BMS 110: Unit 2
1/215
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
216 Terms
What are the 3 components of DNA?
1. Sugar (Deoxyribose)
2. Phosphate Group
3. Nitrogen-containing bases (A, T, C, G)
What is purine?
contains 2 benzene rings
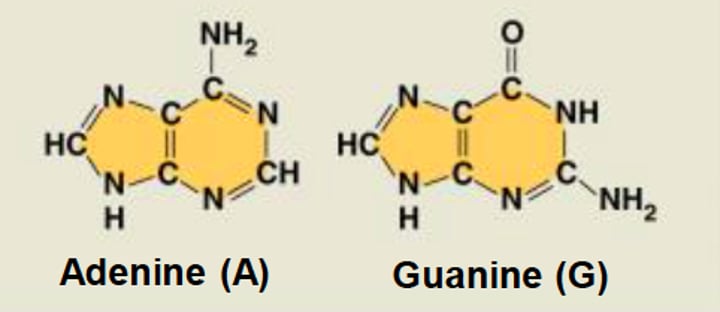
What is pyrimidine?
contains 1 benzene ring
*Uracil is only in RNA*
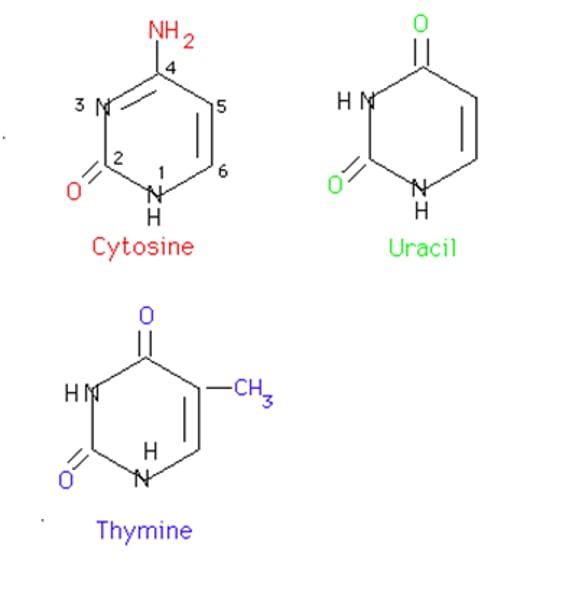
How many hydrogen bond are there between Adenine and Thymine?
2
How many hydrogen bonds are there between Cytosine and Guanine?
3
What is a gene?
nucleotide sequence in DNA molecules that codes for specific polypeptide chains or RNA; segment of DNA in a chromosome
How many genes are in the human body?
23,000 genes (about 3 billion pairs)
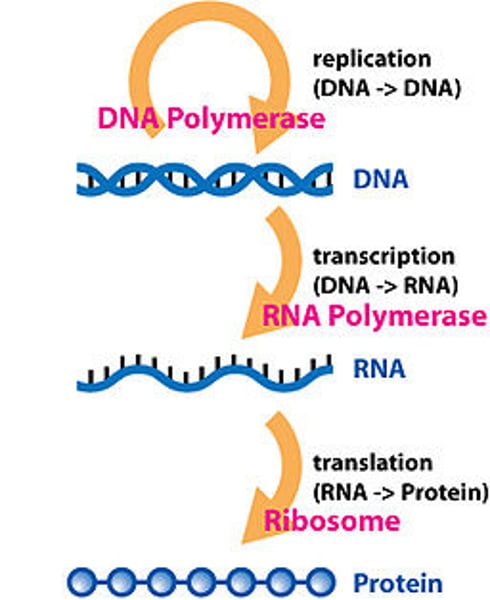
What is the Central Dogma?
DNA -transcription-> RNA -translation->Protein
Who discovered the the double helix structure of DNA?
Watson and Crick (stolen from Rosalind Franklin)
What are the two forms of nucleotides?
purine and pyrimidine
What is a chromosome?
DNA and protein combined; DNA molecule that has been divided
How many chromosomes do human have?
23 pairs (46 individual)
How do we get our 46 (23 pairs of) chromosomes?
23 from the egg (mother) and 23 from the sperm (father)
What are autosomes?
chromosome pairs 1-22
What is the 23rd pair or chromosomes called?
the sex chromosomes
What is DNA replication?
The process of copying DNA prior to division
What is a helicase?
enzyme that breaks the H bonds between nucleotides in order to unwind a DNA molecule
What does the DNA polymerase do in DNA Replication?
assembles new strands of nucleotides onto the original DNA strand
How does the leading strand move?
moves from the end to the replication fork
How does the lagging strand move?
moves from the replication fork to teh end?
