ECONOMETRICS
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
What does regression do?
Minimizes SSR
SSR formula
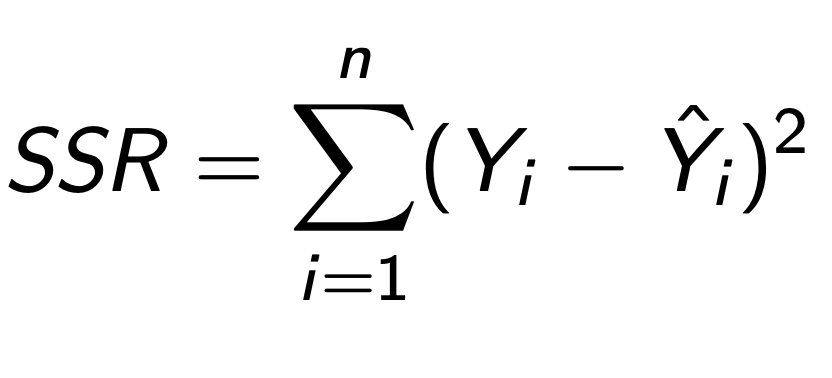
Normal equations
solution of SSR, derivatives of SSR wrt to alpha/beta
FOC wrt alpha
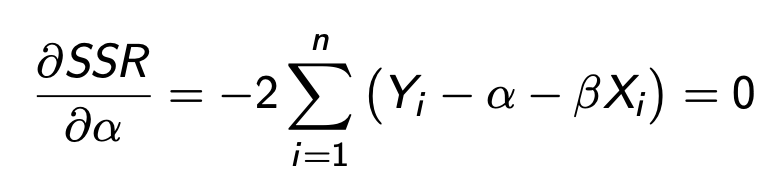
FOC wrt beta
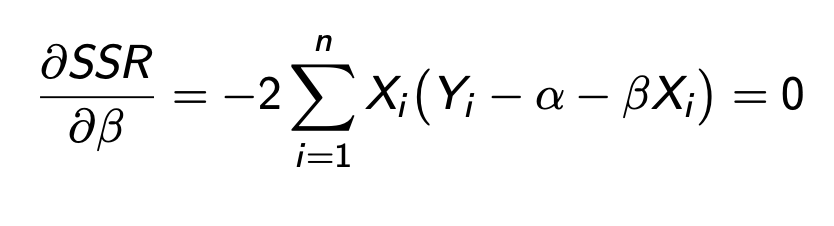
Beta
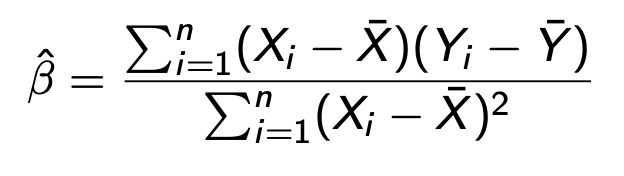
Or cov(x,y)/var(x)
Alpha
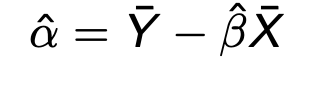
Sample covariance
measures relation between 2 random variables

Sample variance
spread of data
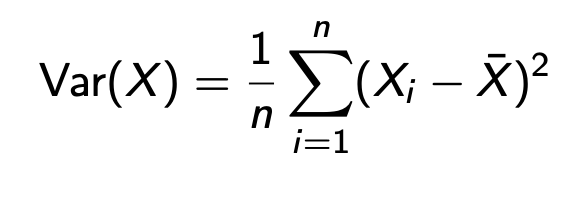
SST
Total Sum Squares
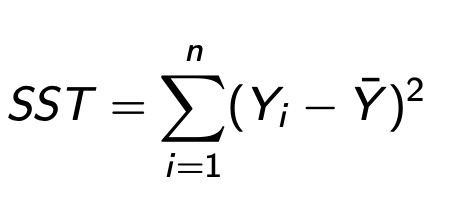
SSE
Explained Sum of Squares
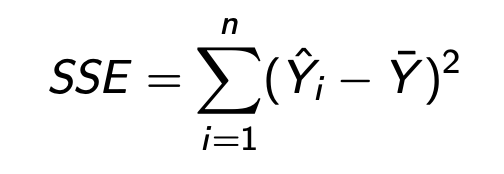
SSR
Residual Sum of Squares
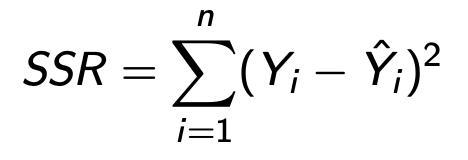
Coefficient of Determination
R² proportion of variation explained by regression
SSE/SST 1 - SSR/SST
Goodness of fit
Gauss Markoff Assumptions
OLS: linearity, random sampling, …
Standard Error
sigma² = SSR/(n-2)
Standard error of beta
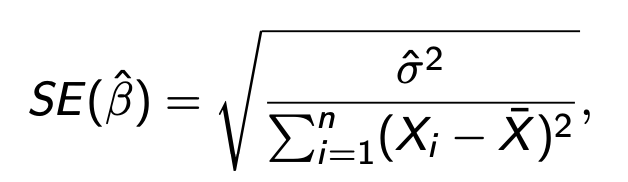
Stanard error of alpha
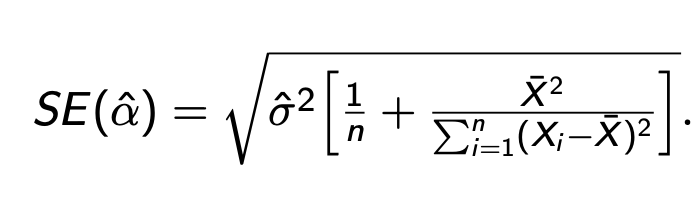
