Module 1-4A
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
neurons communicate via electrical and chemical impulses across ______
synapses
cell body / soma jobs
sends / receives messages
makes proteins and molecules
maintenance of cell and growth
cell body / soma location
most located in the CNS
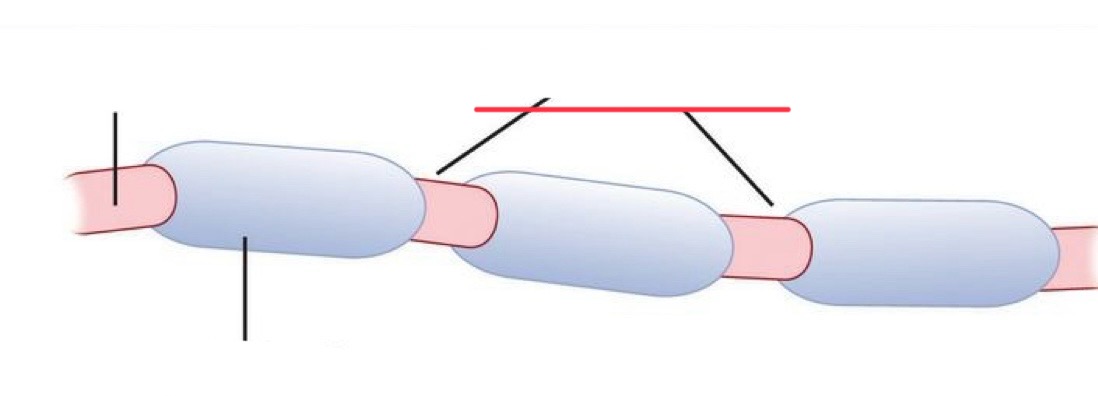
dendrites job
receive impulses, primarily from axons from other neurons
axon jobs
specialized to carry messages
myelin sheath jobs
speeding message transmission
myelin sheath in the CNS is created by ____
oligodendrocytes
myelin sheath in the PNS is created by ____
Schwan cells
axon terminal / end bouton jobs
end projection of the axon that releases neurotransmitters into the synapse
