Chapter 21: Proton-Motive Force (Creating ATP)
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
ETC and ATP
Protons were pumped into intermembrane space during the ETC. A chemical and charge proton gradient is now established.
Two components of ATP Synthase
F0: embedded in inner mitochondrial membrane
F1: Contains the active sites for ATP and protrudes into matrix
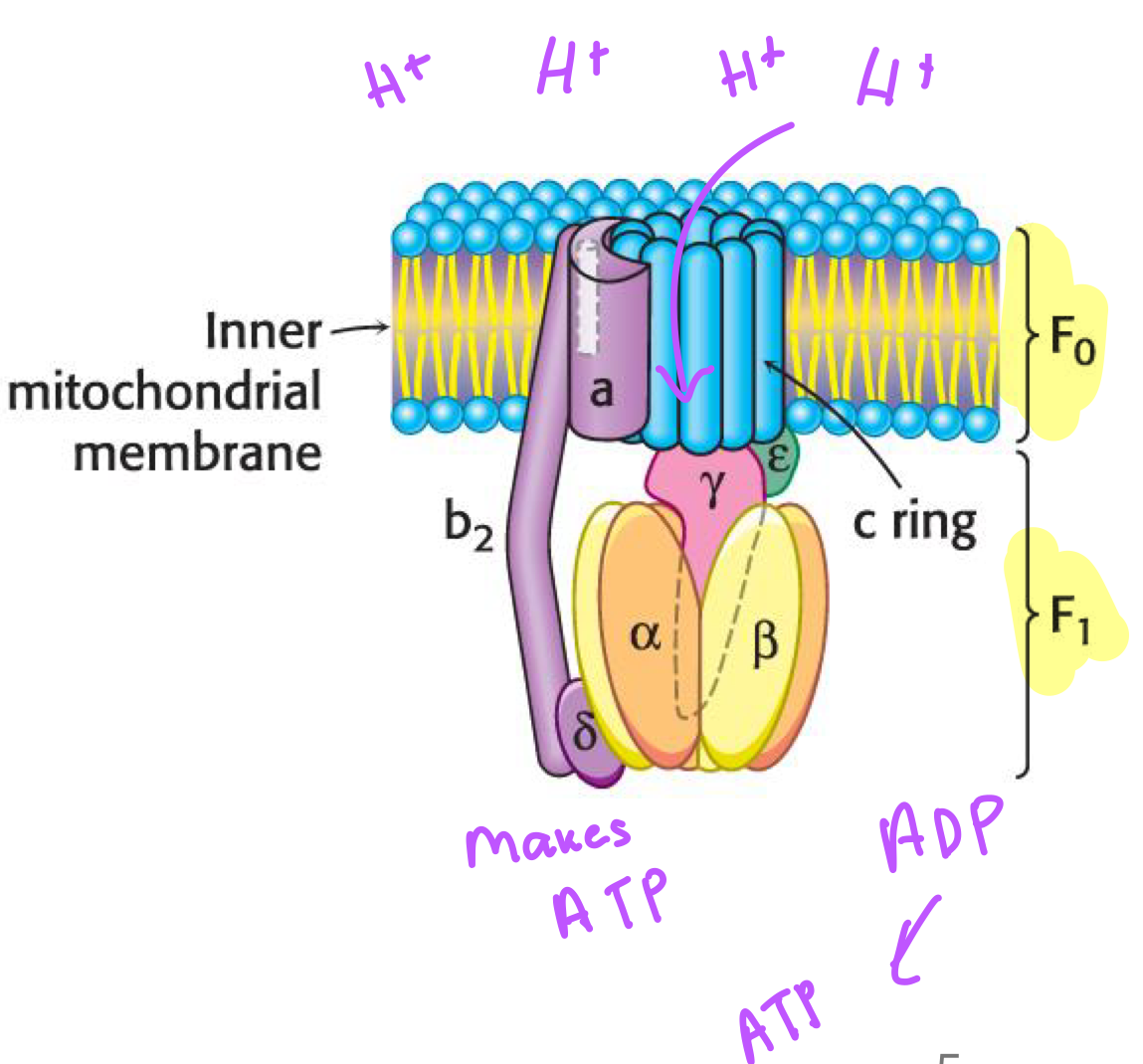
Process of ATP Synthase
F0 channel has two subunits —> Subunit a and c
Protons are pumped through subunit a matrix half-channel
Go through conformation change with subunit C when transfered to an aspartic acid residue
This induces rotation, moving proton to the matrix facing half channel
