Chapter 20 (Induction of Labour)
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Assisted Birth Procedures lecture review.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Preterm Labour
Cervical changes and regular uterine contractions occuring between 20 and 37 weeks of pregnancy
Preterm birth
Any birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Can be caused by preterm labour with intact membrane, preterm PROM, Cervical insufficiency of amnionitis
Intrauterine growth restriction
A condition of inadequate fetal growth
Spontaneous preterm birth
Occurs after an early initiation of the labour process
Indicated Preterm birth
Occur as a means to resolve maternal or fetal risk related to continuing the pregnancy
Spontaneous preterm labour risk factors
•History of previous spontaneous preterm birth between 16 and 36 weeks of
gestation
• Family history of preterm labour
• African descent
• Genital tract infection
• Uterine anomaly
• Use of assisted human reproduction
• Cigarette smoking, substance misuse
• Periodontal disease
• Multifetal gestation
• Bleeding of uncertain origin in pregnancy
• Low prepregnancy weight
• Low socioeconomic status
• Lack of access to prenatal care
• High levels of personal stress in one or more domains of life
Predicting Preterm labour
Fetal fibronectin test
Cervical Length
Signs and Symptoms of Preterm Labour
Uterine Activity
• Uterine contractions more frequent than every 10 minutes, persisting for
1 hour or more
• Uterine contractions painful or painless
Discomfort
• Lower abdominal cramping similar to gas pains; may be accompanied by
diarrhea
• Dull, intermittent low back pain (below the waist)
• Painful, menstrual-like cramps
• Suprapubic pain or pressure
• Pelvic pressure or heaviness; feeling that “baby is pushing down”
• Urinary frequency
Vaginal Discharge
• Change in character and amount of usual discharge: thicker (mucoid) or thinner
(watery), bloody, brown or colourless, increased amount, odour
• Rupture of amniotic membranes
Tocolytics
Medications given to arrest labour after uterine contractions and cervical changes have occured.
First choice is Nifedipine( a calcium channel blocker) that can supress contractions.
Indomethacin (An NSAID) blocks the production of prostaglandins
Magnesium Sulphate Inhibits uterine contraction and decreases intracellular calcium levels
Magnesium Sulphate
Administered to reduce or prevent newborn neurological morbidity(e.g Cerebral palsy).
Given to patients who are at least 24weeks but less than or equal to 33+6 weeks of gestation.
Preterm Premature Rupture of the Membrane
Spontaneuos rupture of the amniotic sac and leakage of amniotic fluid beginning before the onset of labour.
Most likely results from pathological weakening of the amniotic membranes, caused by inflammation, stress from uterine contractions, or other factors that cause increased intrauterine pressure.
Infection of the urogenital tract is a major risk factor associated with it
Chorioamnionitis
It is the bacterial infection of the amniotic cavity
The most common maternal complication of preterm PROM, making it a major complication of pregnancy
Diagnosis of Chorioamnionitis
Clinical findings of maternal fever
Maternal and fetal tachycardia
Uterine tenderness, and
Foul odour of amniotic fluid
Antibiotics for Chorioamnionitis
Broad spectrum IV antibiotics
Ampicillin, Penicillin, Gentamycin
Post Term Pregnancy
is one that extends beyond the end of week 42 of gestation, or more than 294 days from the first day of the last menstrual period
Postterm Risks
Labour dystocia
Severe perineal injuries
Chorioamnionitis
Endomyometritis,
Postpartum hemorrhage, and
Caesarean birth
Macrosomia
Occurs when the placenta continues to provide adequate nutrients to support fetal growth after 40 weeks of gestation.
Dystocia
defined as abnormally slow progress of labour; it is caused by various conditions related to the five P’s of labour
defined as greater than 4 hours of less than 0.5 cm per hour of cervical dilation in active labour or greater than 1 hour of active pushing with no descent of the presenting part and is a common reason for Caesarean birth
Precipitous Labour
Labour that lasts less than 3 hours from the onset of contractions to the time of birth.
May result from hypertonic uterine contractions that are tetanic in intensity.
Version
The turning of the fetus from one presentation to another.
It may be performed externally or internally by the obstetrical health
care provider.
External Cephalic Version
Used in an attempt to turn the fetus from a breech or shoulder presentation to a vertex presentation for birth. It may be attempted in a labour and birth
setting at 36 to 37 weeks of gestation.
ECV is accomplished by the exertion of gentle, constant pressure on the abdomen. At this gestational age, the success rate for ECV is approximately 65% and the risk for Caesarean birth is reduced by 50%
During procedure monitor for:
Fetal heart rate and pattern, especially for bradycardia and variable decelerations
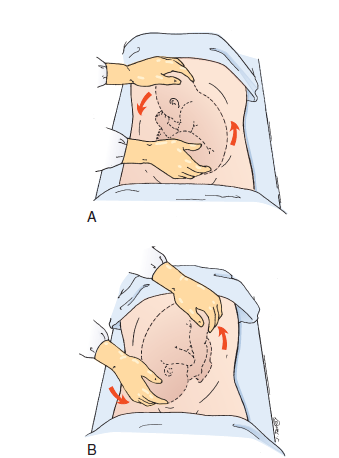
Contraindications to ECV
•Contraindication to labour or vaginal birth
• Uterine anomalies
• Placenta previa or placental abruption
• Multiple gestation
• Oligohydramnios
• Evidence of uteroplacental insufficiency
• A nuchal cord (identified by ultrasound)
• Obvious CPD
Internal Version
The fetus is turned by the health care provider, who inserts a hand into the uterus and changes the presentation to cephalic or podalic.
