Parasite Exam 2 TA
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
Myiasis
parasitic infection feeding on dead or living tissues
predilection site
obligate parasite: stomach, nasal sinuses
accidental parasite: GIT by accidental ingestion
facultative parasite: soiled wounds or bedding, necrotic areas, broad host range, important for forensic entomology
significant animal welfare issue
Calliphordae blowflies
Lucilia
Phormia
Calliphora
Cochliomyia (new world screwworm requires living tissue)
Oestridae bot/warble flies
nostril flies (Oestrus nasal bots in sheep, Gedoelstia),
bot flies (Gasterophilus stomach bots in horses)
Warble flies (Hypoderma cattle grubs and warbles)
Sarcophagidae Flesh flies
Sarcophaga
Wohlfahrtia
Blow flies
host: sheep, pet rabbits
geography: North America, summer season
Morphology: Green, blue, black, metallic, medium-sized
overwinter: pupal form
predisposing factors: ammonia, sulfur compounds, volatile organic acids produced by bacteria in skin wounds, high temp and humidity leading to wool rot, soiled fleece, wounds.
Greenbottles blowflies
LUcilia

Blackbottles blowflies
Phormia

Bluebottles blowflies
Calliphora

Secondary Screwwrom blowflies
Cochliomyia macellaria
Hairy maggot blow fly
Chrysomy rufifacies
Primary flies
initiate a strike on living animal
larvae can penetrate intact skin
Lucillia
fly strike
Secondary flies
feed on decaying and dead flesh
attack areas already affected during primary fly strike
Phormia and Calliphora
Tertiary flies
found when host is near death
Sarcophaga and Wohlfahrtia (ie flesh flies)
blow fly pathology
severe skin damage and traumatic myiasis can cause secondary infections
proteolytic enzymes digest and liquefy tissues
production losses due to death, septicemia, anorexia, distress, poor condition
mortality rate is 10%
fly strike leaves a distinctive grey stain on wool
some maggots feed on fat
obligatory myiasis requires living hosts to complete their life cycle
Calliphoridae New world screwworm
obligate
geography: tropical and subtropical areas of the Americas
feeding: larvae on living tissue eat the host alive
hosts; warm-blooded animals, cattle and sheep most common
Eradication: sterile male technique
Cochliomyia hominivorax
New world screwworm
Calliphoridae blow fly morphology
metallic green to blueish green with 3 distinct horizontal stripes on their thorax (stripes distinguish from blue bottle flies)

Oestridae bot flies
morphology: large, hairy, adults have vestigial mouthparts
feeding: larvae are obligatory parasites of large mammals, adults do not feed
species:
Hypoderma
Oestrus
Gasterophilus
Oestridae Oestrus bot flies
nasal bot of sheep (Oestrus Ovis)
morphology grey fly, black spotted abdomen, short brown hair
repro: VIVIPAROUS
predilection site: nostrils, masture nasal sinuses
migration: frontal sinus as L3
feeding: larvae attach to mucosa
CS: nasal discharge, sneezing, rubbing nose, neuro signs “false gid”
pathology: Pasterurella, immunosuppression, pneumonia, fly worry, panic, lowered feed conversion.
zoonotic

Oestrus ovis
nasal bot of sheep
Oestridae Gasterophilidae botfly
morphology: large dark fly, yellow hair, red eggs around cardia (G. intestinalis), yellow in pylorus and duodenum (G. nasalis)
feeding: adults do not feed
overwinter: inside host
hatching: stimulated by licking
predilection site: stomach of equines, eggs in hair
pathology: none, rarely stomatitis, local inflammation of the stomach
treatment: at owner request

Gasterophilidae intestinalis
red eggs around cardia
Gasterophilidae nasalis
yellow in pylorus and duodenum
Hypoderma
warble flies cattle grubs (heel flies and gadflies)
geography: Northern hemisphere, North America, Mexico, Canada
development: subcutaneously in cattle
morphology: resemble bees, orange-yellow hair with broad band of black hair in the middle
predilection site: hair, lower parts of the body (H. bovis), eggs in row below hocks (H. lineatum)
migration: larvae subcutaneous, CT of esophagus, spinal column
CS: gadding, injury, local inflammation, secondary bacterial infection, bloat, spinal canal paraplegia, hypersensitivity (larvae rupture)
pathology: hole punch effect

