Plants pt 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/103
Last updated 10:20 PM on 1/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
Leaves
Organs where photosynthesis take place
2
New cards
Where are leaves located
At nodes along the stem
3
New cards
petiole
Stalk which connects leaf to stem
4
New cards
2 types of leaves
Compound and simple
5
New cards
Simple leaves
No leaflets
6
New cards
Compound leaves
2+ leaflets
7
New cards
Adaptations of leaves (7)
1. Broad leaflets to trap more sunlight in shady areas
2. Evergreen needles to reduce water loss (can’t freeze in the narrow column)
3. Though, bitter or prickly leaves to discourage hungry herbivores
4. Toxin production as a natural insecticide
5. Tendrils to attach to surfaces (Eg beans and ivy)
6. Bulbs (Eg onions) for water and nutrient storage
7. Attractive petals to attract pollinators
8
New cards
Non-vascular plants + example
Don’t have vessels for transport
Eg mosses
Eg mosses
9
New cards
Vascular plants
Tracheophytes - Have conducting tissues to transport water and carbs throughout plants
10
New cards
Gymnosperms
“Naked seed” plants e.g. conifers
11
New cards
Angiosperms
“Enclosed seeds” flowering plants e.g. tomatoes
12
New cards
Vascular systems
1. Shoots (above soil line)
2. Roots (below soil line)
13
New cards
Tissues
Group of cells working together to carry out a specific function
14
New cards
main plant tissue groups
1. Vascular tissue
2. Ground tissue
3. Dermal tissue
4. Meristematic tissue
15
New cards
Vascular tissue
Occurs in strands
Continuous from root to leaf
Continuous from root to leaf
