2a. Revenue
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:30 PM on 9/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
1
New cards
Total Revenue (TR)
Total Revenue = Price x Quantity
TR = P x Q
Total revenue is total amount of money a firm receives from its sales.
TR = P x Q
Total revenue is total amount of money a firm receives from its sales.
2
New cards
Average Revenue (AR)
AR = TR/Q
If we simplify this formula, we find that Average Revenue = Price (AR = P)
If we simplify this formula, we find that Average Revenue = Price (AR = P)
3
New cards
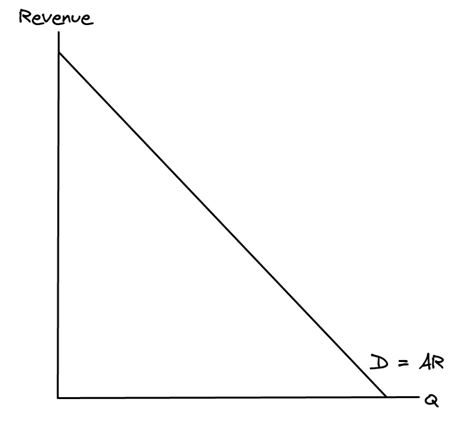
Average Revenue (AR) curve
**Remember:** when drawing an AR curve, you must ensure your curve starts from the **price axis**.
4
New cards
Marginal Revenue (MR)
MR = ∆TR/∆Q
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue from selling **one** extra unit.
Marginal revenue is the additional revenue from selling **one** extra unit.
5
New cards
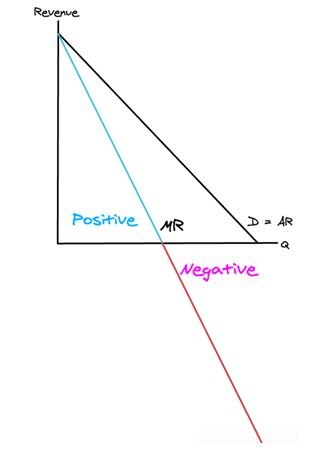
Marginal Revenue (MR) curve
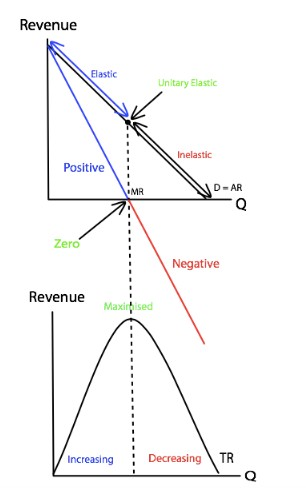
The MR curve must:
1. Start at the same point as AR
2. Cross the Q axis at half the quantity AR crosses at
3. MR should end at the same quantity that AR ends at
\
**An important fact about the Marginal Revenue (MR) curve:**
As price **decreases** and quantity **increases**, MR **decreases.**
MR **decreases** from positive to **negative**.
1. Start at the same point as AR
2. Cross the Q axis at half the quantity AR crosses at
3. MR should end at the same quantity that AR ends at
\
**An important fact about the Marginal Revenue (MR) curve:**
As price **decreases** and quantity **increases**, MR **decreases.**
MR **decreases** from positive to **negative**.
6
New cards
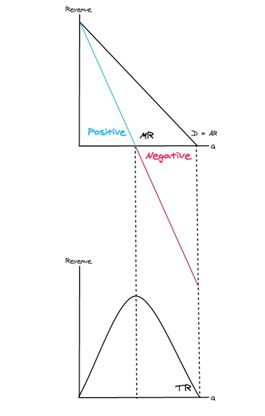
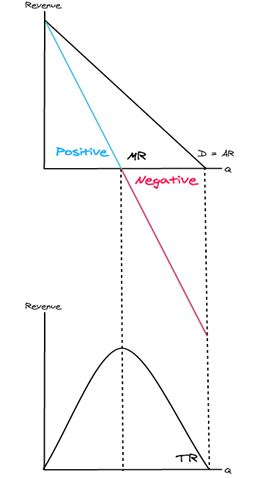
Marginal Revenue (MR) and Total Revenue (TR) relationship?
When MR is **positive**, TR will increase as quantity increases.
When MR is **negative**, TR will **decrease** as quantity increases.
When MR is **negative**, TR will **decrease** as quantity increases.
7
New cards
Total Revenue (TR) curve?
When MR is **positive**, TR will **increase** as quantity increases.
When MR is **negative**, TR will **decrease** as quantity increases.
So the TR curve is **increasing** when MR is **positive** and the TR curve is **decreasing** when MR is **negative**.