Hypoderma pathology
Hole punch effect
Hypoderma predilection site
hair
lower parts of the body (H. bovis)
eggs in rows below hocks (H. lineatum)
Oestridae Cuterebrinae
morphology: large, hairy, blue to black abdomen, adults have vestigial mouthparts
feeding: adults do not feed, larvae in boils of skin
hosts: rodents, rabbits, dogs, cats, warm-blooded animals
geography: western hemisphere, Americas
predilection site: eggs in burrows in bushes, attach to host body and enter the skin through boils, eggs attached to mosquitoes and transmitted through feeding of mosquitoes.
Cuterebra and Dermatobia hominis
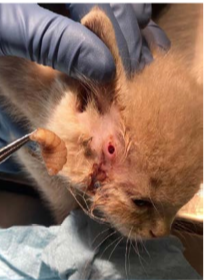
Dermatobia hominis
humans and larger mammals and birds
attach eggs to blood-sucking flies (mosquitoes).
when mosquitoes feed, egg hatch and penetrate skin of host.
Cuterebra spp
parasites of rodents and rabbits (dogs and cats)
western hemisphere, throughout the Americas
eggs laid around burrows as host brushes past eggs hatch and larvae attach to host and enter body and migrate to specific sites.
Sarcophagidae
flesh flies
cutaneous myiasis
hosts: rabbits, dogs, cats, mink, fox, humans.
repro: VIVIPARIOUS
predilection site: larvae on wounds and genitals, pupate in soil

