehyde to primary alcohol
1.) NaBH4 2.) H3O+
reagent for ketone to secondary alcohol
1.) NaBH4 2.) H3O+
reagent for acyl chloride to primary alcohol
1.) 2 NaBH4 2.) H3O+
reagents for acyl chloride to aldehyde
1.) LTBA, −78 °C 2.) H2O
reagents for ester to 2 alcohols (one corresponding to the acyl portion of the ester and one corresponding to the alkyl portion)
1.) 2 eq of LiAlH4 2.) H3O+
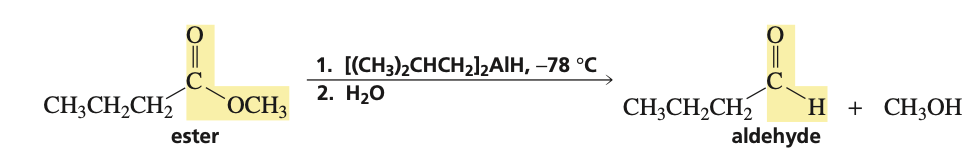
reagents for ester into aldehyde (with alcohol byproduct)
1.) DIBAL, -78C 2.) H2O
reagents for carboxylic acid to primary alcohol
1.) LAH (excess) 2.) H3O+
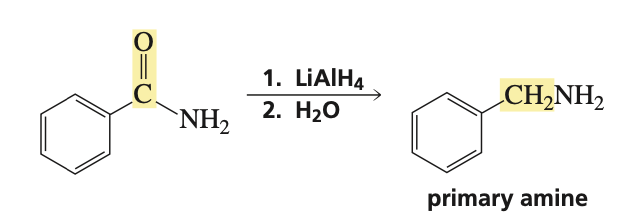
reagents for primary amide to primary amine
1.) LAH 2.) H2O
reagents for secondary amide to secondary amine
1.) LAH 2.) H2O
reagent for tertiary amide to tertiary amine
1.) LAH 2.) H2O
reagents for carboxylic acid to ester (aka fischer esterification)
ROH in excess (where R is the desired ester), HCl catalyst
reagents for alkene to aldehyde
1.) O3 2.) DMS
reagents for acyl chloride to carboxylic acid with an extra carbon in chain (aka wolff rearrangement)
1.) H2CN2 2.) heat 3.) H2O work up
what are the 3 steps of wolff rearrangement
1.) nucleophilic acyl substitution 2.) carbenoid rearrangement 3.) ketone hydration
reagents for curtius acyl chloride to RNH2 or RNHC(O)OR
1.) nucleophilic acyl substitution (NaNH3)
2.) nitrenoid rearrangement (with heat)
3.) H2O or ROH workup
reagents for carboxylic acid to amide
H2NR (aka amine of choice) and DCC
what is the difference between fischer esterification and ester hydrolysis
Fischer esterification is the reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to form an ester, while ester hydrolysis is the reverse reaction, where an ester is broken down into a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
reagents for carboxylic acid to acyl chloride
SOCl2
reagents for 2 eq of carboxylic acid to anhydride
P2O5
how can you go from an acyl chloride to an ester
can work with most nucleophiles (eg NaOEt), just make sure the desired ester is part of the nucleophile being used
reagents for nitrile to amine (via hydride)
1.) LiAlH4 2.) H3O+
reagents for nitrile to ketone
1.) RMgBr 2.) H3O+