Diversification vs Specialization + Integration vs Outsourcing
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is growth in strategy?
Development of a company’s strategic business activities (SBAs).
What is the goal of corporate strategy?
To maximize the company's overall value by selecting the SBAs in which to invest and grow.
What is synergy?
When two or more SBAs (strategic business areas) generate more value together than separately.
What are the three main growth modes?
Internal growth, external growth, alliances.
What are the main growth paths?
Diversification vs specialization
Integration vs outsourcing
Internationalization
What internal efficiency gains can growth generate?
Lower production costs
Lower commercial costs
Lower management costs
What market power benefits can growth generate?
Lower supply costs, Lower financing costs
What other advantages can growth bring?
Risk reduction
Increased differentiation
Increased prestige for managers
Motivation internally
Positive signal to markets
What are the main limits to growth?
Financing constraints
Loss of control
Regulatory constraints
Organizational complexity
Dispersion of resources
High cost of learning new businesses
Costs can increase after a threshold
What types of synergies exist?
Product synergies
Technology synergies
Market synergies
What benefits can synergies provide?
Lower costs
Improved differentiation
Lower cost of differentiation
What are the risks of synergies?
Hard to evaluate ex-ante
Difficult to implement
Implementation costs
What is specialization?
Maintaining a single SBA without adding new skills.
Advantages of specialization?
Efficiency
Critical size
Good visibility (capital markets)
Disadvantages of specialization?
High risks
Dependence on one market
May require refocusing
What is diversification?
Strategy of developing new SBAs, requiring new skills.
Reasons to diversify?
Face new competitors
Develop new skills
Mobilize new resources
What is refocusing?
Reducing the number of activities to improve consistency.
What are the main types of diversification?
Market-driven (same products, new customers)
Product-related (new products, same customers)
Unrelated diversification (new products + new customers; no synergies)
What benefits does diversification bring?
Growth in mature markets
Risk reduction
Synergies & savings
Satisfying manager ambition
What are the disadvantages of diversification?
Strategic heterogeneity
Failure to reach critical size
Coordination costs
Conglomerate discount
What are the four diversification motivations?
Diversification of investment
Diversification of reinforcement
Diversification of redeployment
Diversification of survival
(Depends on attractiveness & competitive position)