Sarcophagidae flesh flies
Wohlfahriis vigil
Sarcophaga haemorrhoidalis
Wohlfahrtia vigil flesh fly
dorsal surface of the thorax is marked with three longitudinal bands, while the dorsal surface of the abdomen exhibits three, well-defined rows of oval black spots which are confluent with one another.
Siphonaptera fleas
morphology: wingless, laterally compressed, 3rd pair of legs enlarged for leaping.
hosts: mammals and few birds, nest animals (nidicolous)
feeding: both sexes take blood meal, larvae feed on organic debris and fecal blood.
adult emergence triggered by vibration, temperature and light intensity.
95% of population in environment
metamorphosis: complete
treat environment for fleas
Ctenocephalides fleas
ubquitous
wide host range including humans
Ctenocephalides felis
cat flea
very common
Ctenocephalides canis
dog flea
Ceratophylus gallinae
bird flea
wild birds, mammals
Xenopsylia cheopis
oriental rat flea
transmits Yersinia pestis (bubonic plague)
Purex irritans
human flea
Echidnophaga gallinacean
stick tight flea
serious chicken flea
affects egg production and feed efficiency
Tunga penetrans
jigger
chique
sand flea
burrows into skin
affects humans and pigs
Spilopsyllus caniculi
rabbit flea sometimes on cats
adapted life cycle
Flea importance intermediate hosts
Dipylidium caninum
Hymenolepis tapeworms
Flea importance pathology
irritation
hypersensitivity
flea allergy dermatitis (hypersesntivity Type 4, Th1 response) within the flea triangle
anemia
elephant skin
thickening
FAD is the most common dermatologic disease of domestic dogs
Flea importance diagnosis
history
chronic lesions
wet white paper test
intradermal allergy tests
vigorous combing
Controlling fleas
target adults on hosts and immature stages in environment
FAD - immedizte intervention to prevent continued reaction
adulticide first
corticosteroids and antibiotics
larvalcide second
rid animal of current infection and prevent re-infection
eliminate the environmental reservoir
1 flea can cause hypersensitivity
drugs: frontline, stronghold, advantage, prac-tic, nexgard
Phthiraptera lice
obligate parasite
morphology: wingless insects, dorso-ventrally flattened 3 pairs of legs with single claws
hosts: host specific, operculate eggs cement to hair shafts
transmission: direct contact, fomites, limited survival off host
seasonality: late winter, early spring
metamorphosis: incomplete
2 groups: sucking and chewing
Sucking lice : Anoplura
host: mammals
morphology: piercing mouthparts, pointed head, narrow head
feeding: blood and tissue fluids
Haematopinus (cattle, pigs, equid), Linognathus (dog, sheep, goat, cattle), Solenopotes (cattle)
chewing lice: Mallophage
host: birds and mammals
morphology: cutting and grinding, broad head
feeding: skin scales, hair, feathers (superficial)
Damalinia bovicola (sheep, goat, cattle, equid), Trichodectes (dogs), Felicola (cats)
Bird lice
Chewing lice only
commonly found: poultry houses
pathology: anemia, fatal in chicks, damage to feathers
feeding: superficial causing irritation
predisposition: overcrowding, unhygienic situation, debeaking, improper grooming
Goniocotes gallinae
fluff louse
Menacanthus stramineus
chicken body louse
Cuclotogaster heterographus
chicken head louse
Lipeurus caponis
chicken wing louse
Menopon gallinae
shaft louse
Lice pathology
light infestation is considered normal
heavy infestation: pediculosis, pruritis, alopecia, hide damage, weight loss, anemia, myiasis, secondary bacterial infection.
vectors for: swinepox, Mycoplasma, anaplasma, dermatomycosis
intermediate host: trichodectes canis for dog tapeworm
diagnosis: CS, egg detection, adult detection, ID based on host species, site of infection, and morphology
predilection site: head, neck, back, tail
controlling lice
several flea products effective against lice
second treatment required 2 weeks later to kill emerging lice
sucking lice: injectable avermectins
biting lice: ivermectin pour on
prevent reinfection: clean grooming equipment
seasonal: just before housing for winter
Acricide
any drug or formulation for killing acarids (mites or ticks)
Insecticide
any drug or chemical used for killing insects
pesticides
substances/mixture of substances for preventing, destroying, repelling or mitigating any pest - used in crop protection
Endectocide
parasiticides (macrocyclic lactones) that affect both nematodes and arthropods
Curative
cure/heal sick animals following the diagnosis of infection
Metaphylaxis
treatment of whole group of animals after diagnosis of infection in part of the group to prevent the spread of infectious disease
Preventative
treatment of a group of animals before clinical signs to prevent the occurrence of disease or infection (can cause resistance)
Strategic
treatment at certain time points according to parasite biology
MItes
Morphology: 2 body parts, 4 pairs of legs, pedipalps (sensory organ), larvae only have 3 pairs of legs, pedicles can end in claws or suckers
metamorphosis: incomplete
host: majority are free living, some plant predators, some obligate parasites
pathology: 85% of asthma sufferers are allergic to free living dust mites, mange, cutaneous hypersensitivity, anemia
intermediate host: tapeworms of cattle, sheep, horses
feeding: blood, lymph, skin debris, sebaceous secretions
life cycle: parasitic mites spend their entire lives on the host
transmission: direct contact between hosts
seasonal: winter is a problem
classification: burrowing or non-burrowing
demodex folliculorum - mange, cigar shaped
Orbatida free living mites
beetle like
habitat: soil and vegetation on pastures
transmission: ingested
hosts: sheep and other grazing animals
intermediate hosts: cestodes, moniezia and anoplocephala
Non-Burrowing MItes
morphology: oval body, long legs
predilection site: surface of skin
transmission: direct contact, indirect via scratching
feeding: skin scales and tissue, superficial blood sucking
diagnosis: skin scrape at edge of lesion, serum ELISA
pathology: dermatitis
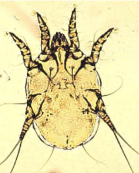
Non-burrowing mites
Psoroptidae
Psoroptes
Chorioptes
Otodectes
Cheyletidae
Dermanyssidae
Psoroptidae Psoroptes
sheep, cattle, horses, rabbits, highly contagious mange
sheep scab, cattle scab, elk scab, Psoroptes cuniculi in ear of rabbit it dormant
Psoroptidae Chorioptes
sheep, cattle, goats, horses, rabbits
notifiable
differentiate from Psoroptes by short non-segmented pedicel and rounded mouthparts instead of pointed
most common mange in cattle, can survive off hosts
Psoroptidae Otodectes
ear mites of cats and dogs with unsegmented pedicel
Psoroptidae Cheyletidae
Psorergates
Cheyletiella
walking dandruff in dogs primarily (surface mite)
zoonotic
claws on palps
Psoroptidae Dermanyssidae
Dermanyssus
Ornithonyssus
pneumonyssoides
Otodectes Cynotis
common ear mite
host: dogs, cats, foxes
morphology: unsegmented pedicle
predilection site: deep ear canal
CS: grey to black exudate with crusts
pathology: hematoma, head shaking, pruritis, secondary bacterial infection
Diagnosis: dark debris, moving white specks on otoscope
Raillietia
ear mites
hosts: cattle and goats
pathology: blockage of auditory canal, inflammation, hearing loss
Diagnosis: dark debris, moving white specks on otoscope
Dermanyssidae Pneumonyssoides caninum
canine nasal mite
morphology: oval, pale yellow
CS: head shaking, inverted sneezing, nasal secretions
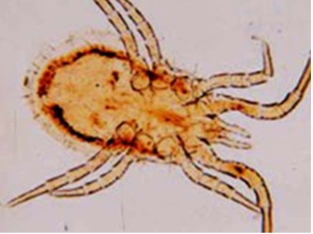
Dermanyssus gallinae
red mite of poultry or pigeon mite
morphology: large, elnogated chelicerae and stylet like piercing mouthparts, greyish white, but red when engorged
predilection site: cracks and crevices
not a permenanet ectoparasite
only one which punctures skin
feeding: larvae don’t feed, nymphs feed and fall off, can live for 8 months without feeding
zoonotic

