Isotopes and relative atomic mass
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Explain the meaning of the term isotope
Isotopes are different atomic forms of the same element, which have the same number of protons but different number of neutron
What must isotopes have?
Same proton number but different mass number
Example of a pair of isotopes:
Carbon -12, carbon- 13
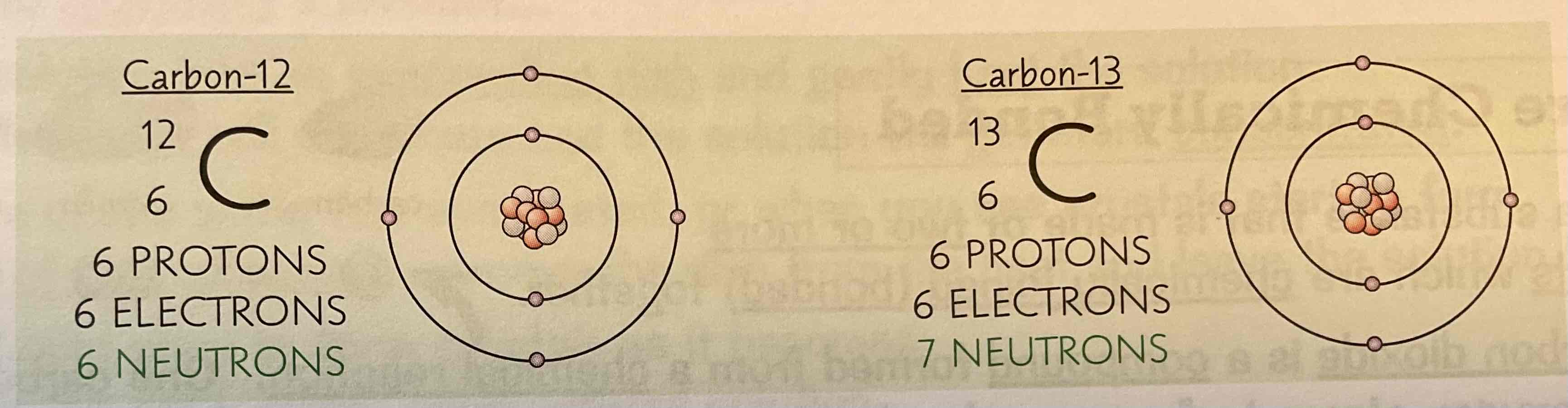
What does relative atomic mass take into account?
All stable isotopes
What does Ar describe?
How heavy different atoms are compared with the mass of an atom of carbon-12. So carbon-12 has an Ar of exactly 12
What does Ar allow for?
It’s the average mass of all the isotopes of an element. It has to allow for the relative mass of each isotope and its relative abundance
What does relative abundance mean?
How much there is of each isotope compared tot he total amount of the element in the world. This can be a ratio, a fraction or a percentage
How do you calculate relative atomic mass?
Multiply the mass of each isotope buy its relative abundance
Add those together
Divide by the sum of the relative abundances
E.g. Ar = (35.0 × 3) + (37.0 × 1) / 3 + 1 = 35.5