Pumped out on other half-channel into matrix
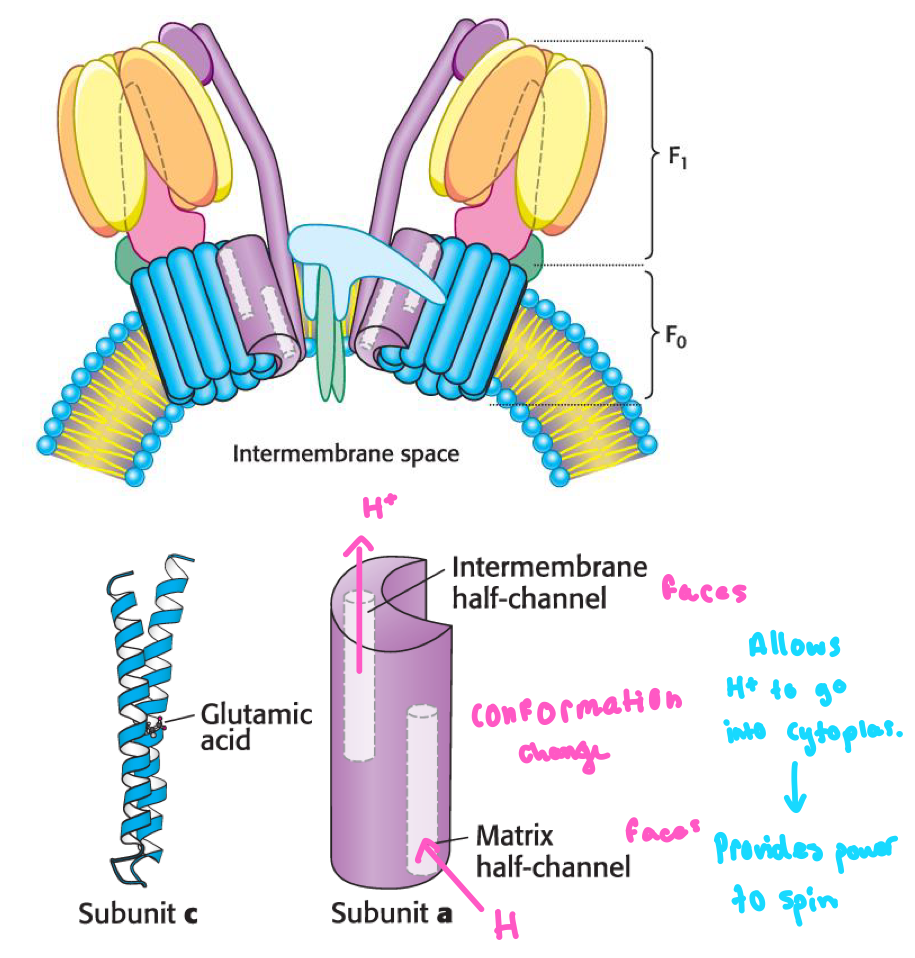
C Subunit Rotation
y and E subunits are connected to C subunit
8 subunits in humans
10 in yeast
Spin rate 100 r/s
F1 Subunit
6 Subunits (3 Beta and 3 Alpha)
Beta contain enzymatic activity (ADP, P1, ATP)
States of Beta Subunits
O: Empty (ADP +P1)
After rotation ATP is released in O state
L: Loose (Bound to ADP and P1)
T: Tight (Bound to ATP)
Conformation of gamma subunit determines active state
Molecules moving through mitochondrial membrane Muscle
NADH able to enter through glycerol phosphate shuttle
Protons move to FAD
Moved to Q
QH2 goes to Q cycle
Creates ATP
Two glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenases
(Cytoplasmic and Mitochondrial)
