Patient Assessment 2: GI + GU OSCE
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
xiphoid process
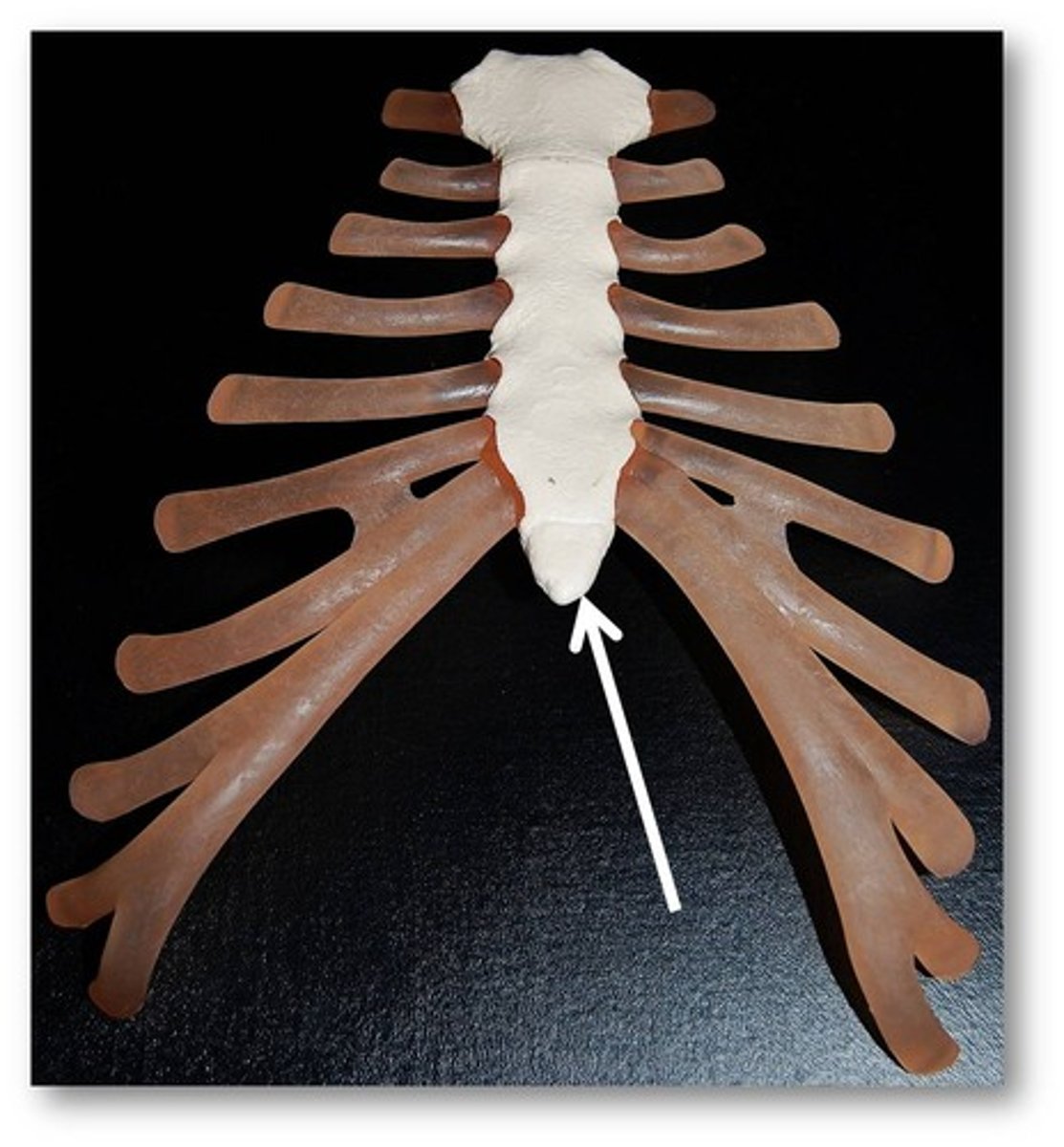
costal margin
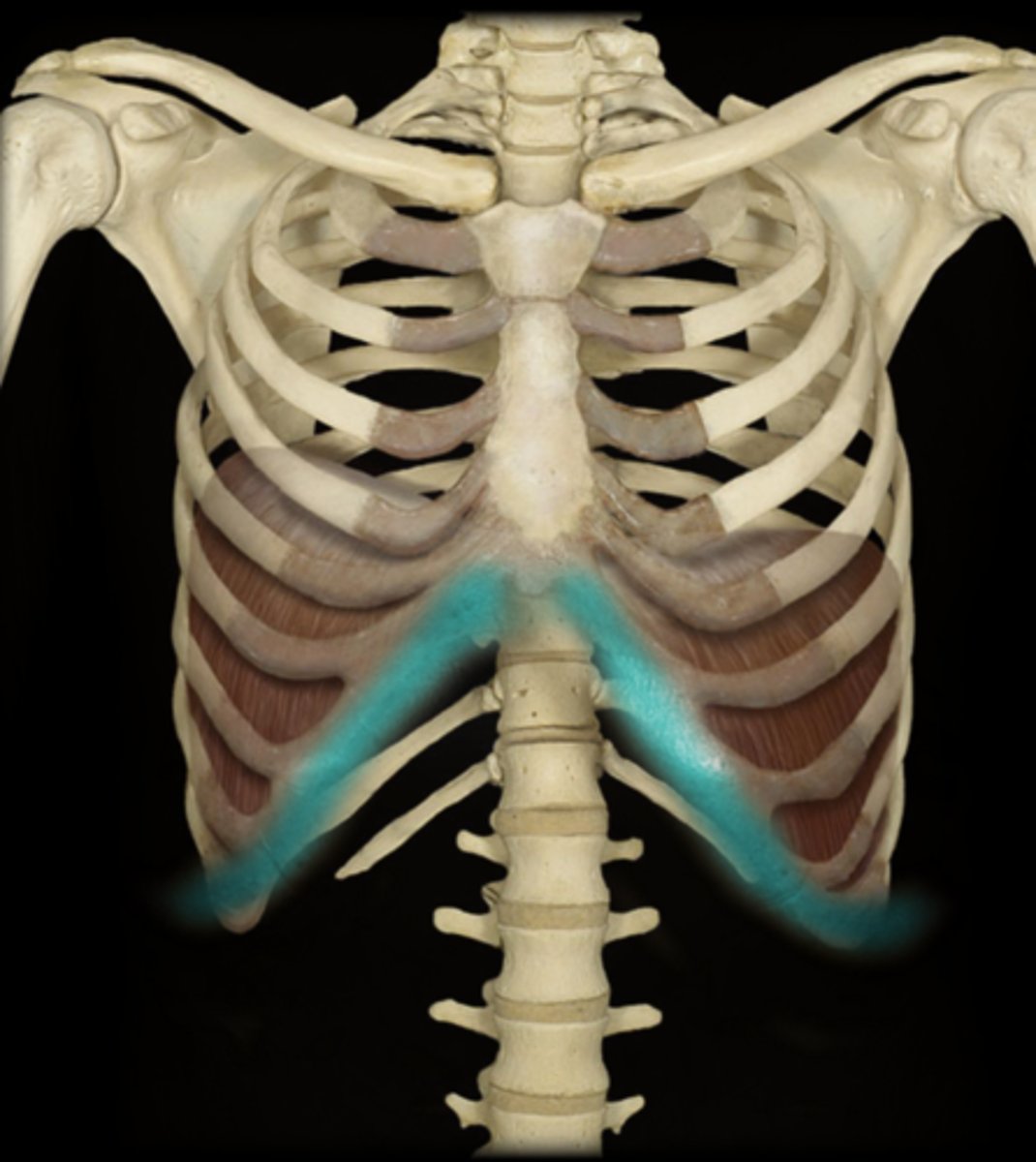
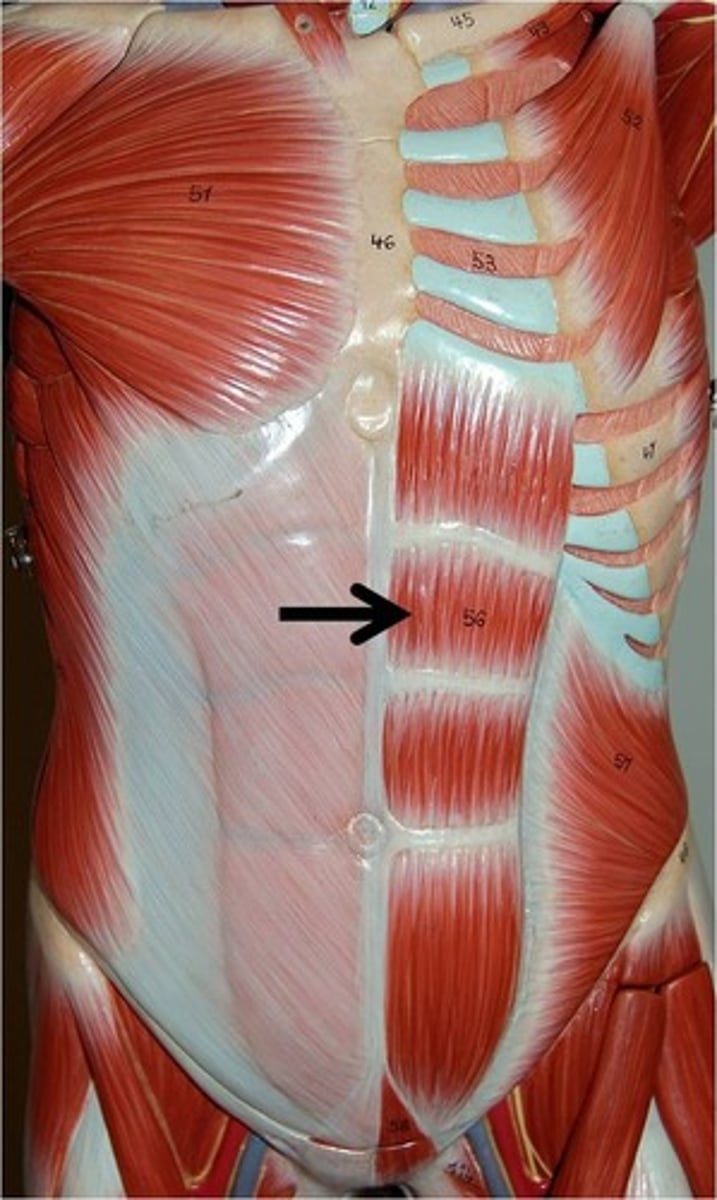
rectus abdominis muscle
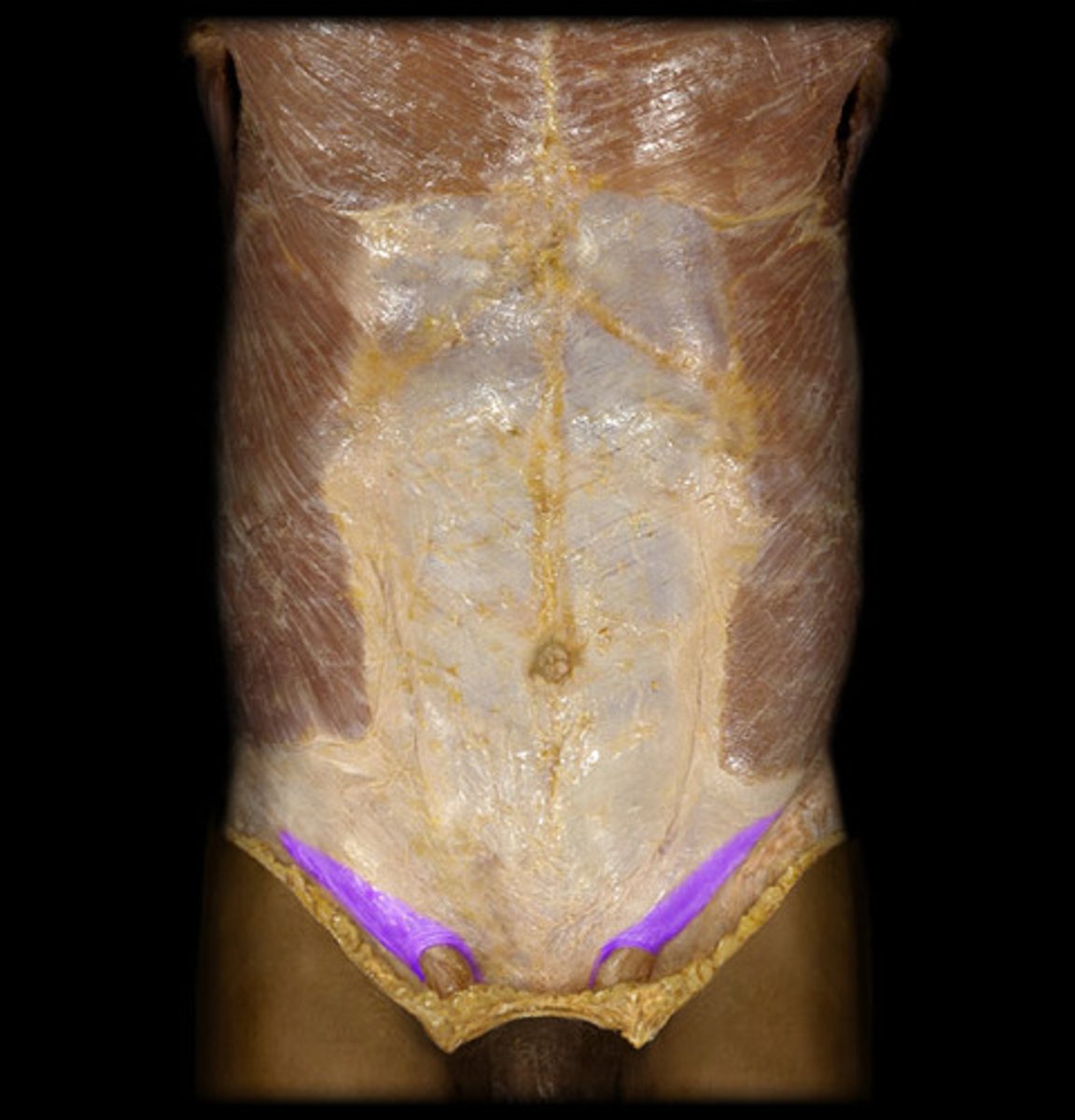
inguinal ligament
pubic tubercle
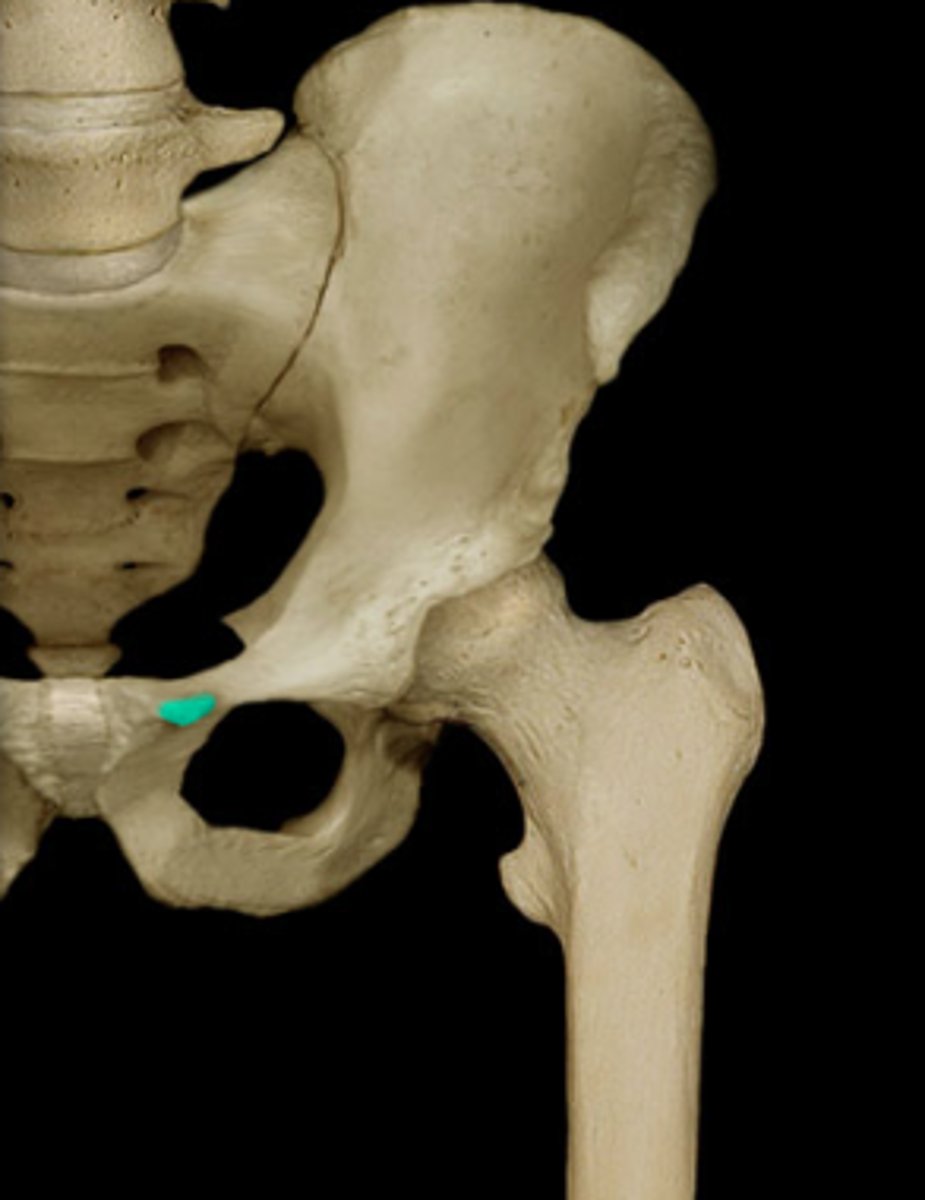
symphysis pubis
gnawing, burning, cramping or aching
caused by an organ that is contracted distended or stretched (e.g. hepatitis) OR ischemia
Describe visceral pain. What are some causes?
intense steady, achy pain that worsens with movement or coughing
caused by inflammation of the peritoneum (e.g. peritonitis from appendicitis)
Describe parietal pain. What are some causes?
pain at a distant site which is innervated at approx. the same spinal level as the affected organ/structure
