Replication of mt, cp and plasmids
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Do bacteria most often use theta or rolling circle replication?
Theta!
T or F: rolling circle replication also has an oriC
True!
The oriC for bacteria is rich in what bases?
As and Ts!
Rolling circle replication can be used to replicate…
Plasmids
What’s different about the initiation of rolling circle replication from theta replication?
We do NOT form a bubble in rolling circle! We “nick” the strands.
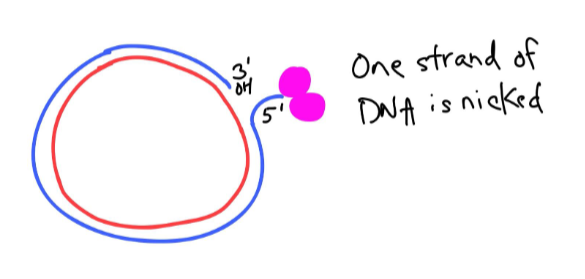
What molecule binds to the oriC in rolling circle replication?
Rep A
What is exposed after RepA binds to the oriC and the strand is “nicked” in rolling circle replication?
The hydroxyl group on the 3’ end of one strand. This acts as a primer.
What happens after the -OH group is exposed on the 3’ end of one strand of the plasmid in rolling circle replication?
DNA Pol III “grabs” the -OH, and helicase is recruited to where the 5’ end is.
What happens after DNA Pol III and helicase are recruited in rolling circle replication?
The DNA Pol III begins extension starting at the 3’ hydroxyl end, and begins to displace the original strand.
There are ssbp’s on the displaced original strand to prevent reannealing.
We fully replace the original strand with a new strand.
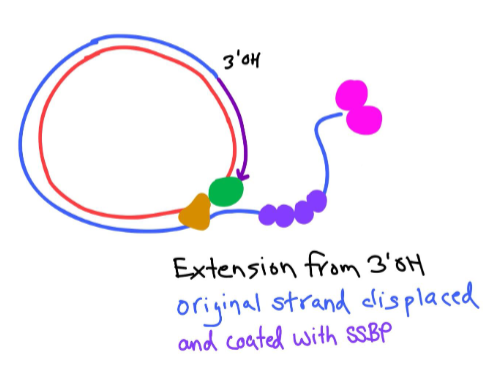
What happens after the full displacement of the original strand in rolling circle?
Ligase seals the gap on the new strand, and the displaced strand needs to be replicated since it is ss.
How is the displaced strand replicated in rolling circle?
It is first primed, then extended by DNA Pol III
What is the primary difference between rolling circle and strand displacement?
In strand displacement, the DNA is not “nicked, and so it never becomes linear like in rolling circle.
What type of chromosome is strand displacement used for? What type of polymerase does it use?
Mitochondrial!
Uses DNA Pol Gamma
Describe strand displacement replication
One strand is fully displaced before replication begins
The separated strands are each replication, and ONLY involve a leading strand. Uses DNA Pol Gamma
T or F: rolling circle and strand displacement replication have both a leading and lagging strand, like theta replication
False! No lagging strand!