VT 111 Lec. 9 Muscles
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
How Muscles Work
Muscles are engines
They burn fuel (glucose)
They produce mechanical movement
They move loads
Definitions
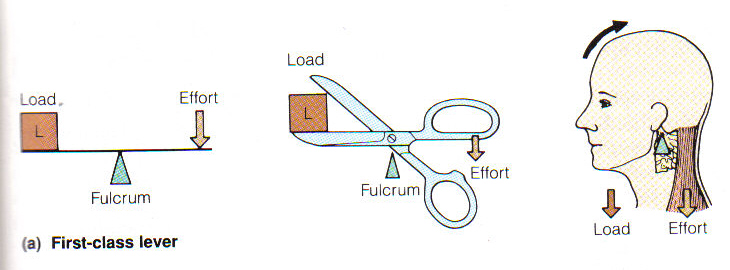
Muscles act on the principle of leverage
The bone is a lever
The joint is the fulcrum
The muscle is the motor
The load is the body part or anything that is attached
First Class Lever System
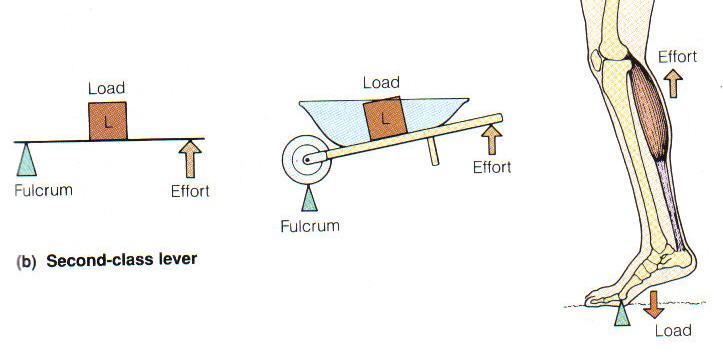
Second Class Lever System
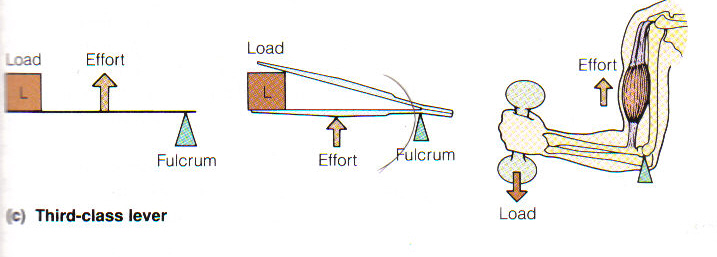
Third Class Lever System
Movements of Muscles
A muscle that is the major mover of something is a prime mover (agonist)
A muscle that acts against the prime mover is an antagonist
A muscle that helps another muscle is a synergist
Skeletal Muscle Action
Agonist = prime mover
Directly produces a desired movement
Antagonist
Directly opposes the action of an agonist
Synergist
Contracts at same time as agonist to assist its action
Fixator
Stabilizes joints to allow other movements
Naming Muscles
Location: “brachialis” (upper arm)
Shape: “teres” (round shaped)
Size: “maximus” (greatest/largest)
Direction of fibers: “rectus” (straight/longitudinal)
Attachments: “brachioradialis” (humerus → radius)
Number of origins: “triceps” (3)
Action: “flexor” (closes joint angle)
Movement in Animals: Basic Principles
Muscle contraction is based in contractile proteins
Muscles only do work when they contract
Vertebrates have opposing muscle in the same plane.
