Chem Unit 4 Vocab
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
-ΔG
spontaneous
+ΔG
non-spontaneous
-ΔS
increasing order
+ΔS
increasing disorder
-ΔH
exothermic
+ΔH
endothermic
open system
transfer matter and energy
closed system
transfer only energy, not matter
isolated system
transfer neither energy nor matter
state functions
enthalpy, entropy, Gibbs free energy, only final minus initial
path functions
path matters, heat and work (q and w)
work
path function, concerted/controlled flow of energy, w
heat
path function, chaotic flow of energy, q
extensive properties
additive, volume, mass, energy, moles
intensive properties
defines system, not additive, temperature, pressure, density
first law off thermodynamics
ΔUuniverse=0 (energy of universe is conserved)
source of all potential/kinetic energy in a system
U (energy)
calorimetry says:
ΔUsurroundings=-ΔUsystem
ΔH=
ΔU+PΔV
in a closed system:
V (volume) is constant, so ΔU=qv
in an open system:
P (pressure) is constant so ΔH=qp
calculating internal energy
ΔU=q+w
“do work” means:
negative work, leaving the system
specific heat
heat needed to raise the temp by 1 degree
specific heat increases with:
size, amount, and IMFs
C of water
4
C of most metals
0.3-0.4
if heat added to two compounds is the same:
m1C1ΔT1=m2C2ΔT2
higher change in temperature means:
lower specific heat
work done for gases:
W=PΔV OR W=-ΔNgRT
positive work
work done on system/by surroundings
negative work
work done by system/on surrounds
equation for warming ( no phase change)
q=mCphaseΔT
equation for solid melting
q=mΔHfus
equation for liquid vaporizing
q=mΔHvap
only time ice and water can exist in equilibrium
0oC
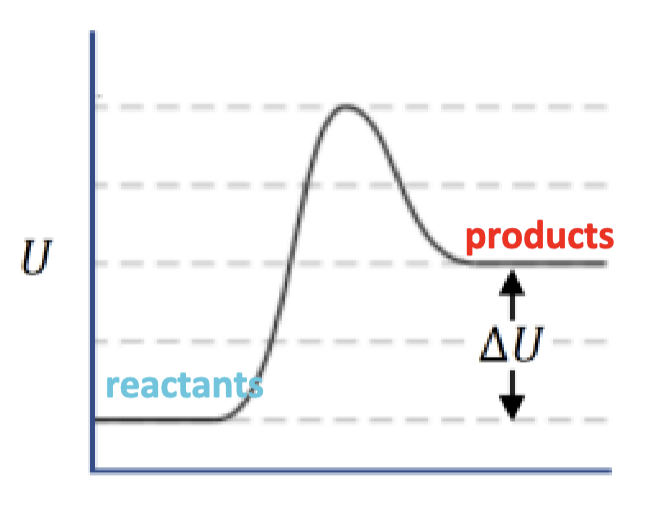
positive net ΔU, endothermic
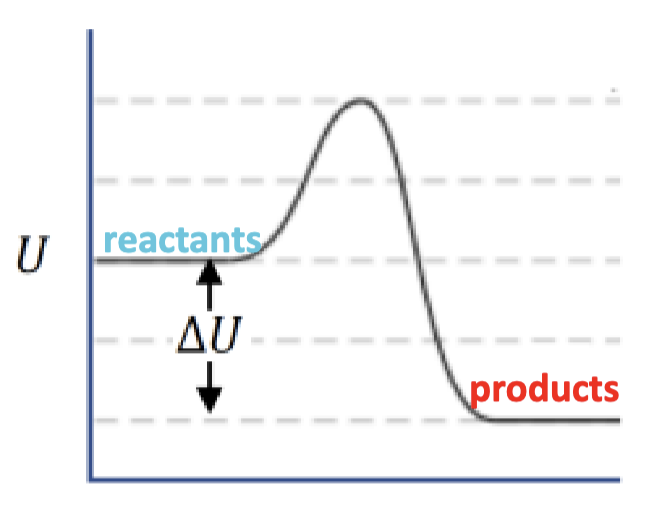
negative net ΔU, exothermic
part of a bomb calorimeter:
insulated container, water inside with submerged sample, thermometer, O2 supply, and ignition box/wires
Bomb calorimetry: igniting the bomb calorimeter…
starts the reaction of the sample
bomb calorimetry: the water serves as…
a heat sink to measure the temperature change
bomb calorimetry: the setup requires…
constant stirring to ensure accurate ΔT
Bomb calorimetry: bomb calorimeters measure…
heat change at a constant volume: ΔU=qv
bomb calorimetry calculation:
q=mCwaterΔT+CcalΔT
for calorimetry, temperature is in…
celcius
heat of formation rules:
produce one mole of a substance
reactants are elements in standard state
under standard conditions, room temp (298K) and at 1 atm, represented by o symbol
number of microstates
number of ways to distribute energy
as number of microstates increases,
disorder/entropy increases
as volume increase,
number of microstates increases
as size/complexity of a molecule increases,
number of microstates increases for trans, vib, and rot. models of motion
if a process happens (spontaneous)…
ΔS of the universe is positive