Molecules move through mitochondrial membrane liver and heart
NADH doesn’t move to FAD and is more efficient
Malate Asparte Shuttle move electrons from NADH in heart and liver
How we get NAD into matrix
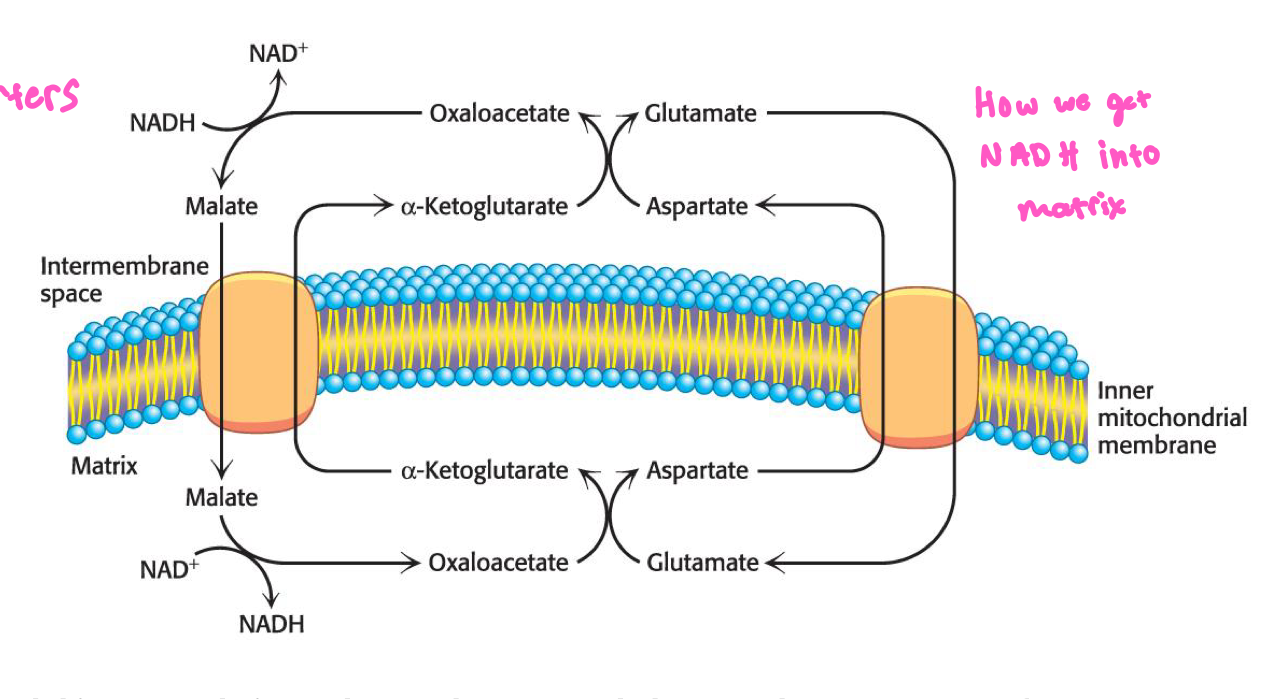
How we get ATP out of matrix into cytosol
one unit in one unit out (ATP and ADP)
ADP goes to matrix ATP goes to cytoplasm
Regulation of Oxidative Phosphorylation by ADP
Acceptor or respiratory control
We have a lot of ATP, slow down enzymes and store pyruvate in fat stroage
Inhibitors and Uncouplers of Metabolism
2-4 Dinitrophenol
Uncouples UCP-1
Allows protons to pump out and does not create ATP in inner membrane
Heat is generated instead
Also form of weight loss drug