16
New cards
Types of vascular tissue
Xylem and phloem
17
New cards
Xylem
Conduct water and suspended minerals from roots to plant
Consists of dead cells at maturity
Consists of dead cells at maturity
18
New cards
Phloem
Vascular tissue which transports water and dissolved sugars (carbs) from leaves to roots, shoots or fruits
Consists of living cells at maturity
Consists of living cells at maturity
19
New cards
Ground tissue
Surrounds vascular tissue
20
New cards
Types of ground tissue
Parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma
21
New cards
Parenchyma
Living, spherical, thin-walled cells
Photosynthesize and store nutrients/water
E.g. Apple flesh, potatoes, radishes
Photosynthesize and store nutrients/water
E.g. Apple flesh, potatoes, radishes
22
New cards
Sclerenchyma
Dead, thick-walled cells (very rigid) with cellulose and lignin
Strengthen support and protect plant
E.g. nut shells
Strengthen support and protect plant
E.g. nut shells
23
New cards
Collenchyma
Living, thick-walled cells
Strengthen and support plant
E.g. celery stalk
Strengthen and support plant
E.g. celery stalk
24
New cards
Types of dermal tissue
Epidermis and periderm
25
New cards
Epidermis
Dermal tissue that is the outer protective layer of leaves, stems and roots
Usually only one cell thick
Usually only one cell thick
26
New cards
Periderm + example
Dermal tissue that protects inner tissues from injury
Replaces epidermis in later growth
Cells are dead at maturity
E.g. cork
Replaces epidermis in later growth
Cells are dead at maturity
E.g. cork
27
New cards
Meristematic tissues