t test hypothesis
Ho: B = Bo
Ha: B ≠ Bo
if tcrit (wrt 1-alpha/2 and df - 2) < t reject ho
t
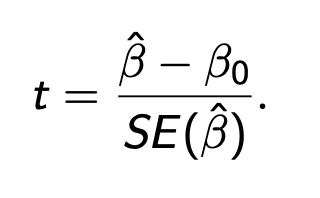
Confidence Interval
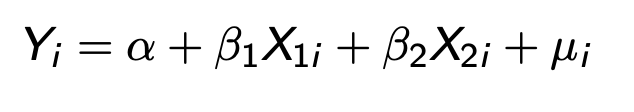
Coeffs in regression with mmultiple parameters
Partial effects
Effect of Xi on Y holding X2 constant and vv
Take deriv wrt each B to get new beta
Adjusted R²
R² automatically inflates artificially, R² bar (adj) penalizes irrelevant regressors
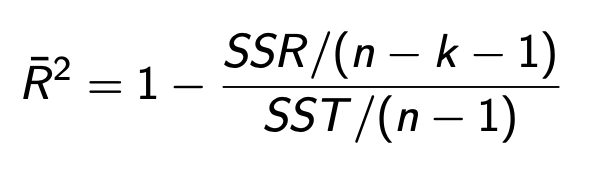
Omitted var bias, what is effect on included coeff?
omitting relevant vars that are related to vars in model creates bias for coeff in existing vars
effect on existing vals (if there is relation bt X1/X2
LOOK AT NOTES FOR MATRIX FORM
Du
Dummy Variables
allos to handle cat vars and encodes qualitative characteristics
Interaction term
lets us see affect of 1 var to depend on another
beta (x1*x2)
ex if education * male, beta is diff in return to educ bt men/somen
What are the 5 assumptions of OLS
Random sampling, linearity in param, no perfect multi-collinearity, zero conditional mean, homoskedasticity
A: Random sampling, what happens if it is violated?