Muscles connect to the skeleton through tendons
Types of Muscles
Skeletal: voluntary, striated, multinucleate
Cardiac: involuntary, striated, usually mononucleated but sometimes multinucleate, intercalated discs
Smooth: involuntary, non striated, mononucleate, spindle shaped
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary striated muscle
Well-defined group of cells surrounded by fibrous connective sheath = epimysium

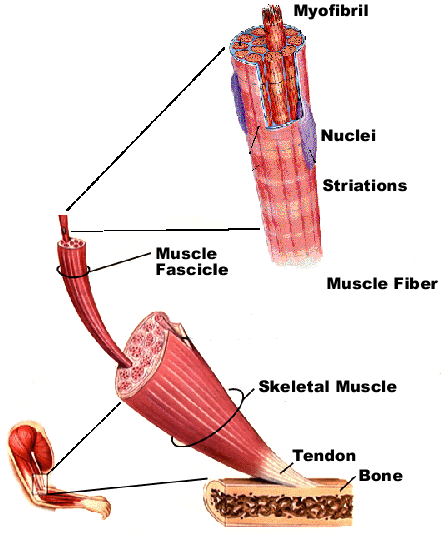
Gross Structure of Muscle
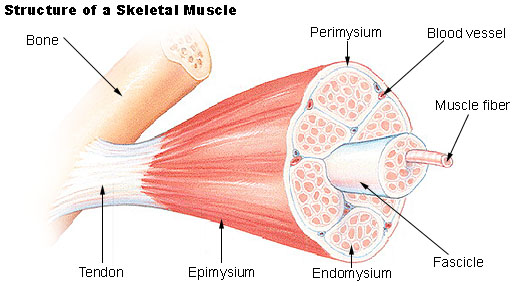
Gross Structure Continued…
Cutaneous Muscles
Thin, broad superficial muscles
Found in connective tissue just beneath skin
Little or no attachment to bones
Head & Neck Skeletal Muscles
Functions
Control facial expressions
Enable mastication
Move sensory structures
Support the head
Raise the head and neck
Move the head laterally
Close the jaw
Extend the head and neck and pull the front leg forward
Flex the head and neck
Abdominal Skeletal Muscles
Functions
Support abdominal organs
Help flex the back
Participate in defecation, urination, parturition, vomiting, and regurgitation
Have a role in respiration
Arranged in layers
External abdominal oblique muscle
Internal abdominal oblique muscle
Rectus abdominis
Transversus abdominis
Left and right parts come together at linea alba
Thoracic Limb Skeletal Muscles
Functions mainly for locomotion
Superficial muscles of the brachium
Adductor muscles –latissimus dorsi, pectoral muscles
Abductor muscle—deltoid muscle
Brachial muscles
Flexor and extensor muscles—biceps brachii, triceps brachii
