Zool 110 Lec: Origins of Tetrapods + Amphibians plus some fossils
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Sarcoptyergian fishes
tetrapod relatives are _____
Eusthenopteron
a choanate fish, best known form of sarcopterygian fishes
Ichthyostega and Acanthostega
what are the two known early tetrapods
temnospondyls and anthracosaurs
later fossil tetrapods include _____ and _____
not equal
the origin of tetrapods does ____ the origin of terrestriality
1. phenotypes that no longer exist in nature 2. when groups of organisms appeared and diversified 3. transitional features that help us understand evolution
what three things can fossils tell us
taphonomy
all of the things that happen between an organism's death and it being found as a fossil
1. old localities (looking in the literature and going there) 2. new localities (studying geologic maps)
what are the two ways we find fossils
Tiktaalik roseae
new "missing link" found in 2004, has a neck and wrist
99%
what percent of life that has existed on Earth is now extinct
Lissamphibia
modern amphibians, 3 living amphibian groups, form a monophyletic group
1. Order Anura (frogs and toads) 2. Order Urodela (salamanders) 3. Order Gymnophiona (caecilians)
what are the three orders of living amphibians
class amphibia
lissamphibians and fossil forms that aren't amniotes
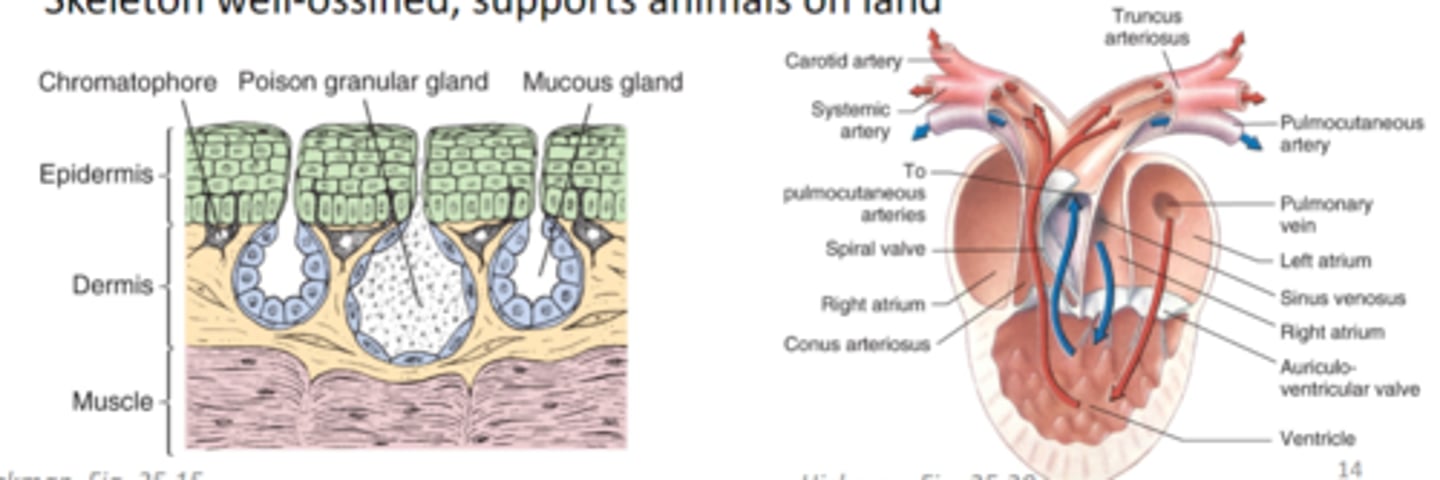
Characteristics of Class Amphibia
cutaneous respiration, poison glands in skin for protection, reproduction often tied to water because of mesolecithal eggs, heart with two atria and one ventricle
Order Urodela (salamanders)
most generalized, over 600 species, reproduce with spermatophores, have aquatic larvae and semiterrestrial adult
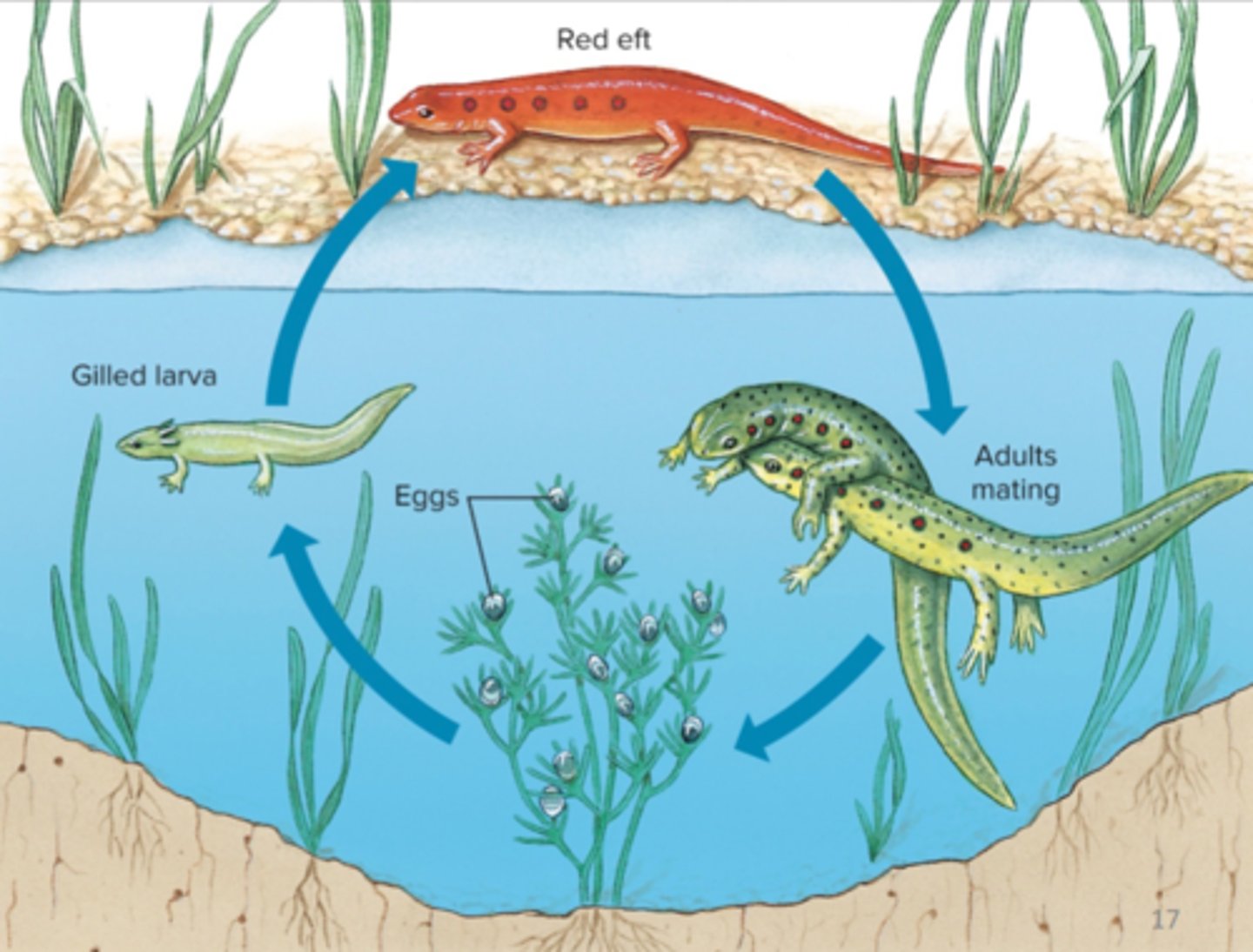
neotenic (paedomorphic)