e.g. pancreatic pain can be referred to the back
Describe referred pain. What are some causes?
liver, gallbladder, pylorus, duodenum, hepatic flexure of the colon, head of the pancreas
(e.g. cholecystitis, hepatitis)
What structures are in the RUQ? What are common causes of RUQ pain?
stomach, duodenum, or pancreas
(e.g. PUD, GERD, pancreatitis)
What are common causes of epigastric pain?
small intestine, appendix, or proximal colon
What are common causes of periumbilical pain?
rectum or bladder (e.g. UTI) colon, bladder, or uterus
What are common causes of suprapubic pain?
dysphagia, odynophagia, recurrent vomiting, evidence of GI bleed, early satiety, weight loss, anemia, palpable mass, painless jaundice
What are considered alarm symptoms for GI? (9)
cecum, appendix, ascending colon, terminal ileum, right ovary
Appendicitis, ruptured ovarian cyst
What structures are in the RLQ? What are common causes of RLQ pain?
spleen, splenic flexure of the colon, stomach, body and tail of the pancreas
splenic infarct
What structures are in the LUQ? What are common causes of LUQ pain?
sigmoid colon, descending colon, left ovary
diverticulitis, C. diff colitis
What structures are in the LLQ? What are common causes of LLQ pain?
renal colic
What are common causes of flank pain?
Crohns disease, gastroenteritis, SBO
What are common causes of diffuse abdominal pain?
flank pain that radiates to the groin
Where does ureteral pain present?
flank pain that wraps around to the R or L UQ
Where does kidney pain present?
supine with knees bent
How should the patient be positioned for an abdominal exam?
pale conjunctiva (anemia), Virchow's node, acanthosis nigrans, koilonychia
clubbing of the fingers, palmar erythema, asterixis, gynecomastia
What are some external signs of abdominal disease? (8)
Virchow's node, acanthosis ingrains
What external signs of abdominal disease indicate possible gastric cancer?
pale conjunctiva, koilonychia
What external signs of abdominal disease indicate anemia?
clubbing of the fingers, palmar erythema, gynecomastia
What external signs of abdominal disease indicate cirrhosis?
Asterixis
What external signs of abdominal disease indicate hepatic encephalopathy?
the left supraclavicular lymph node
Where is Virchow's Node located?
Inspection -> Auscultation -> Percussion -> Palpation -> Special Tests
What is the order of the abdominal exam?
Dilated veins around the umbilicus, associated with cirrhosis of the liver.
