Part 2 - RBC Disorder (Hemolytic Anemia)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Haptoglobin
Hemopexin
In serum, what indices is decreased in both fragmentation and macrophage-mediated hemolysis
Fragmentation (Intravascular)
A hemolysis associated with Coffee-Brown Plasma color
Fragmentation (intravascular)
macrophage-mediated is negative on these
A hemolysis is positve free hemoglobin, methemoglobin, and prussian blue staining urine sediments
Fragmentation = Schistocytes [fragment cells]
Macrophage = Spherocytes [katong paakan diba]
What RBC morphology is associated with:
Fragmentation (Intravascular) Hemolysis
Macrophage-mediated (Extravascular) Hemolysis
Vertical Structures:
Actin + protein 4.1 complex
Ankyrin + Protein 4.2 complex
PROTEIN STRUCTURE:
Prevents loss of membrane and decrease in surface area-to-volume ration of RBC
Horizontal Structure:
Spectrin-actin-protein4.1 junctional complex
PROTEIN STRUCTURE:
Membrane eslasticity
Prevents the membrane from fragmenting due to mechnical stress
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia (MAHAs)
RBC = shistocytes
Group of disorder characterized by RBC fragmentation and thrombocytopenia
Caused by mechanical shearing of RBC membrane as it rapidly passes through areas of small blood vessels that are blocked by microthrombi (clot)
Abnormal narrowing of blood vessels
(+) what is the associated RBC morphology?
Acquired (Pseudo) Stomatocytosis
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
May occur as a drying artifacts on Wright-stained peripheral blood films
Other Causes:
Malignancies
Acute Alcoholism
Cardiovascular Disease
Spur Cell (Acanthocytes) Anemia
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
Patients with severe liver disease
Caused by excess free cholesterol resulting to remodeling of membrane into acanthocytes
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
Absence of CD55 and CD59 of RBCs surface making then susceptible to spontaneous lysis by complement
Mutation in PIGA gene
MAJOR MANIFESTATIONS:
anemia
thrombosis
bone marrow failure
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
Associated with:
Smooth muscle dystonia
Budd-Chiary syndrom (hepatic vein thrombosis)
Chronic Renal Disease
G6PD Deficiency
G6PD — protects hemoglobin from oxidative denaturation
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
RBCs are vulnerable to oxidative damage and subsequent hemolysis of oxidant stress
