APES Unit 7 Vocab
1/28
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Combustion
the process of a fuel type reacting with heat and oxygen which leads to chemicals, light and energy being released. Complete combustion releases non-toxic chemicals such as water vapor and heat however in majority of the cases incomplete combustion occurs
Industrial Smog
ndustrial smog is a type of smog that is formed by the emission of pollutants from industrial processes and the burning of fossil fuels. It is characterized by a thick, yellowish haze, and it is most commonly found in areas with heavy industrial activity
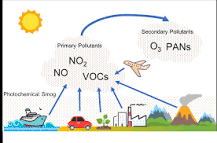
Photochemical Smog
Photochemical smog is a mixture of pollutants that are formed when nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react to sunlight, creating a brown haze above cities
Decibel
a unit of measurement used to quantify the intensity or loudness of sound
Acid rain
rain that has been made acidic by certain pollutants in the air
Ground Level Ozone
tropospheric ozone which is harmful to humans; forms when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) react in the presence of sunlight
Air Quality
the concentration of pollutants in the atmosphere; influenced by wind patterns, temperature changes, etc. so subjective to each region.
Noise Pollution
excessive or disturbing levels of sound that can negatively impact human health and well-being; measured in decibels
Clean Air Act
ACT that regulates all sources of air emissions. The 1970 CAA authorized the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to establish National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) to protect public health and the environment.
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
a U.S. governmental agency established in 1970 tasked with enforcing laws designed to protect the environment and public health.
Lead
toxic metal
Primary Pollutants
are those that are emitted directly from a source. Primary sources include internal combustion vehicles, wildfires, factories, coal-burning power plants, agriculture, and volcanoes
Secondary Polluants
have undergone a change from a primary pollutant. These changes are often due to the gasses interacting with water vapor and/or sunlight. Smog and acid precipitation are both examples of secondary pollutants
Volatile Organic Chemicals
They are emitted by a variety of sources, including industrial processes, paints, and cleaning products. VOCs are a primary pollutant that can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter. They can also have adverse effects on human health, including respiratory problems and cancer.
PANs (Peroxyacetyl Nitrates)
a family of compounds which result from photochemical reactions between contaminants released to the atmosphere by combustion of organic fuels
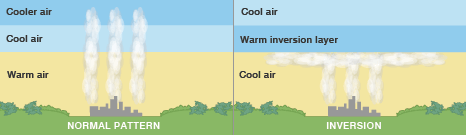
Thermal Inversion
Sick Building Syndrome
a condition where occupants experience acute health effects or discomfort while spending time in a particular building. The symptoms are often linked to poor indoor air quality
Particulate Matter
a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets that are suspended in the air. It is a primary pollutant that can have adverse effects on human health, including respiratory problems and cardiovascular disease. PM can be emitted by a variety of sources, including power plants, industrial processes, and transportation. It is classified by size, with being particles that are 10 micrometers or smaller in diameter, and being particles that are 2.5 micrometers or smaller in diameter. is particularly harmful because it is small enough to be inhaled and can penetrate deep into the respiratory system
Carbon Monoxide
a colorless and odorless gas that is produced by the incomplete burning of fossil fuels, such as gasoline and natural gas. It is a primary pollutant that can have serious health effects, including headaches, dizziness, and nausea. In severe cases, it can lead to coma and death.
Criteria Air Pollutants
air pollutants for which acceptable levels of exposure can be determined and for which an ambient air quality standard has been set. Examples include: ozone, carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and PM10 and PM2. 5.
Asbestos
A group of naturally occurring fibrous minerals used for insulation in buildings. Impact: All forms of asbestos are carcinogenic to humans.
Radon
occurs in areas where people have basements; uranium deposits as it decays eventually becomes radon
a radioactive gas that occurs naturally from the decay of uranium in soil, rocks, and water. It can seep into buildings and accumulate to dangerous levels, increasing the risk of lung cancer.
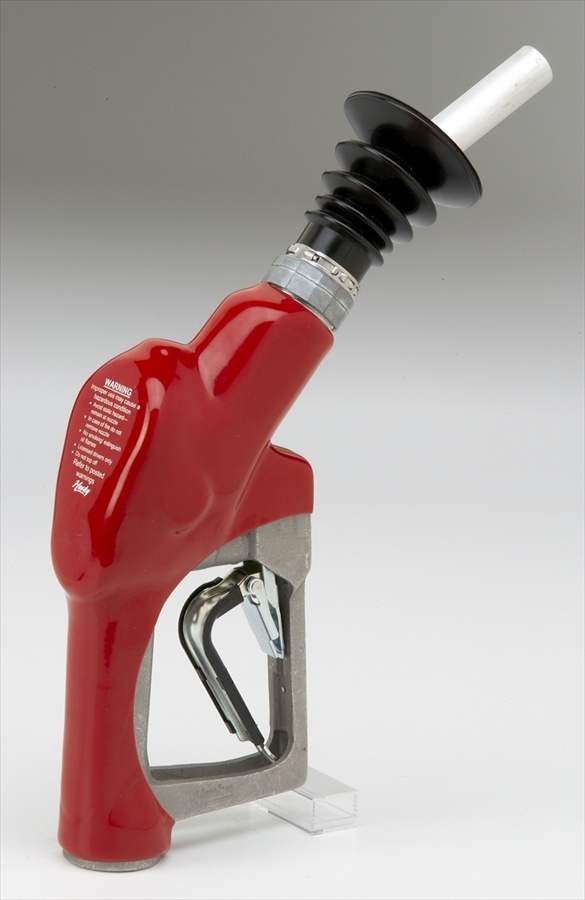
Vapor Recovery Nozzle

Catalytic Converter
an air pollution control device for internal combustion engines that converts pollutants in exhaust into less harmful molecules.
Wet/Dry Scrubbers
a way to mimic the cleansing benefits of rain; channel the exhaust through a chamber that is spraying scrubbing liquid (usually water). Particulates and dissolved gasses are caught in the liquid which is then filtered.
Dry scrubbers use dry reagent instead of water
electrostatic precipitator
~; A device used for removing particulates from smokestack emissions. The charged particles are attracted to an oppositely charged metal plate, where they are precipitated out of the air.
Sulfur Dioxide
a gas that is produced by the burning of fossil fuels that contain sulfur, such as coal and oil. It is a primary pollutant that can contribute to the formation of particulate matter and acid rain.
desulfurization
Nitrogen oxides
a gas that is produced by the burning of fossil fuels and the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen in the atmosphere. It is a primary pollutant that can contribute to the formation of ground-level ozone and particulate matter.
Limestone
*