G and E EXAM 4
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
161 Terms
spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
life-threatening consequence of cirrhosis and associated ascites
HBsAG negative, AntiHBs IgG positive
dental student immunized for Hep B, would have what serology
IgM Anti-HBc positive, HBsAg positive, HBV DNA positive
serology of acute Hep B infection
IgG Anti-HBc positive, HBsAg positive, HBV DNA positive
serology of chronic Hep B infection
IgG anti-HBs positive and IgG anti-HBc positive
serology of immunity due to natural infection
HBsAg
surface antigen from the hepatitis B virus that indicates ACTIVE infection
Anti-HBs
antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen; indicates IMMUNITY after infection or vaccination
Anti-HBc igG
antibody to core of hep b virus indicated past or chronic infection
acetaminophen toxicity
most common cause of ACUTE liver failure in USA
glutathione
antioxidant vital in detoxifying acetaminophen and other toxins in the liver
Drug induced liver injury
patient on 2-week course of antibiotics (augmentin) reports jaundice and dark urine. likely diagnosis?
augmentin (amoxicillin-clavulanate)
most common cause of drug induced liver injury (DILI) worldwide
hemochromatosis
disorder of iron metabolism, commonly due to HFE gene defect
hemochromatosis
excess iron deposited in liver, pancreas (diabetes) , heart, and skin (bronze appearance)
common bile duct at sphincter of oddi (below pancreatic duct)
patient with elevated conjugated bilirubin and elevated amylase diagnosed with obstructing gallstone. The gallstone is likely lodged in the:
cholelithiasis
gallstones in gall bladder
choledocholithiasis
gallstones in common bile duct
cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder, often due to gallstones in gallbladder (cholethiasis)
cholangitis
inflammation of the bile ducts, due to gallstones in common bile duct (choledocholithiasis)
long chain fatty acids
cause damage to stellate cells through TNFa
stellate cell
promote fibrosis and scar tissue formation in response to liver injury
MASLD
buildup of fat in the liver not due to alcohol consumption, potentially leading to inflammation and liver damage
hepatic encephalopathy, coagulopathy, hepatocellular carcinoma, portal hypertension
complications of cirrhosis
varices, ascites, hepatorenal syndrome
complications of portal hypertension
cirrhotic ascites
ALWAYS associated with portal hypertension
intra-hepatic portal hypertension
due to nodular compression and fibrosis of sinusoids
hemochromatosis
patient with bronzing skin, fibrotic liver, and diabetes. likely diagnosis?
wilson’s disease
which disease presents with greenish golden crescents on the cornea (kayser-fleischer rings)
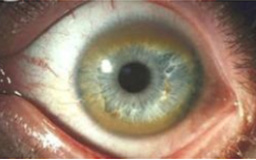
wilson’s disease
disorder that results in copper accumulation in the liver, brain, and eyes
alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency
EMPHYSEMA due to reduction of serum A1AT levels
albumin and INR
test to determine ability of LIVER to SYNTHESIZE compounds (function)
ALT/AST
test to assess active hepatic cellular disease
alkaline phosphatase fractionated
test to determine biliary obstruction
reactive quinone metabolite (of acetaminophen) toxic to hepatocyte
acetaminophen toxicity is due to:
maternal/fetal, blood, sexual contact
transmission routes of hep B
absorbed by the ileum and returned to the portal vein for reuse
after secretion into the duodenum the majority of bile salts are:
bile
fluid produced by the liver that aids in digestion and fat absorption
bile salts
allow digestion of lipids by creating micelles
micelles
small aggregates of fatty acids, bile salts, and other lipids that facilitate lipid digestion and absorption in the intestine
bilirubin
metabolic waste of hemoglobin brreakdown
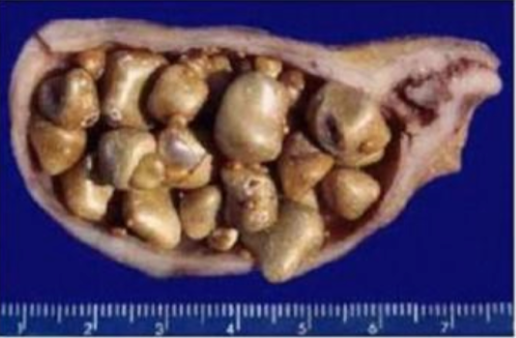
cholelithiasis (gallstone of gallbladder)
best diagnosis based on the findings
most likely to progress to end stage liver disease
compared with other forms of hepatitis acquired in adulthood, untreated HEP C:
gilberts disease
presents with icteric sclera (yellow eyes) and UNCONJUGATED hyperbilirubinemia after STAYING UP LATE, but otherwise normal
increased bleeding
from a dentist's POV pts with advanced chronic liver disease are most at risk for infection, poor medication metabolism, and:
ammonia
advanced chronic liver disease causes asterixis and cognitive changes due this factor that affects the brain:
Hep C
most likely cause of chronic liver disease in patient with history of IV drug use
recovered hepatitis B infection
what does the follwoing hepatitis panel indicate:
HBsAg : -
Anti-HBs IgG: +
Anti-HBc IgM: -
Anti-HBc IgG: +
Anti-HAV (antibody to Hep A )
patient present with nausea, anorexia, malaise, fever, and abdominal pain. develops dark urine, jaundice, and pruritus. He denied needle use or sexual contact and just came back from traveling. which lab test is likely positive?