Produces new cells by mitosis - undifferentiated
28
New cards
Types of meristematic tissue
Apical and lateral
29
New cards
Apical tissue
Meristematic tissue at root and shoot tip
Responsible for primary growth- lengthens roots and shoots
Responsible for primary growth- lengthens roots and shoots
30
New cards
Lateral tissue
Aka cambium
Meristematic tissue responsible for secondary growth to increase root and shoot diameter
Meristematic tissue responsible for secondary growth to increase root and shoot diameter
31
New cards
Stems divisions
Nodes and internodes
32
New cards
Nodes
Hold buds
33
New cards
Buds
grow into leaves, flowers, cones or other stems
34
New cards
Internodes
Distance between nodes on stems
35
New cards
Functions of stems
Support
Transport link between root and rest of plant
Storage of nutrients
Transport link between root and rest of plant
Storage of nutrients
36
New cards
Types of stems
Woody
Herbaceous
Herbaceous
37
New cards
Woody stems
* thick, rough, long-lived
* Capable of supporting great heights
* Undergo secondary growth in xylem (new wood increases stem diameter each year)
* Make cork cells from cork cambium
* Surrounded by bark
* Composed of heartwood
* Composed of sapwood
E.g. oak trees, conifers, shrubs
* Capable of supporting great heights
* Undergo secondary growth in xylem (new wood increases stem diameter each year)
* Make cork cells from cork cambium
* Surrounded by bark
* Composed of heartwood
* Composed of sapwood
E.g. oak trees, conifers, shrubs
38
New cards
Bark
Tissue from cambium outward in woody stems
39
New cards
Heartwood