It is rarely used, although it is most often used in twin gestations to assist with birth of the second fetus.
The safety of this procedure has not been documented; maternal and fetal injuries are possible.
Induction of Labour
The chemical or mechanical initiation of uterine contractions before their spontaneous onset for the purpose of bringing
about the birth.
Most common ways to induce labour
IV Oxytocin
Amniotomy
Most important predictor of Sucessful Induction
Cervical ripening
With Bishop score of 7 or more induction is usually successful
Cervical Ripening agents
Preparations of Prostaglandins
PGE1 (Misoprostol): ripen the cervix before oxytocin induction of labour when the Bishop score is 4 or less
PGE2 (Dinoprostone): Ripen the cervix before oxytocin induction when Bishop score is 6 or less
Augmentation
The process of accelerating spontaneous labor.
Usually implemented for the management of hypotonic uterine dysfunction resulting in a slowing of labour
Indications for Induction
Post maturity of fetus
PROM( Can be caused by chorioamnionitis)
Intrauterine growth restriction
Maternal conditions
Uncomplicated twins
History of intrauterine fetal demise
Cord Prolapse
Occurs when the umbilical cord drops through the open cervix into the vagina ahead of the baby.
Cephalo-Pelvic Disproportion (CPD)
When a baby's head is too large to fit through the mother's pelvis.
Placenta Previa
When the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
Classical Uterine Incision
An incision made vertically in the upper part of the uterus during a cesarean section.
Unripe Cervix
A cervix that is not soft, thin, or dilated, indicating it's not ready for labor.
Tachysystole
Excessively frequent uterine contractions during labor.
Bishop Score
A pre-labor scoring system to assist in predicting whether induction of labor will be successful.
Biophysical Profile (BPP)
A prenatal test used to check on a baby's well-being. It combines fetal heart rate monitoring (nonstress test) and fetal ultrasound to evaluate a baby's heart rate, breathing, movements, muscle tone, and amniotic fluid level.
Fetal breathing movements
Assessment of whether the fetus is practicing breathing movements, which is a sign of well-being.
NST
Non-Stress Test, fetal heart rate monitoring to assess fetal well being.
AROM
Artificial Rupture Of Membranes, also known as amniotomy.
Patient temperatue should be checked at least every two hours after ROM and more frequently if there are signs of infection
Oxytocin
Hormone normally produced by the posterior pituitary gland.
It stimulates uterine contractions and aids in milk letdown.
Caution for Oxytocin Use
•Multifetal presentation
• Breech presentation
• Presenting part above the pelvic inlet
• Atypical fetal heart rate and pattern not requiring emergency birth
• Polyhydramnios
• Grand multiparity
• Previous Caesarean birth
• Maternal cardiac disease; hypertension
Contraindication for Oxytocin use
•Cephalopelvic disproportion, prolapsed cord, transverse lie
• Abnormal fetal heart rate
• Placenta previa or vasa previa
• Prior classic uterine incision or other uterine surgery
• Active genital herpes infection
• Invasive cancer of the cervix
• Previous uterine rupture
Foley Catheters
A mechanical dilator used to ripen the cervix.
Laminaria Tents
Mechanical dilators made from seaweed, used to ripen the cervix.
Operative Vaginal Delivery (OVD)
Delivery of a baby using instruments such as forceps or vacuum extractor.
Forceps-assisted Birth
A delivery method using forceps to guide the baby's head out of the birth canal.
Vacuum-assisted Birth
A delivery method using a vacuum cup attached to the baby's head to assist in delivery.
Caput Succedaneum
Swelling of the scalp in a newborn, typically resolves within 24 hours.
Cephalhematoma
A collection of blood between a baby's scalp and skull, typically resolves in 3 to 6 weeks.
Caesarean Birth
Delivery of a baby through an incision in the mother's abdomen and uterus.
Uterine Rupture
The symptomatic disruption and separation of the layers of the uterus or previous scar.
Can result in the ejection of fetal parts or the entire fetus into the peritoneal cavity.
Major risk factor is a scarred uterus as a result of previous Caesarean birth or other uterine surgery
Amniotic Fluid Embolism
Rare but devastating complication of pregnancy characterized by the sudden, acute onset of hypoxia, hypotension, cardiovascular collapse, and coagulopathy.
Occurs during labour, during birth, or within 30 minutes after
birth.
A foreign substance is introduced into the circulation, resulting in disseminated intravascular coagulation, hypotension, and hypoxia