Dermanyssidae Ornithonyssus sylviarum
northern fowl mite
abundant in US
main ectoparasite of laying birds
Trombiculidae
mostly free living with some parasitic adaptations
morphology: orange - red
seasonal: late summer, early autumn
habitat: grain storage areas
predilection site: ears, eyes, toes (in humans = feet)
parasitic: only larval stages
hosts: not host specific, dogs, cats, birds, rabbits zoonotic
Neotrombicula, Trombicula, Neoschoengastia americana (chigger mites, scrub itch mites, harvest mites)
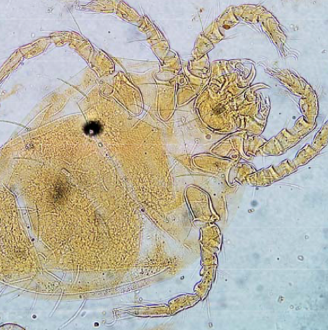
Burrowing mites
morphology: small, round, short legs
Sarcoptidae (Sarcoptes, Notoedres, Trixacarus, Knemidocoptes)
Demodicidae (Demodex)
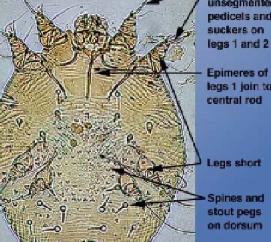
Sarcoptes
scab mite, scabies
morphology: numerous transverse ridges and triangular scales on dorsum
hosts: all domestic animals except cats and guinea pigs, zoonotic
predilection site: stratum coleum of skin, all development within burrows in skin, dogs= ears, muzzle, face, elbows, pigs=ear
feeding: pierce skin to suck lymph, epidermal cells
pathology: inflammation, exudate, crusts, alopecia, allergic reaction to feces, molts, saliva, death in wildlife, papular eruptions in humans, strong sour odors
diagnosis: skin scrape with some bleeding in paraffin oil
Notroedes cati
cat scabies
morphology: thumb print like striations on dorsum
predilection site: skin of face, neck and ears
Knemidocoptes
poultry scabies, only burrowing mite of birds
morphology: stalked pulvilli in males, no spines or scales, legs do not go past body
pathology: scaly leg (mutans), deplumbing itch (gallinae, burrow in hair shaft), tassel foot and scaly face/beak (pilae, non feathered parts)
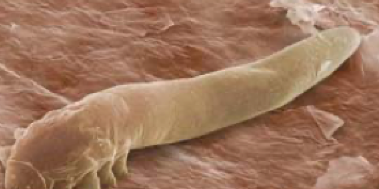
Demodex
burrowing mite
common comensal of all animals
hosts: mammals have their own host adapted species, most commonly the dog
predilection site: hair follicles, sebaceous glands
demodectic or follicular mange
morphology: small, elongated cigar shaped
not contagious
transmission: mom to baby during suckling
diagnosis: deep skin scrapings
treatment: rare, if needed antibiotics for secondary bacterial infection or steroids for inflammation
Demodex localized form
good prognosis, few lesions of small diameter
Generalized form demodex
prognosis good, several lesions of large diameter
demodex squamous demodicosis
good prognosis, similar to dandruff
pustular demodicosis demodex
poor prognosis, pruritic due to secondary baccterial infection
demodex gatoi
in cats is very itchy without secondary infection and is contagious
Varroa destructor
bee mite
predilection site: under wings
host: honeybees
feeding: body fat of adult bees and bee larvae
vector: viral diseases in bees
geopgraphy: originally from asia, now worldwide
pathology: death

