[ANAL-LEC-MID-01] CALCULATIONS OF RESULTS AND ERRORS
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
THIS FLASH CARDS IS ABOUT ANALYSIS II; CALCULATIONS OF RESULTS AND ERRORS.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Recording
When we say calculations of results, it is about?
Errors
Measurements invariably involve _____ and uncertainties.
No — impossible.
Is it possible to perform a chemical analysis that is totally free of errors or uncertainties?
Acceptable accuracy
We can only hope to minimize errors and estimate their size with?
Errors
These are caused by faulty calibrations or standardizations or by random variations and uncertainties in results.
Faulty calibrations
Standardizations
Random variations
Uncertainties in results
Errors are caused by?
Frequent calibrations
Standardizations
Analyses of known samples
These three (3) can sometimes be used to lessen all but the random errors and uncertainties.
Error
Refers to the difference between a measured value and the “true” or “known” value.
Measured value
True or known value
Errors refer to the difference between a?
Errors
These can often denotes the estimated uncertainty in a measurement or experiment.
| absolute error - true value |
————————————— x 100%
true value
What is the formula for error and percentage error?
Measured value
What is the synonym of absolute error?
Researcher
Example only:
Who is the one that determined the measured value?
Manufacturer
Example only:
Who is the one that determine the true value?
Numerical value
Source and Nature of Errors:
It is only in rare cases that this value of an experimental result can be directly determined.
Different measurements and observations
Source and Nature of Errors:
As a rule, it is necessary to calculate the result from these measurements and observations that have been made.
Statistics
The side of experimentation involves?
Statistics
This is the science of collecting and analyzing data to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and determine whether results are real or due to chance.
Duplicate results
Source and Nature of Errors:
These results that check very closely are not an assurance of accuracy.
Reliability of the methods
Results that agree closely when obtained by two different methods of analysis are a good indication of the?
Accuracy
This indicates the closeness of the measurement to the true or accepted value and is express by the error.
Result and the accepted value
Accuracy measures agreement between a?
Accuracy
This is often more difficult to determine because the true value is usually unknown.
Accepted value
Since the true value is usually unknown, this value must be used instead.
Absolute or relative error
Accuracy is expressed in terms of either?
Precision
This describes the agreement among several results obtained in the same way.
Reproducibility of measurements
Precision describes the?
Precision
This is readily determined by simply repeating the measurement on replicate samples.
Standard deviation
Variance and coefficient of variation
Precision of a set of replicate data may be expressed as?
Acceptable accuracy
“We can only hope to minimize errors and estimate their size with?”
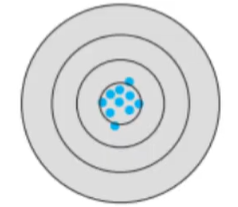
Low accuracy, low precision
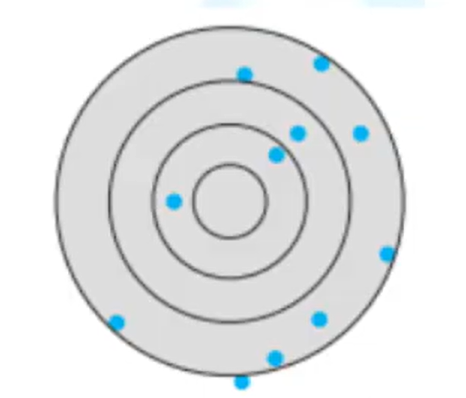
Low accuracy, high precision
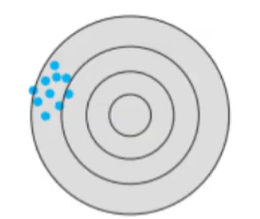
High accuracy, low precision
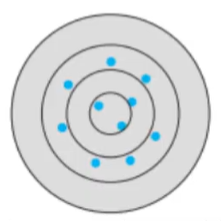
High accuracy, high precision
Source and nature of errors
The results of repeated analyses or measurements will fail to agree, in general, when made by the same analyst or by different analysts to the full precision of which the method or instrument is capable.
Discrepancies
The __________ in the results are caused by various sources of error to which all experimental data are subject.
Subject
The discrepancies in the results are caused by various sources of error to which all experimental data are?
Indeterminate errors
Determinate errors
What are the two (2) different types of errors?
Indeterminate errors
This type of error manifest themselves by slight variations in a series of observations made by the same observer under identical conditions..
Sligh variations
Indeterminate errors manifest themselves by?
Differences in the judgement
Skill of the analyst
Indeterminate errors results from causes difficult to detect, such as?
Intangible
Impossible
Indeterminate errors are (1)_____, and their elimination by the analyst is (2)_____.
Determinate errors
This type of error is of such nature that they recur in a constant manner in each of a series of determinations.
Constant manner
Determinate errors recur in a?
Yes — possible.
In determinate errors, is it possible partially to determine their value and reduce their effect on the final result?
Personal errors
Errors:
Made by the individual analyst.
(e.g., inability to judge color changes sharply, resulting in habitual reading of end points in titration too late).
Errors of method
Errors:
Caused by faulty procedure.
(e.g., incorrect sampling, contamination of precipitates, and improper selection of indicators).
Apparatus errors
Errors:
Due to poor construction or calibration.
(e.g., inaccuracy in the calibration of burets or pipets, inequality in the length of the arms of the balance, and incorrect weights).
Apparatus errors
Errors of this type are usually detectable and so may be eliminated to a large extent.