What is the purpose of portfolio matrices?
To evaluate SBA coherence and guide investment decisions.
What are the two axes of portfolio matrices?
Competitive position
Environmental attractiveness
What are the typical strategic outcomes?
Invest / maintain
Selective investment
Maintain and “milk”
Divest
What are the four categories of the BCG matrix?
Stars (High RMS→ Relative Market Share, High growth)
Cash Cows (High RMS, Low growth)
Question Marks (Low RMS, High growth)
Dogs (Low RMS, Low growth)
What is the strategic action for Cash Cows?
Limit investments and use cash flow to fund other SBAs.
What is the strategic action for Question Marks?
Invest heavily or divest.
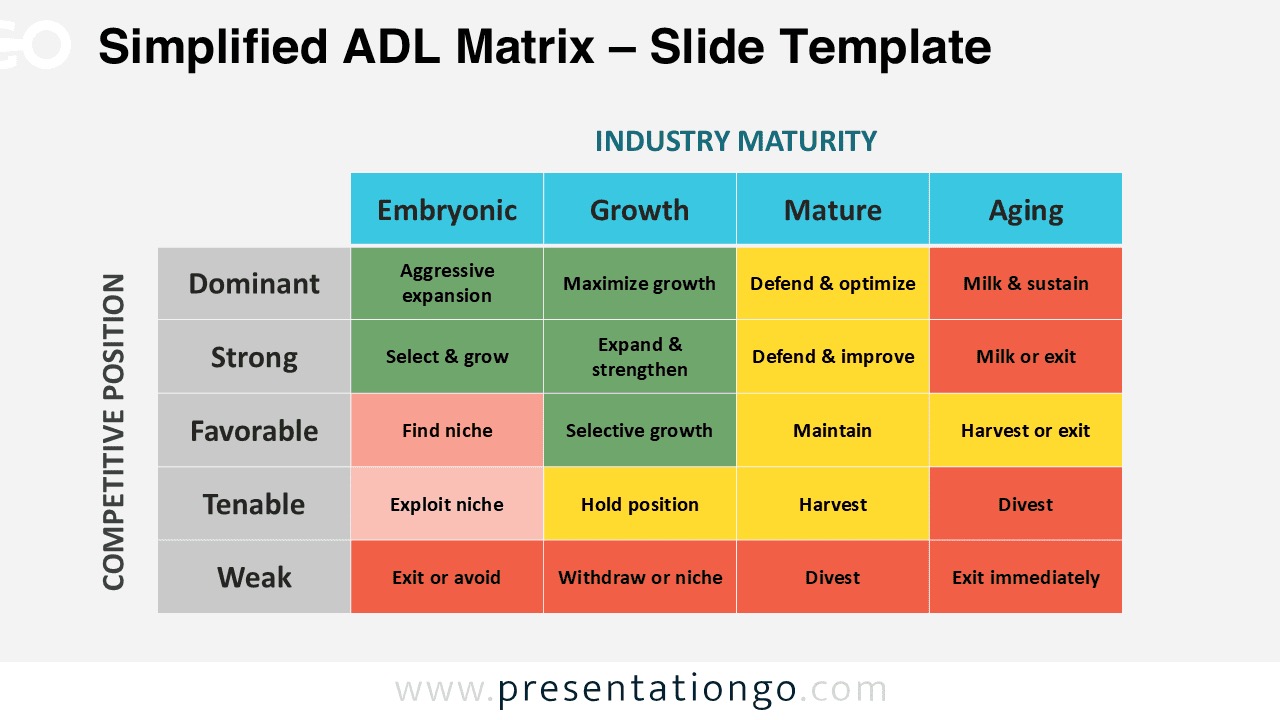
What dimensions does the ADL (Strategic Condition Matrix) matrix use?
Business maturity
Competitive position
What are its strategy categories?
Winning activities (maintain)
Dilemma activities (select)
Losing activities (withdraw)
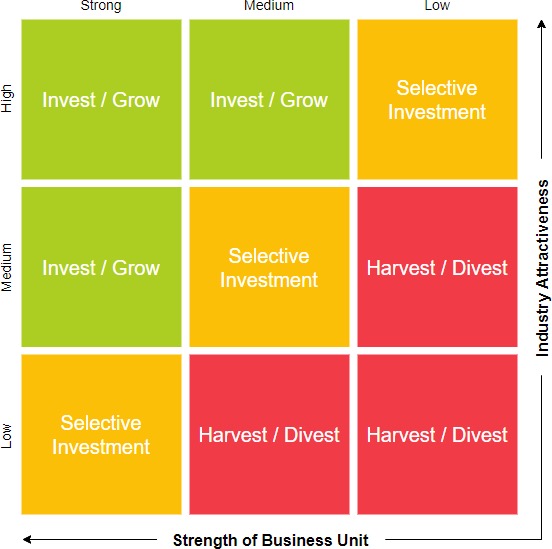
What dimensions does the McKinsey matrix analyze?
Business attractiveness
Competitive strength
Possible strategic recommendations?
Invest strongly
Hold position
Selective investment
Milk
Withdraw
What is vertical integration?
Taking over upstream or downstream activities in the value chain.
Upstream integration?
Securing supply sources, controlling processes.
Downstream integration?
Controlling distribution, improving differentiation, securing outlets.
Benefits of vertical integration?
Control over value-creating activities
Access to scarce resources
Secure supply & outlets
Reduced uncertainty
Lower transaction costs
Reduced competitive pressure
Financial benefits
Control areas of differentiation
What are the limits of integration?
Similar to diversification risks
May undermine core competencies
Risk of strategic autarky
High fixed investments
Reduced flexibility
Higher complexity
What is outsourcing?
Transferring previously internal tasks to external, legally autonomous partners.
What forms can outsourcing take?
Subcontracting
Outsourcing
Impartition
Key benefits of outsourcing?
Focus on core competencies
Lower capital investment
Flexibility
Lower procurement costs
Economies of scale
Demand risk reduction
Access to suppliers’ innovation
What are the main risks of outsourcing?
Dependency on suppliers
Loss of know-how
Loss of confidentiality
Loss of strategic capabilities
Fragility due to focus
Monitoring/control costs
Social cost (worker exploitation)
Environmental issues
What variables influence the choice between integration and outsourcing?
Impact on competitive advantage
Risk type & level
Transaction frequency
Specific investments
Financial capacity
The BCG Matrix

The ADL matrix
The McKinsey Matrix