Carpal and digital muscles
Flexor and extensor muscles—extensor carpi radialis, deep digital flexor
Pelvic Limb Skeletal Muscles
Functions mainly for locomotion
Muscles of the hip joint
Extensor muscles
Luteal muscles and hamstring muscle group
Muscles of the stifle joint
Extensor muscles
Quadriceps femoris
Muscles of the tarsus and digits
Flexors and extensors
Gastrocnemius muscle
Achilles tendon
Skeletal Muscles of Respiration
Function to increase and decrease size of thoracic cavity
Inspiratory muscles
Diaphragm
External intercostal muscles
Expiratory muscles
Internal intercostal muscles
Abdominal muscles
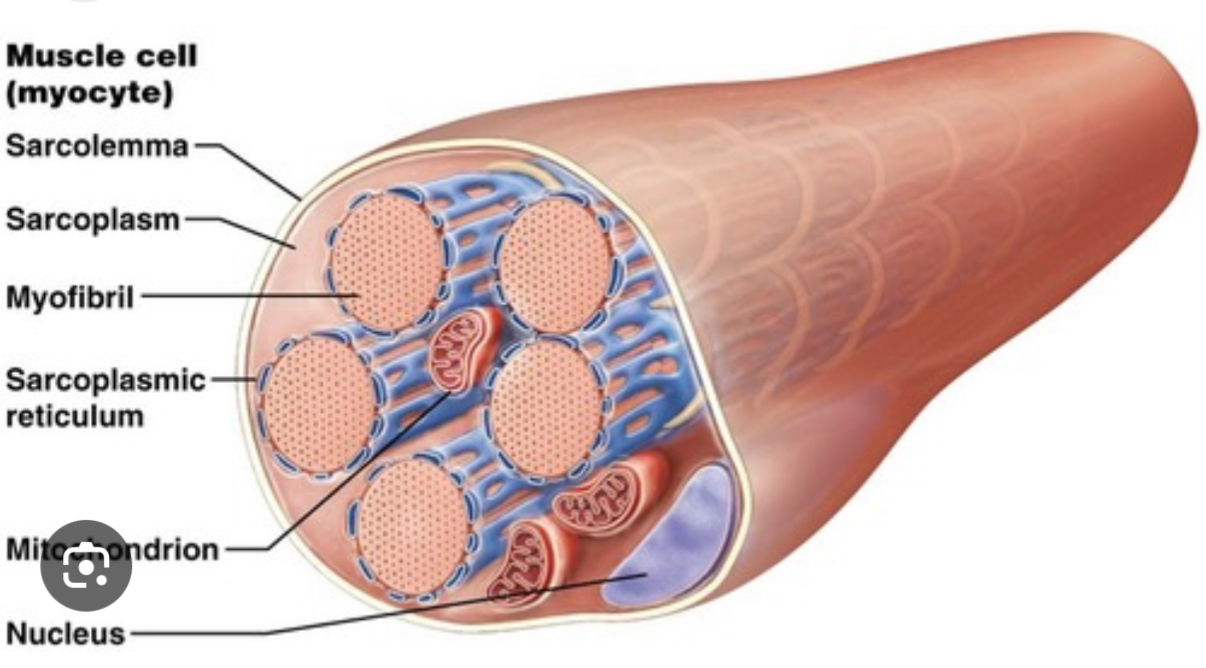
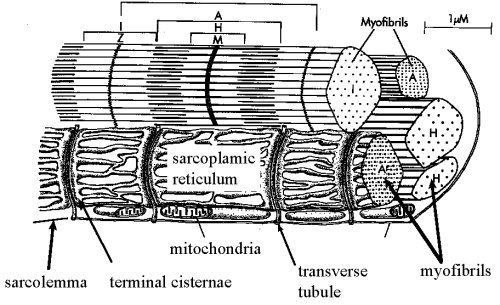
Skeletal Muscle Cell = Muscle Fiber
Very large, quite long and thin
Multinucleate
Myofibrils form interior of muscle fiber
Network of sarcoplasmic reticulum
System of T tubules (transverse tubules)
Sarcomere = series of protein filaments that make up contractile units of muscle cells
Many sarcomeres lined up end to end = one myofibril
Sarcomere
2 primary protein filaments responsible for contraction
Thick, dark myosin
Thin, light actin
Filaments comprise various visible bands
A band
H band
I band
Z line
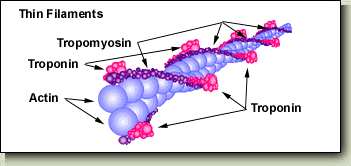
Thin Filament Structure
Actin
Tropomyosin
Troponin
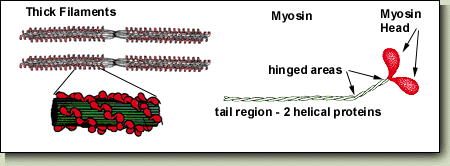
Thick Filament Structure
Myosin subunits
Heads
Tail region
Filament Structure
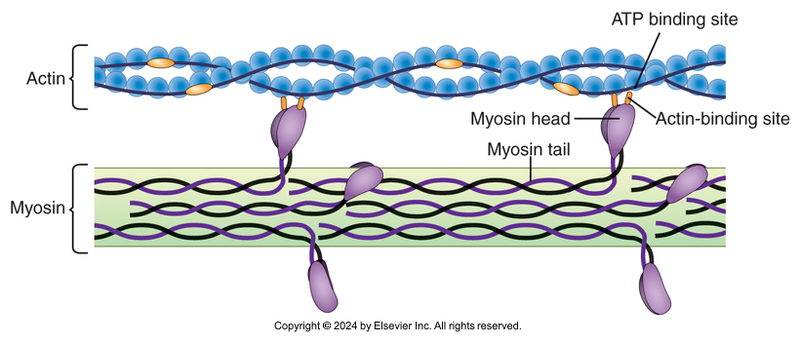
Structure of Sarcomere
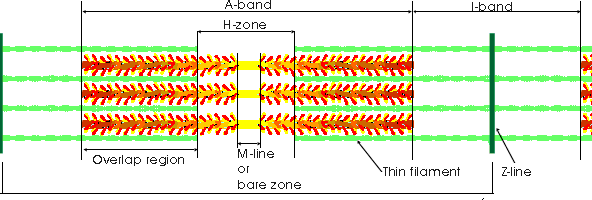
Electron Microscope: Sarcomere

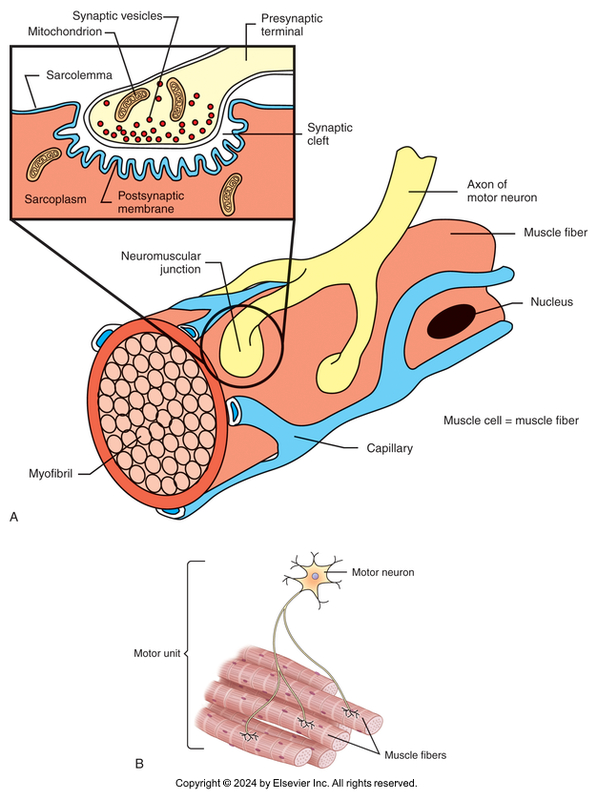