When MR is **negative**, TR will **decrease** as quantity increases.
So the TR curve is **increasing** when MR is **positive** and the TR curve is **decreasing** when MR is **negative**.
8
New cards
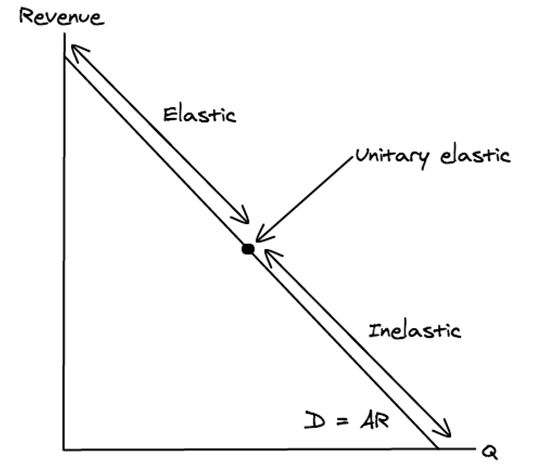
PED changes along the demand curve?
At **high** prices, demand is **elastic** because a % change in price will have a **big** impact, so consumers will be **very responsive.**
E.g. 10% of £1000 = **£100**
At **low** prices, demand is **inelastic** because a % change in price will have a **small** impact, so consumers will be **unresponsive.**
E.g. 10% of £10 = **£1**
E.g. 10% of £1000 = **£100**
At **low** prices, demand is **inelastic** because a % change in price will have a **small** impact, so consumers will be **unresponsive.**
E.g. 10% of £10 = **£1**
9
New cards
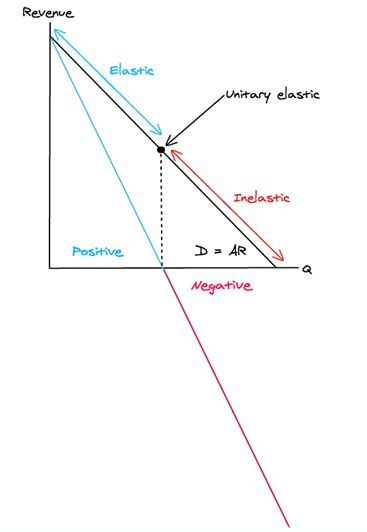
PED and Marginal Revenue (MR)?
When MR is **positive,** demand will be **elastic.**
When MR is **0**, demand will be unitary **elastic.**
When MR is **negative**, demand will be **inelastic.**
When MR is **0**, demand will be unitary **elastic.**
When MR is **negative**, demand will be **inelastic.**
10
New cards
Revenue maximisation?
A firm’s total revenue is maximised when MR = 0 (no more revenue can be gained at this point).
11
New cards
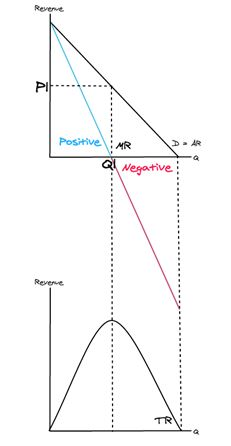
Revenue maximising price?
A firm’s total revenue is maximised when MR = 0, at quantity Q1, so the price is **P1.**
12
New cards
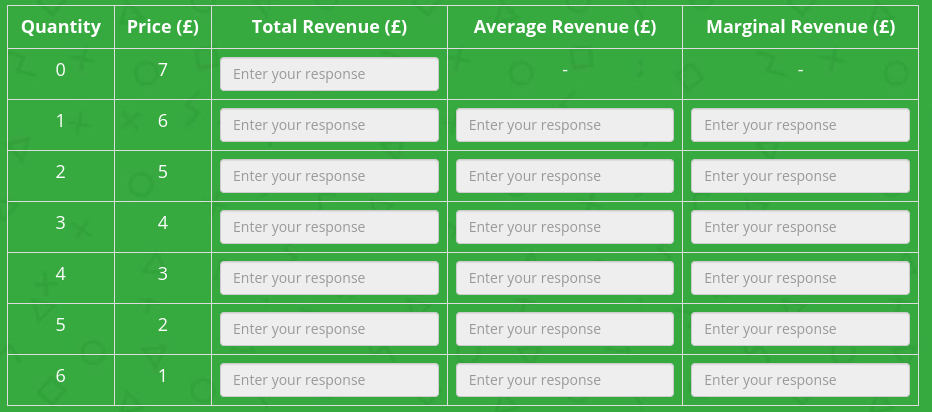
Complete the table
Model Ans.