Darker , older, dead xylem which makes up woody stems along with sapwood
40
New cards
Sapwood
Lighter, younger, living xylem which makes up woody stems along with heartwood
41
New cards
Herbaceous stems
Thin, soft, short-lived
Usually short (expedition: palm trees)
Usually short (expedition: palm trees)
42
New cards
Types of herbaceous stems
Monocot and dicot
43
New cards
Monocot stems
Herbaceous stems with:
* scattered vascular bundles
* 2 distinct parts (xylem and phloem)
* No bark, annual rings or wood
E.g. corn stem
* scattered vascular bundles
* 2 distinct parts (xylem and phloem)
* No bark, annual rings or wood
E.g. corn stem
44
New cards
Dicot stems
Herbaceous stems which have:
* vascular bundles in a circular arrangement
* 3 distinct parts - xylem, phloem, cambium
E.g. bean stem
* vascular bundles in a circular arrangement
* 3 distinct parts - xylem, phloem, cambium
E.g. bean stem
45
New cards
Functions of roots
1. Anchor plant to soil
2. Absorb water, nutrients, and minerals from soil/growth medium
3. Store food/carbs
4. Produce hormones
5. Propagate/reproduce/grow a new plant
46
New cards
Types of roots
Primary and secondary/lateral
47
New cards
Primary roots
First root to develop from seed
48
New cards
Secondary/lateral root
Branches from primary root
49
New cards
types of roots in different plants
Tap, fibrous, adventitious
50
New cards
Tap root
Single deep root that stores food and obtains deep ground water
E.g. carrots, beets, radishes, dandelions, oak trees
E.g. carrots, beets, radishes, dandelions, oak trees
51
New cards
Fibrous roots