if a process doesn’t happen
ΔS of the universe is negative
for exothermic processes ΔS of surroundings:
is positive
for endothermic processes ΔS of surroundings:
is negative
things that affect entropy ranking:
phase (most important), size, mixture/pure, ridgidity
how does phase affect entropy?
gas is most, then liquid, then solid
how does size affect entropy?
larger (higher MW) molecules have higher entropy
mixtures are ____ disordered than pure substances
more (so higher entropy)
floppy structures are _____ disordered than ridgid structures
more (so higher entropy)
cyclo-
ring structure, means more ridgid/lower entropy
how does phase change affect entropy?
as you go from solid to liquid to gas, ΔS is positive/entropy and enthalpy increase
other way, ΔS is negative/entropy and enthalpy decrease
how does number of moles affect entropy?
if number of moles increases, entropy is positive
if number of moles decreases, entropy is negative
ΔS of the universe is ______ for spontaneous reactions
positive
for a process to happen, ΔSuniv must…
increase
equation for change in entropy of surroundings:
ΔSsurr=-ΔHsys/T (T in Kelvin)
an exothermic reaction ____ the entropy of the surroundings
increases
an endothermic reaction _____ the entropy of the surroundings
decreases
pay attention to the ___ in ΔH and ΔS:
units
ΔH is typically in kJ
ΔS is typically in J/K
to calculate Gibbs Free Energy you need:
ΔHrxn, ΔSrxn, and T in Kelvin
_____ TΔS by 1000 to convert to joules from kJ
divide
for gibbs free energy, temperature is in:
kelvin
ΔG will typically be very close to:
ΔH (ΔS is usually very small)
when calculating ΔSrxn and ΔHrxn, don’t forget:
to multiple by n
combustion reaction
oxygen and hydrocarbon create carbon dioxide and water
combustion reactions are _____ so ΔH is ____
exothermic, negative
sublimation
going from solid to gas
when going from solid to liquid to gas, ΔS:
is positive
when number of moles ___, ΔS is positive
increases
when temperature _____, ΔS is positive
increases
when molecular size ____, ΔS is positive
increases
at low temp:
ΔG (-), ΔH (-), ΔS (-)
at all temps (always happens)
ΔG (-), ΔH (-), ΔS (+)
at all temps (never happens)
ΔG (+), ΔH (+), ΔS (-)
at high temps
ΔG (-), ΔH (+), ΔS (+)
(+) ΔG ____ happens
never
to calculate the transition temp:
T=ΔH/ΔS
at temperatures below the transition temp, a reaction is:
non spontaneous
at temperatures above the transition temp, a reaction is:
spontaneous
compounds are most stable at standard temp that:
have the lowest/most negative gibbs free energy
if the volume of a system increase, work is done ____ the system
by
when a reaction does not involve a change in gas volume, ___ is similar to ___
ΔU, ΔH
in an open system, ΔH accounts for:
work done against the atmospheric pressure
combustion reactions are ____ so they ____ energy in joules
exothermic, lose
internal energy is a ____ function and _____
state, extensive