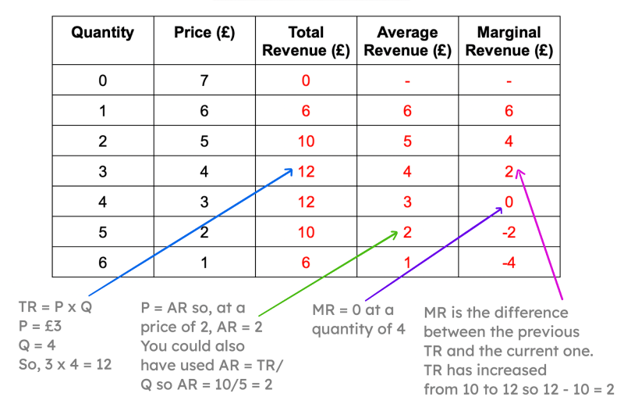
13
New cards
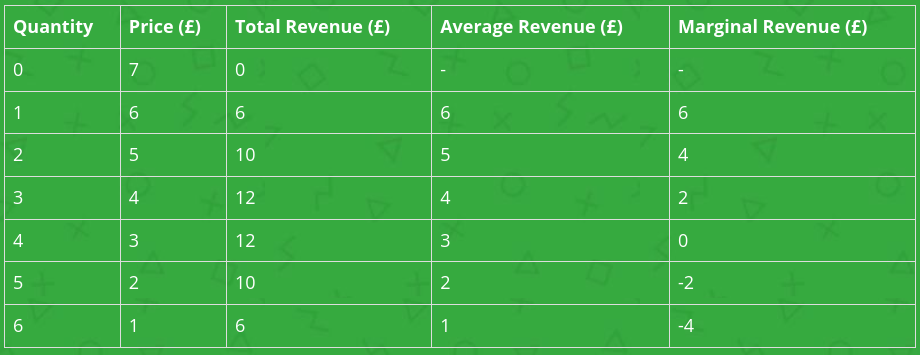
At what level of output will marginal revenue equal zero?
Marginal revenue is the revenue gained from selling one **extra** unit. At a quantity of 3 units, total revenue is 12 and this remains at 12 when one more unit is sold. So at a quantity of 4 units, marginal revenue is 0 (12 -12).
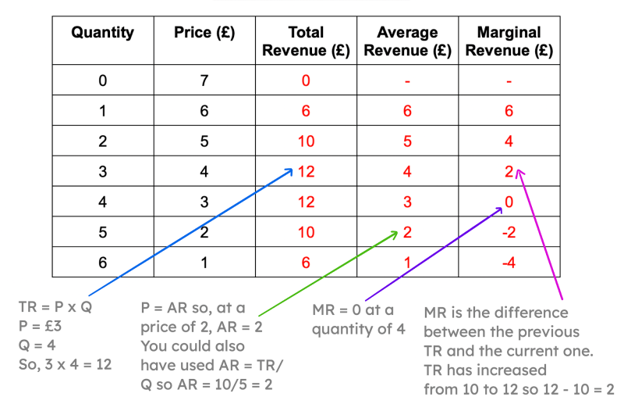
14
New cards
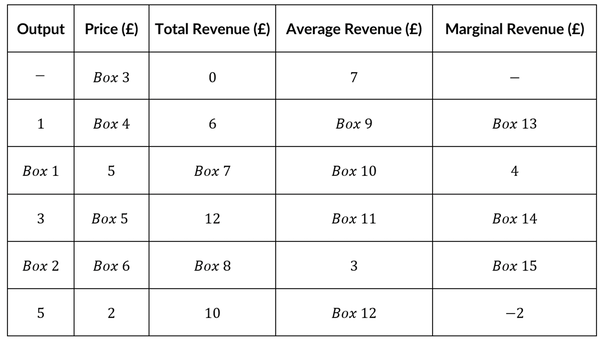
Complete the following table
Model Ans.
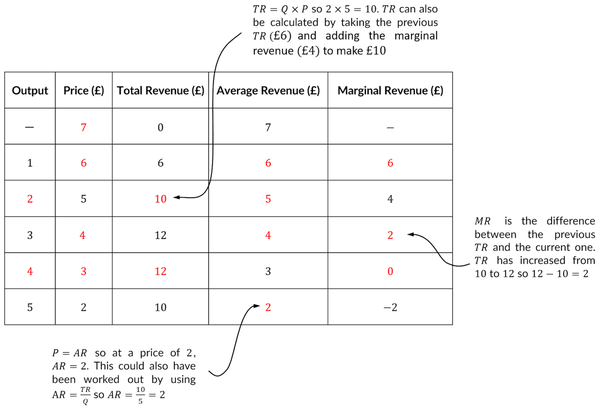
15
New cards
Over what range of output is total revenue increasing?