cell membrane (aka phospholipid bilayer) attributes
proteins span that layer forming channels or receptors
molecules an pass through these channels when they are opened
charged particles (ions)
examples of ions
calcium, sodium, etc.
electrical characteristics of neurons
under “rest” conditions, there is a difference in electrical charge between the inside of the cell body and the extracellular fluid
a “voltage difference” across the cell membrane, due to the distribution of charged ions inside vs. outside the cell body
at rest, there are more _______ ions outside the cell body
positive
at rest, there are less _______ ions outside the cell body
negative
the voltage inside the cell body is ____ relative to outside
negative
resting voltage inside the cell body
-70 mV
why is the resting voltage inside the cell body negative?
moves in two ways:
electrostatic gradient
concentration gradient
electrostatic gradient (movement inside the cell body)
ions tend to move down electrostatic gradient
change wants equilibrium, the positive charges want negative charges and vice versa
concentration gradient (movement inside the cell body)
ions flow from higher to lower concentration
__ mostly outside the cell
Na+
__ mostly inside the cell
K+
membrane is ___ to K+ than Na+
leakier
more ___ ions leave the cell interior than get in, net result is the interior of the cell body at rest is ____ charged relative to the exterior
positive, negative
how do cells generate an electrical signal
all living cells are polarized
cells have a semi-permeable membrane
unlike other living cells, neurons can alter polarization for brief period of time (aka action potential)
what does it mean to have a polarized cell
positive or negative charge
neurons are ____ charged at rest
negatively
when charged particles (ions) cross the semi-permeable membrane, ___
it changes the charge of the cell
what is an action potential?
all or nothing event where the neuron rapidly changes its resting electrical potential from negative to positive, then back to negative again
action potential generation
action potentials are generated when the neuron reaches a threshold voltage, initiating conduction down the length of the axon
