environmental engineering
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
strategic environmental assessment
required by european directive2001/42/EC — add in earliest point to stich in environmental protection (plans & programmes, even jobs located, county development plan etc. is the environmental capacity ) SYSTEMATIC, PREDICTION, MONITOR
BOD biochemical oxygen demand
Amount of oxygen utilized by microorganisms in oxidizing (degrading) carbonaceous and nitrogenous organic matter
Measured strength of water / waste water
Dissolved Oxygen
At any give temperature and pressure water can contain some maximum concentration of dissolved oxygen determine through Henry’s law
environmental risk
hazard is not the same as risk (hazard has potential to cause harm, risk is likelihood of harm in defined circumstances) —→ environmental risk could include waste, emissions, resource depletion
environmental justice case
EIA
class of development may or may not require, but it must be screened, (Screeening PROCESS) —→ can consider mitigation
how to limit risk
risk = f(hazard, exposure) reduce exposure to hazard but if those fail risk is a function of hazard, develop solutions using less hazardous components
four components of risk assessment
hazard assessment 2. dose-response assessment 3. exposure assessment 4. risk characterisation
what does risk assessment seek to answer
chemicals/substance present —- problems chemicals cause ——probability of adverse affect post exposure —- severe
hazard assessment includes
whether chemical is linked to particular health concern —> review and analyse toxicity data, weigh evidence of toxic effects, evaluate toxic effects in one situation occur in other
dose-response assessment —-if an adult male, weighing 70 kg, drinks a glass of water contaminated with 0.015 mg/L of lead, what
is the dose? Assume he drinks 2L/day
(0.015 mg/L x 2 L/day) / 70 kg = 4.3 x10-4 mg/kg-day = 0.4 μg/kg-day
carcinogens no threshold, noncarcinogenic threshold so there is a NOAEL (no observable adverse effect) and reference dose based on that and safety factor
EIAR
prepared by DEVELOPER —-description of project, signifcant effects, non-technical summary etc (detailed description of project)
exposure assessment
EXTENT FREQUENCY sources chemical —pathway to exposure — how much people exposed to —how often people exposed —some people more at risk
risk characterisation CARCINOGENS
ACCEPTABLE LEVEL — from three other steps —- Risk = dose * risk per unit dose think about exposure
EIA
PROCESS (by competent authority)
screening —> scoping —> EIA report —> consultation —→ evaluation —> decision —> monitoring
risk characterisation NON-CARCINOGENS
Non carcinogens have a threshold dose. Acceptable risk is determined by calculating a hazard
quotient (HQ). This is evaluated by comparing the daily intake with the reference dose:
HQ = average daily dose / RfD (reference dose)
If HQ ≤ 1 , then there is no adverse risk.
If HQ > 1, then there is a possibility of an adverse impact
marginal analysis
cost-benefit analysis
SWOT DIAGRAM
INTERNAL about achieving objects (strengths & weaknesses ) EXTERNAL situations (opportunities & threats)
decision matrix
list of pros/cons with level of importance to each factor (lists relevant parameters/criteria/factors ) weights importance of factor to decision, lists decision alternatives and the value
pareto analysis
statistical technique (uses pareto principle or 80.20 rule) identify significant aspects problem to focus effort (plot bars based on use such as water use which causes most focus on those with the line adding each value)
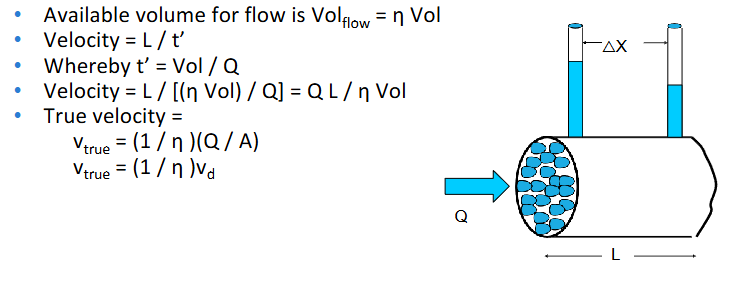
POROUS MEDIA FLOW —> An aquifer has been contaminated by a leaking underground storage tank at a petrol station. A well that serves as the drinking water supply for a small village is 200 m down-gradient of the petrol station. Tests on the aquifer have shown it to have a porosity of 39% and a hydraulic conductivity of 45 m/d. How long will it take for the contamination to reach the village well if the
hydraulic gradient is 40 cm over the 200 m?
• What is the Darcian velocity (vd)? [Hint: Q = - k A (dh / dx)]
• What is the true velocity (vtrue)?
• Can you calculate time required for the contamination to reach the village well, based on the distance it has to travel and the true velocity?
