SBI3U genetics unit part 1 review
1/55
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
chromosomes
DNA
aka deoxyribonucleic acid
made up of nucleotides
DNA is classified as a protein
yes
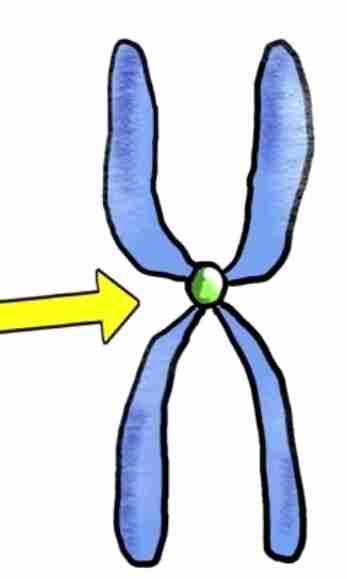
centromere
it links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division
nucleotide
chromatin
made up of dna & histone proteins
found during interphase of the cell cycle
What is the complementary base pairing rule
Adenine (A) bonds with Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C) bonds with Guanine (G)
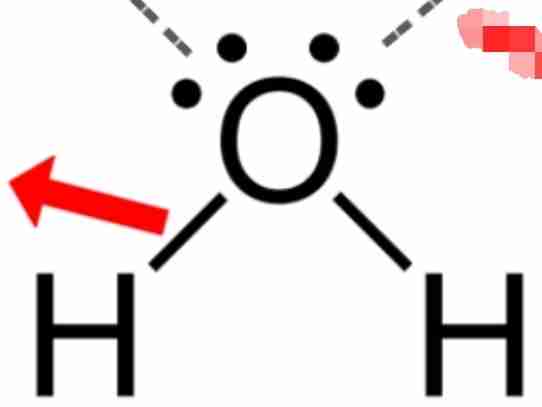
what is hydrogen bonding
a type of chemical bond that weakly attaches a molecule to another molecule
how many H-bonds are between A & T
2 hydrogen bonds
how many h-bonds are between C & G
3 hydrogen bonds
meaning of anti-parallel
what is a gene
a piece of heredity material that is passed on from parent to offspring
what is an allele
a version of a gene at a particular position on a chromosome
what is heredity
the process of passing traits from parents to offspring
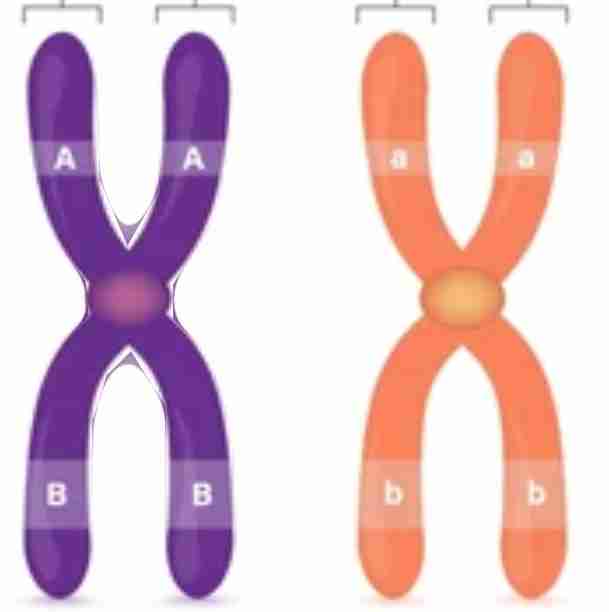
what is homologous chromosomes
a pair of chromosomes w/ the same type of genes
haploid cells (n)