DNA is considered to be what type of process?
Semiconservative
What is a gene mutation?
small-scale change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene
What is RNA comprised of?
1. Sugar (Ribose)
2. Phosphate group
3. Nitrogen containing bases (A, U, G, C)
What is transcription?
using genes as the template for RNA synthesis
Where does transcription take place?
nucleus
What is the job of an RNA polymerase?
has to be put on the RNA at the promoter region and joins nucleotides together until a termination sequence is reached (moves 5' -> 3')
What happens to introns?
they go IN the TRash; removed by RNA splicing
What happens to exons?
they are EXpressed; sequences for proteins
What happens to matured mRNA?
moves from the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm or on the rER for protein production
What occurs during gene transcription?
each cell determines which genes are active and inactive, so some genes are turned on at certain times, some turn off permanently before birth , or some are switched on and off throughout a person's life.
What are regulatory proteins?
proteins that bind with non-coding DNA sequences which can affect the transcription of neighboring genes
What are the types of regulatory proteins?
activators and repressors
What do activators do?
encourage transcription
What do repressors do?
stop transcription
What is mRNA?
messenger RNA that carries DNA genes info out of the nucleus and to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm or rER
What is a codon?
- 3 nucleotide bases on mRNA
- 64 make up the genetic code
- complimentary to the DNA gene info
What is the function of codons?
coded in groups of 3 for 1 of 20 amino acids; most amino acids have more than 1 codon.
What is the function of a start codon?
establishes the "reading frame" for translation
Ex. AUG
What is the function of a stop codon?
indicates where translation stops
True or False: All mRNA becomes proteins?
FALSE
What is tRNA?
transfer RNA that "decodes" the mRNA
What is the function of the tRNA?
deliver the "correct" amino acid to the correct location along the mRNA
What is rRNA?
ribosomal RNA is a component of catalytically active ribosome enzymes
What is the function of rRNA?
combined with protein to make the two subunits of ribosomes; act as temporary workbench for the production of protein during translation
What are the stages of translation?
1. initiation
2. elongation
3. termination
What happens during the initiation stage of translation?
tRNA with start codon attached binds to mRNA codon, then AUG binds with small ribosome subunit, large ribosome subunit binds to form the initiation complex
What happens during the elongation stage of translation?
peptide bonds from between incoming amino acids
What happens during the termination stage of translation?
stop codon is reached, new polypeptide is detached
What is a polysome?
cluster of ribosomes all translating the same mRNA
What are the 3 sites of the ribosome?
A, P, E
What occurs at site A of a ribosome?
entry site form incoming tRNA
What occurs at site P of a ribosome?
holds the growing polypeptide chain
What occurs at site E of a ribosome?
exit site of the tRNA
What happens when the stop codon reaches the A site of the ribosome?
a release factor binds to the A site, a water molecule is added to the carboxyl terminus of the newly forming polypeptide, and the ribosomal subunits are dissociated from the mRNA
How is DNA repaired?
DNA polymerase and other enzymes
How can damage to DNA occur?
polymerase, environment, and free radicals
What are thymine dimers?
2 Thymine try to hydrogen bond to each other even though they are already attached by the backbone; causes a ^
What are the 4 types of gene mutation?
1. base-pair substitution
2. deletion
3. insertion
4. transposable
What occurs in a base-pair substitution mutation?
the incorrect nucleotide is pared with an exposed base during DNA replication; could cause the translation of a new amino acid
What occurs in a deletion mutation?
a base is lost causing a shift in the reading frame
What occurs in a insertion mutation?
a base is added causing a shift int he reading chain if 1-2 are added, but adds an amino acid to the chain if 3 bases are added
What occurs in a transposable mutation?
bits of DNA can be moved from one location to another in the same or in a different DNA molecule
What does it mean if a cell is diploid?
There are two sets of chromosomes (2n)
What is a sister chromatid?
Pair of duplicated chromosomes
What are homologous chromosomes?
corresponding paired chromosomes (not identical)
What is the life-cycle?
series of reoccurring events in which individuals grow, develop, maintain themselves, and reproduce.
What are the two types of cell division?
mitosis and meiosis
What is mitosis?
the division of somatic cells in order to grow, replace dead or worn out cells, and repair tissue
What is meiosis?
division of germ cells in order to produce gametes for the first stage of sexual reproduction
What are the stages of the cell cycle, and what occurs at each stage?