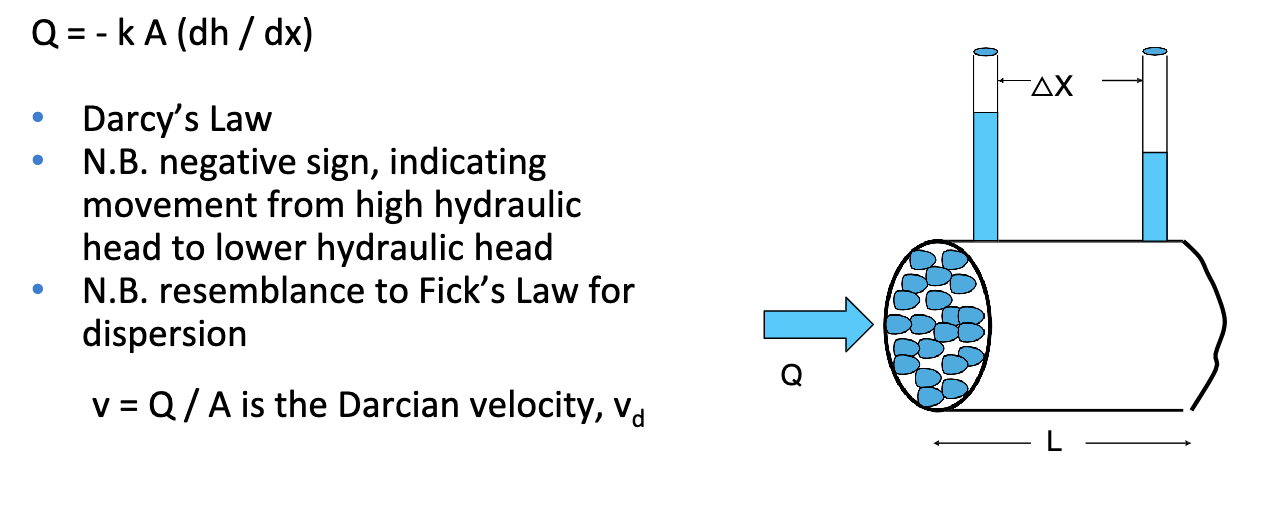
First find the Darcian velocity, vd —> Q = - k A (dh / dx)
Q / A = vd = - k (dh / dx) vd = -45 m d-1(- 0.4 m / 200 m)= 0.09 m d-1 ——> True velocity (vtrue) > vd vtrue = (1 / η ) vd vtrue
= (1 / 0.39)(0.09 m d-1) = 0.23 m d-1 —→ Thus for the contamination to travel 200 m, it will take
t = 200 m / 0.23 m d-1 = 869 d = 2.4 years
appropriate assessment
protect habitats & species (EIA more general)
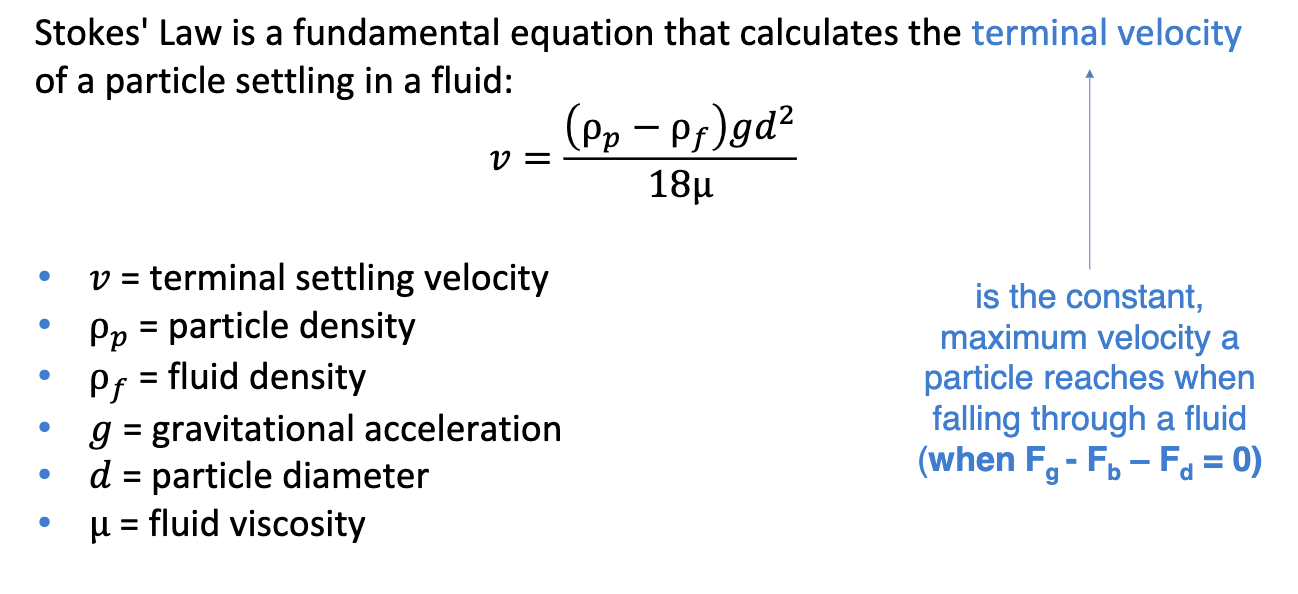
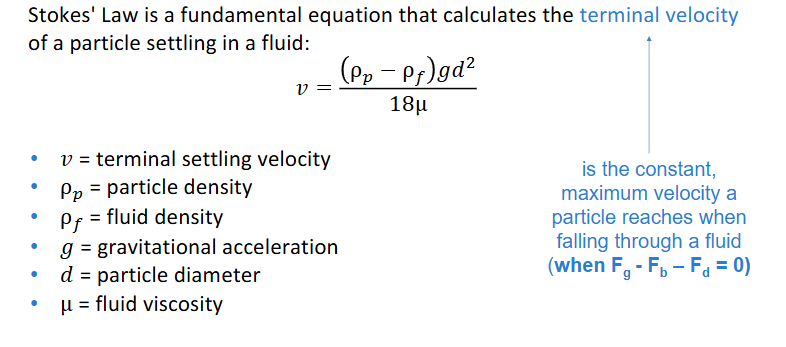
STOKES Grit is a common element in raw municipal wastewater and must be removed so that it does not damage machinery in the plant, e.g. pumps. Removal can take place by gravity settling. If the smallest particles to be removed have diameter, DP = 100 μm and a density of 2.65 g/cm3, how fast will they settle? If water has a viscosity of 0.01185 g/cm-1s-1 and a density of 1 g/cm3. Use Stokes’ law vs = g [(ρp – ρf ) / 18μ] * Dp2
Apply the Stoke’s law formula here:
vs = g [(ρp – ρf ) / 18μ] Dp2 = [(980 cm s-2 (2.65 g cm-3 – 1 g cm-3)) / (18 (0.01185 g cm-1s-1)] * (100 X 10-4cm)2 = 0.76 cm s-1 (27 m h-1)
theoretical oxygen demand
oxygen required to oxidize organic pollutants
ADJECTIVE FLUX A municipal wastewater effluent is discharged into a river. The effluent contains 5 mg P/l and is discharged at the rate of 1 m3/s. Upstream of the discharge, the river contains a background concentration of 0.01 mg P/l and flows at a volumetric rate of 25 m3/s. What is the flux density of P downstream of the effluent discharge if the river has a cross-sectional area
of 30 m2?
• How will you construct the materials balance equation in this case?
• What is the concentration of Phosphorus (mg P/l) downstream?
• What is the average velocity of flow (m/s) downstream?
Qmix = Q1 + Q2
Qmix Cmix = Q1C1 + Q2 C2
Cmix = ((Q1C1) + (Q2C2 )) / (Q1 + Q2)
Substitute values and calculate for Cmix
Cmix = ((25 0.01) + (1 * 5 )) / (25 + 1) = 0.20 mg L-1
vave = Qmix / A = [(25 +1)] / 30 = 0.87 m s-1
avection
bulk transport with fluid — material moves with mean fluid flow