all xi/yi come from same pop drawn independenly
sample is representative of pop
2. biased estimates
A: Linearity in parameters
x/y relation doesnt have to be linear but parameters must enter linearly
y = alpha + beta x² + u is stil linear in parameter
A: Zero cond mean
error has mena zero —> all determinatns are captured and only pure noise remains
A: Homoskedasticcity
variance X depend on any regressor
Gauss Markov Theorem
under classic linear reg assumptions
(linearity, expected mean = 0 and homeoskedasticity)
then OLS estimators (a/b) are BEST LINEAR UNBIASED ESTIMATORSB
BLUE
Best linear unbiased estimators
- Linear: expressed as linear combination of Y
- unbiased (expected val of alpha/beta = a/b)
- best: minimum variance among all linear unbiased estimators
Unbiased
expected value of estimator B is B
Consistency
consistent if predicted value converges to real value as sample size approaches infinity
Perfect vs near MC
one regressor is exact linear combo of others other is very close (high corr)
CANNNOT ESTIMATE MODEL IN PERFECT MC
Aux regression for perfect MC
Residual variation must be positive otherwise for R²j we have perfect MC
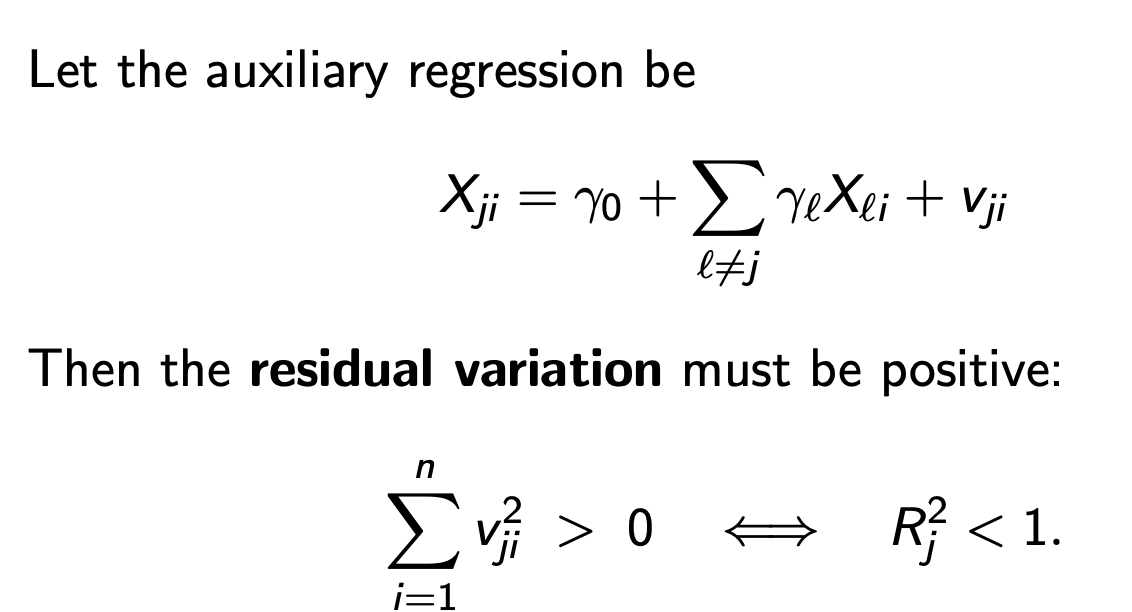
What does MC near do/not do
DOES NOT BIAS OLS COEFFICIENTS
Does:
increase var
wide CI
small t
makes coeff sensitive
VIF
Variance Inflation Factor
Rj² is from aux reg of Xj on all other regressors
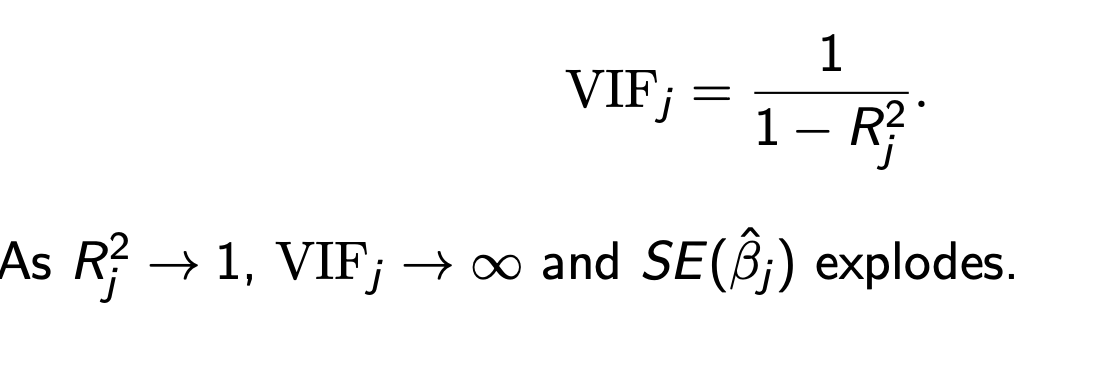
How to dieagnosse MC
pairwise corr among regressors
scatterplots/corr heatmaps
collect Rj²
get VIF
VIF GREATER THAN 10 IS SEVERE
What are sources of MC
Dummy var trap, deterministic identities, similar proxies, high order polynomials
source of MC: Dummy var trap
including all factor of dummies and an intercept - remove and use one cat as ref
source of MC: deterministic identities
vars are exact cobinations/sum to one paired with other vars
source of MC: too simiar proxies
add highly corr measures of same concept
source of MC: high order polynomials
x/x²/x³/x^4 can be highly corr with finite samples
helps to center xHo
how to fix MC
simplify: drop redunant vars/combine proxies
Transform: center/standardize regressors
Theory first: justify variables by model want to test
Prediciton: regularization methods