1. Interphase (longest phase)
- G1: cell growth
- S: DNA chromosomes are replicated
- G2: preparation for cell mitosis
2. Mitosis
3. Cytokinesis: cytoplasm divides
What are the 4 stages of mitoosis?
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
What occurs during Prophase?
- coiling and condensing of chromosomes into thick rods
- microtubules begin to form
What occurs during Metaphase?
- pre-metaphase
- nuclear membrane breaks apart
- microtubules penetrate the nuclear region
- microtubules attach to the centromere of the chromosomes
- duplicated chromosomes align at the metaphase plate (midway) between the poles of the cell
What occurs during Anaphase?
- sister chromatids spit to become independent chromosomes
- pulled by the microtubules towards the pole regions
spindles elongate, pushing poles farther apart
What occurs during Telophase?
- chromosomes are no longer attached to the spindles
- chromosomes are threadlike, once again forming chromatin
- nuclear envelope forms around each cluster
What occurs during cytokenesis in mitosis?
the cytoplasm divides so the two, identical, new cells are no longer touching; cleavage furrow
What is fertilization?
combines the sperm and egg to produce the first cell of the new individual (zygote)
What are the stages of meiosis?
Meiosis I
1. Prophase I
2. Metaphase I
3. Anaphase I
4. Telophase I
Meiosis II
5. Prophase II
6. Metaphase II
7. Anaphase II
8. Telophase II
Which meiosis is the most similar to mitosis?
meiosis II
What kind of division is meiosis said to be?
reductional because it reduces the number of chromosomes to a haploid number
What is does it mean if a cell is haploid?
there is only one copy of chromosomes (n)
What occurs during meiosis I?
1. Prophase: each chromosome has two sister chromatids; crossing over
2. Metaphase: homologous chromosomes move to central plain in pairs, oriented to opposite poles
3. Anaphase: separation of paired chromosomes (disjunction) and separated homologues move towards opposite poles (independent assortment)
4. Chromosomes reach poles and daughter cells are separated by membranes, each chromosome still has 2 sister chromatids
What occurs during meiosis II?
1. Prophase: sister chromatids are attached by spindle fibers from opposite poles
2. Metaphase: Chromosomes align at equatorial plane
3. Anaphase: Chromatids move towards opposite poles (disjunction)
4. Separated chromatids (now chromosomes) are gathered at opposite poles and each daughter cell contains a haploid set of chromosomes
What occurs during cytokinesis during meiosis?
Cytoplasm divides into 4, not identical, daughter cells
What is crossover?
non-sister chromatids break at the same place along their length and exchange corresponding segments
What is the implications of crossover?
daughter cells are unique; genetic diversity 2^23
What is epigenics?
genes may have different chemical forms and can be passed on to offspring
What is spermatogenesis?
the process of created sperms from spermatogonia
What is the process of spermatogenesis?
1. Spermatogonia go through mitosis to create two daughter cells
- one cell remains a stemm cell
- one cell (spermatocyte) undergoes meiosis to make sperm
2. After puberty, spermatocytes continually undergo meiosis to make sperm
3. Spermatozoa are made in the 900 seminiferous tubules of the testes
- producing about 300 million sperm/day
4. Sperms finish maturing in the epididymis
What is oogenesis?
the process of making eggs
What occurs during oogenesis?
1. meiosis begins in embryos
2. division stops part way through prophase I
3. after puberty, 1 egg (oocyte) is ovulated each month
4. oocyte progresses through meiosis I and then stops
5. meiosis II only occurs when the egg is fertilized
*Occurs in the ovaries
How do we get a new organism by sexual reproduction?
- haploid sperm + haploid egg = diploid zygote
- haploid sperm and egg are made through meiosis
- diploid zygote undergoes mitosis to make more cell which create a new organism
What are the 6 C's of reproduction?
- Chromatin: DNA and protein combined
- Chromosomes: DNA molecule with protein attached
- Chromatids: chromosome and its copy
- Centrosome: 2 centrioles
- Centrioles: poles of the cell
- Centromere: pinched in region of a sister chromatid where the microtubules attach
What is carcinogenesis?
process by which cells become cancer cells
What is a chromosomal mutation?
larger region of chromosomes is changed; affects multiple genes
What are genome mutations?
affects chromosome number (Ex. monosomy & trisomy)
What are the 4 types of point mutations?
1. frameshift
2. silent mutation
3. missense mutation
4. nonsnese mutation
What is a silent mutation?
nucleotide in codon is changed but codon still encodes the same amino acid
What is a missense mutation?
nucleotide in codon is changed so it encodes a different amino acid
What is a nonsense mutation?
nucleotide in codon is changed so it encodes a STOP codon