Model Ans.
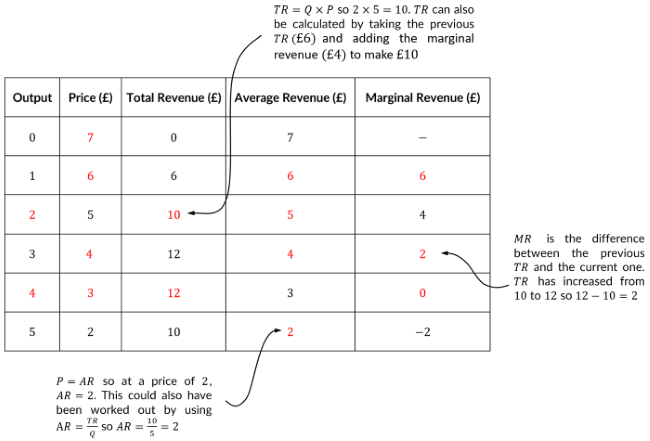
16
New cards
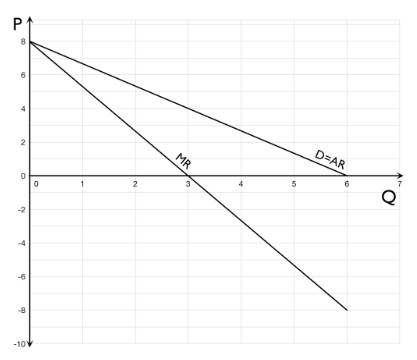
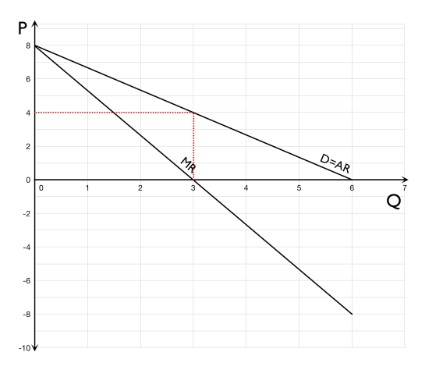
The graph shows the demand and marginal revenue schedules for a company selling books.
What is the price when marginal revenue equals zero?
What is the price when marginal revenue equals zero?
Marginal revenue equals zero at a quantity of 3. To work out price at a quantity of 3 you need to go up to the demand curve and across to the price axis. Price is £4.
17
New cards
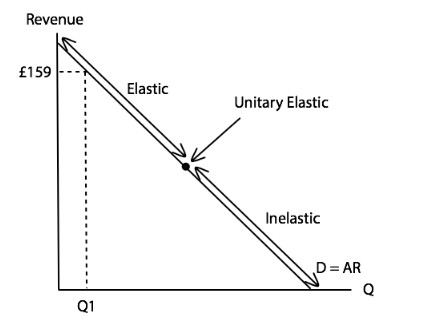
At a high price of £159, is demand for Apple Airpods likely to be elastic or inelastic? Why is this?
A given percentage of a higher price will lead to a larger decrease in the actual price and this will then have a larger impact on demand. And so it is elastic.
18
New cards
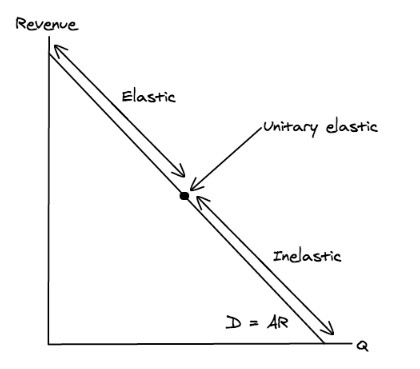
As price decreases, demand will:
As price decreases and quantity increases, demand will go from elastic to unitary elastic to inelastic. So demand will become **more inelastic**.
This is because at low quantities and high prices, a % change in price will have a big impact so demand will be elastic. Whereas at lower prices, a % change in price will have a smaller impact, so demand will be inelastic.
This is because at low quantities and high prices, a % change in price will have a big impact so demand will be elastic. Whereas at lower prices, a % change in price will have a smaller impact, so demand will be inelastic.
19
New cards
If MR is positive, demand will be:
Demand is **elastic** when prices are higher and this is where marginal revenue is **positive**.
20
New cards
Is demand elastic, inelastic or unitary when total revenue is decreasing?
Inelastic
The diagram shows that when total revenue is **increasing**, marginal revenue is **positive** and demand is **elastic**.
The diagram shows that when total revenue is **increasing**, marginal revenue is **positive** and demand is **elastic**.