Many branched roots which absorb surface water quickly
E.g. grasses, rye
E.g. grasses, rye
52
New cards
Adventitious roots
Grow from plant shoots and eventually form a fibrous root system
E.g. climbing aerial roots of ivy and prop roots of mangrove trees
E.g. climbing aerial roots of ivy and prop roots of mangrove trees
53
New cards
Root hairs
Small, hair-like extensions of root epidermal cells which increase surface are for water absorption
54
New cards
How water gets from roots to plant
Enters root hairs - cortex - phloem - xylem
Root pressure pushes water up the roots xylem
Root pressure pushes water up the roots xylem
55
New cards
How water is transported in the xylem (root to leaf) steps
\
Osmosis
Transpiration
Root pressure
Adhesion
Cohesion
Osmosis
Transpiration
Root pressure
Adhesion
Cohesion
56
New cards
How water is transported by the xylem: osmosis
Water enters the root across the semi-permeable membrane by osmosis
57
New cards
How water is transported by the xylem: transpiration
Water is lost in leaves through evaporation through the stomata which pulls other molecules to replace them
58
New cards
How water is transported by the xylem: root pressure
Plant roots build up pressure that worked water upwards into the plant
59
New cards
Adhesion
water molecules are attracted to xylem vessels (capillary action)
The narrower the tube, the higher the water climbs
The narrower the tube, the higher the water climbs
60
New cards
How water is transported by the xylem: cohesion
Attraction of water molecules to e/o
61
New cards
How sugars is transported by the phloem