many species of salamanders are ____ which means they are sexually mature in larval form
direct-developing
salamanders can also be ____ meaning they lay eggs on land in moist places, includes some local plethodontid (lungless) salamanders
Newt life cycle
Order Gymnophiona (Caecilians)
wormlike (burrow and limbless), sensory tentacle in front of rudimentary eye, primitive species with aquation larvae, others direct-developing or live-bearing

to feed on uterine lining or skin of their mother
why do caecilian hatchlings have special teeth
Order Anura (frogs and toads)
found worldwide except artic/antarctic, tail-less as adults, hindlimbs elongated, typically a tadpole larva, well developed sense of hearing, males call (croak) to establish territories and attract females
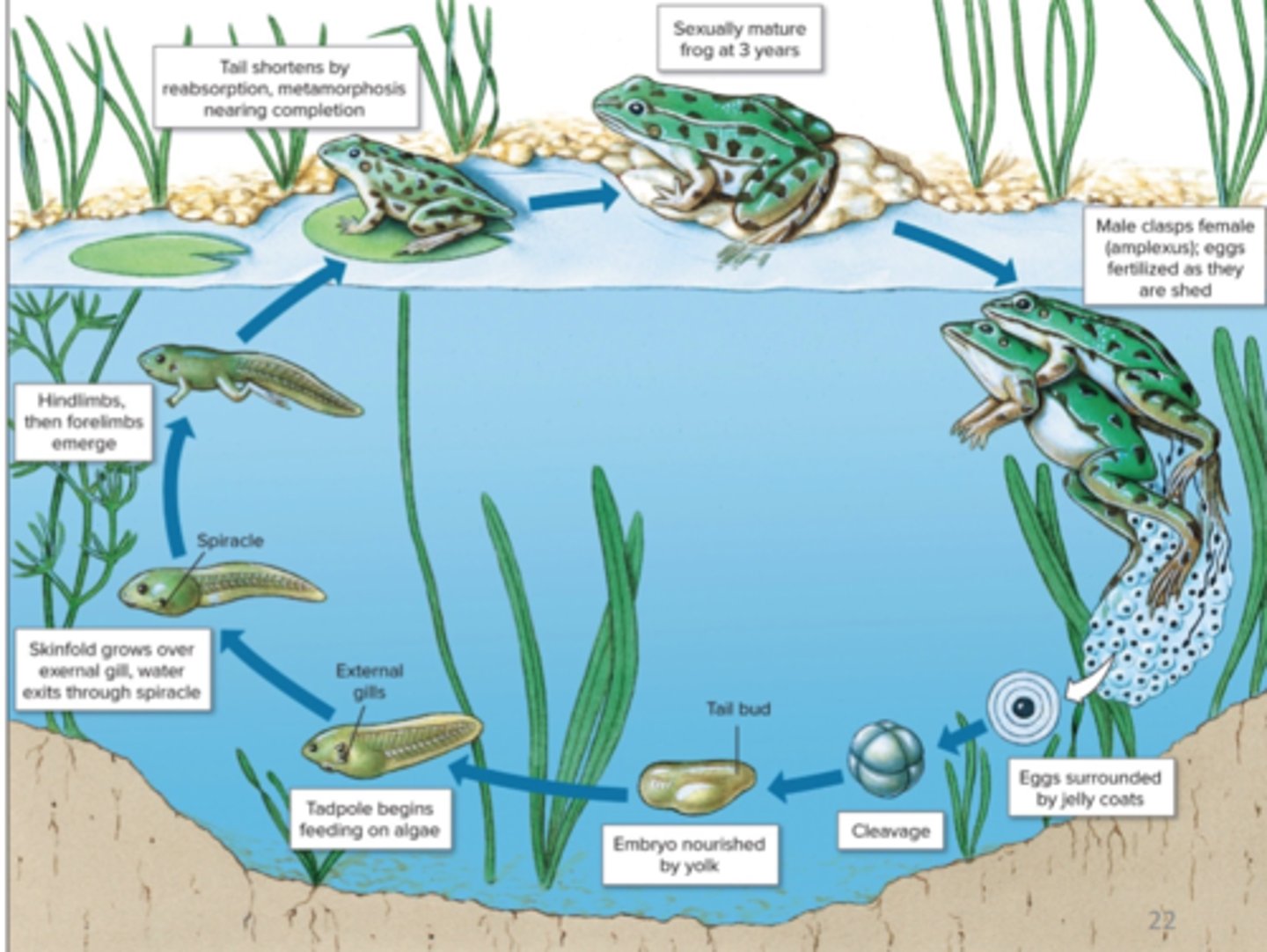
metamorphosis
through what process do tadpoles become terrestrial juveniles