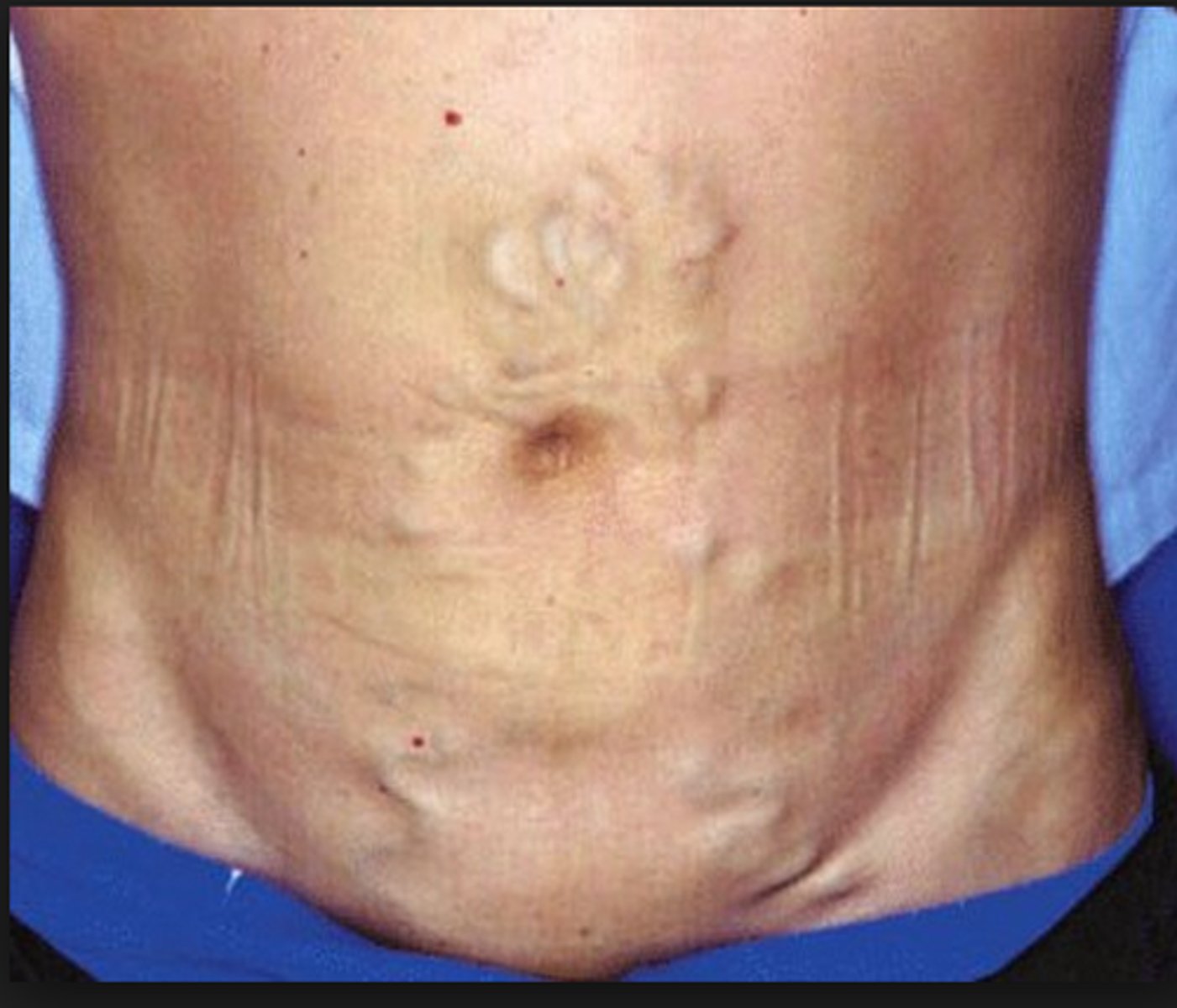
pink/purple striae from Cushings Disease
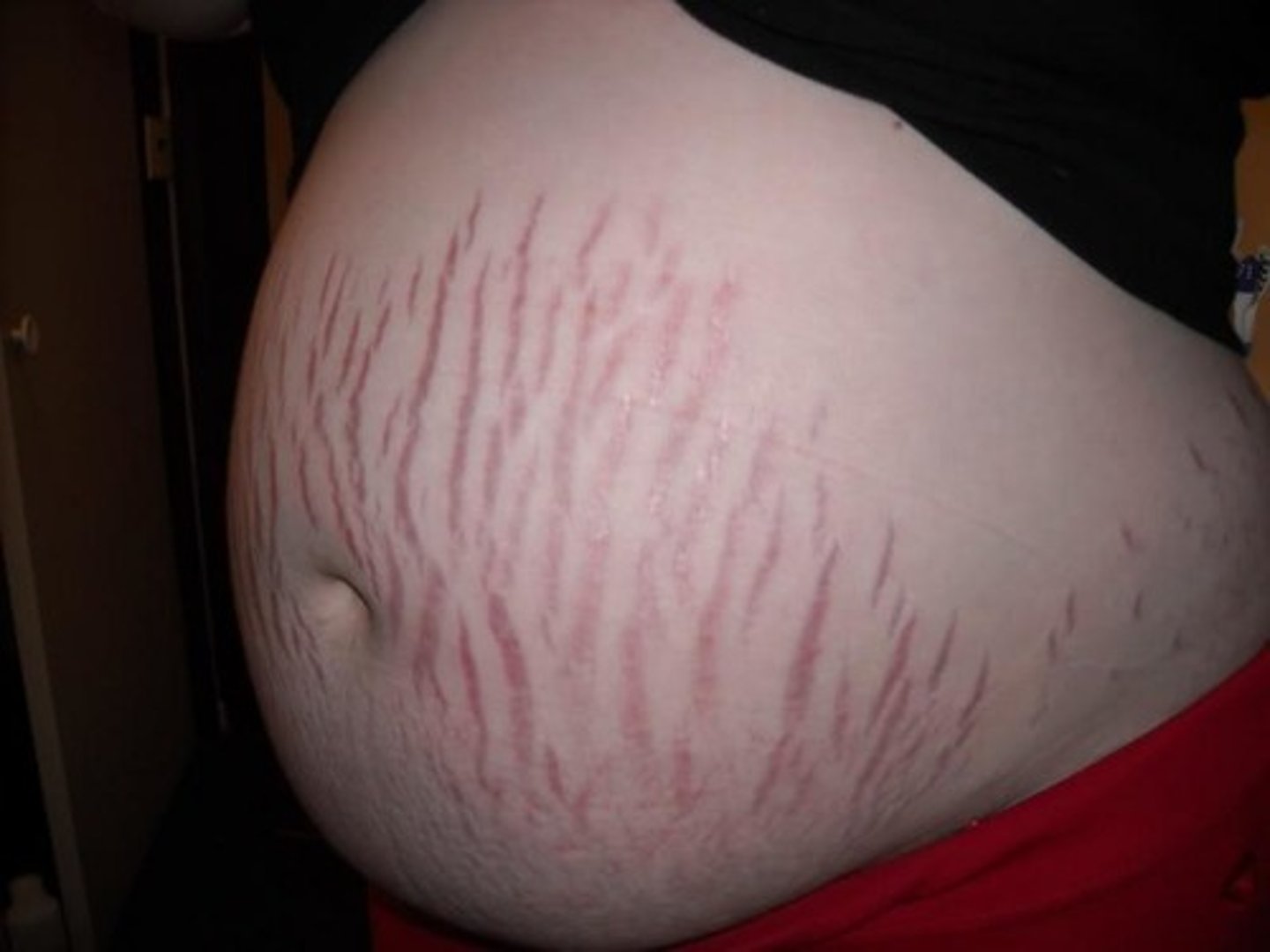
Cullen's sign (necrotic pancreatitis)
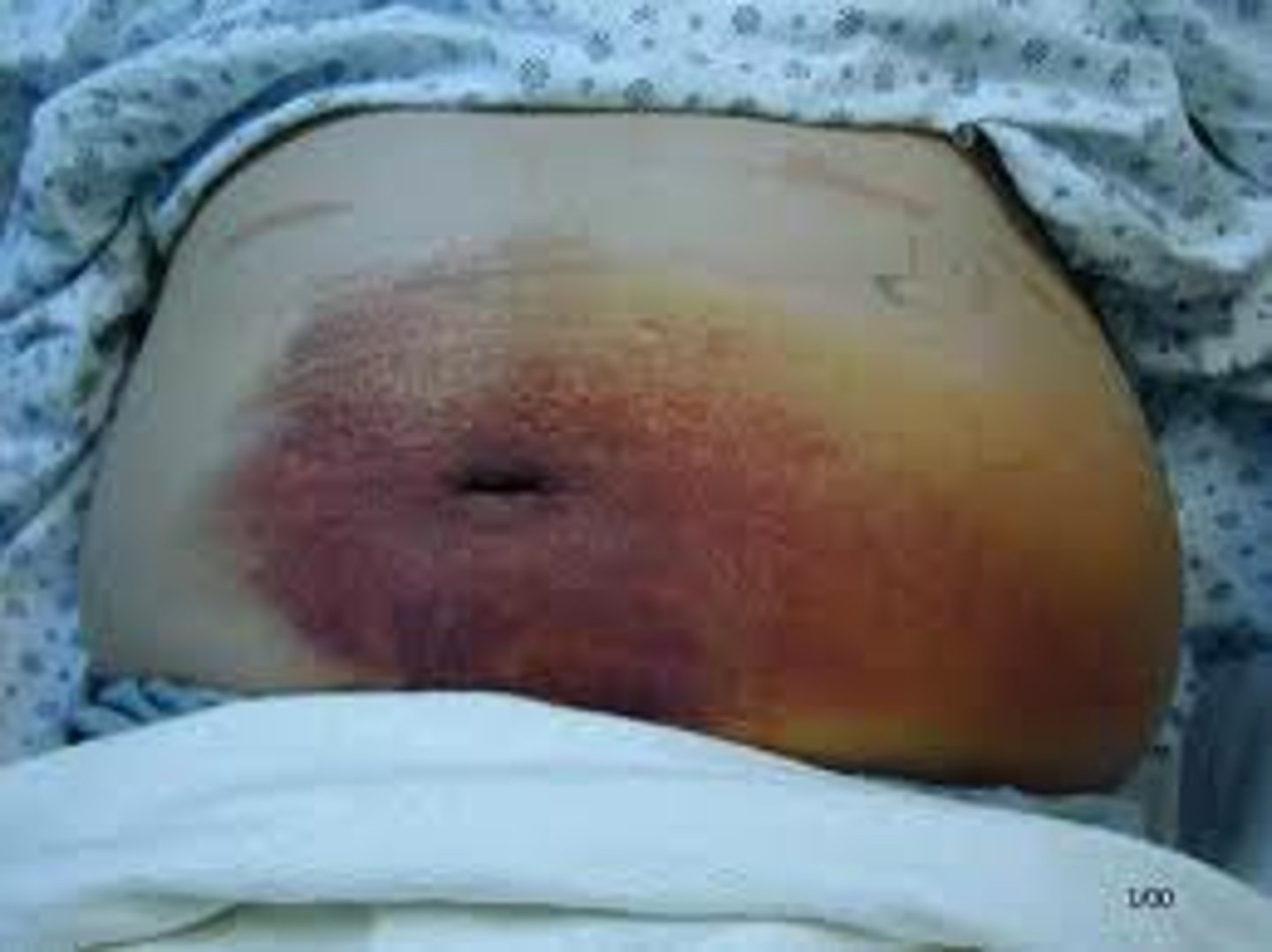
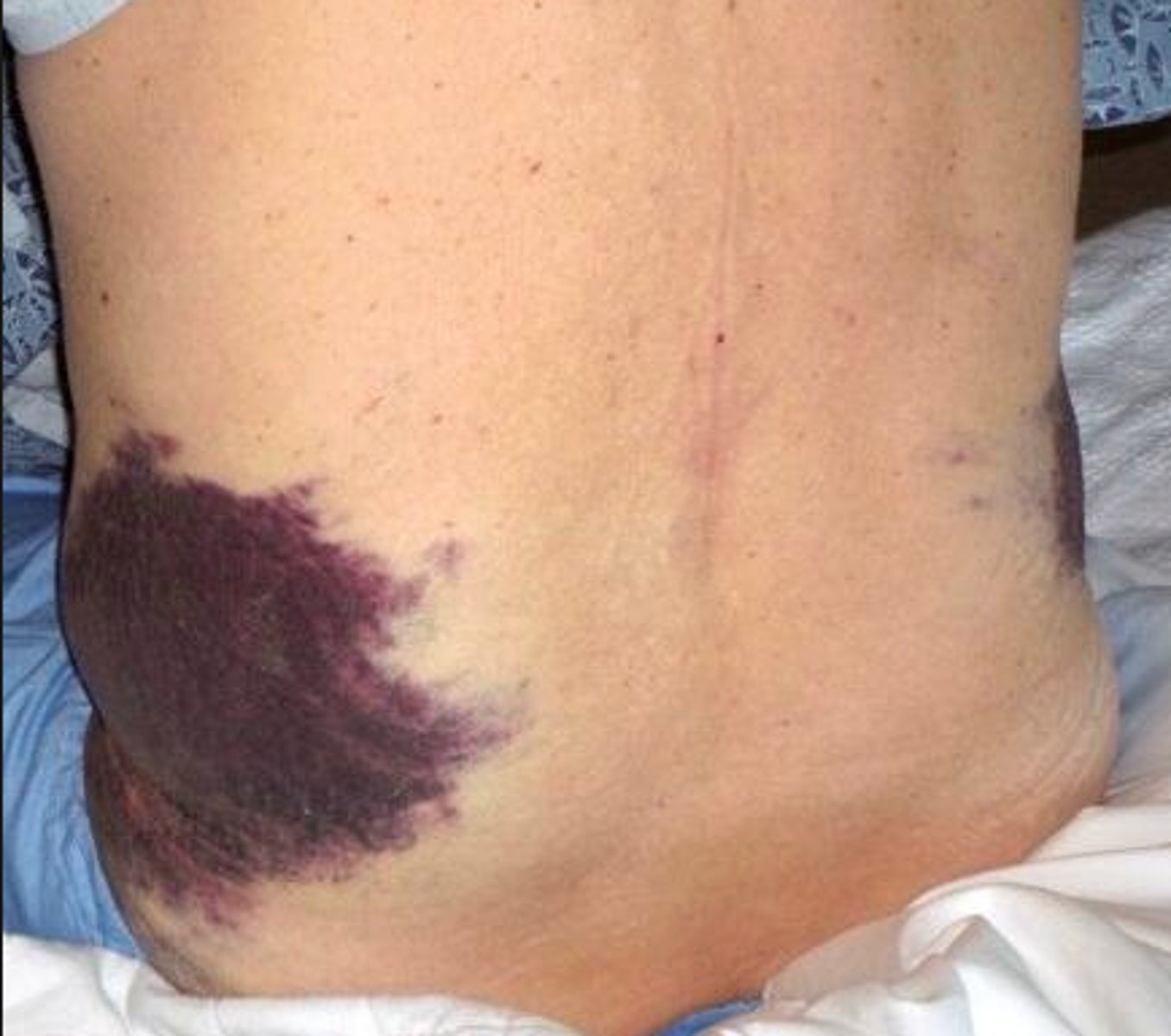
Grey-Turner's sign (necrotic pancreatitis)
the diaphragm
What part of the stethoscope do you use to auscultate bowel sounds?
the bell
What part of the stethoscope do you use to auscultate bruits?
the bell
What part of the stethoscope do you use to auscultate friction rubs?
areas of gas
What does tympany on percussion indicate?
fluid, feces, organs
What does dullness on percussion indicate?
Guarding/Rebound/Rigidity
have the patient cough and access where it causes pain, palpate the abdomen, and heel tap