Sugars are translocated through sieve-tube elements in the phloem in more then 1 direction (upward, downward, sideways) simultaneously
62
New cards
Pressure flow hypothesis/mass flow theory
Relies on combination of osmosis and pressure differences between source cells and sink cells
63
New cards
Source cells
High sugar cells (Eg leaf cells)
64
New cards
Sink cells
Low sugar cells (eg root cells)
65
New cards
How water is transported by the xylem: steps
\
Leaf produces sugar
Sugar enters sieve tube of phloem
H2O enters phloem from nearby cells
Pressure inside phloem increases
Contents of elements are pushed from cell to cell
Leaf produces sugar
Sugar enters sieve tube of phloem
H2O enters phloem from nearby cells
Pressure inside phloem increases
Contents of elements are pushed from cell to cell
66
New cards
Blade
Thin, flattened, main portion of the leaf
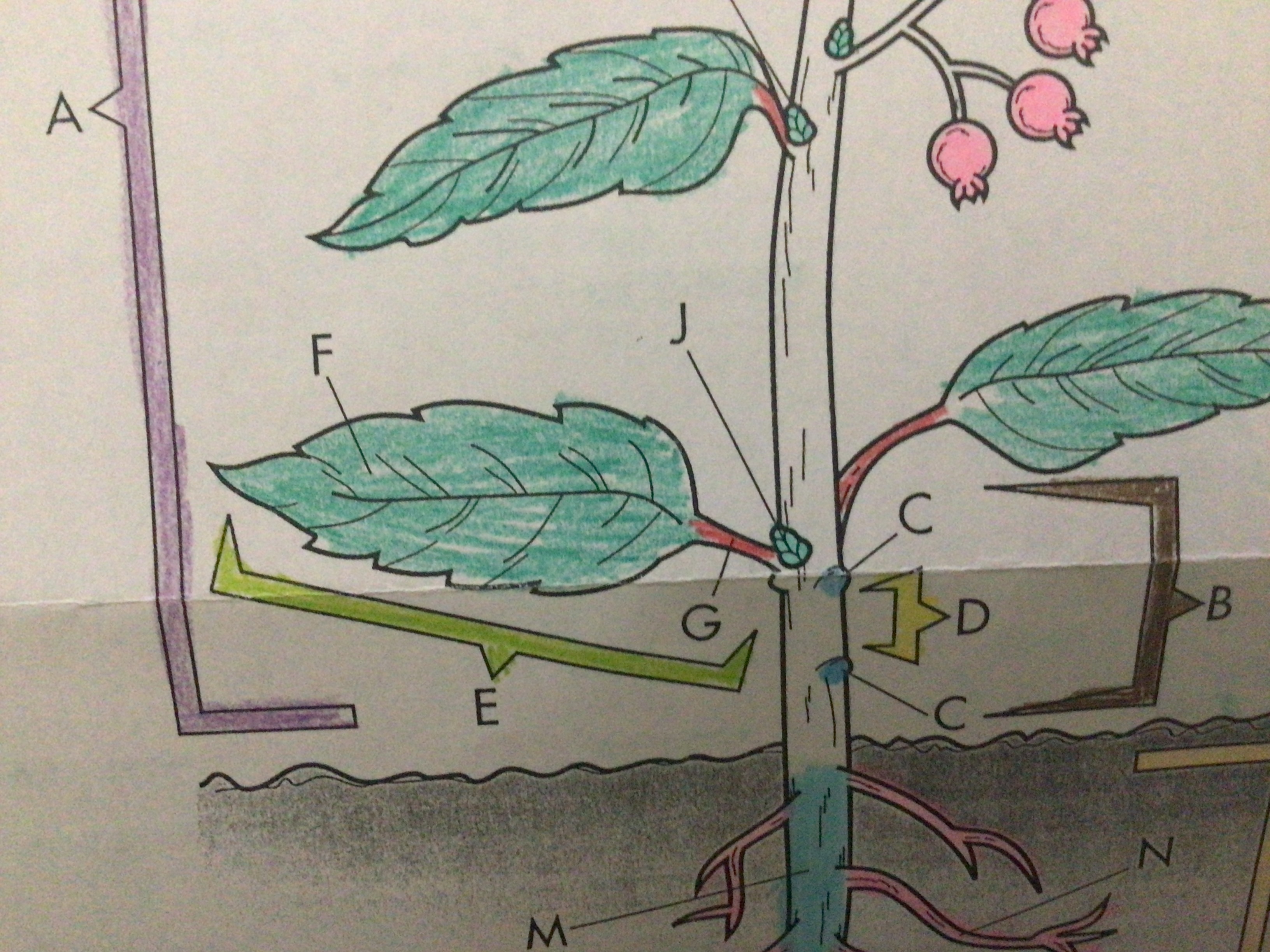
67
New cards
Petiole
An extension which joins the blade to the stem
68
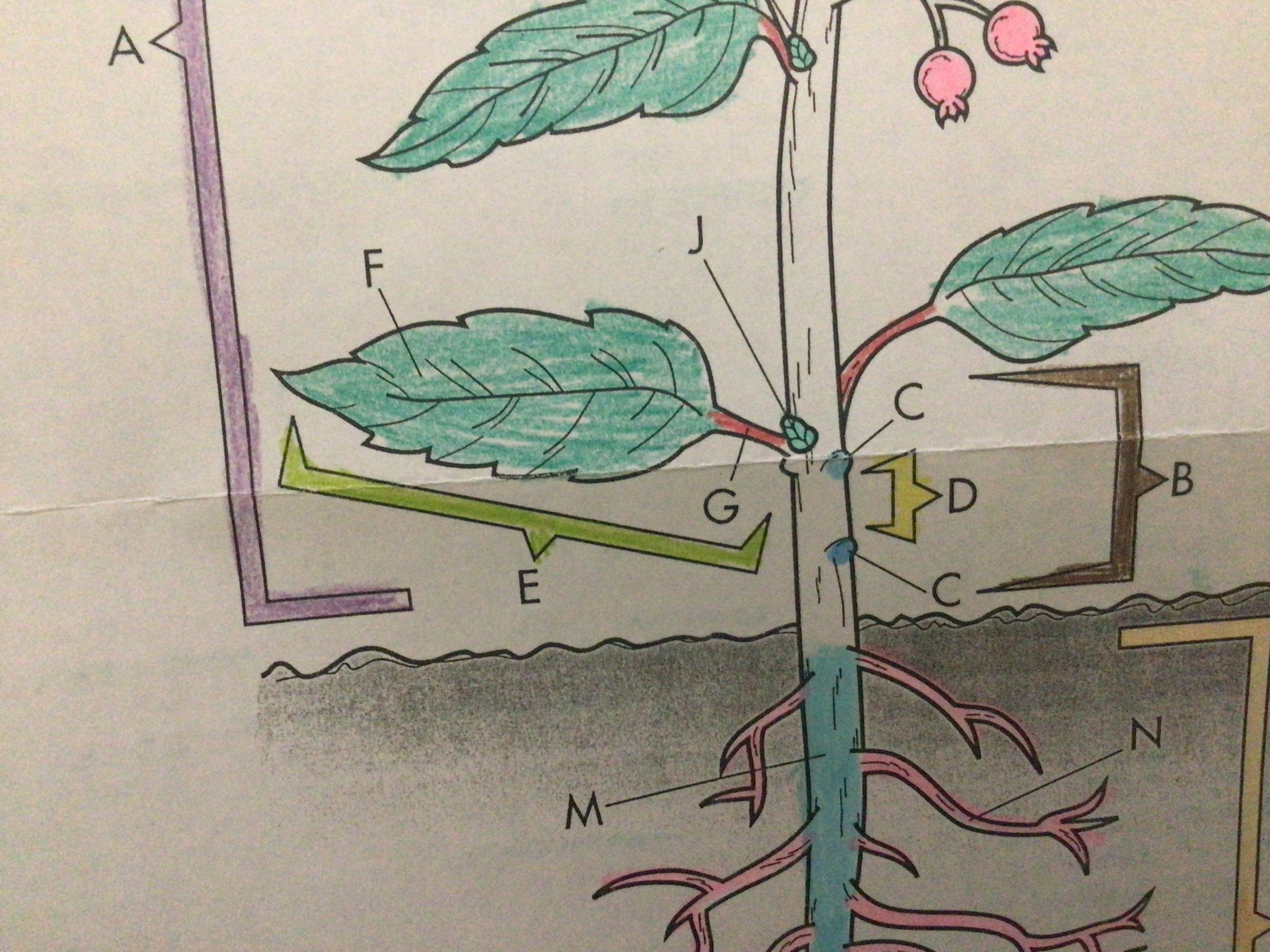
New cards
Lateral bud
Young inactive shoot that will eventually grow into a new branch
Located above where the leaf attaches to the stem
Located above where the leaf attaches to the stem
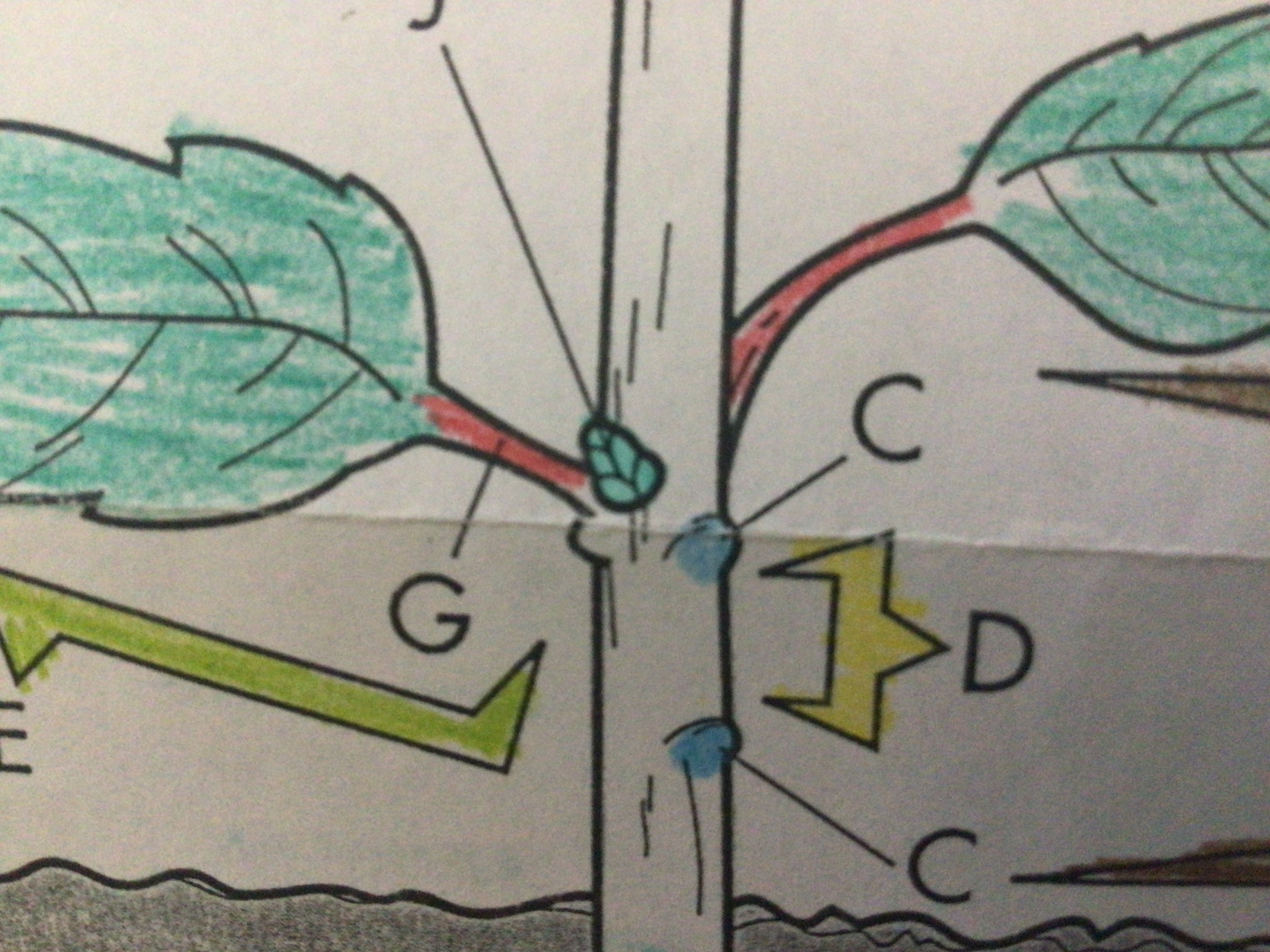
69
New cards
Shoot apex
Upper portion of a stem where growth occurs
70
New cards
Shoot system
part of the plant located above ground
71
New cards
Types of cells in xylem
Tracheids
Vessel elements
Vessel elements
72
New cards
Tracheids
Long, narrow, overlapping cells located in the xylem with pits to transport H2O
73
New cards
Vessel elements
Xylem cells with thickened walls and large pores