Heterskedasticity vs homoskedastity
variance of u given x is constant (sigma²) over i
HETERO it RELIES ON sigma² of i - VARIES ON i/Xi
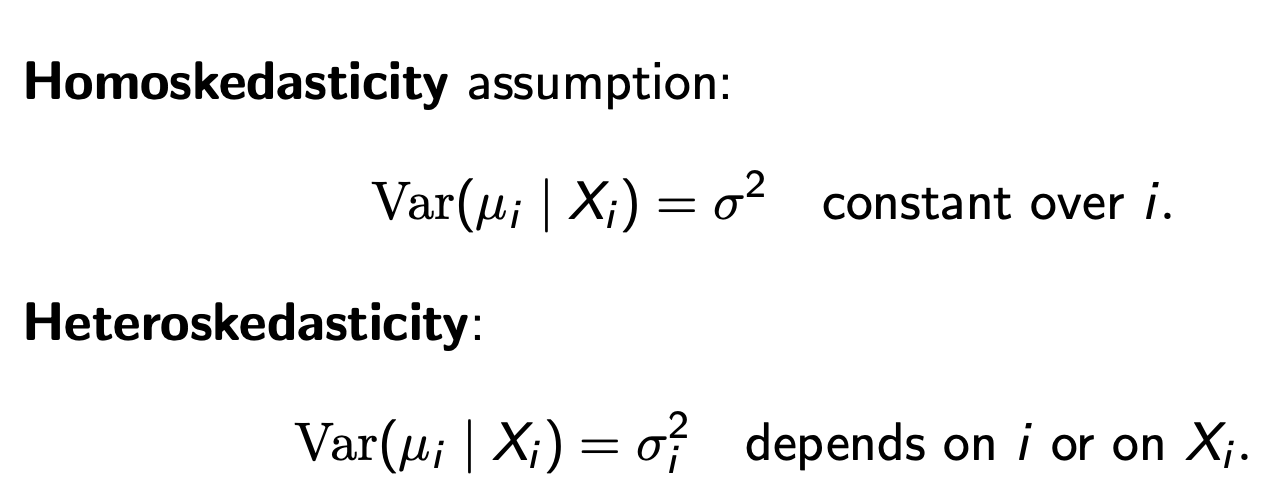
Effects of heteroskedasticy on OLS
OLS coeffs are UBIASED AND CONSISTENT
OLS SE are INVALID
therefore t/F tests based on SE are invalid
Breush Pagan Test
Tests whether error variance depends on regressors
Ho: homoskedasticity
test stat = nR² (follows X²m distribution ) (m = number of regressors in aux)
Breush Pagan test steps
Estimate OLS, get resid
regress squared resid on variables
compute nR² from aux
White Test
Ho: constant variance of errors, model is correctly specified
regresses resid on X but also on X² and interactions
null: nR² follows X²q (q = nuber of aux regressors
NED LARGE N (aux reg is big)
can use subset
heteroskedasticity robust standard error
all diff obs have individual SE - use each squared resid in variance calc
SE robust > SE OLS (heteroskedasticity is present)
White’s (1980) heteroskedasticity-consistent estimator
each squared residual used directly
Weigted Least squares
impproves coefficients
get ui from ols
model squared resid as function of x
run WLS using weight of w= 1/sigma²
may need to repea
When to use robust SEs?
misspecified variance
What to do for heteroskedasticity
plot resid against fitted vals
use BP/white test to diagnose
report hetero-robust SE
consider WLS if variance pattern present
What are main sources of model misspecification?
wrong regressors
measurement errors
wrong functional forms
Misspecification: Wrong regressors/omitted vars
estimated coeff = B1 + b2 (cov x1*x2 / var x1)
omitting pos cor regressive increases biases in corr regressors
Misspecification: Wrong regressors/endogeneity
regressor corr w error (covariance between regressor/resid ≠ 0)
FAILS ZERO MEAN COND
could be from omitted vars
simultaneity/reverse causlaity
measurement error in x
CAUSES BIASED/INCONSISTENT OLS
fix w better design/controls/instrumental vars
Misspecification: Wrong regressors/irrel vars
B1 remains unbiased
variance of B1 increases (R2 increases bc extra regressors)
lowers power of tests/wide CI
Misspecification: Wrong form/curvature
what is it, what are effects, how to diagnose?