Neuromuscular Junction
Site where ends of motor nerve fibers connect to muscle fibers
Motor nerve
One nerve fiber and all the muscle fibers it innervates
Few muscle fibers per motor unit
Small, delicate movement of muscles
Huge numbers of muscle fibers per motor unit
Large, powerful movement of muscles
Synaptic vesicles at end of nerve fiber contain neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Neuromuscular Junction Diagram
Sliding Filament Theory I
Action potential travels down axon and reaches axon terminal.
Synapse between axon and muscle cell is called the myoneural junction or the neuromuscular junction.
Neurotransmitter of the somatic nervous system is acetylcholine
Sliding Filament Theory II
Nerve impulse travels over muscle fiber sarcolemma and into T tubules
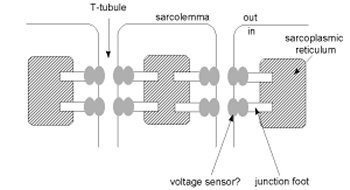
Sliding Filament Theory III
Nerve impulse triggers Ca release from S/R (Sarcoplasmic reticulum)
Ca floods cytoplasm and attaches to troponin
Troponin moves and pulls tropomyosin with it.
Myosin binding site on actin is exposed
T Tubule/Myofibril System
Sliding Filament Theory IV
Myosin heads function as ATPase. This cleaves ATP to ADP.
Myosin head can bind only if ADP is formed
Once binding takes place, ADP and Phosphate group is released.
Release of ADP causes the cross bridge to change orientation, resulting in the power stroke of the myosin head
Sliding Filament Theory V
At the end of the power stroke, Myosin head binds new ATP
Binding causes myosin cross bridge to break bond with actin.
Myosin ATPase cleaves ATP to ADP in preparation for a new cycle.