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential (EPSP)
depolarization within the dendritic zone (in the soma where action potential might happen)
travels through this zone to reach the axon
there is a brief interval at the end of the voltage change during which the cell is ____
hyperpolarized (in the refractory period)
what happens when the cell is hyperpolarized (refractory period)
the negative intracellular potential is more negative than it is at rest
action potentials are generated at the ____
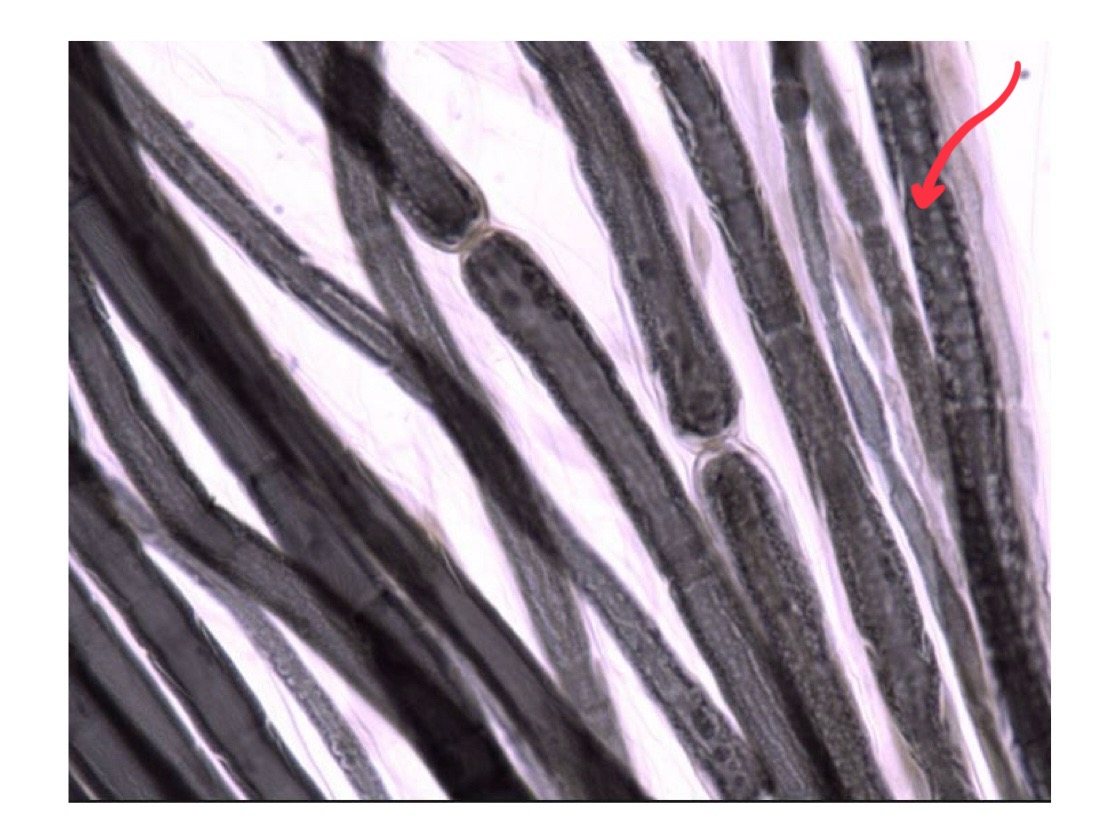
nodes of ranvier
nodes of ranvier
“jumps” between unmyelinated axon sections
action potential speeds
narrow diameter = slow
wide diameter = faster
unmyelinated = slow
myelinated = fast
action potential failure: tetrodoxin