conditional mean nonlenear, model estimated only in x not x²
OLS BIASED AND INCONSISTENT
diagnosis:
resid vs fitted values = systematic pattterns
scatter of y/x reveal curve
fix by adding x², poly, or transform
Y = b ln x
<> y for 1% <> in X
ln y = bx
Percent <> in y for 1 unit <> in x
ln y = bln x
b = elasticity, partial deriv of y wrt x
misspecifications; functional form: interactions
effect of x depends on x2
omitting interaction = misspec and biased slope on x1/x2
expected val of y given x wrt x1 = b1 + b3x2
Ramsey RESET
form check
if functional form correct higher order functions of fitted vals should not add explanatory power
1. estimate baseline and get y^
reestimate w extra powers of y^², y^³
use f test for joint sig of added terms
Ho: no nonlinear terms or interactions
general check (doesnt identify exact form needed)
Endogeniety problem
mean value of residuals is not zero
biased/inconsistent cov
from reverse causality, omitted vars, measurement error
Why does OLS fail with simultaneity
regressors are not exogenous (corr with error term)
Endogenous
jointly determined within system
ex. price/quantity within a market
Exogenous
proxy for ability/regressor
ex) weather and income
Proxy variable
proxy for ability/regressor that is included inregressionIn
Instrumental variable
z, instrument that affects x (helps predict) but is uncorrelated with our dependent variable (but only trhough x not directly)
helps us to isolate exogenous variation in endogenous regressor x
ex. weather shocks affect regressor agricultural supply but X consumer demand directly
What are conditions for a valid instrument (2)?
Revelance: must be corr with x (cov and must have non-zero coeff in auxilariy)
Exogeniety (inclusion restriction)
Z affects y only thorugh X (not directly or through omitted variables
Weak relevance
fails relevance
Strong invalid instrument
fails exogeniety
How to test relevance
1st stage regression
if x = pi0 + pi Z + V and pi ≠ 0, then z is relevant (good)
2nd stage: estimate structural model by LS (replace endo reg 2 fitted xx^ from first stage)
How to test exogeniety?
cannot, U is unobserved must justify using economic reasoning
F stat
Ho: instruments are irrelevant (pi = 0)
F STAT > 10 is strong instrument
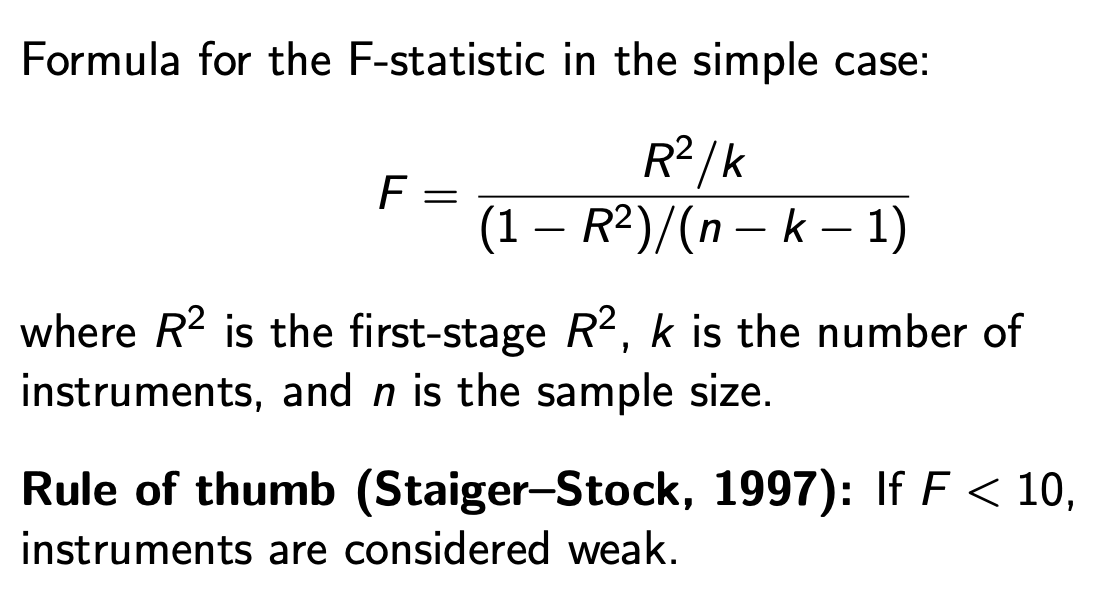
What is the coefficeint of the IV estimator?