fecal/oral
hepatitis A transmission
hepatic encephalopathy
Medications that suppress the central nervous system (CNS) should be used with caution in patients with chronic liver disease because they can cause:
decrease acetaminophen dose
patient with severe chronic liver disease requires pain medication after dental procedure, you should:
use universal precautions (as you would for all patients)
if a patient informs you they are a chronic carrier of hepatitis C you should
elevated estrogen
cause of palmar erythema and spider angiomata in patient with chronic liver dysfunction
hepatocellular carcinoma
recent increase in alpha fetoprotein is associated with
duodenum
where is iron absorbed
Ileum
where is vitamin B12 absorbed
ileum
where are most bile salts absorbed
small chain fatty acids
what are carbohydrates absorbed as in the COLON
celiac sprue
destruction of intestinal villi caused by gluten intolerance
autoimmune T cell attack
how are intestinal villi destroyed in celiac sprue
irritable bowel syndrome
chronic abdominal pain and altered bowel habits (constipation or diarrhea) of unknown cause
celiac
can cause nutritional deficiency in healthy person due to malabsorption
gliadin
a gluten protein that triggers intestinal damage in celiac disease
transglutaminase
marker for celiac disease
celiac
causes iron deficiency anemia from malabsorption
steatorrhea
fat in stool, often symptom of celiac disease
colon
does most of Na+ and water absorption
crohns, ulcerative colitis, carcinoma, pseudomembranous colitis
main diseases of the colon
crohns disease
inflammatory bowel disease anywhere in GI tract, characterized by transmural inflammation and skip lesions.
ulcerative colitis
continuous ulceration of colon that starts at rectum and moves proximally
pseudomembranous colitis
antibiotic-associated colitis due to C. diff
colon carcinoma
2nd most common cancer death in the US
ulcerative colitis
greatly increases risk of carcinoma
ulcerative colitis
patient presents with bloody stool, chronic diarrhea and rectal tenderness. likely diagnosis?
blood loss
cause of iron deficiency anemia in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's patients
ulcerative colitis
ALWAYS involves RECTUM and continuous colon inflammation with ulcers
albumin, coagulation factors, urea, bile salts
molecules synthesized by liver
conjugated
type of hyperbilirubinemia associated with acute hepatic necrosis (ex: hepatitis or DILI)
conjugated
bilirubin that is excreted in urine
elevated conjugated bilirubin
bilirubinuria indicates
unconjugated
hyperbilirubinemia that occurs in Gilbert’s disease
central vein
hepatic artery and portal vein drain into?
Portal vein and hepatic artery
What vessels deliver blood to the liver?
Portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct
components of portal triad
Space of disse
where exchange of substances occurs between the blood in sinusoids and hepatocytes
Vitamin A
Stored by stellate cells
Kupffer cell
type of macrophage found in the liver that plays a role in immune response and the breakdown of old red blood cells
liver acinus
Functional unit of the liver, where blood flows from portal triad through sinusoids to central venule
Low oxygen
Why is zone 3 of liver acinus susceptible to hypoxic damage?
Zone I
What liver acinus zone does viral hepatitis damage?
albumin
What does unconjugated bilirubin complex with in the blood to make it more water soluble?
Conjugated
water-soluble bilirubin
conjugated
all bilirubin leaving the liver cell is ____
Conjugated bilirubin converted by glucuronidases
Where does unconjugated bilirubin come from in the bile duct?
Bilirubin (mesobilifusions) not present to color stool
Why does stool become pale with obstruction of the biliary system?
unconjugated
defect in one of the first 5 steps of bilirubin metabolism what type of hyperbilirubinemia arises?
intrahepatic cholestasis
block of bile flow inside liver
extrahepatic cholestasis
Block of bile flow outside of liver (ex: bile ducts)
no (unconjugated no water soluble)
Would you expect to see dark urine with UNCONJUGATED hyperbilirubinemia
acute liver disease
high INR + normal albumin