blocking of sodium channels
looks like sodium enough to get to channel but can’t fit
membrane can’t depolarize
causes health concerns
classic tetrodoxin story
sailors ate pufferfish which are poisonous
multiple sclerosis
failure of the action potential
scars in nervous tissue
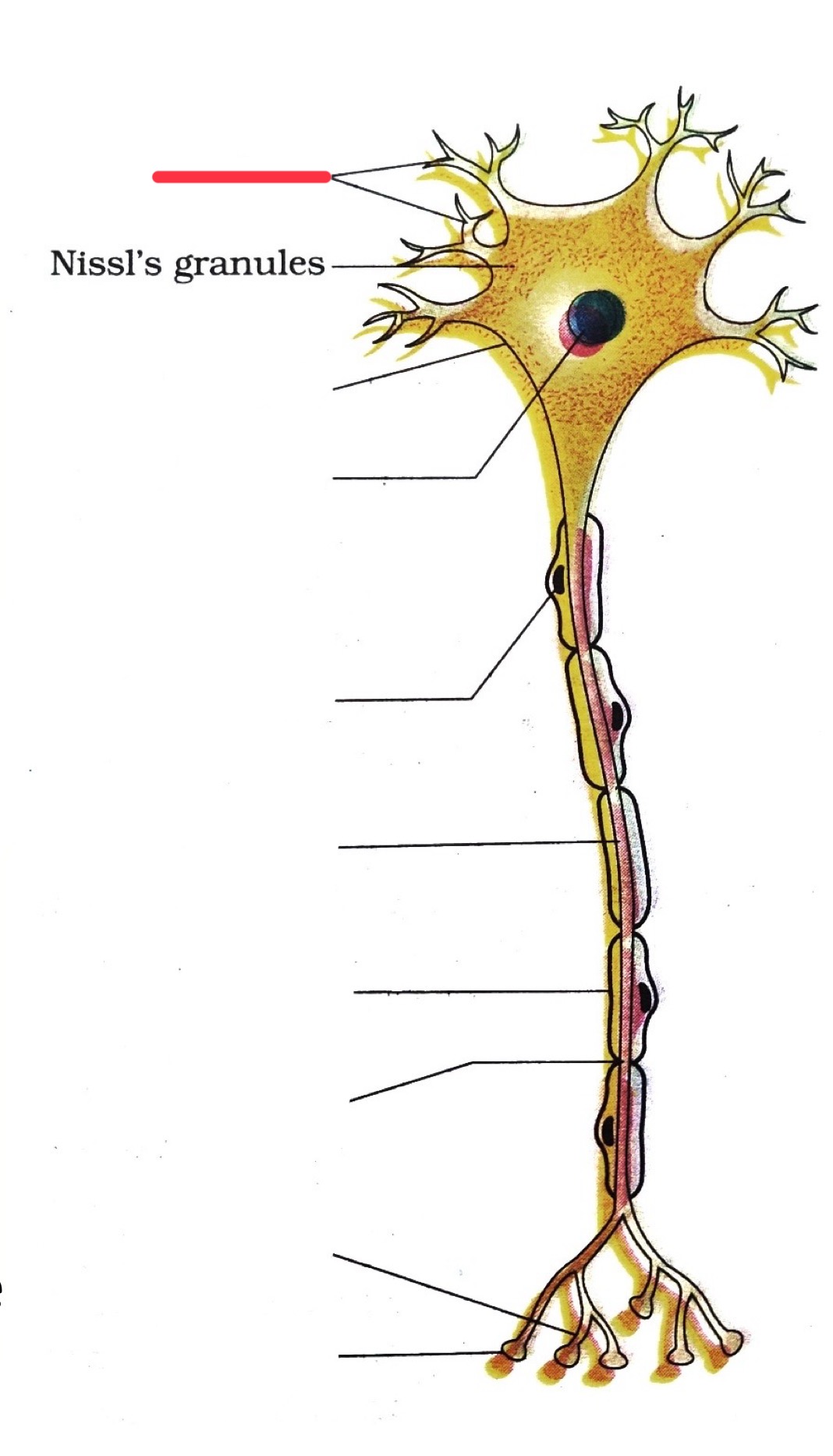
dendrites
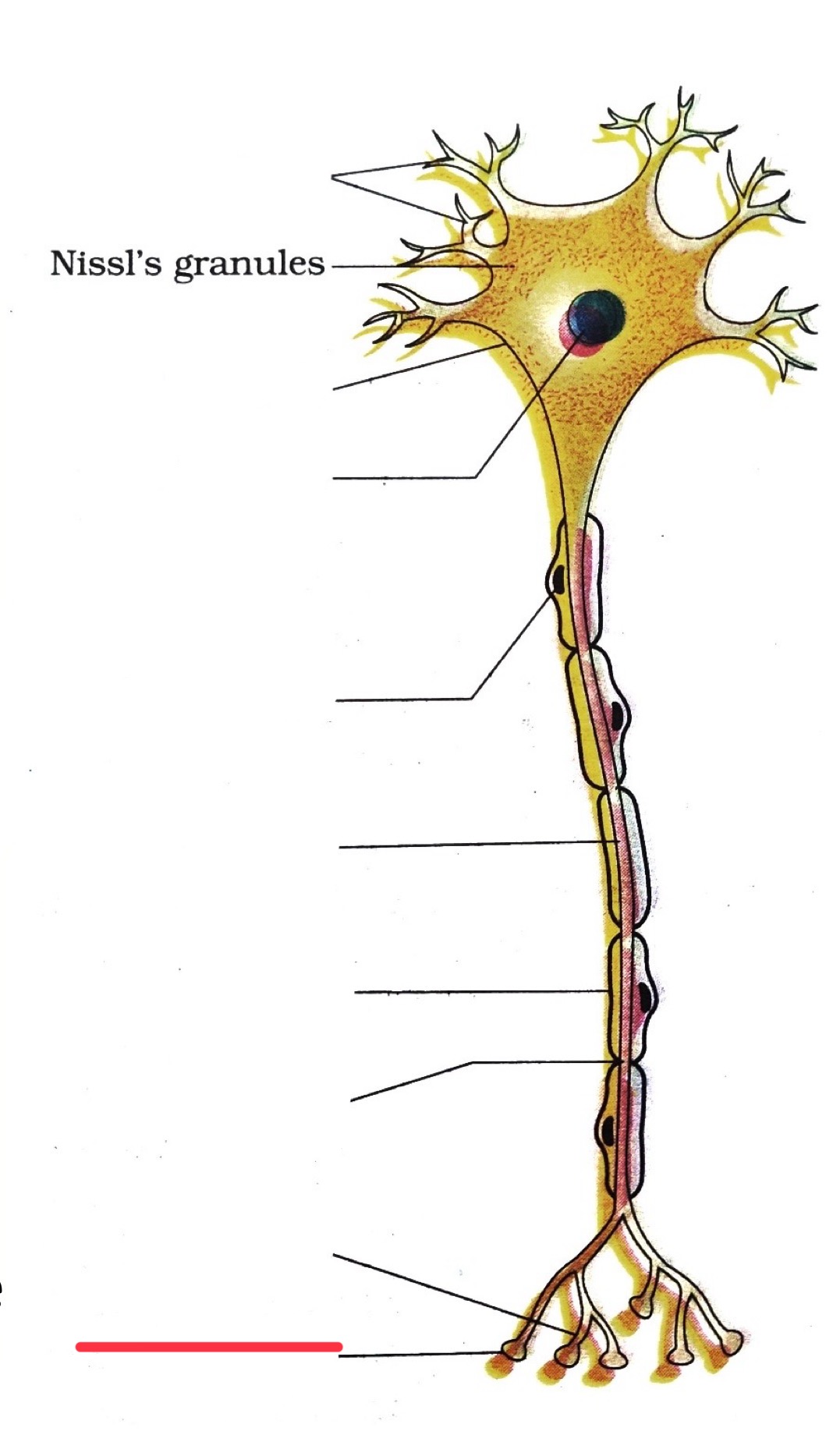
end bouton
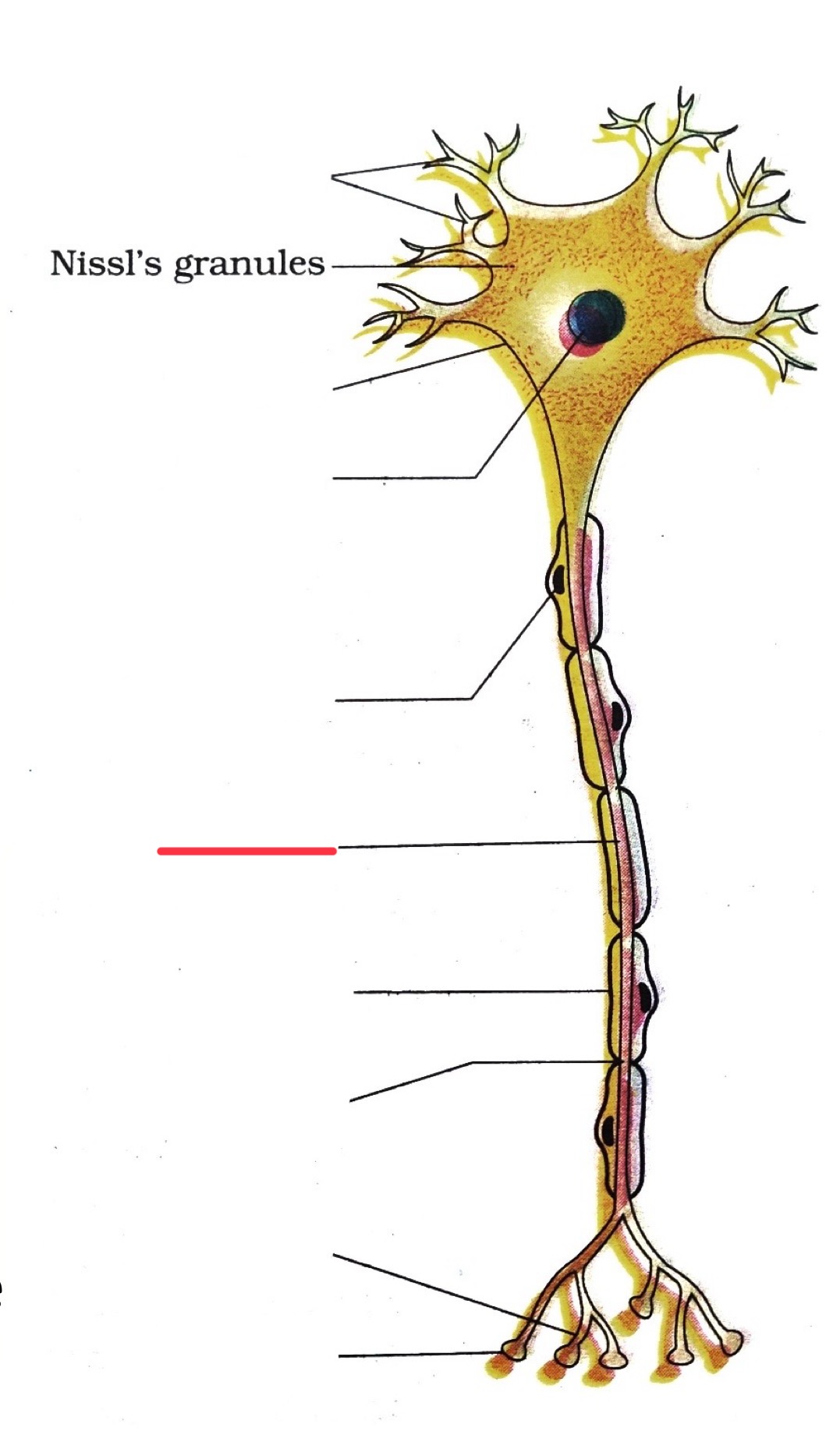
axon
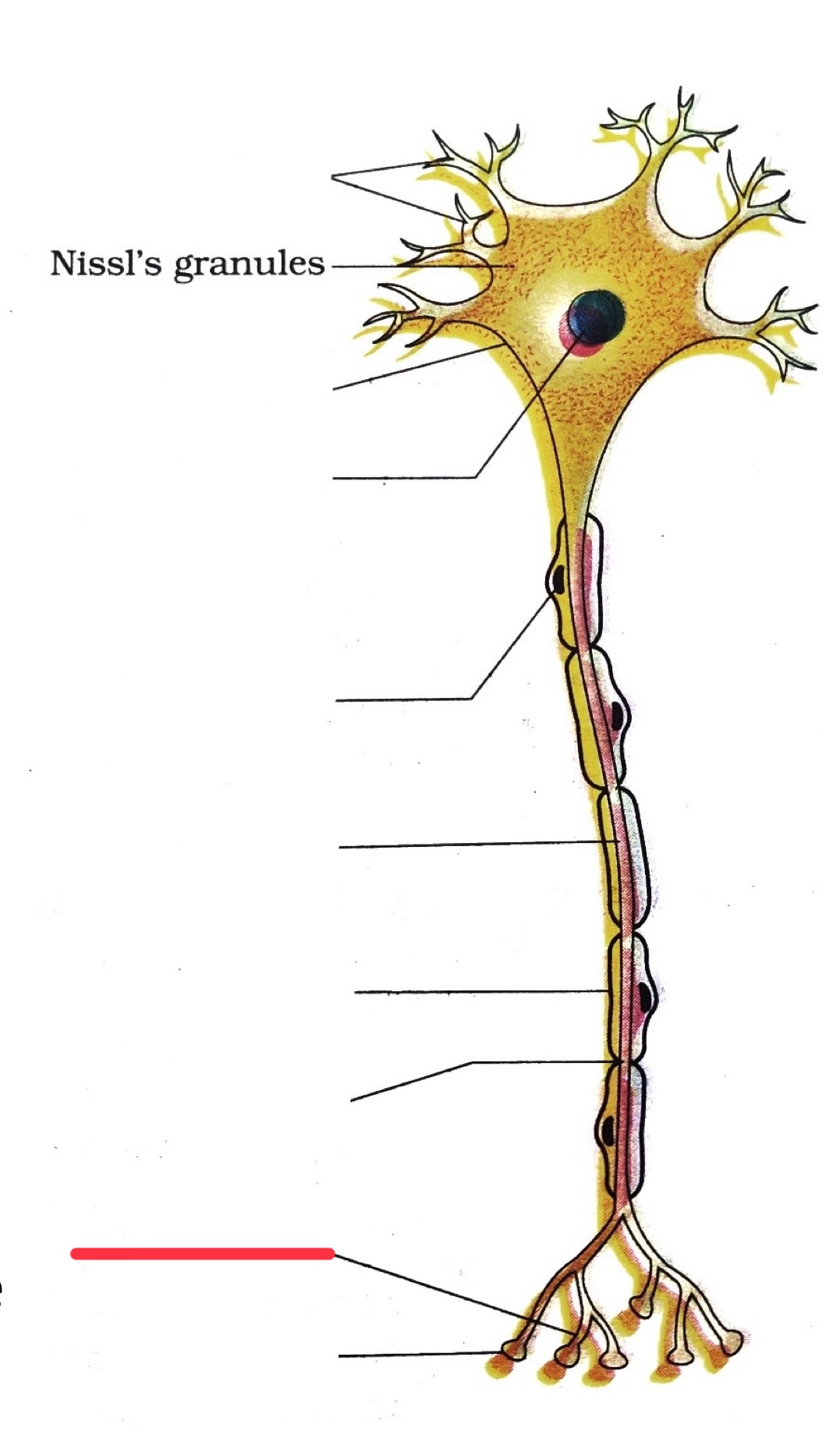
axon terminal
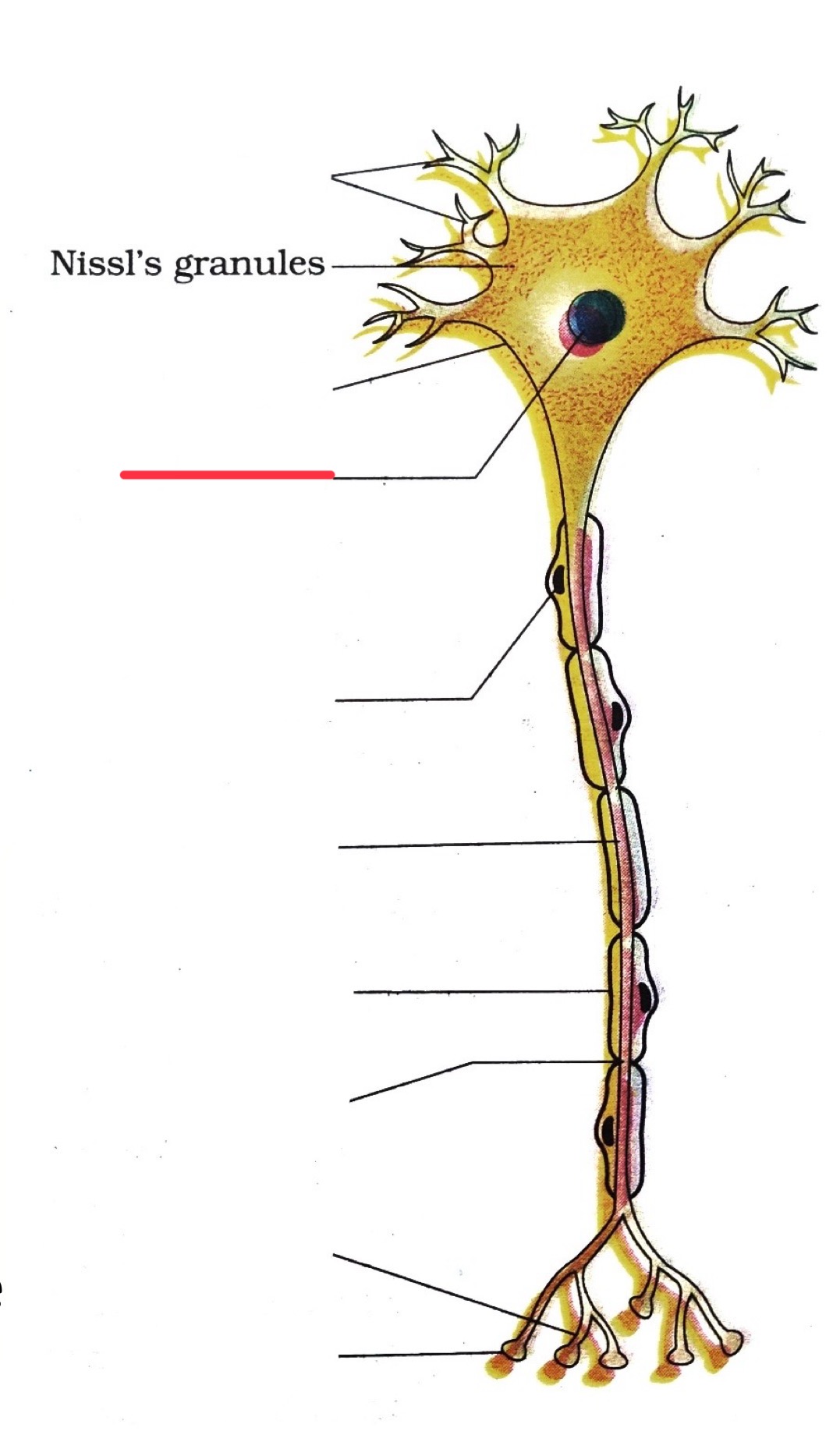
nucleus
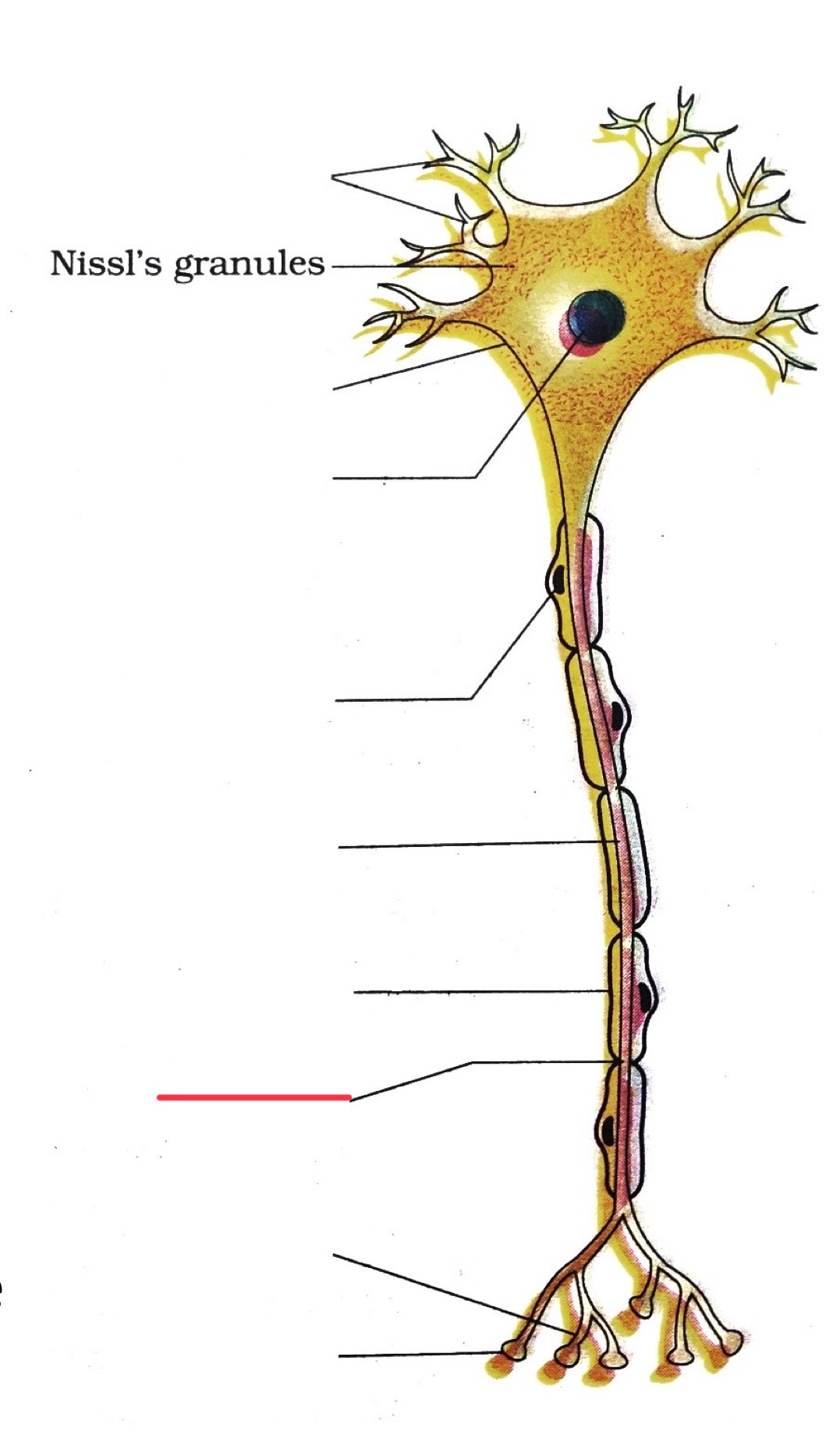
node of ranvier
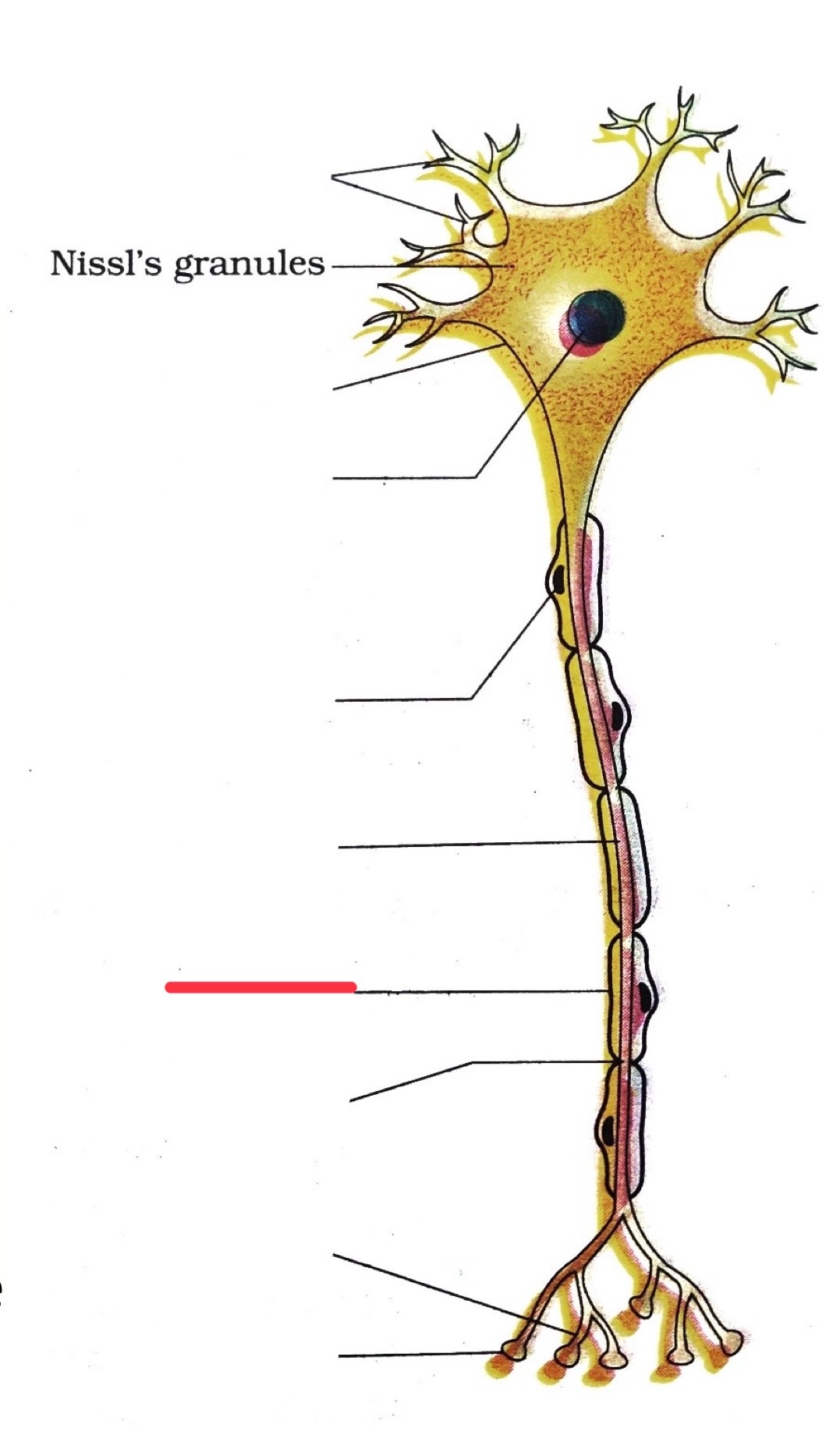
myelin sheath
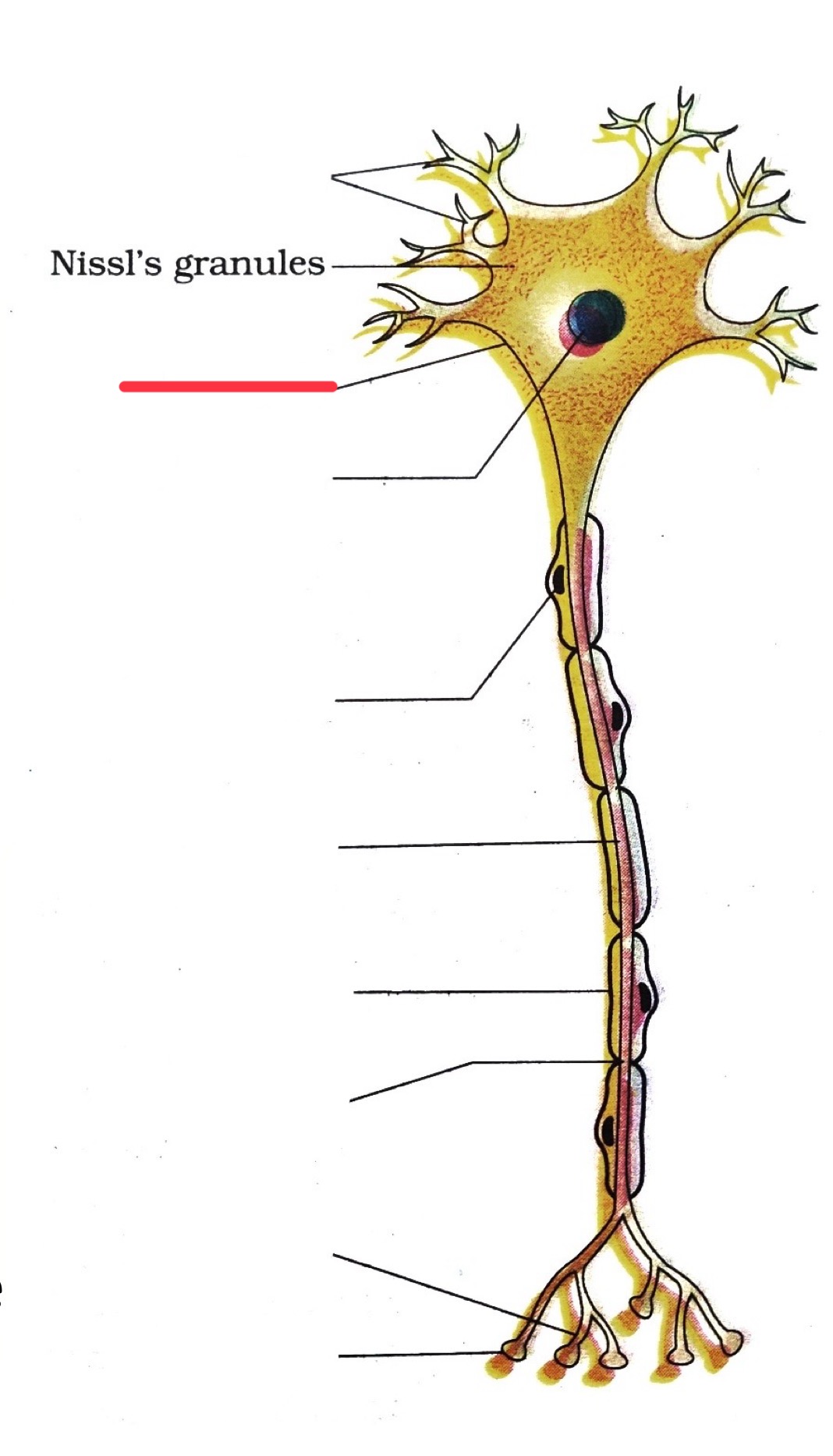
cell body
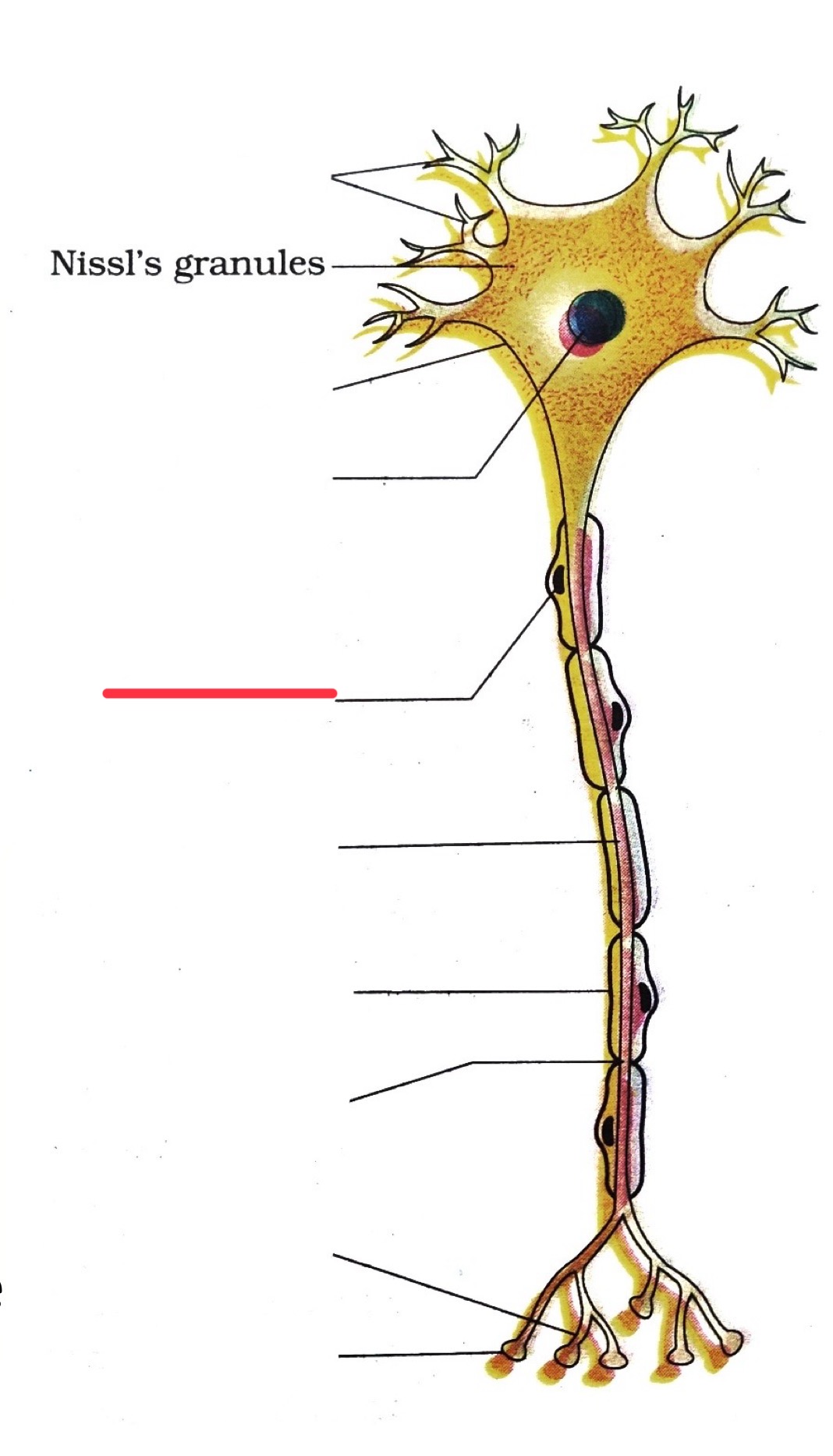