B^ iv = cov(z,y) / cov(z,x)
if x is its own instrument you get cov(x,y)/var(x) = regular OLS
2SLS
Two stage least squares estimates
CAN DIFFER SIGNIFICANTLY FROM STANDARD OLS
x^ = purged version of X
removes endogenous part of x before running wnd stage reg
When/why to use 2SLS
if regressors are exogenous
if not OLS is unbiased and more efficient than 2SLS
How to compare OLS/2SLS?
Hausman (Durbin-Wu-Hausman) test
if both consistent (regressor exogenous) they should be close
if only 2SLS consistent (regressor endogenous) they differ systematically
Hausman Test Interp/Steps
Ho: OLS is okay (exogenous)
Ha: OLS is inconsistent (endogenous)
Steps:
Estimate model by OSL/2SLS
Compute diff bt coeff vec
test whether this diff is stat sig
What are main objectives when using time series?
dynamic modeling, forecasting
(understand structure/response to shocks and accurate predictions)
Persistence
Lasting effects of shocks
Financial returns stylized facts
weak/no autocorr
voliatity clusters (lg <> followed by lg <> and VV)
asymmetric volatality (neg shocks inc volatility more than + shocks)
Beta in time series
CAPTURES SYSTEMATIC RISK (that X be diversified away)
B measures sensitivity of stocks return to movt in overall market
>> Response of asset returns to market returns
slope of regression of Ri onto Rm
trend
Spurious regression
if Xt1/xt2 affect yt, ommiting t can bias regression
2 related variables trend over time
including a B3t3 allows yt to have its own effect on trend after controlling for x1t/x2t
unrellated variables may trend togethre over time —> corr ≠ causation
multiplicative decomposition
Yt = Tt * Ct * St * ut *
take logs to get into additive form: ln(y) = ln(t) + ln(C)
Methods of removing seasonality
remove dummy variables
mean average smoothing
Remove seasonality with dummy variables
regress yt on szl dummy variables
D = 1 if obs in that time period
et = resid
* Note that m = 2, do not do all otherwise perfect MC
FITTED COMPONENT CAPTURES SZL
RESIDUAL = DE-SZNL SERIES (can always add Y back in)
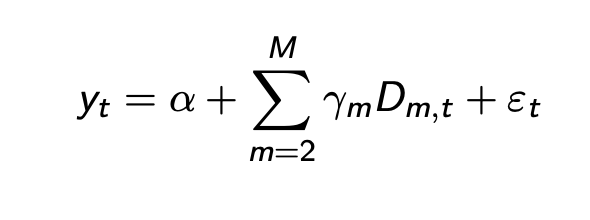
Moving average smothing
larger q = smoother trend
estimated trend is avg of q obs

centered moving avg
uses past/future obs
non-centered moving avg
only present/past obs
Trend-Cycle decomp
long/med movt
often estimated together bc difficult to seperate
How to sep trend-cycle?
HP filter
HP filter
Hodrick-Prescott filter: separates long-term comp from short term cyclical fluctuations (Ct = yt - Tt)
Term 1: ensures trend Tt follows yt closely
Term 2: penalizes <> in slope of T to ensure smoothness
Standard smoothing parameter: lamda = 1600, …
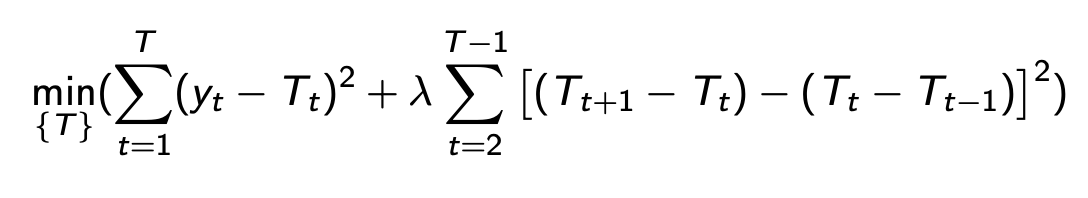
X-13ARIMA-SEATS
method of szn adjustment in nat stat offices
X13ARIMA: TS decomp based on moving averages/ARIMA
SEATS: extracts sznl trend/irregular
>> getrs rid of recurring szn patterns, estimate underlying trend/cylical movt, improve comparability across timeW
White Noise
ut ~ (0, sigma²)
no autocorr
Random walk
summed sequence of random shocks/white noise terms
yt = yt-1 + ut
yt = y0 + u1 + … ut
ex) stock prices