a cell w/ a single set of chromosomes
humans sex cells have 23 chromosomes
diploid cells (2n)
a cell that has 2 complete sets of chromosomes
that # for humans is 46 chromosomes
somatic cells
any cell that is not a sex cell
are also diploid cells
gametes (sex cells)
the reproductive cells of any animal or plant
humans only have 23 chromosomes in their sex cells
are also haploid cells
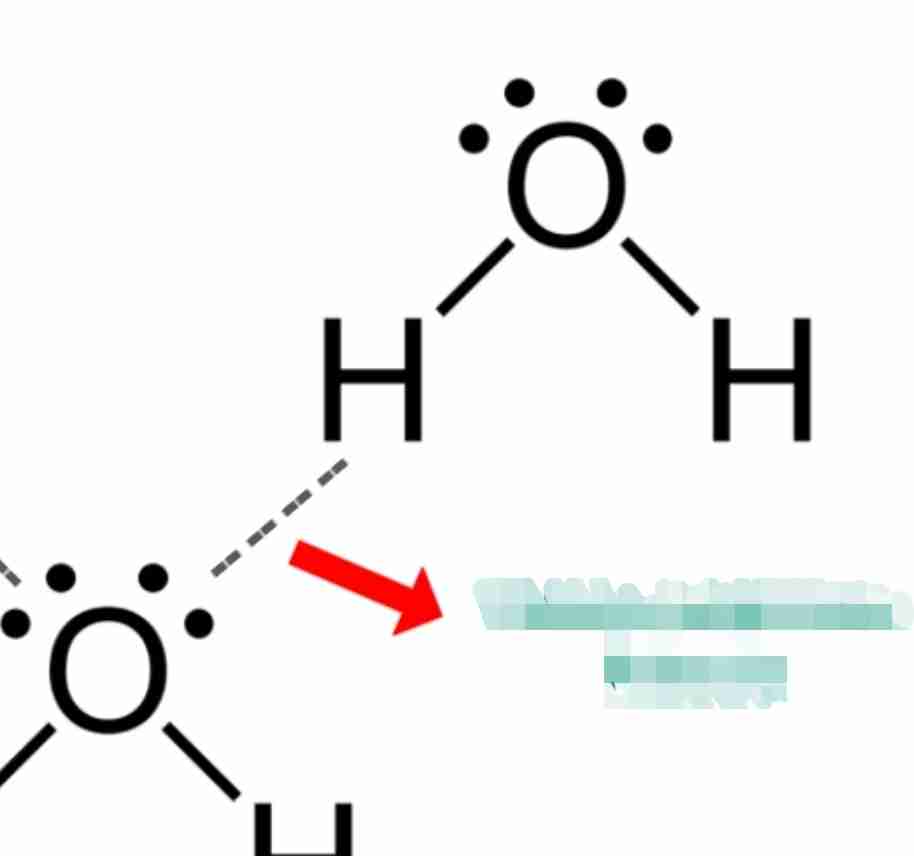
intramolecular bonds
forces that hold atoms together within a molecule
intermolecular bonds
forces that exist between molecules
stages of mitosis
Interphase (G1,S, G2)
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
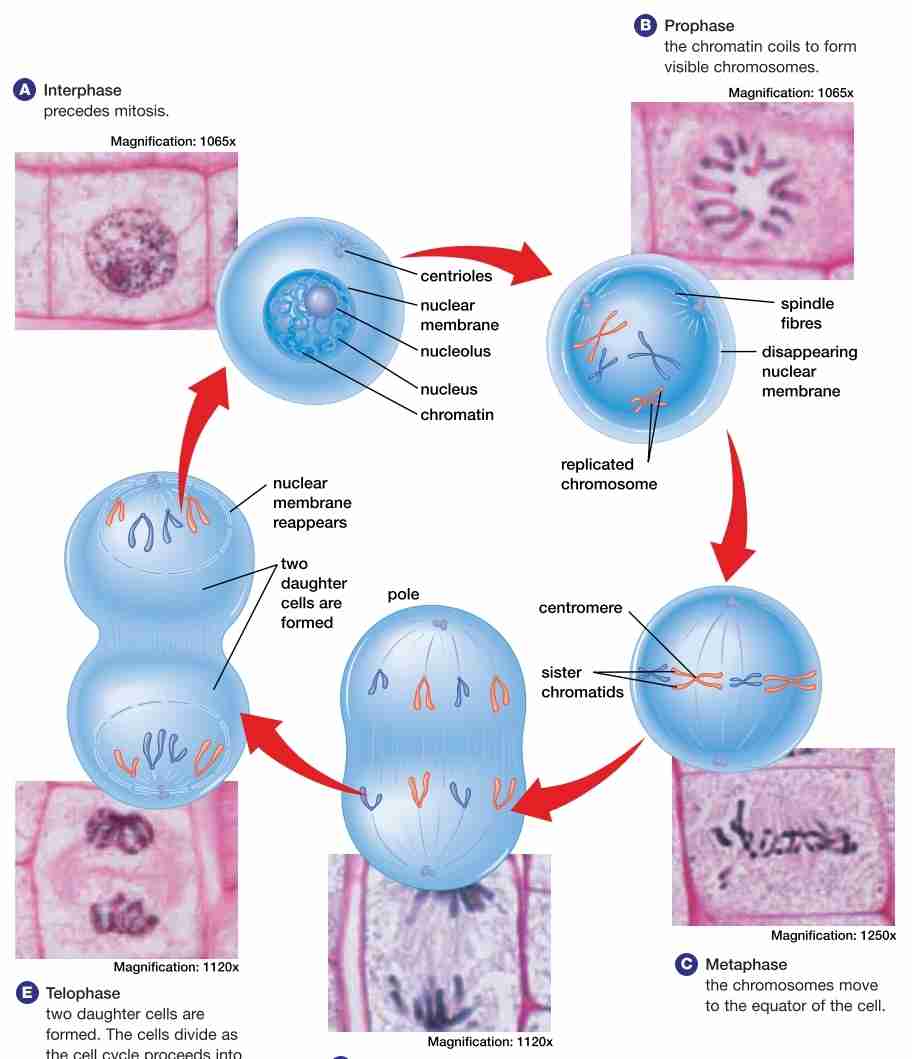
purpose of mitosis
is cell divison ; for a mother cell to produce 2 daughter cells in the end
total # of chromosome for a human cell at the prophase stage of mitosis
46 chromosomes
the "n" description of the cell at interphase
2n
total # of chromosomes for a human cell at the prophase stage of mitosis
46 chromosomes
the "n" description of the cell at prophase
2×2n
total # of chromosome for a human cell at the end of the telophase stage of mitosis
46 chromosomes
the "n" description of the cell at the end of telophase