schwann cell
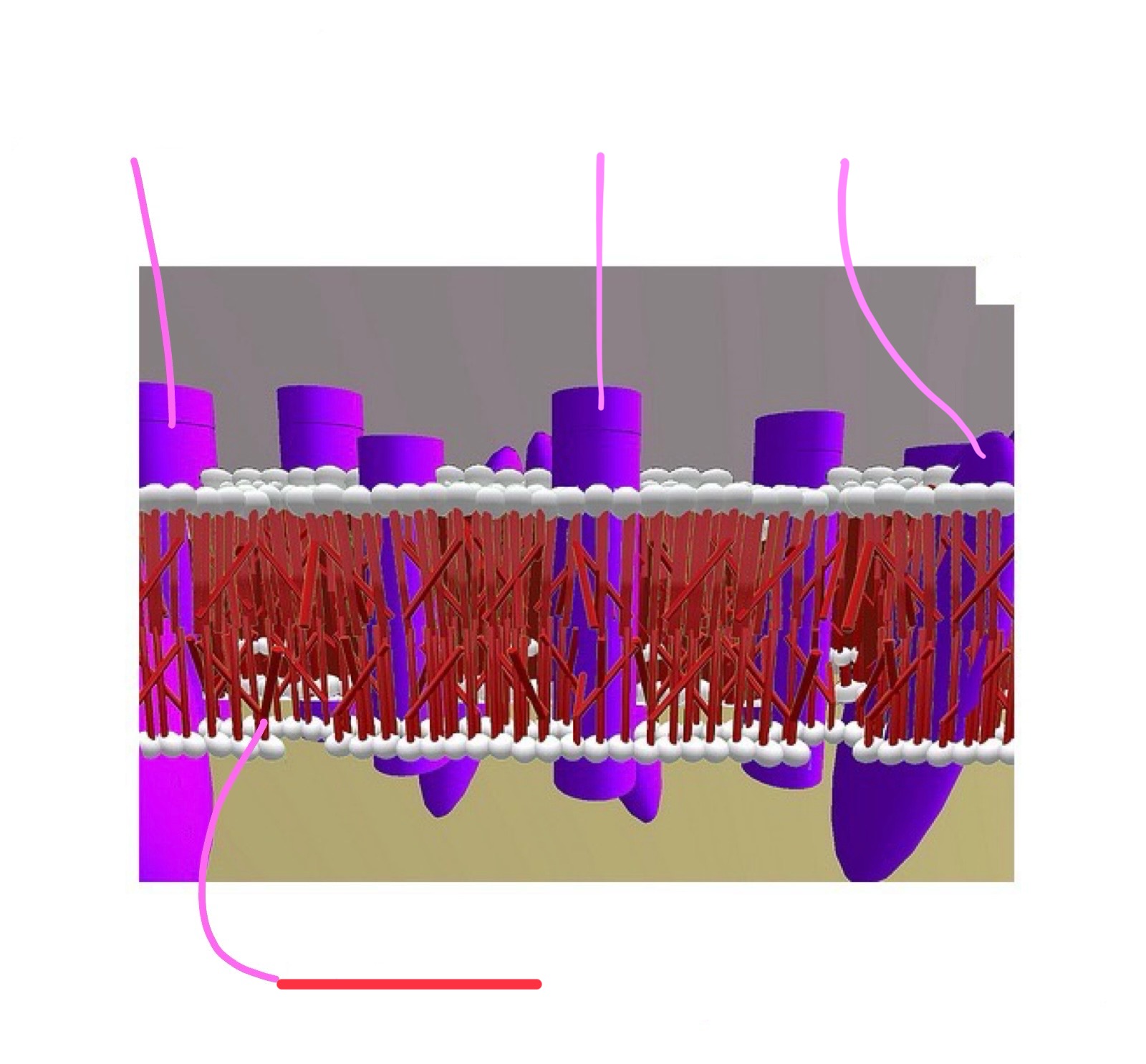
cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
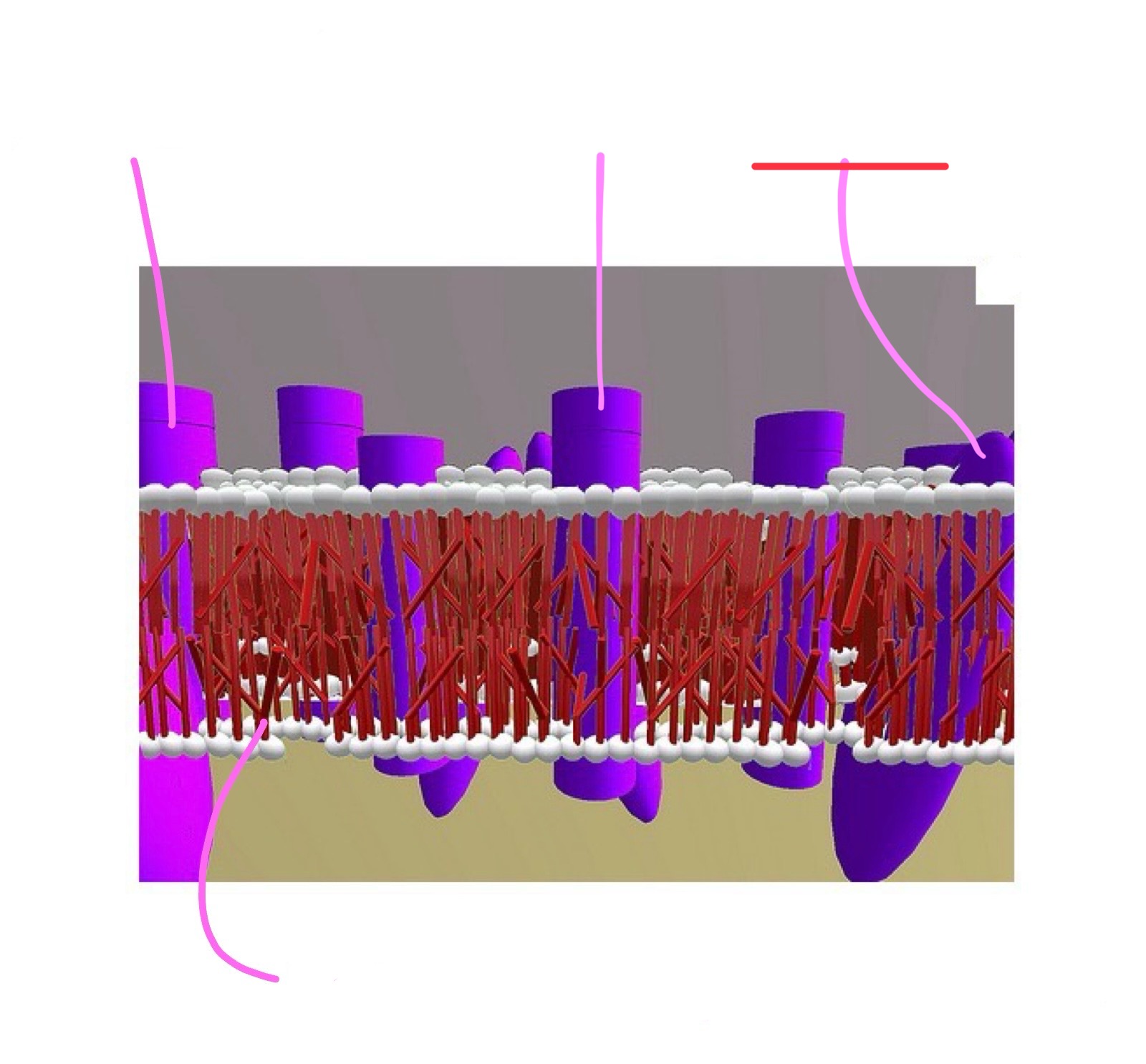
closed channel
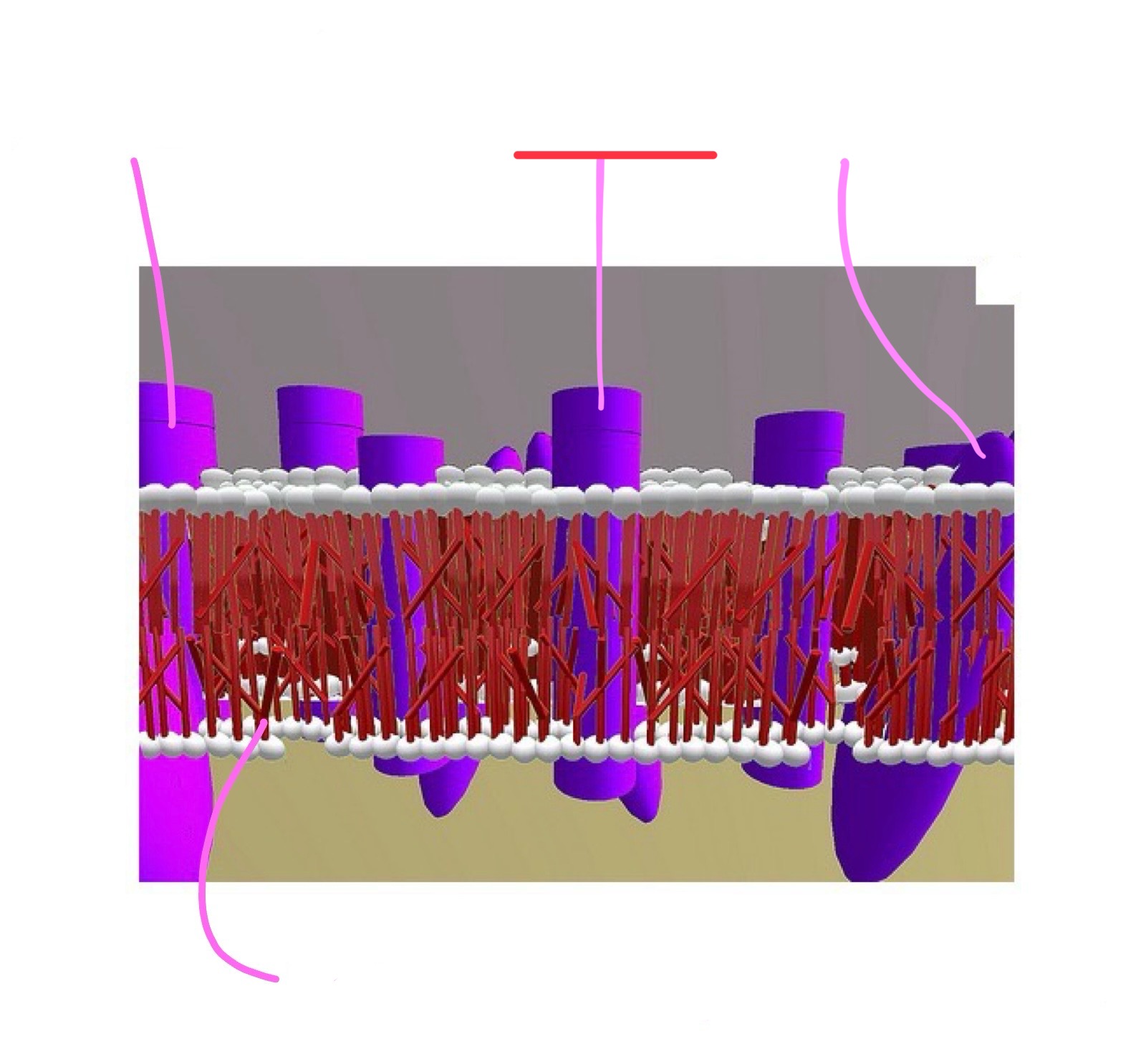
open channel
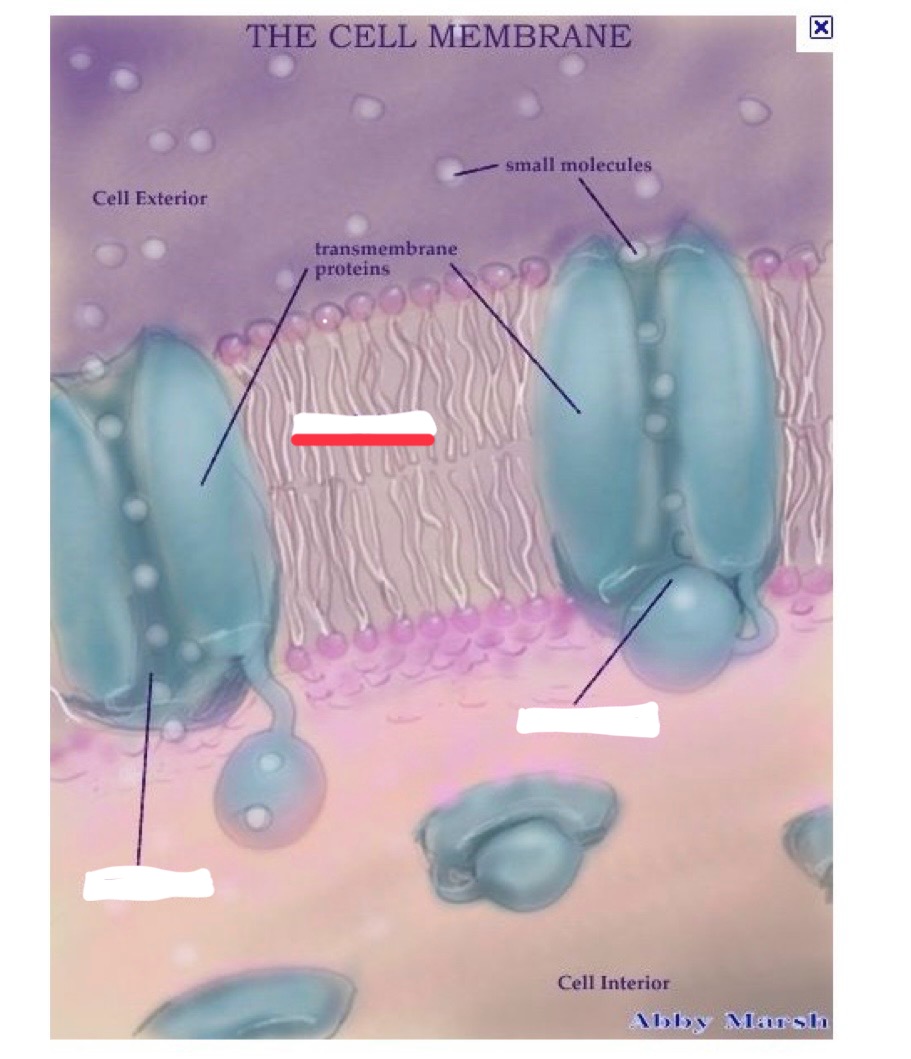
cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer)
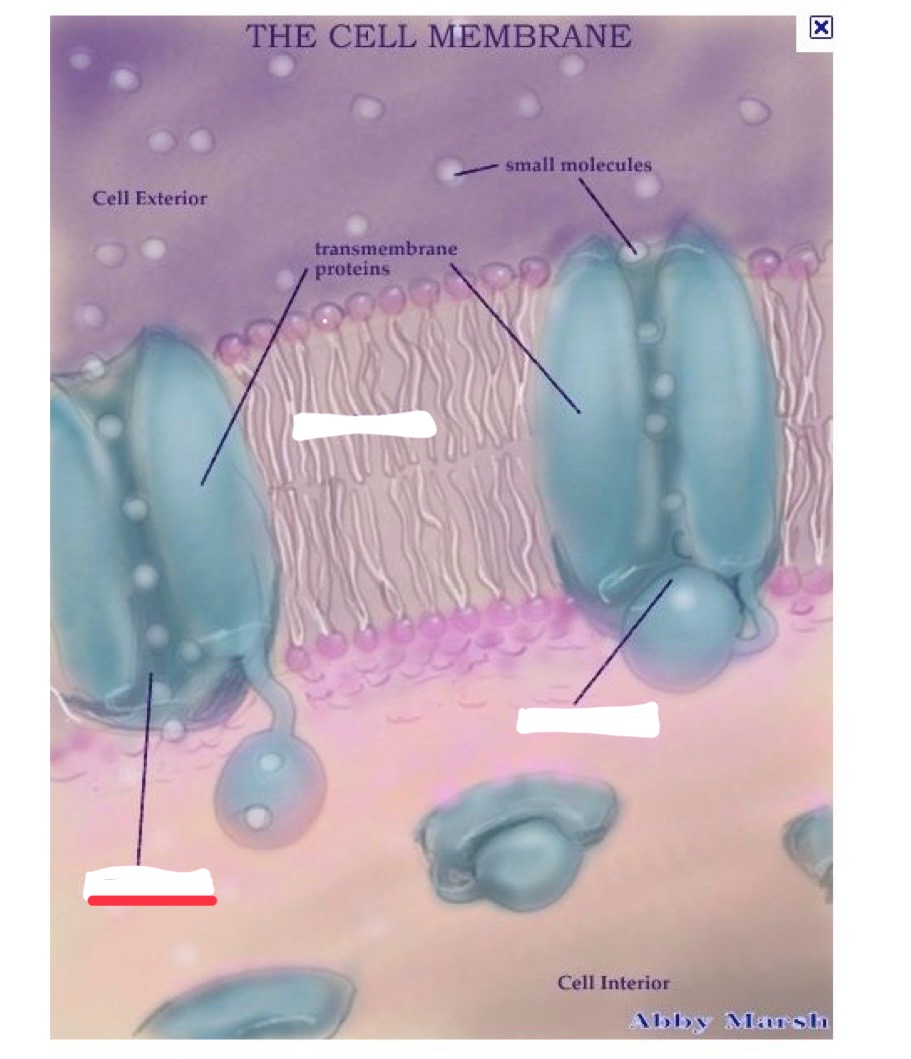
open ion channel
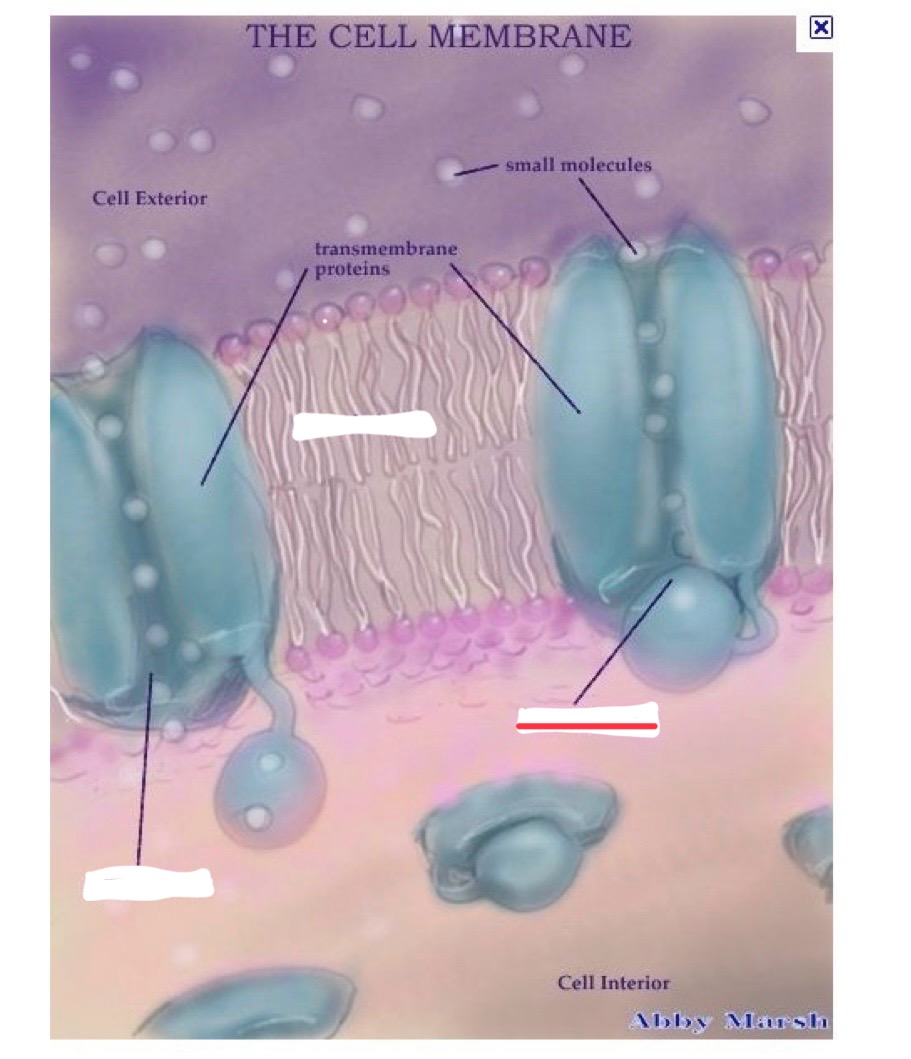
closed ion channel
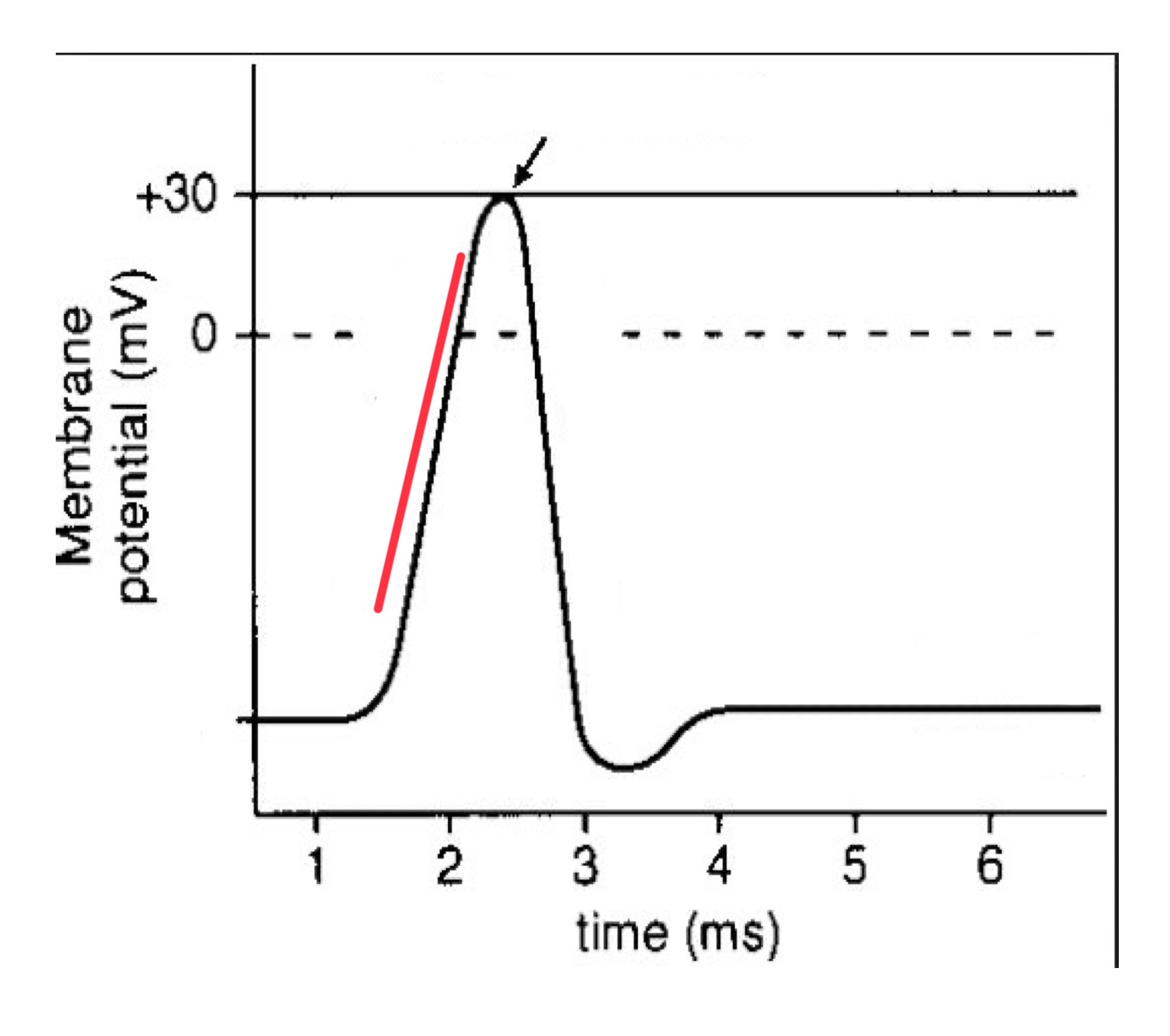
depolarization
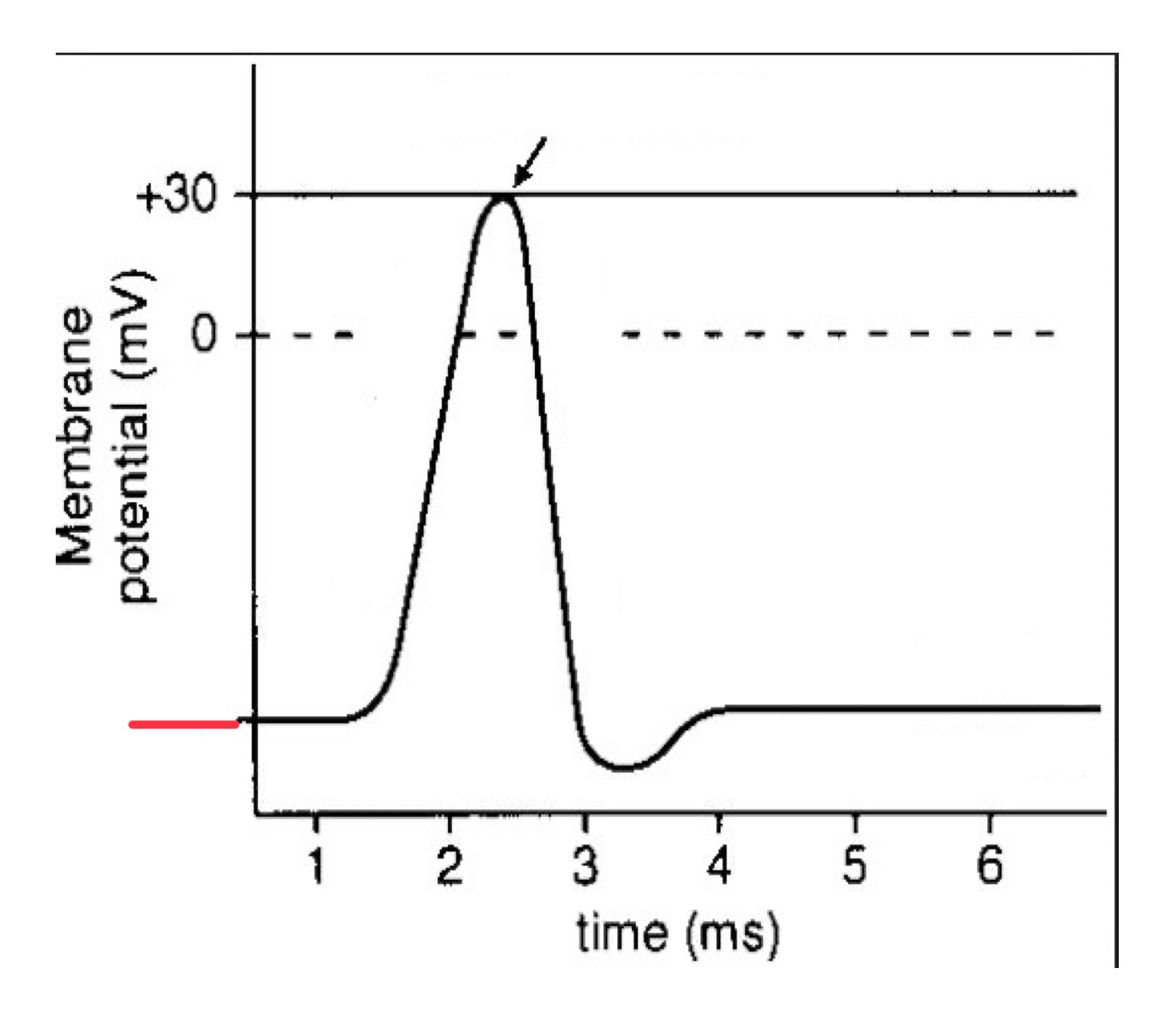
-70 mV
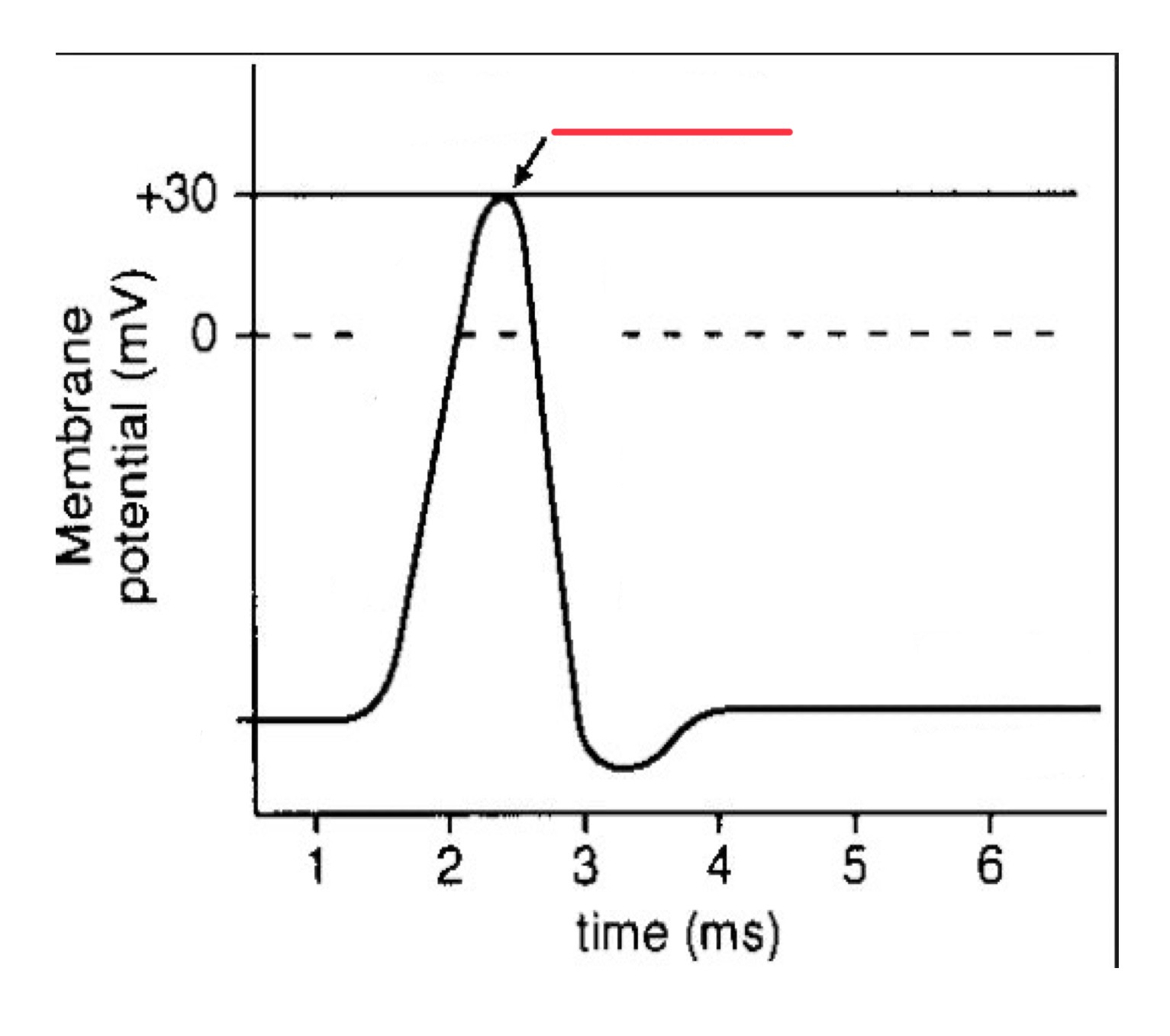
action potential
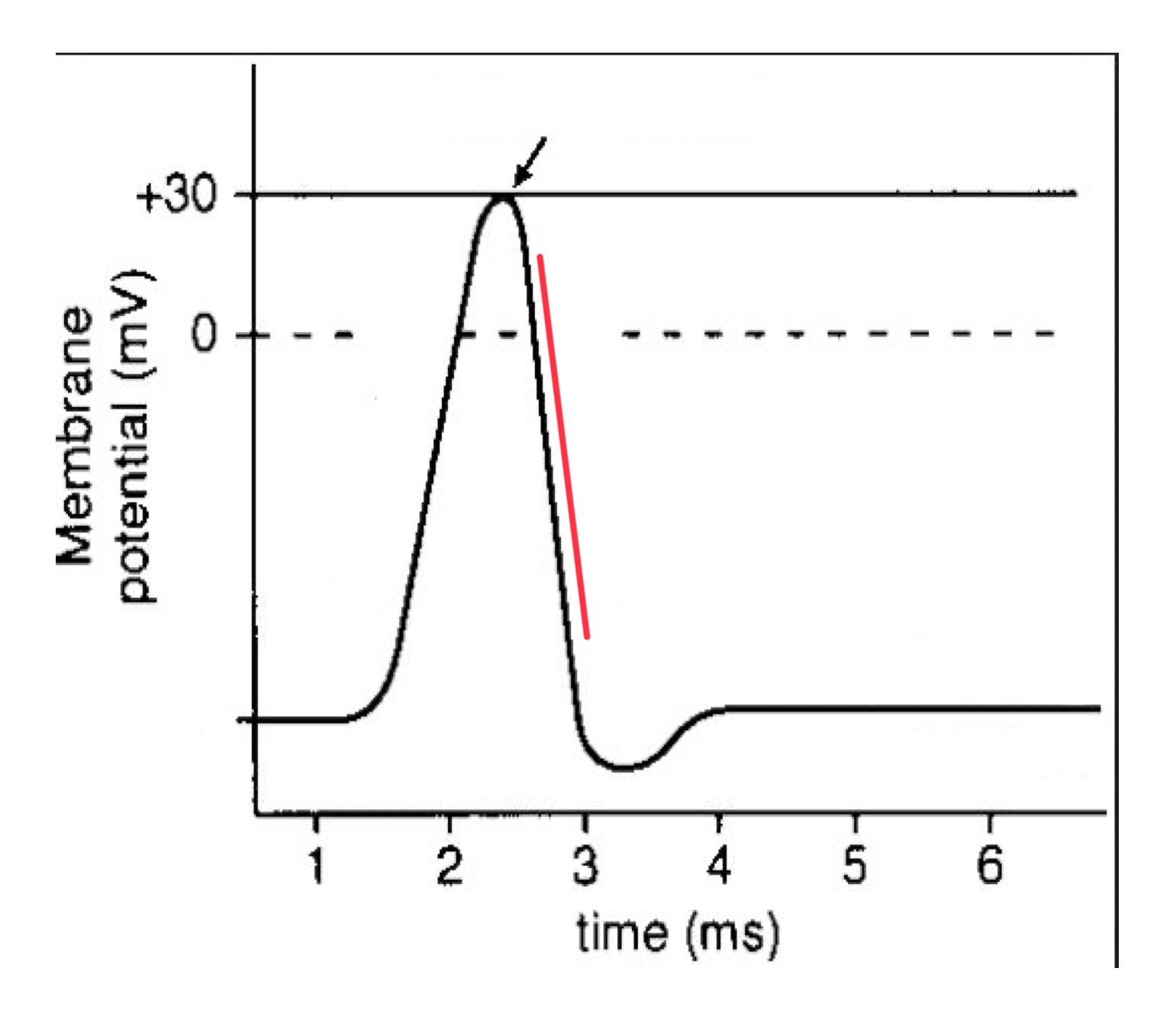
repolarization
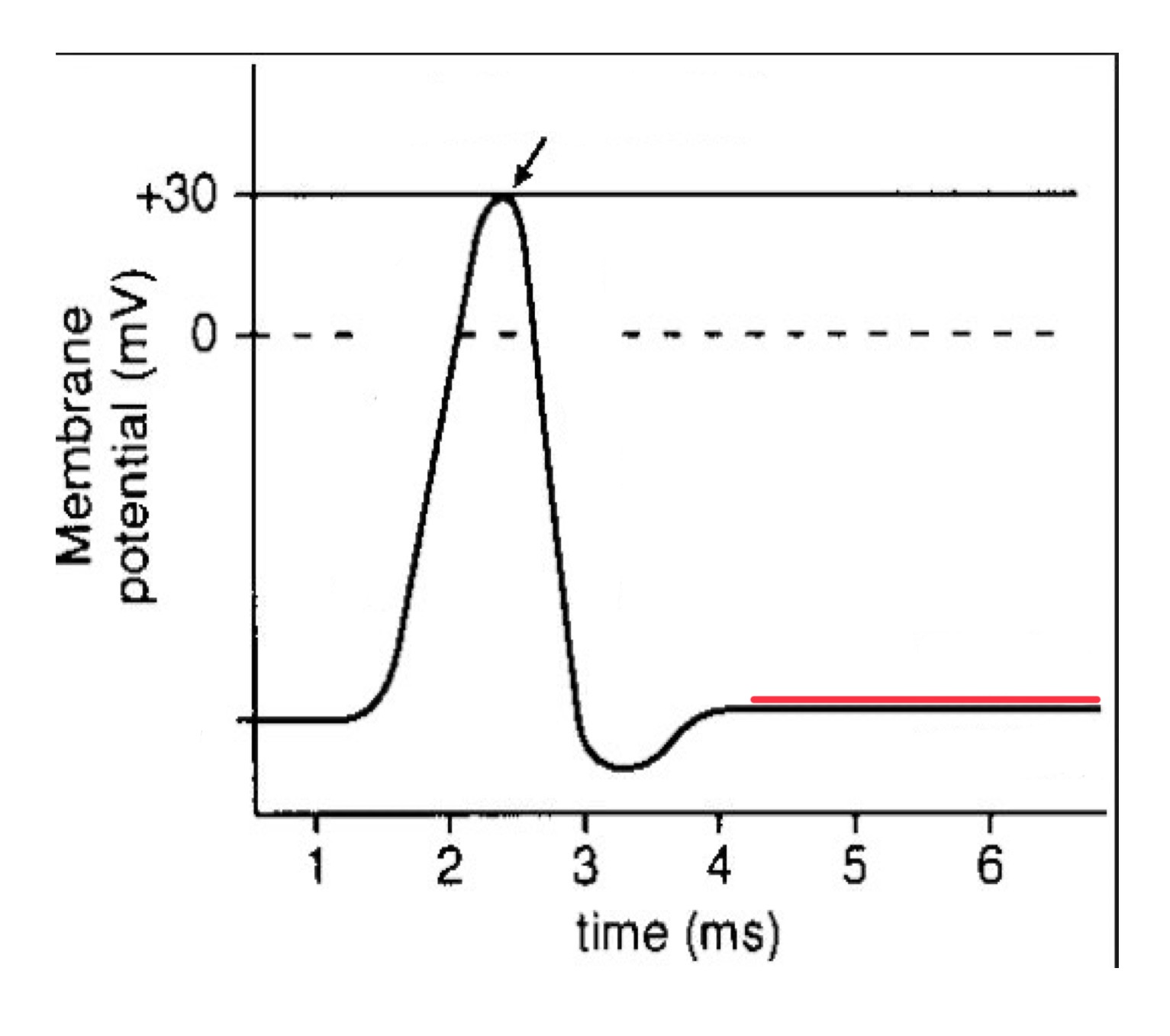
resting potential