returns to the water and becomes aquatic
in the newt life cycle, the larva metamorphs to a terrestrial form that eventually does what
they have color vision which is rare in most vertebrates
what makes the eyes of frogs special
the stapes
frogs have a good sense of hearing because of what hearing bone
1. dorsal pouch 2. tadpoles adhere to back 3. dorsal brooding pouches 4. mouth brooding
what are the 4 different parental care types of eggs/larvae of anurans (frogs and toads)
frog life cycle
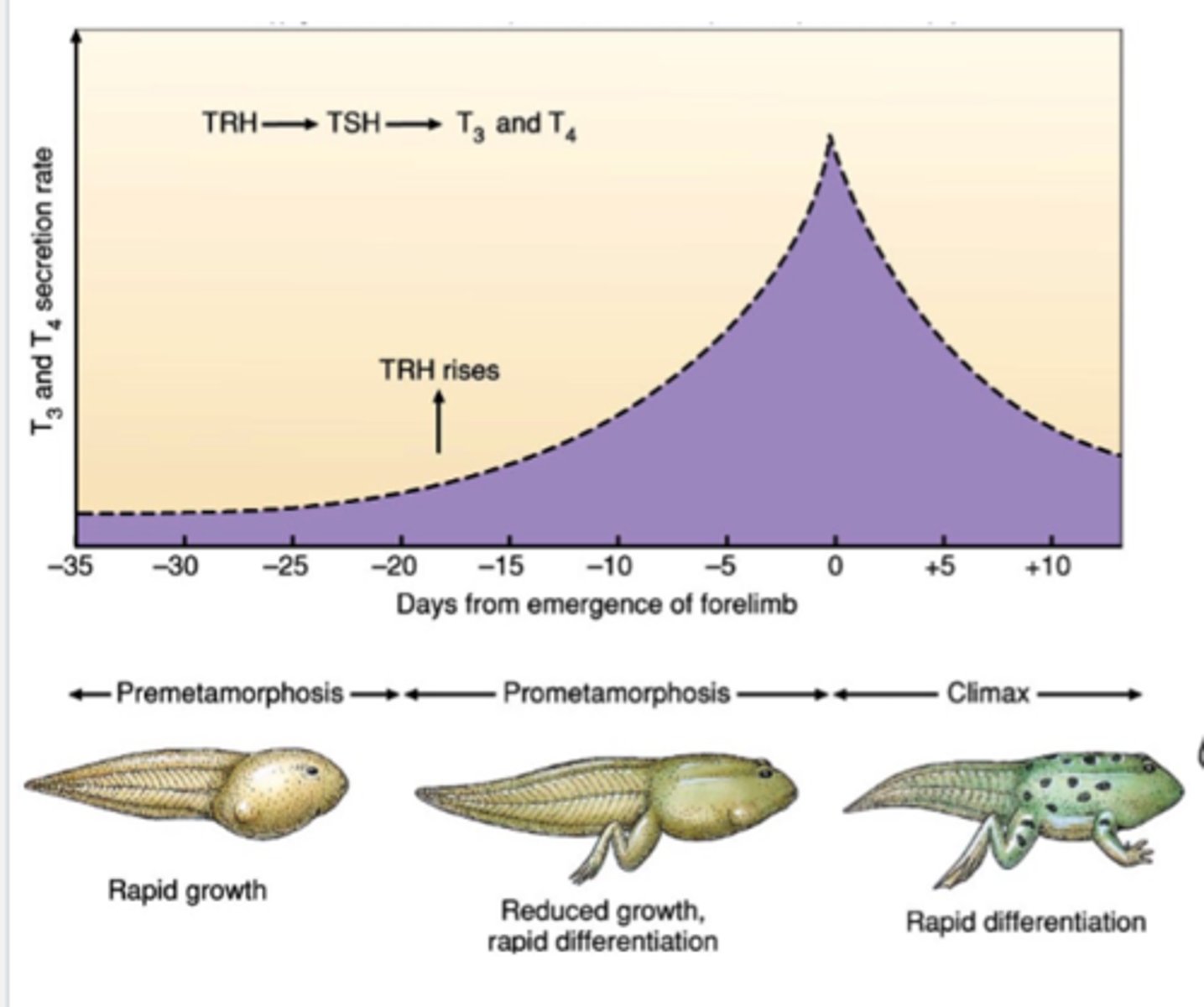
Amphibian metamorphosis
stimulated by thyroid and affects locomotion and all organ systems
they suction feed like fish
how do salamander larvae feed
they scrape algae with keratinized mouthparts
how do frog larvae feed
carnivorous
are adult salamanders and frogs carnivorous or herbivores
they have projectile tongues that can capture prey at a distance
how do adult frogs feed