2n
where does mitosis occur
in somatic cells
G1 phase of Interphase
cell does most of its growing; making it take in more nutrients
DNA is spread throughout the nucleus as chromatin
cell increases in size
cell has 2n diffuse chromosomes (diploid)
S Phase (synthesis phase) of Interphase
cell continues to grow
the diffuse chromosome duplicates, producing a 2x2n # of diffuse chromosomes
G2 phase of Interphase
cell has 2x2 n chromosomes within the nucleus
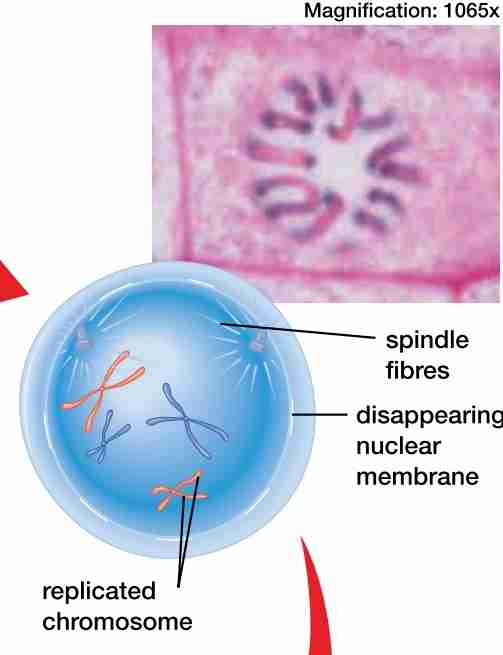
prophase
nuclear membrane dissolves
chromatin condenses into chromosome, each w/ 2 sister chromatinds attached by a centomere
spindle fibers & centrioles assemble
centrioles move to the poles of the cell
2x2n
what is meiosis
a special cell division that involves the production of reproductive cells
purpose of meiosis
to produce sex cells (sperms & eggs) that have half the genetic information of somatic cells
stages of meiosis
In meiosis I
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
In meiosis II
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II
Telophase II
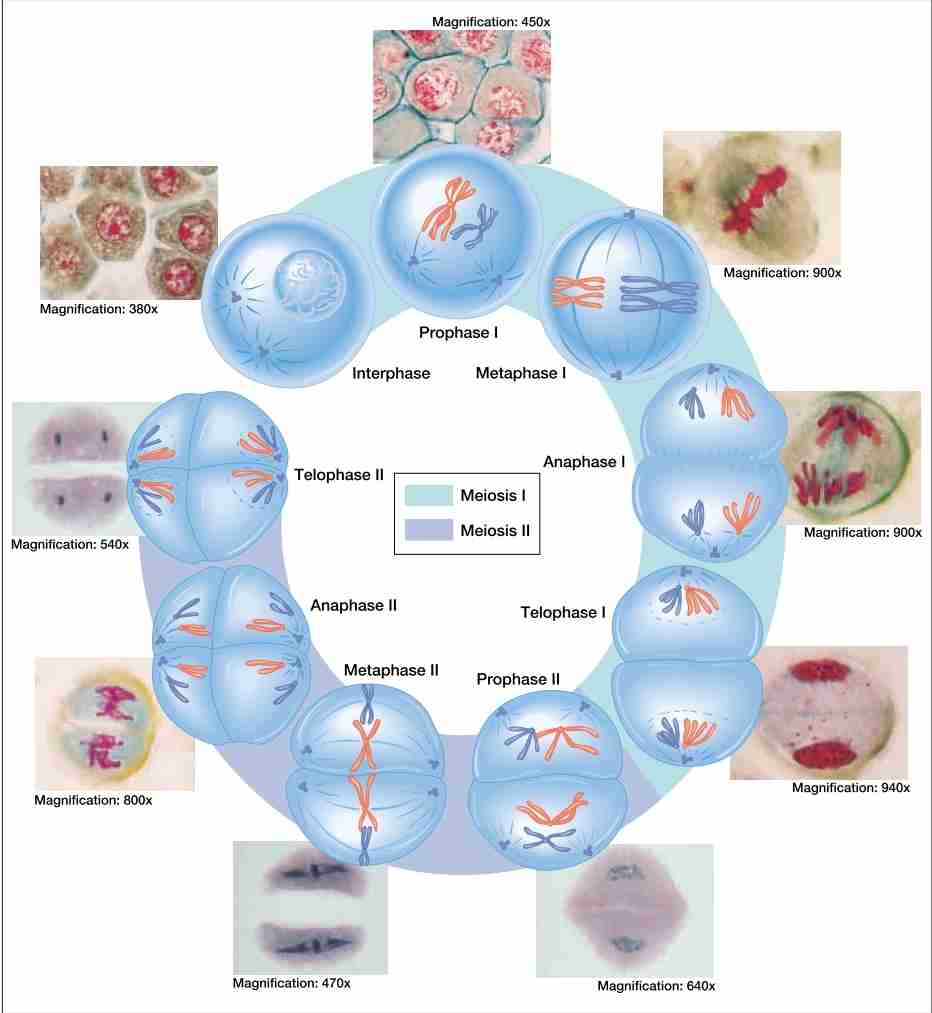
where does meiosis occur
in sex cells
synapsis
when 2 duplicated homologous chromosomes line up side by side