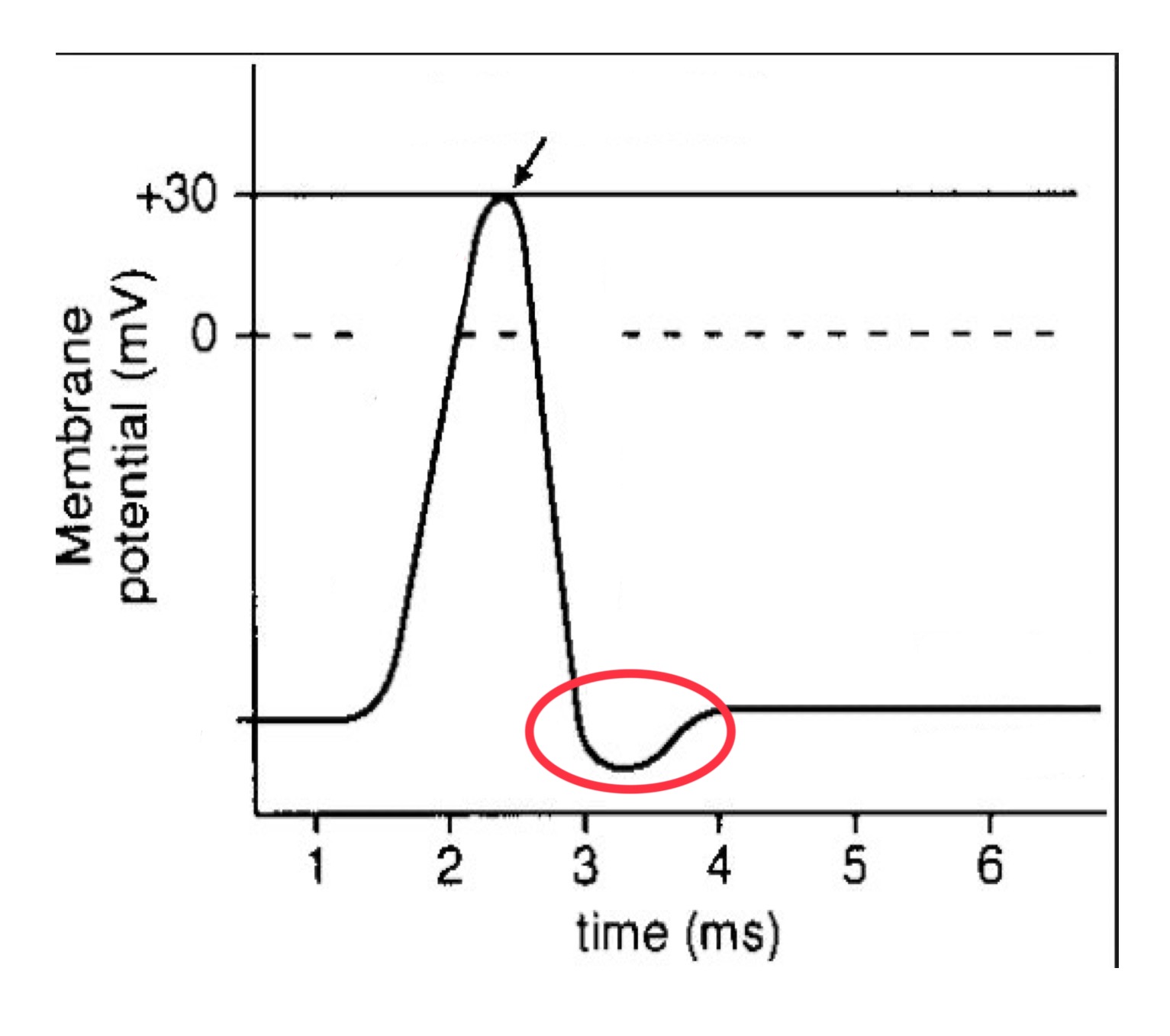
refractory period
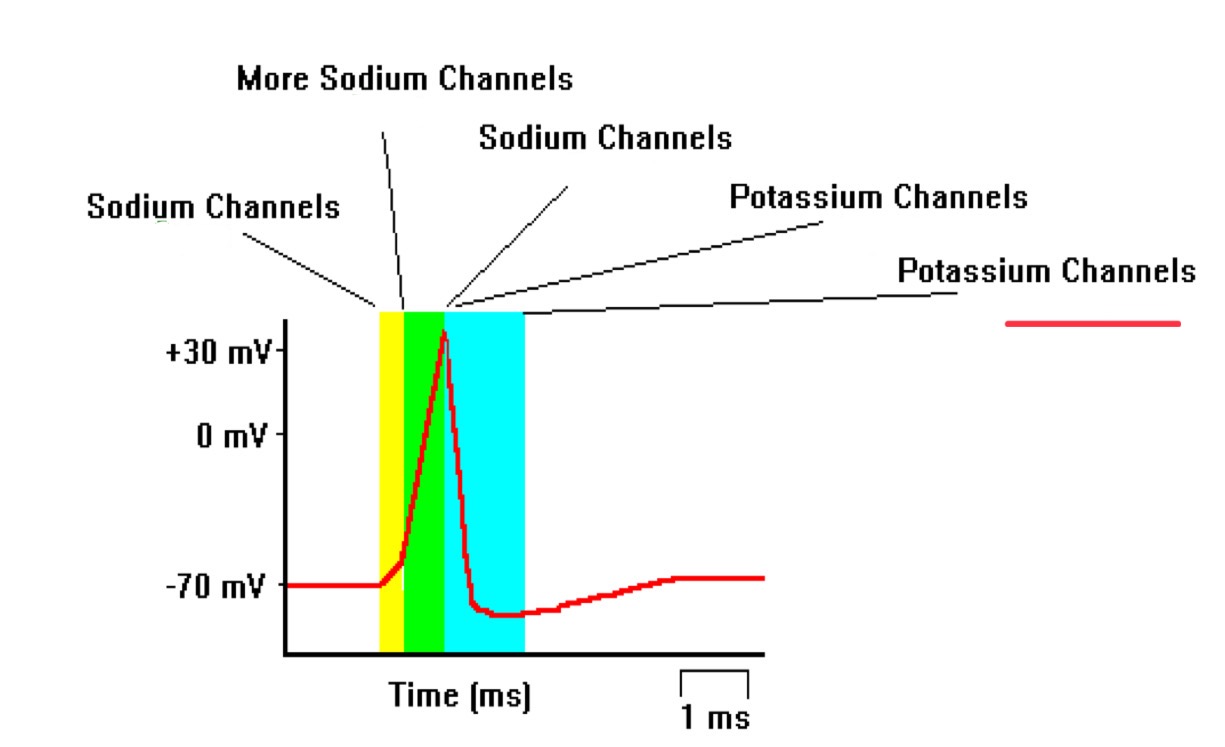
potassium channels close
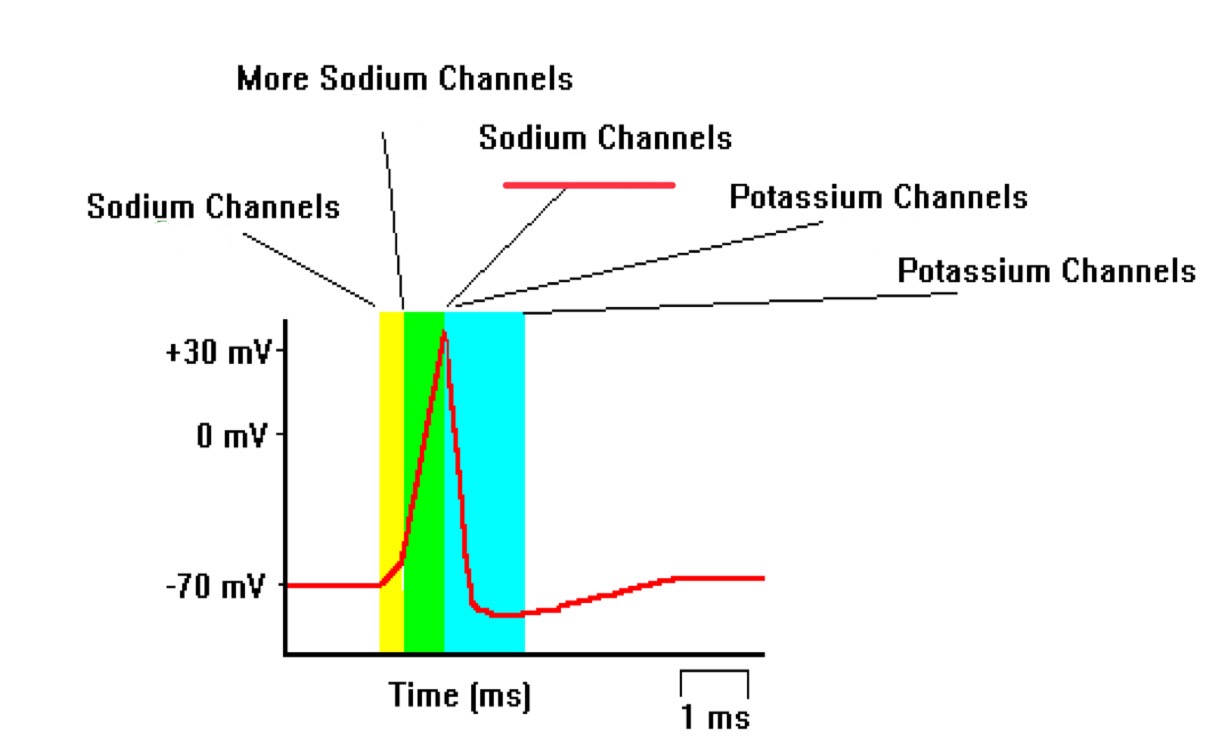
sodium channels close
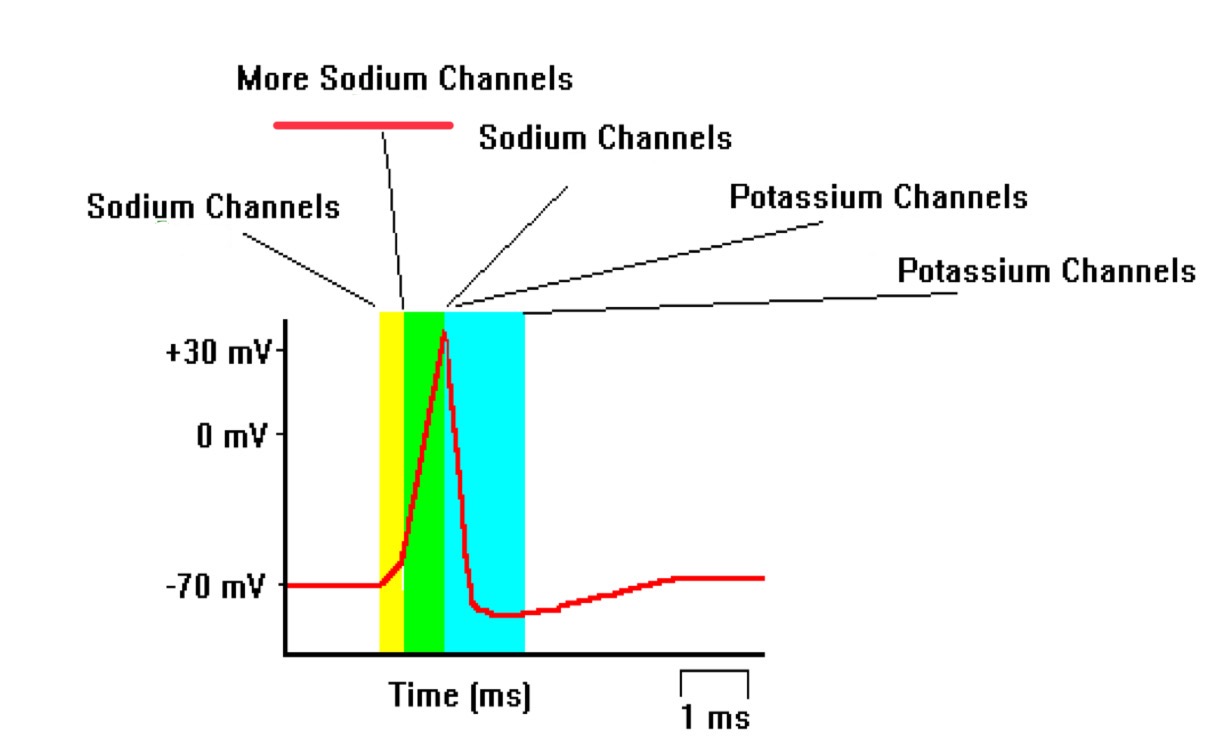
more sodium channels open
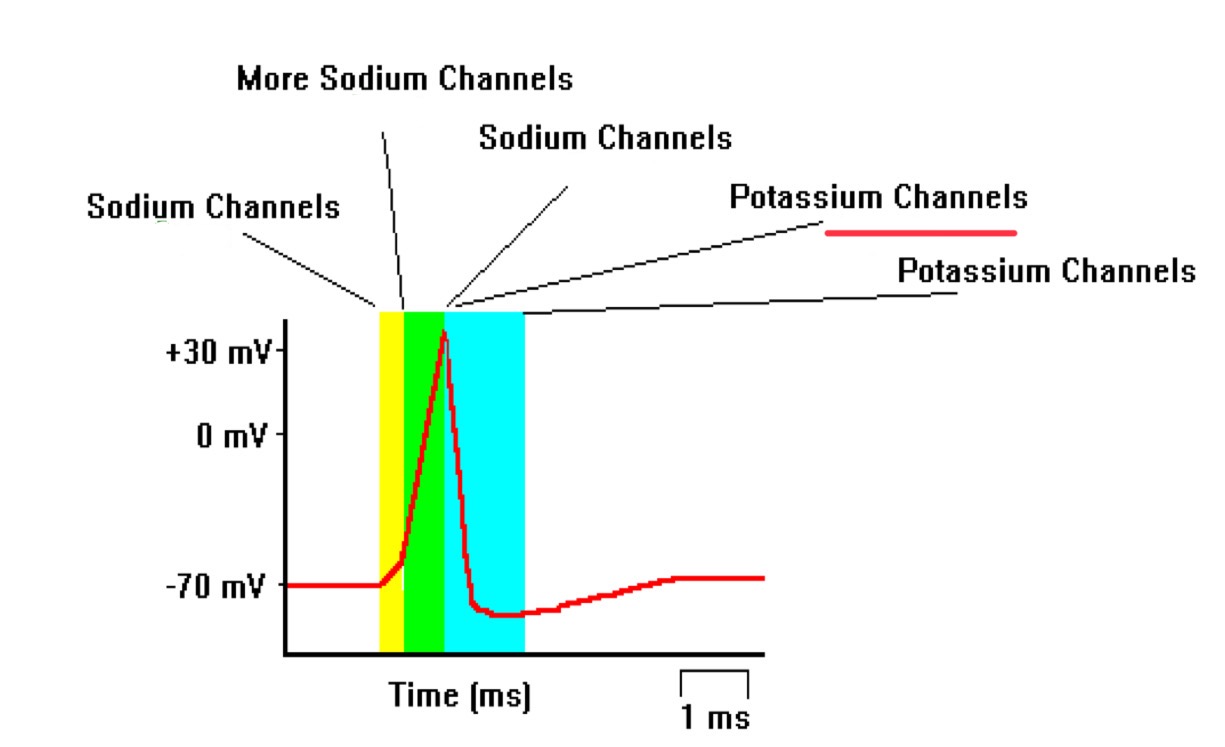
potassium channels open
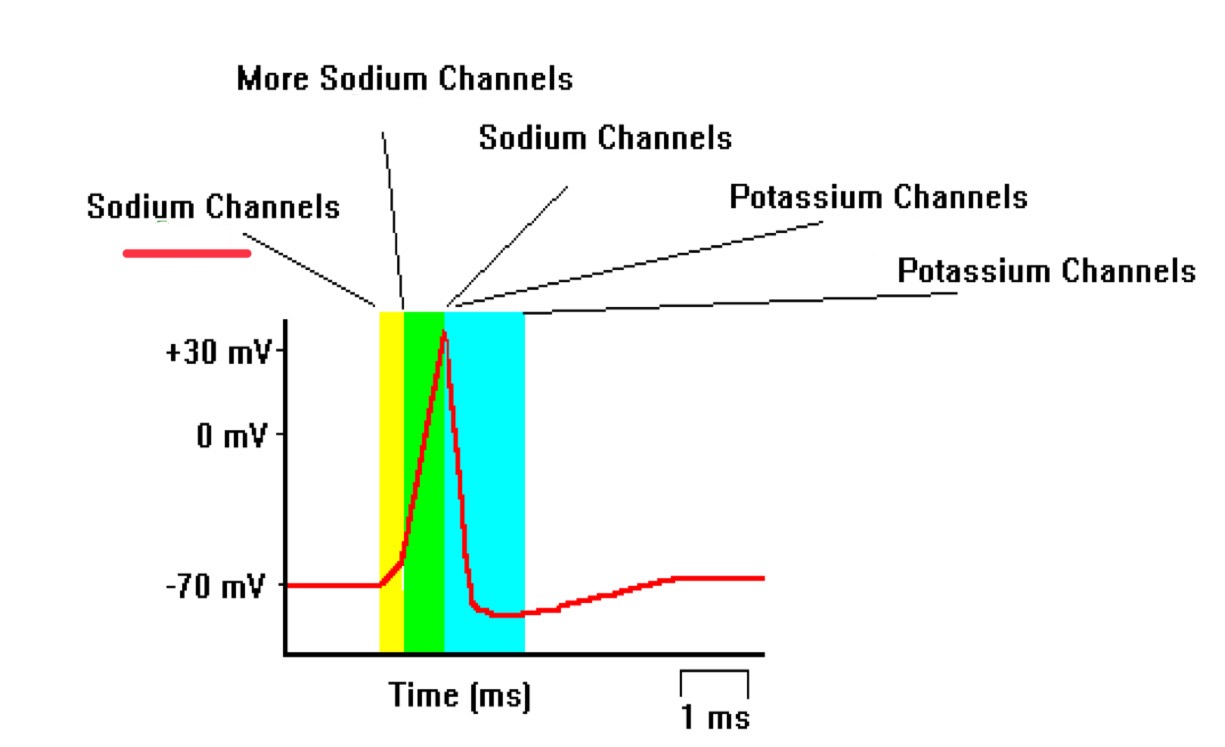
sodium channels open
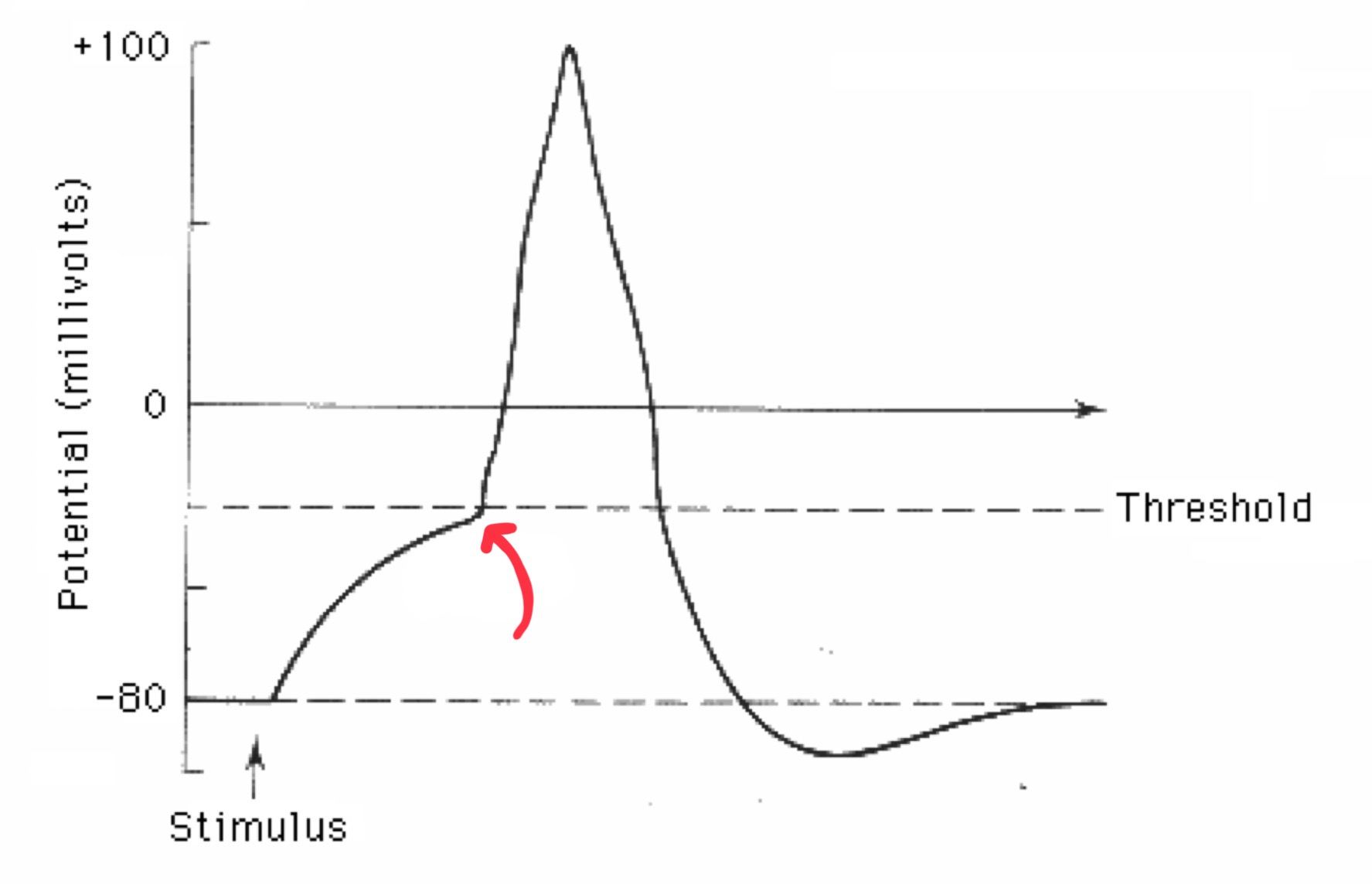
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potential (EPSP)
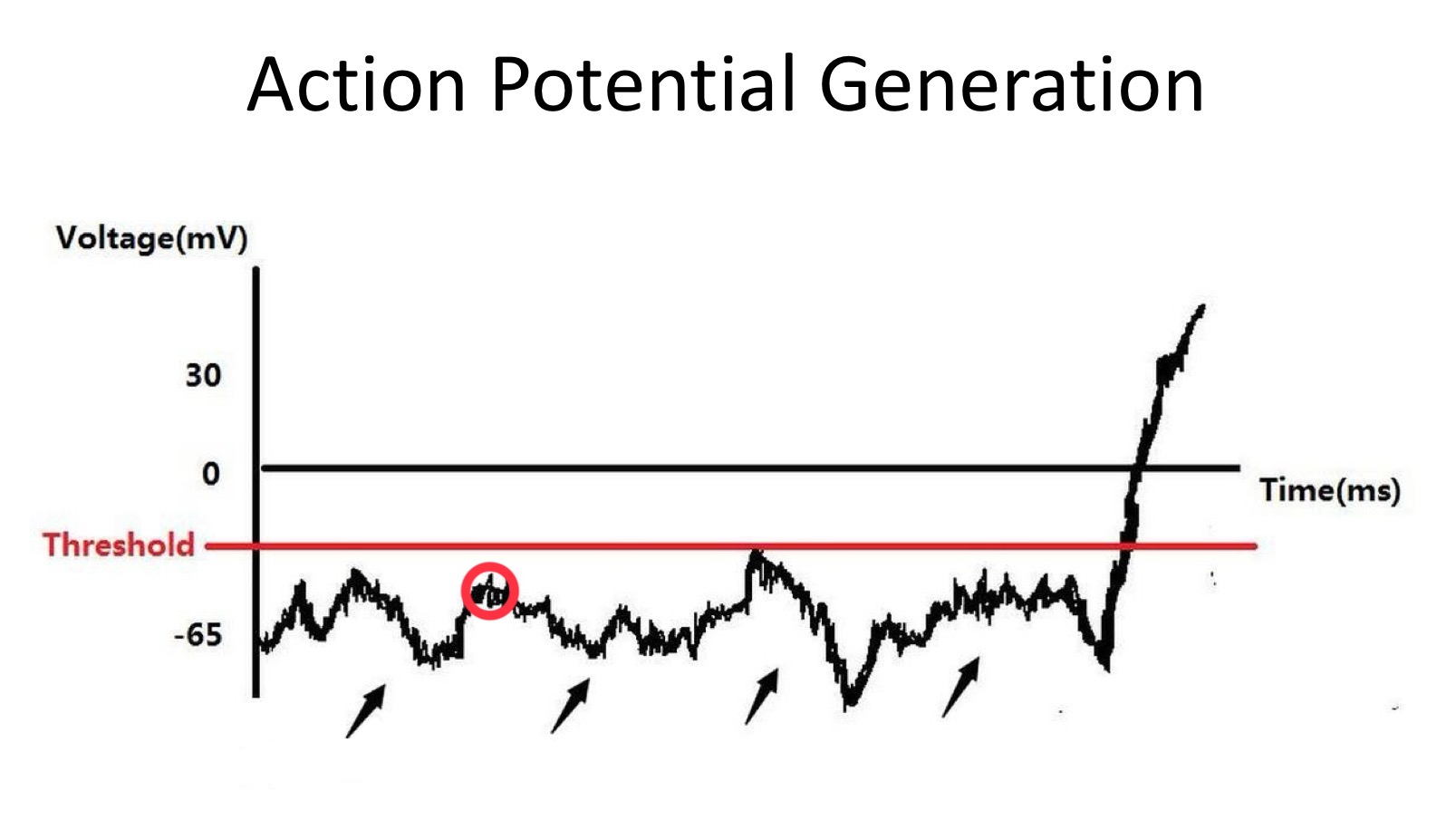
Excitatory Post Synaptic Potentials (EPSP’s)
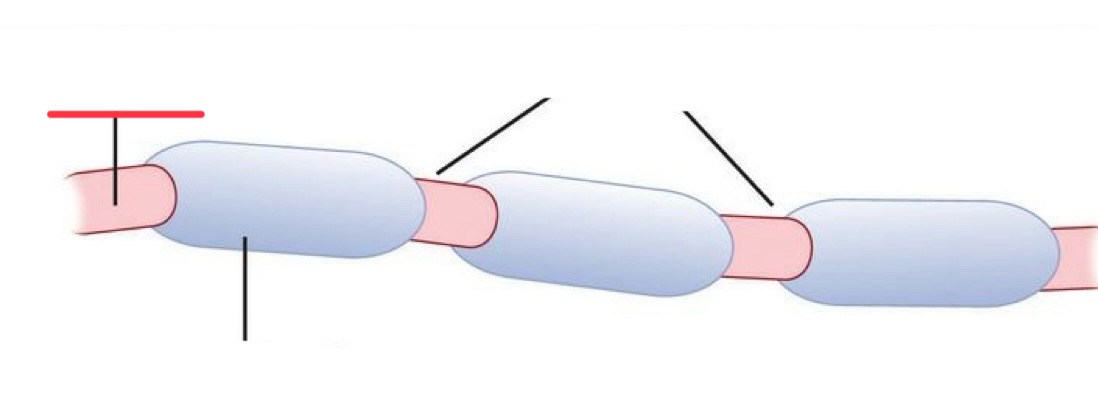
axon
myelin
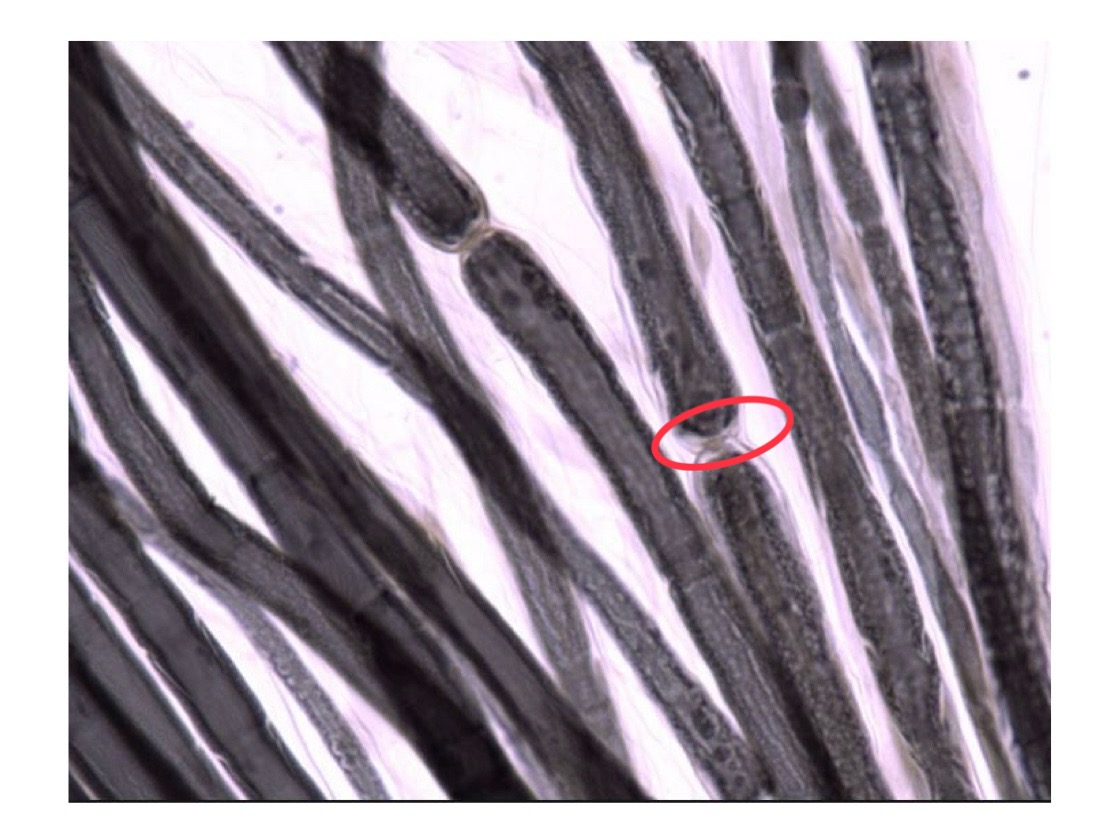
node of ranvier
nodes of ranvier
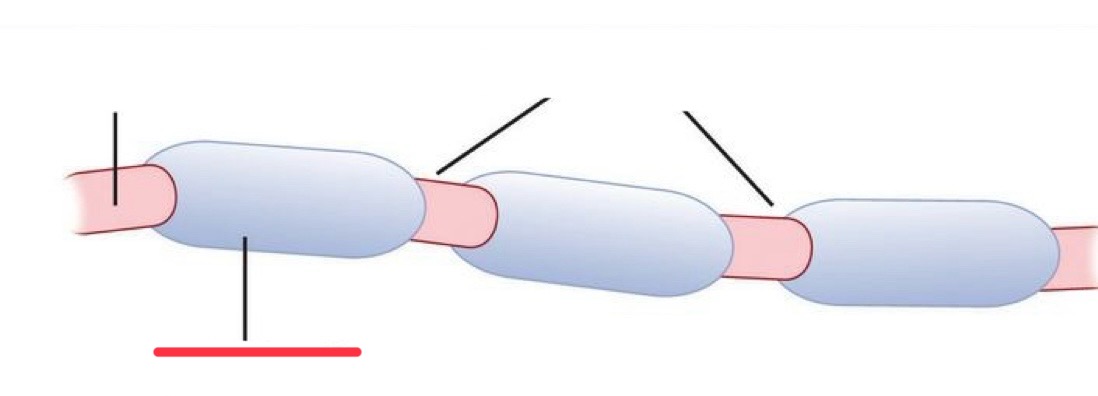
myelin sheath