What are the peritoneal signs? How do you assess for them?
hooking technique
What technique is used in obese patients to assess the liver?
4-8 cm lower than the midsternal line
6-12 cm lower than the mid clavicular line
Where is the liver edge located?
percussion from border of cardiac dullness at the 6th rib down to anterior
if dullness is past the mid axillary line, indicates an enlarged spleen
How do you access for an enlarged spleen?
False. the right may be palpable, but the left is usually not palpable
T/F: both kidneys are palpable.
CVA Tenderness
What PE finding indicates inflammation of the kidneys?
shifting dulness when the patient shifts from supine to side lying OR fluid wave
What PE finding indicates ascites?
Rosving Sign - press in LLQ causes pain in RLQ (McBurney's point)
Psoas sign
Obturator Sign
also rebound tenderness at McBurney's point
What PE signs indicate appendicitis?
Murphys sign
What PE sign indicates cholecystitis?
have the patient do a crunch, the hernia will protrude
How do you test for a ventral hernia?
Normal active BS, ND/NT, no rebound
What is the abbreviated version of an abdominal exam?

alcohol abuse, viral hepatitis, and colon cancer
What tests are included in a GI screening?
how many times in the past year have you had 4 or more drinks a day (women) or 5 or more drinks a day (men)?
What is the initial screening question for alcohol use in adults?