Ticks
geography: worldwide
arthropods
morphology: 1mm to 3cm
survive off host for long periods of time, but usually host seeking
second to mosquitoes in public health crisis
pathology: skin lesions, secondary bacterial infections, economic losses
Ixodidae
hard ticks
morphology: scutum, prominent mouthparts, festoons, ornate, stigmata, eyes (depending on species)
acarina: has a Haller’s organ to detect scent, CO2, humidity.
feeding: blood
chelicerae are used to pierce the skin and begin securing the tick to the host
hypostome anchors the tick and is responsible for saliva flowing out of the tick and blood flowing in
species: Ixodes, Dermacentor, Rhipicephalus, Haemaphysalis, Hyalomma, Amblyomma

One host tick life cycle
remain on the host for the whole life cycle until drop off to lay eggs
Dermacenor nitens
Rhipicephalus
two host tick life cycle
1st host is usually small mammals or birds
2nd host is large animals, small animals, not host specific
usually takes about 2 years
Rhipicephalus
Hyalomma
Three host tick life cycle
1st host is usually small mammals
2nd host is small mammals
third host is non-specific
usually takes about 3 years
Ixodes
Dermacentor andersoni and variabiles
Rhipicephalus sanguineus
Haemaphysalis
Amblyomma
Ixodes
hard tick
morphology: small, lack of eyes, distinct anal groove, inornate, 3 host ticks
worldwide
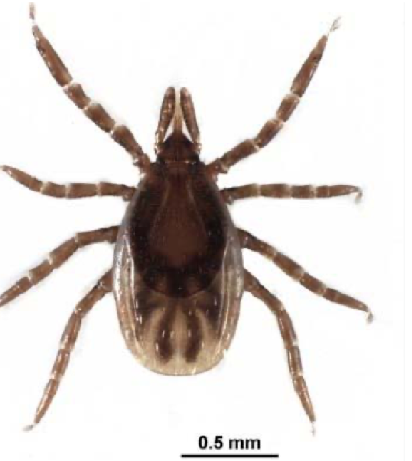

Ixodes ricinus
sheep and caster bean tick
host: mammals, birds, reptiles
seasonality: varies
Europe
Anoplasma, Babesia, Borrelia
Ixodes scapularis
blacklegged deer tick
host: small mammals, lizards, birds, cattle
seasonality: early spring, fall
US and mexico
Borrelia, Anaplasma, Babesia
Ixodes pacificus
western blacklegged tick
host: mammals
seasonality: fall and winter
western US
Borrelia, Anaplasma