74
New cards
Types of cells in the phloem
Companion cells
Sieve plate
Sieve plate
75
New cards
Companion cells
Nucleated cells in the phloem tissue which carry out the cell functions of the adjacent sieve cells
76
New cards
Sieve cells
make up the sieve plate which has large pores for passage of material
77
New cards
Cuticle
Waxy layer on top of epidermis
Prevents water loss
Prevents water loss
78
New cards
Palisade mesophyll cell
Site of most photosynthesis
79
New cards
Vascular bundle
‘Vein’ of leaf
80
New cards
Spongy mesophyll cell
Site of some photosynthesis
Air spaces between these cells allow for gas exchange
Air spaces between these cells allow for gas exchange
81
New cards
Guard cell
Controls opening of stomafor gas exchange
82
New cards
Stoma/stomate
Pore which opens and closes for gas exchange on underside of leaf
83
New cards
T/F - all epidermal cells contain chloroplasts
F - guard cells around the stomate are the only épidermal cells containing chloroplasts
84
New cards
How does the stomate open
Dawn: photosynthesis begins in the guard cells. sugar accumulates and water concentration decreases
Water from surrounding cells diffuses onto the guard cell by osmosis causing them to swell and curve
Now curved, the stomate to open and CO2 to enter the leaf
Water from surrounding cells diffuses onto the guard cell by osmosis causing them to swell and curve
Now curved, the stomate to open and CO2 to enter the leaf
85
New cards
Process of stomate closing
Sunset: photosynthesis stops but respiration continues causing sugar to build up in surrounding cells