If no further action potentials arrive, Ca is taken back into S/R by active transport pumps

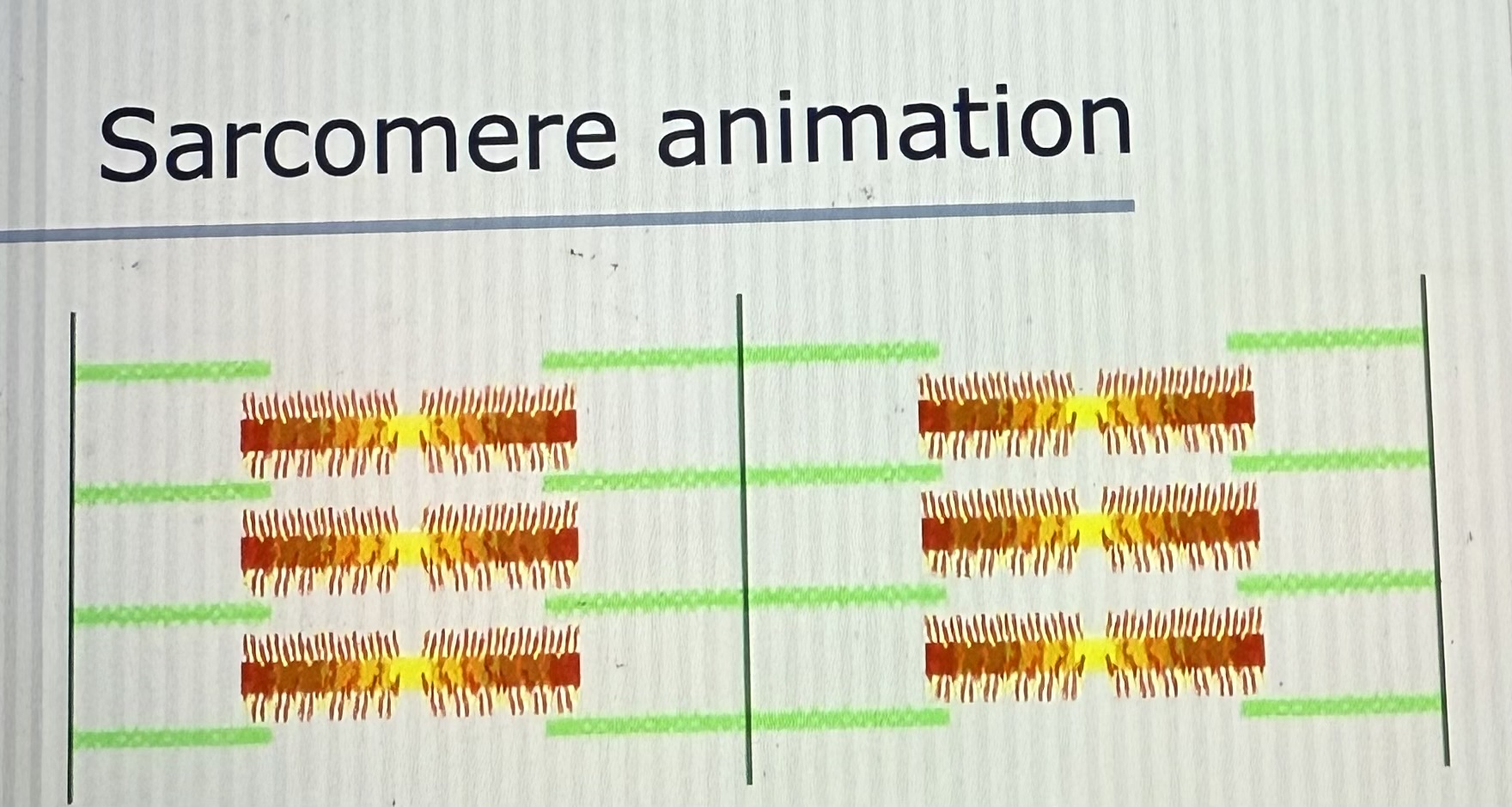
Sarcomere Animation
Refer to PowerPoint
Muscle (Contraction) & Relaxation
Nerve impulse comes down motor nerve fiber
Impulse reaches end bulb of nerve fiber
Acetylcholine released into synaptic space and binds to receptors on sarcolemma surface
Impulse travels along sarcolemma and through T tubules to interior of the cell
Impulse reaches sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ca++ ions released into sarcoplasm
Ca++ diffuses into myofibrils and starts contraction
Energy supplied by ATP
Muscle (Relaxation) & Contraction Continued…
Sarcoplasmic reticulum begins pumping ca++ back in again
Ca++ is pulled out of myofibrils
Energy supplied by ATP
Contraction stops
Muscle returns to original length
Mechanics of Muscle Contraction
Muscle fibers in relaxed state
Actin and myosin filaments slightly overlap
Muscle fibers stimulated to contract
Cross-bridges ratchet back and forth
Actin filaments pulled toward center of myosin filaments
Sarcomere is shortened
Muscle contraction = shortening of all sarcomeres in a muscle fiber
Characteristics of Muscle Contractions
All-or-nothing principle
When stimulated, individual muscle fiber contracts completely—or not at all
Nervous system controls number of muscle fibers stimulated
Twitch contraction
A single muscle fiber contraction
Latent phase
Contracting phase
Relaxation phase
Muscle Contraction
Maximum contraction efficiency
When nerve impulses arrive 0.1 second apart
Result is series of complete muscle fiber twitches
Smooth, sustained muscle contractions
Average out activity of all muscle fibers
Twitches
Contractions out of sync with each other
Chemistry of Muscle Contraction
ATP provides energy to allow sliding of actin and myosin filaments
CP (creatine phosphate) coverts ADP back to ATP
Catabolism of glucose and oxygen help to produce ATP and CP
Glucose stored in muscle as glycogen
Oxygen stored as myoglobin
Aerobic metabolism
Adequate oxygen supply for energy needs of muscle fiber
Maximum energy extracted from each glucose molecule
Anaerobic metabolism
Need for oxygen exceeds available supply
Lactic acid formed in incomplete glucose breakdown
Lactic acid is what makes muscles burn when working out
Heat Production
Muscle activity generates heat
Mechanisms to eliminate excess heat
Panting or sweating
Spasmodic muscle contractions that increase heat production
