Microbiology Chapter 5; Eukaryotes
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What are protists?
A polyphyletic group, used to categorize diverse eukaryotic microorganisms within the domain Eukarya.
Can be unicellular, multicellular, photosynthetic, etc.
What are Protozoa?
A class of Protists that are;
Nonphotosynthetic
Motile
Unicellular
Often parasitic
What is a protozoan called during feeding and growth life cycle?
A Trophozoite.
Feed on bacteria.
What can some trophozoites develop into? Why?
Encapsulated cysts, when the environmental conditions are too harsh.
What organelles do protists contain?
Contractile vacuoles; move water in and out.
Pellicles; protein bands that aid in rigidity.
Pseudopodia; anchoring lobes
Cilia; hair-like for locomotion
What does it mean for protozoans to be heterotrophic?
They consume other organisms/matter for nutrients.
Holozoic protozoans ingest whole particles.
Saprozoic protozoans ingest small soluble ones.
What Eukaryotic supergroups contain protozoans?
Amoebozoa — contain amoeboids for movement.
Chromalveolata — infect livestock, insects, humans.
Toxoplasma gondii — transmitted via cat feces, unwashed produce and undercooked meat.
Excavata — parasites, sexual transmitted diseases.
Trichomonas Vaginalis.
What does Giardia spp. cause?
Diarrhea.
What are parasitic helminths?
They are parasitic worms with microscopic eggs and larvae.
What are the two types of parasitic helminths?
Roundworms (Nematoda)
Flatworms (Platyhelminths).
What does it mean to be monoecious?
To have both female and male reproductive organs in a single organism.
What does it mean to be dioecious?
To have either female or male reproductive systems.
Are parasitic helminths mono or dioecious?
They can be both.
What are the characteristics of Nematodes?
Roundworms.
Unsegmented worms, with full digestive system.
Eggs often found in feces or around the anus.
Cause abdominal pain, cramps, vomiting.
Intestinal parasites transmitted by undercooked foods.
Ascaris Lumbricoides; largest nematode in humans.
Pinworm; most common, itchy bum.
What are the characteristics of Platyhelminths?
Flatworms; flukes, tapeworms, turbellarians.
Flukes/trematodes; nonsegmented with an oral sucker.
Tapeworms/cestodes; segmented with hooks.
What are fungi?
A eukaryotic group with chitinous cell walls.
Can be uni or multicellular.
Can be microscopic (yeast and spores) or large (molds and mushrooms).
Are heterotrophic saprozoic.
What is mycoses?
An illness caused by pathogenic fungi.
What are multicellular fungi called? Made of?
They are called molds, and are made of filaments called hyphae.
What is septate hyphae?
Hyphae filaments that have walls between cells.
What is non septate/coenocytic hyphae?
Hyphae that lack walls and membranes between cells.
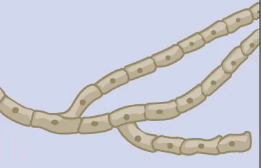
What is this?
Septate Hyphae.
What is this?
Coenocytic Hyphae.
What are unicellular fungi called?
Yeasts.
How do yeasts reproduce?
Yeasts reproduce asexually by budding off a small daughter cell.
If the daughter cells stick together it is termed pseudohyphae.
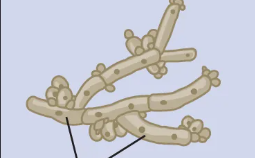
What is this called?
Pseudohyphae
What are the medically significant groups of fungi?
Zygomycota
Ascomycota
Basidiomycota
Microsporidia
The mycota’s and sporidia.
What is unique to the members of “mycota” fungal groups?
They produce deadly toxins.
What can antifungals target?
Ergosterols in fungal membranes.
***Cautiously because of the similarities between fungi and human cells.
Often have toxic adverse effects.
What is an exmaple of a photosynthetic microorganism?
Algae.
WHat causes malaria?
Plasmodium, a protozoan genus.
What is the common cause of yeast infectinos?
The Candida spp.