Water exist the guard cells by osmosis and the guard cells become limp and wilted
Once wilted, the thick wall closes and the stomate straightens and closes
Water exist the guard cells by osmosis and the guard cells become limp and wilted
Once wilted, the thick wall closes and the stomate straightens and closes
86
New cards
Thick and thin walls of the stomate
Thick inner wall and thin outer wall
87
New cards
Transpiration
Loss of water from leaves by evaporation
Caused by opening and closing of stoma
Caused by opening and closing of stoma
88
New cards
Inner root layer
Transport/vascular tissue
89
New cards
Middle layer of root
Store water and food for the root
90
New cards
Outer root layer
Contains root hairs
91
New cards
Root cap
Protects a root tip from damage as it grows into the soil
Make of dead cells
Make of dead cells
92
New cards
What materials are carried up from roots by vascular tissue
Water + dissolved nutrients
93
New cards
What material do vascular tissue carry down to roots from leaves
Glucose (food)
94
New cards
New root growth mainly occurs from the _____
Tip
95
New cards
Most water enters a plant through the _____
Root hairs
96
New cards
Meristem
Undifferentiated cells that give rise to new cells at the bottom of a root
97
New cards
Region of maturation
Location of root where cells specialize into other types of tissues
98
New cards
Region of elongation
Region open root where cells increase in length to push root deeper into soil
99
New cards
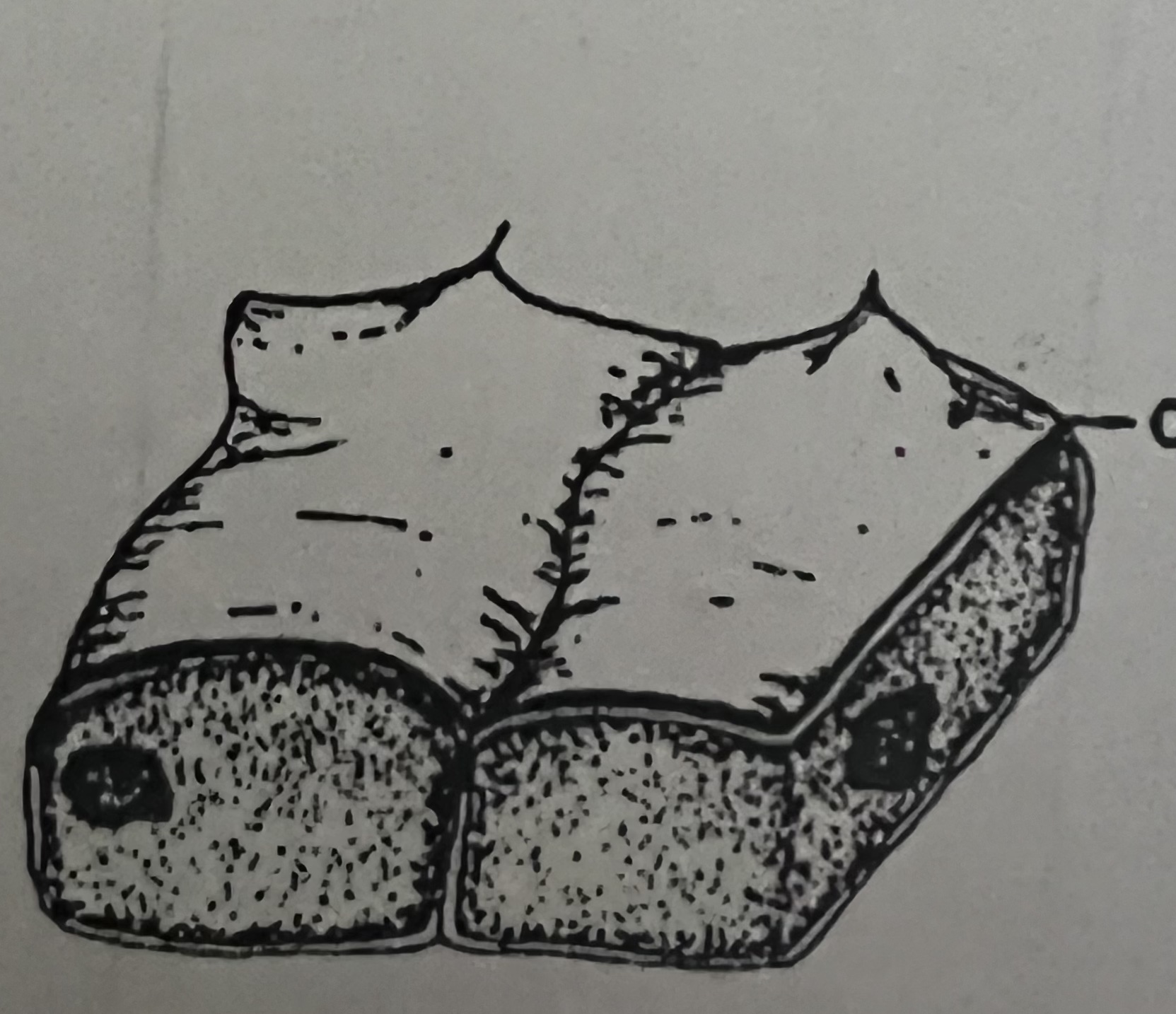
Epidermal
100
New cards
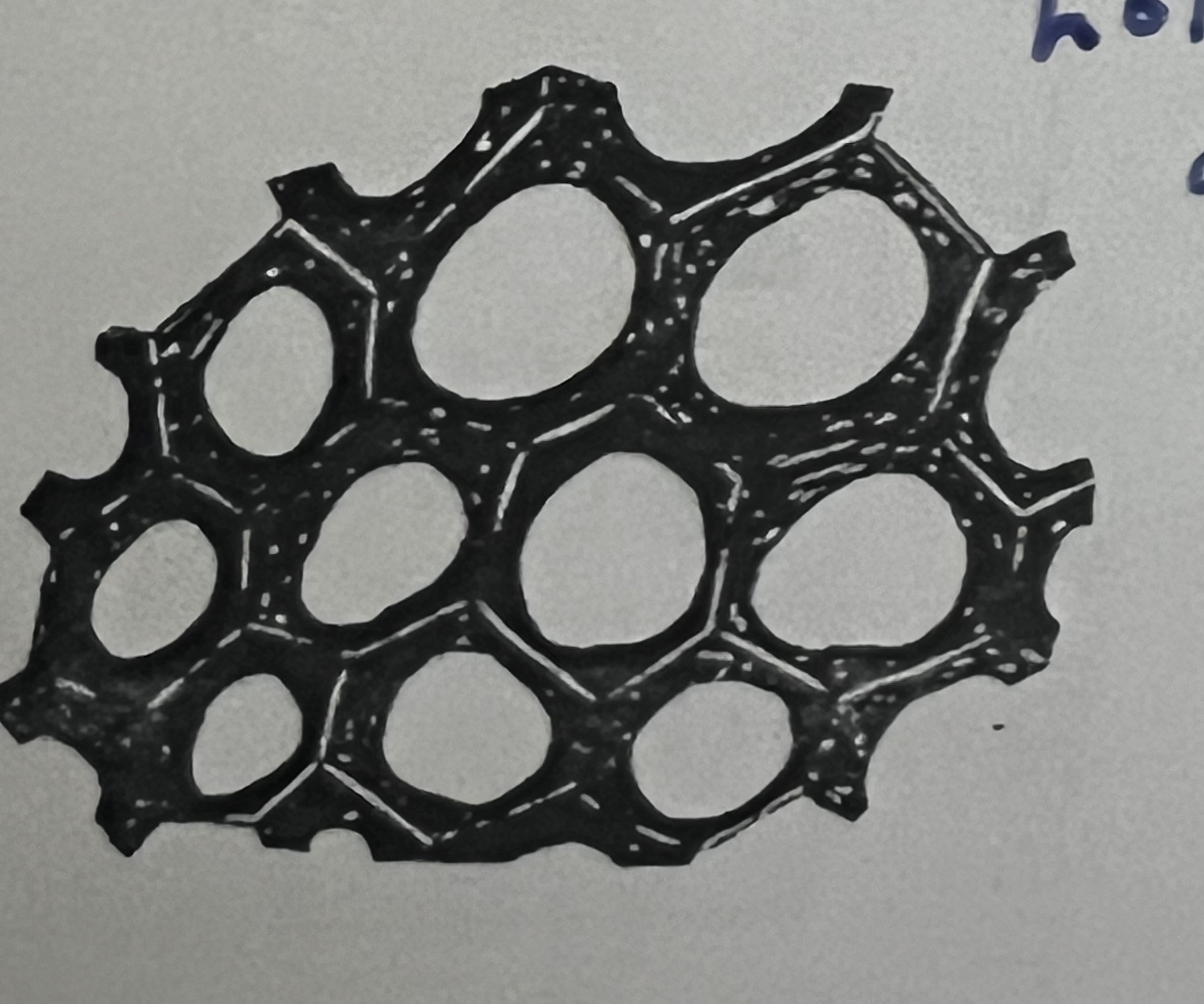
Xylem