Leads to FAVISM if ingesting fava beans
Quantitative Spectrophotometric assay
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
Gold Standard to determine G6PD activity
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
PIGA gene mutation = PNH
INTRINSIC DEFECTS:
Most common form of hereditary nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia
Mutations in PKLR gene
MANIFESTATIONS:
↓ ATP
↑ 2,3-BPG
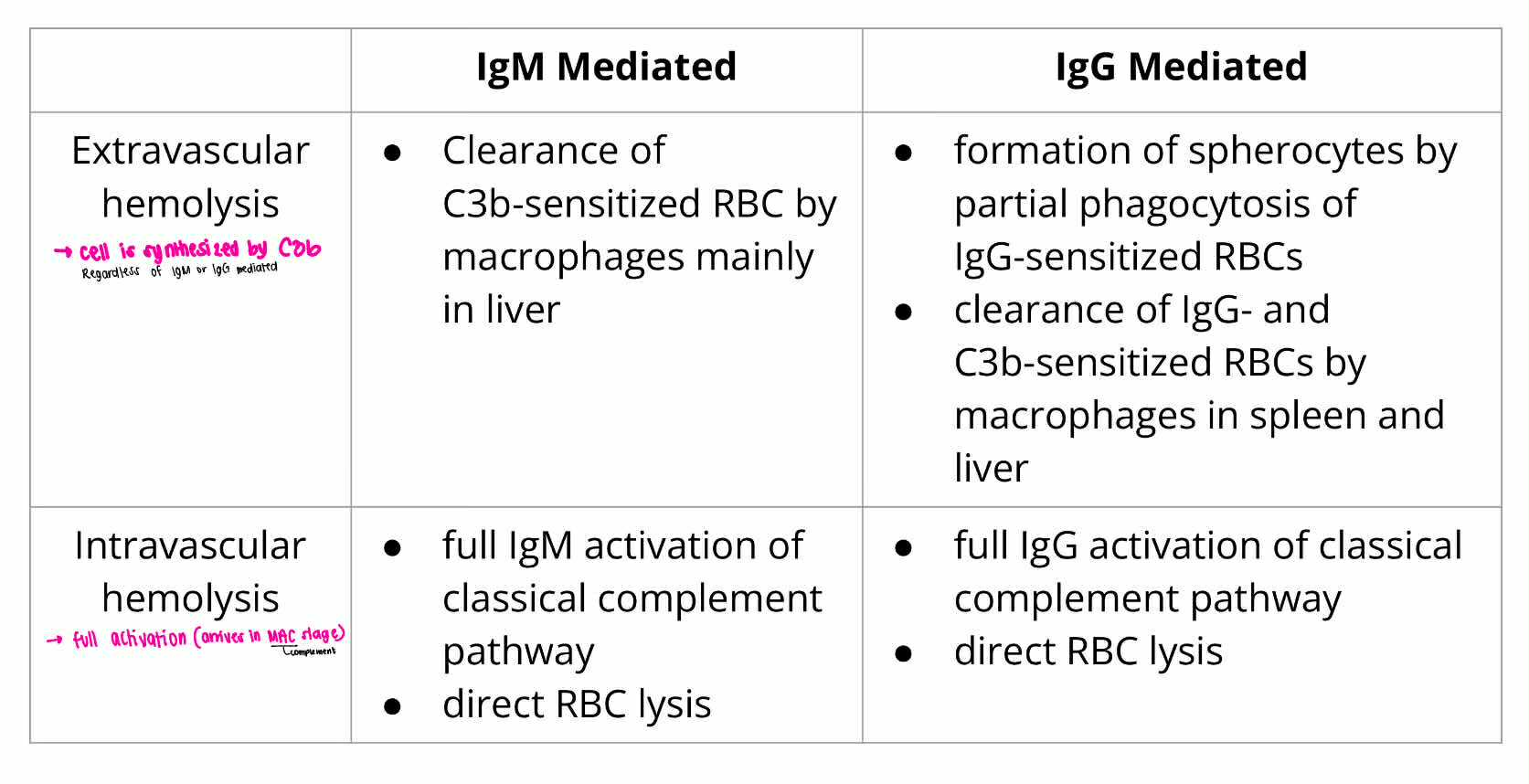
EXTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS
IgM Mediated
IGM or IGG MEDIATED HEMOLYSIS:
Clearance of C3b-sensitized RBC by machropgae mainly in liver
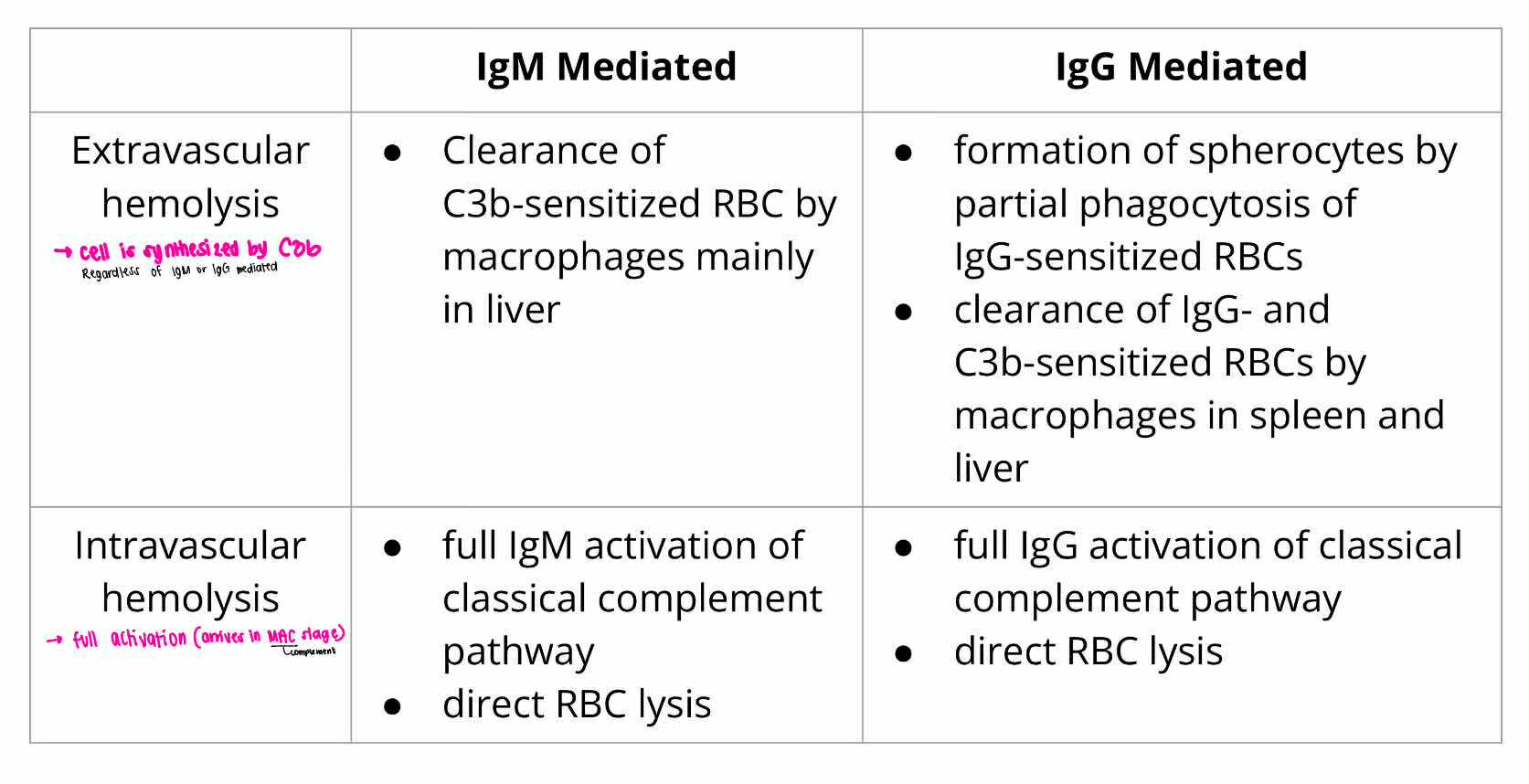
INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS
IgM Mediated
IGM or IGG MEDIATED HEMOLYSIS:
Full IgM activation of classical complement pathway
direct RBC lysis
![<ul><li><p><strong>EXTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS</strong> [macrophage]</p><ul><li><p>IgG Mediated</p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6fea784a-d27d-4152-94ef-ec2cde50aac4.png)
EXTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS [macrophage]
IgG Mediated
IGM or IGG MEDIATED HEMOLYSIS:
Formation of spherocytes by partial phagocytosis of IgG-sensitized RBCs
Clearance of IgG and C3b-sensitized RBCs by macrophages in spleen and liver
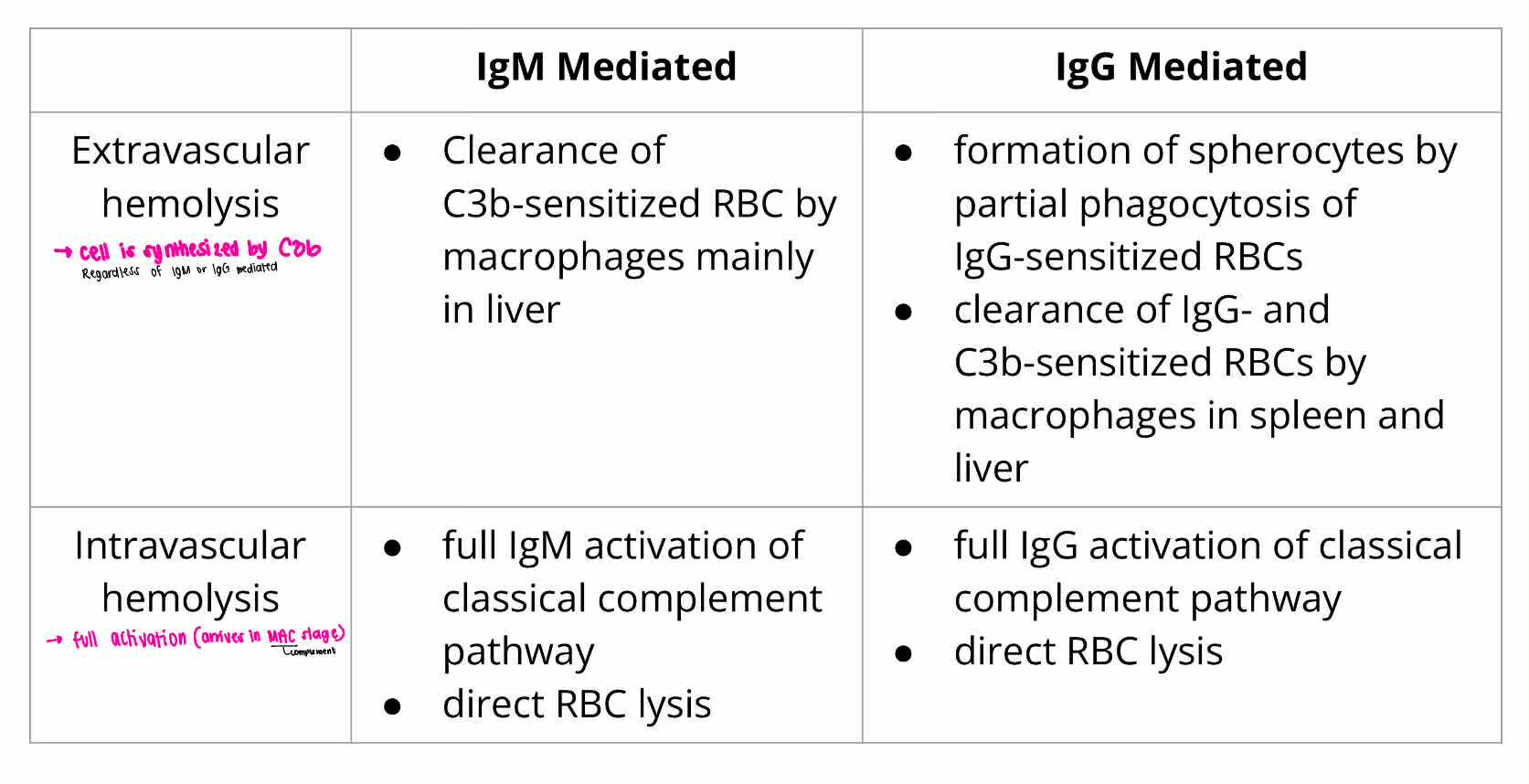
INTRAVASCULAR HEMOLYSIS
IgG Mediated
IGM or IGG MEDIATED HEMOLYSIS:
full IgG activation of classical complement pathway
direct RBC lysis
Warum Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (wAIHA)
IgG
AUTOIMMUNE HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA:
autoantibodies reast at 37*C
Typical Findings = Polychromasia and Spherocytes
Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD)
AUTOIMMUNE HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA:
IgM classes react optimally at 4*C
Pathologic agglutinins can react at room temp
Symptoms = acrocyanosis (bluish discoloration)
Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria (PCH)
AUTOIMMUNE HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA:
Due to biphasic IgG autoantibody with anti-P specificity
At cold temp = antibody binds to P-antigen (donath landtevier), partially activating complement
At 37*C = full complement activation and hemolysis occur
Drug-Induced Immune Hemolytic Anemia
AUTOIMMUNE HEMOLYTIC ANEMIA:
Decrease in Hemoglobin
Positive DAT result