Intro to Gastrointestinal System
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Hiatal hernia
Heartburn sx and reduced breath sounds to lung with “gurgling”
Intake, breakdown, absorption, clearance
GI System goal is
A) __ of food
B) __ of food
C) __ of water and nutrients of food
D) __ of waste products
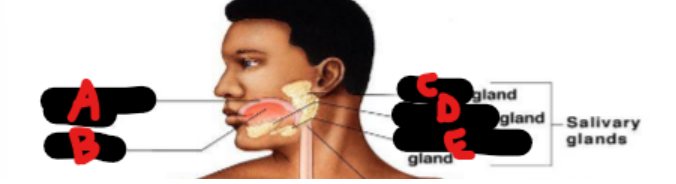
Mouth, tongue, parotid, sublingual, submandibular
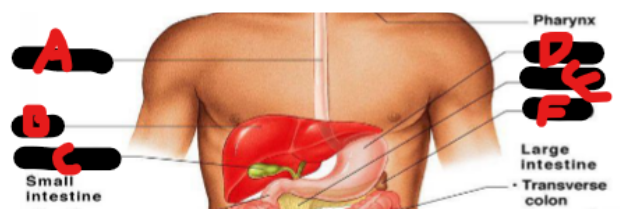
Esophagus, liver, gallbladder, stomach, pancreas, spleen
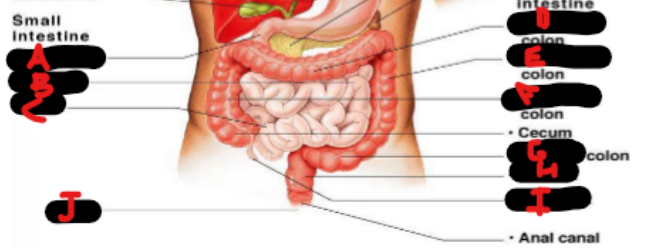
Duodenum, jejunum, ileum, transverse colon, descending colon, ascending colon, cecum, sigmoid colon, rectum, appendix
Sphincters
Circular muscle rings with resting tone normally closed until detecting signal to relax
Chyme
Sphincters
Regulate directional movement of __ through GI tract
Upper esophageal sphincter
GI muscle between pharynx and larynx
Lower esophageal sphincter
GI muscle between esophagus and stomach
Hiatus, closed, reflux
Lower esophageal sphincter
Combines with __ to keep esophagus “__” at baseline
Prevents __ of GI contents
Pyloric sphincter
GI muscle between stomach and small bowel
Ileocecal sphincter
GI muscle between small bowel and colon
Internal anal sphincter
GI muscle between rectum and anus, with involuntary smooth muscle
External anal sphincter
GI muscle between rectum and anus with voluntary skeletal muscle
Proteins, glucose, metabolism, excretion, bile
Roles of Liver
Production of __ (i.e. albumin, clotting/anti-clotting factors)
__ management
__ of substances
waste __
__ production
Gallbladder
Region of bile storage and can become inflamed
Digestive, glucose, inflammation, obstruction
Roles of Pancreas
Secretes __ enzymes into GI tract
__ management
Prone to ___, tract __, cancer, diabetes
Large pancreatic head tumor, stone in common bile duct, and sphincter of oddi stenosis
Which are the 3 common causes of bile “backing up” into liver and jaundice?
Choledocholithiasis
Stone in common bile duct
Myenteric plexus
Neurological structure responsible for intrinsic regulation of GI muscle contractions
myenteric plexus
From epithelia
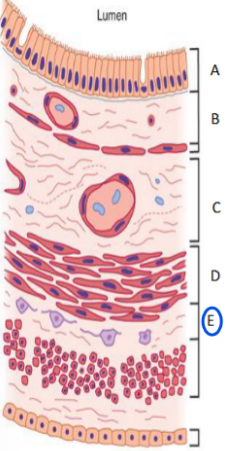
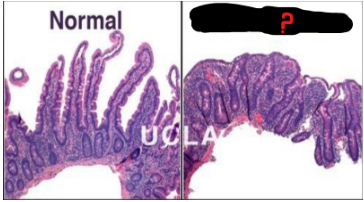
Stretch out, volumes, surface area
Why does stomach have lots of folds?
Easier to __ __ and expand __ after eating/drinking
Why does small intestine have villi and crypts?
Increased __ __ → Increased absorption
Absorption, osms, diarrhea, malnutrition, celiac
What happens if villi atrophy or are blunted?
Decreased surface area = Decreased __
Extra __ in GI tract lead to __ and __ (sx)
Ex: Excess gluten consumption from a __ disease patient
Celiac disease
Enteric nervous system
Coordinated relaxation and contraction to mix and move chyme through GI tract via reflexes
Emesis
Action of __ moves chyme from GI tract back out of mouth
Oral phase
Tongue pushes bolus into pharynx
Stretch receptor signal to medulla and initiate reflex
(swallowing phases)
Pharyngeal phase
Soft palate raised, epiglottis covers airway
UES relaxes, Peristaltic wave in pharynx
(swallowing phases)
Esophageal phase
Peristaltic wave moves bolus through esophagus
LES relaxes
(swallowing phases)
Achalasia
Dysfunction of myenteric nerve plexus in esophagus and LES
Idiopathic, Chagas, relax
Achalasia
__pathic and associated with __ disease
Lack of signal to __ from the plexus
Segmentation, peristalsis
__ is the act of mixing chyme
__ is the act of moving chyme from stomach to small bowel
Vomiting
Anti-peristalsis where small bowel contents travel back up stomach
Breath, UES, glottis, posterior nares, abdominal, LES
Vomiting Steps
(1) Taking a deep __
(2) larynx raises and opens the __
(3) __ closes to protect lungs
(4) Soft palate raises to close the __ __
(5) Diaphragm further contracts and __ muscles contract to squeeze stomach
(6) __ relaxes = Vomitus expelled
Ileus
Post-traumatic inflammation of ileum, often from abdominal surgery
Stunned, sympathetic, peptides, diabetic neuropathy
In ileus
“__ bowels”
Increase in inhibitory __ stimulation and inhibitory __
Gastroparesis = Can result from __ __ (neuro pathology)
GERD
Pressure in stomach greater than pressure of LES
Pyloric stenosis
Obstruction with non-bilious emesis of partially digested food
Nausea
Conscious recognition of excitation in medulla near/in vomiting center
Medulla, chemical, distension, vestibular, histamine, chemoreceptor trigger, cerebral inputs
Nausea caused by input to vomiting center in the __ (brain)
Impulses from GI tract - __ irritation or __
Motion sickness - __ system muscarinic and __ Rs
Direct stimulation of __ __ zone by opioids, chemo drugs, 5-HT
__ __ - sight, sounds, smells, thoughts