Shivering
Cardiac Muscle = Striated Involuntary Muscle
Found in only the heart
Small cells with single nucleus
Longer than wide, with multiple branches
Intercalated disks fasten cells together
Physiology & Anatomy of Cardiac Muscle
Cells contract with no external stimulation
Groups of cells contract at the rate of the most rapid cell in the group
Contractions are rapid and wavelike
Microscopic anatomy
Striated like skeletal muscle cells with many of the same organelles and intracellular structures
Much smaller than muscle cells
Single nucleus per cell
Longer than they are wide with multiple branches
Cardiac Conduction System
Sinoatrial (SA) node
Located in wall of right atrium
Generates impulse to start each heartbeat
Impulse follows controlled path through the heart
Structures in heart transmit, delay, and redirect
Walls of heart chambers contract in coordinated manner
Nerve Supply to Cardiac Muscle
Not needed to initiate contractions
Heart innervated from 2 systems
Sympathetic system
Stimulates heart in fight-or-flight response
Parasympathetic system
Inhibits cardiac function
Smooth Muscle Anatomy
Gross anatomy
2 main forms
Visceral smooth muscle
Large sheets of cells in walls of some hollow organs
Multiunit smooth muscle
Small, discrete groups of cells -> ex. iris
Microscopic anatomy
Small and spindle shaped with single nucleus in the center
Smooth, homogeneous appearance
Actin and myosin filaments crisscross at various angles
Smooth Muscle = Involuntary Muscle
Cells not under conscious control
Cells small and spindle shaped
Single nucleus in center
Smooth, homogeneous appearance
Cell balls up as it contracts
Microscopic Anatomy of Smooth Muscle Cells
Actin and myosin filaments arranged as small contractile units that crisscross the cell
Dense bodies at each end correspond to Z lines of skeletal muscle
Visceral Smooth Muscle
Found in walls of many soft internal organs
Stomach, intestines, uterus, urinary bladder
Contracts in large, rhythmic waves
Contracts without external stimulation
Reacts to stretching
Innervated from 2 systems
Sympathetic system decreases activity
Parasympathetic system increases activity
Multiunit Smooth Muscle
Individual smooth muscle cells or small groups of cells
Found where small, delicate contractions are needed
Iris and ciliary body of eye, walls of small blood vessels, and small air passageways in lungs
Contraction requires impulses from autonomic nervous system