> or equal to 2 positive answers
What is considered a positive CAGE?
1. Have you ever felt the need to CUT down on your drinking?
2. Have you ever felt ANNOYED by criticism of your drinking?
3. Have you ever felt GUILTY about drinking?
4. Have you ever had to take a morning EYE OPENER?
What are the CAGE questions?
fecal oral
How is Hep A transmitted?
all children at age 1 year
people with:
chronic liver disease
clotting factor disorders
IV drug use
men who have sex with men
working with primates
travel to Hep A prevalent areas
Who should be immunized against Hep A?
Hep A vaccine or single dose of immune globulin within 2 weeks of exposure
what is done for postexposire prophylaxis to HepA?
2 shots
Hep A vaccine is a series of _______ shots
exposure to blood, semen, or other bodily fluid
How is Hep B transmitted?
persons with HIV
IV drug users
men who have sex with men
women in the first trimester of pregnancy
Who should be screened for Hep B?
sexual contacts of patients with + surface antigens
patients with more than one sexual partner in the last 6 months
patient getting tx for STI
men who have sex with men
people with percutaneous exposure to blood
HIV+
chronic liver disease
Who should be immunized against Hep B?
percutaneous exposure to blood
How is HepC transmitted?
people with risk factors for blood Bourne infection
people born between 1945-1965
Who should be screened for Hep C?
1st degree relative with colorectal cancer at < 60 yo
or multiple 1st degree relatives with colorectal cancer
What family history puts a patent at increased risk for colon cancer?
average risk: all adults age 45-75 years
75-85 on an individual basis
high risk: 10 years prior to the youngest case in their family
Who should be screened for colon cancer?
FIT and FOBT
FIT is more sensitive
What are the non-invasive tests for colorectal cancer? Which is more sensitive?
annually
How often are FIT and FOBT screenings performed?
computed tomography colonography (CTC) - 5 years
capsule colonoscopy - 5 years
screening colonoscopy - 10 years (5 years if high risk)
What are the invasive test for colon cancer and how often are they performed?
above the symphysis pubis
Where would a distended bladder be palpable?
liver distention from hepatitis
visceral pain in the RUQ suggests ____________
early acute appendicitis
visceral periumbilical pain can be suggestive of _____________
intestinal mesenteric ischemia
if the patients visceral pain is disproportionate to the physical findings, suspect ___________
steady, aching pain more severe than visceral pain that is localized over the involved structure
Describe somatic/parietal pain
peritonitis = immobile
renal stone = moving
Patients with peritonitis will be (moving/immobile) whereas patients with renal stones will be (moving/immobile).
back, right scapular region or posterior thorax
Where does pain of duodenal or pancreatic origin referred to?
epigastric area
Where does pain from pleurisy or inferior MI refer to?
5-hydroxytrytophan and substance P
Which neuropeptides are involved in symptoms of abdominal pain, bowel dysfunction, and stress?
15-30%
What percentage of patients with non-specific abdominal pain in the ER need surgery?
inferior MI
What cause of epigastric pain is precipitated by exertion and relieved by rest?
heartburn and effortless regurgitation
If patients report _________ and __________ together more than once a week, it is 90% a GERD diagnosis
failing empiric therapy
> 55 years onset
alarm symptoms
What criteria warrants an EGD for a GERD diagnosis?
Dysphagia, odynophagia, recurrent vomiting, evidence of GI bleeding, early satiety, weight loss, anemia, risk factors for gastric cancer, palpable mass, painless jaundice.
What are abdominal alarm symptoms?
50-85%
Of those with suspected GERD _____% haven disease on endoscopy.
10% of patients with heartburn have Barrett's, which is metaplastic changes in the esophageal lining from normal squamous to columnar epithelium
What is Barretts Esophagus? How prevalent is it?
RLQ pain that migrates from the periumbilical region
What referred pain pattern is characteristic of appendicitis?
cramping pain radiating to the flank or groin accompanied by urinary symptoms
What clinical symptoms suggest nephrolithiasis?
Pain in the LLQ accompanied by diarrhea in a patient with a history of constipation
What clinical symptoms suggest diverticulitis?
Nonspecific diffuse abdominal pain with abdominal
distention, nausea, emesis, and lack of flatus and/or bowel movements
What clinical symptoms suggest bowel obstruction?
diffuse abdominal pain and guarding w/ or w/o abdominal distention
What is a characteristic symptom of peritonitis?
late-stage colon cancer
A change in bowel habits with a palpable mass warns of...
1. intermittent pain for
12 weeks of the preceding 12 months with relief from defecation
2. change in frequency of
bowel movements, OR change in form of stool (loose, watery, pellet- like)
What is the diagnostic criteria for IBS?
bulimia
induced vomiting without nausea is indicative of...
severe constipation with the inability to pass both stool and gas, often indicative of a bowel obstruction
Obstipation
insufficient saliva
Xerostomia
esophageal dysphagia
A patient who identifies pain below the sternoclavicular notch suggests...
esophageal stricture (Schatzki ring) webbing or narrowing or neoplasm
What are disorders that cause dysphagia to solid foods only?
achalasia
What disorder cause dysphagia to both solids and liquids?
NSAIDs, ASA, caustic indigestion, radiation, infection with candida, CMV, HSV, or HIV
What are common causes of esophageal ulceration?
excessive repetitive air swallowing
Aerophagia
False. it is typically non-infectious like IBS or a food allergy
T/F: chronic diarrhea is typically infectious.
acute diarrhea that starts in a hospital setting typically after 72 hours
Nosocomial diarrhea