Chiasmata
the points of overlap where crossing over occurs
independent assortment
non-disjunction mistakes
when homologous chromosome fail to separate properly during cell division
mistakes during crossing over
duplication
deletion
inversion
translocation
duplication
when one chromosome ends up with two copies of a gene

deletion
the other chromosome would have no copies of that gene

inversion
the gene order on a chromosome switches
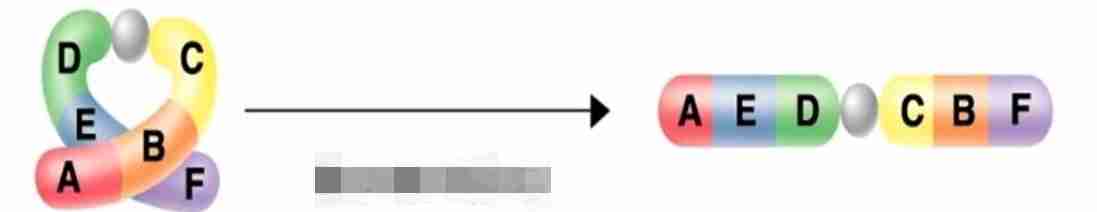
translocation
a gene from one chromosome ends up on a non-homologous chromosome

aneuploidy
the presence of an abnormal # of chromosomes in a cell
polyploidy
cells that have more than 2 sets of homologous chromosomes
would a human w/ polypIoidy survive
no
gametogenesis
the process where diploid gametes undergo meiosis to produce haploid gametes
polar body
a useless cell formed during oogenesis; it has chromosomes, but not much else
do all ovulated oocytes finish meiosis
oocytes only finish meiosis if they become fertilized
name of each cell that enters the body during spermatogenesis
spermatocyte
name of the cells that enter the body during oogenesis
oocyte
who determines the gender of a zygote
the father