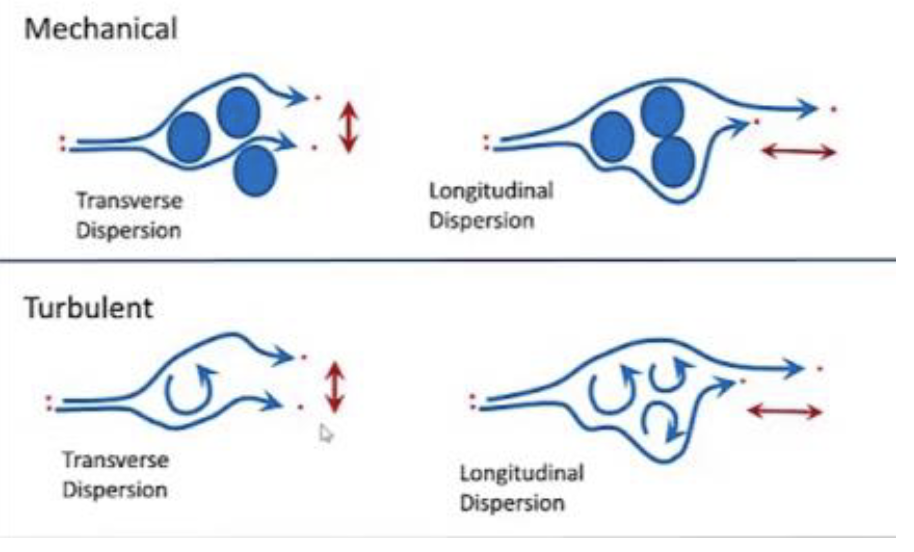
dispersion
movement by random motion within a fluid 1. molecular is strictly random motion of molecules 2. turbulent is random motion of fluid in mass transport
plug flow reactor
no mixing assumed before after plug - that it is advective transport (actually gaussian distribution)
stoke’s law
calculates terminal velocity of a particle settling in a fluid where terminal velocity is the constant max velocity a particle reaches when falling through a fluid so Fg-Fb-Fd = 0)
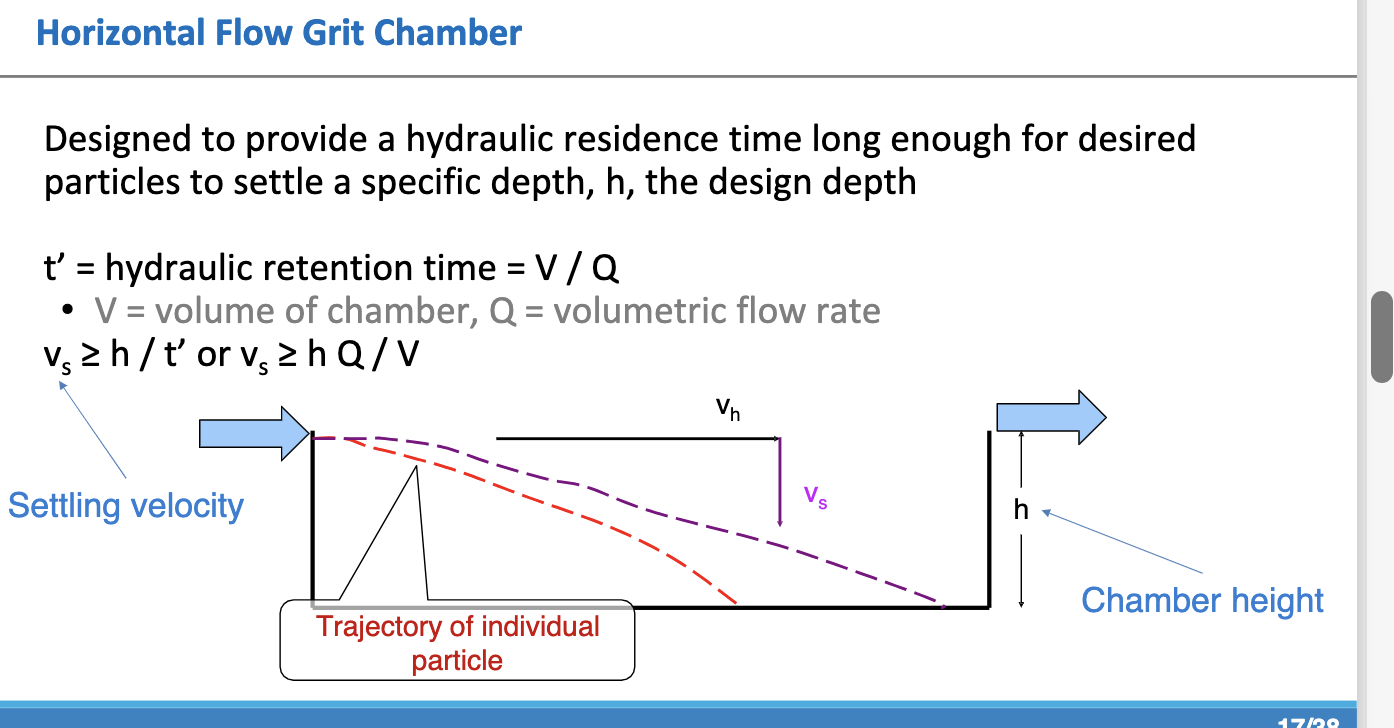
horizontal flow grit chamber
provide hydraluic residence time long enough for desired particles to settle specific depth, h, design depth
primary clarifier vs grit chamber
primary clarify removes through gravity settling —- grit chamber removes debris like ragging of clogging and usually spins in reactor (stokes low in horizontal flow or aeration helical flow pattern)
hydraulic gradient
rate of loss of energy due to friction delta h / delta x in porous media flow
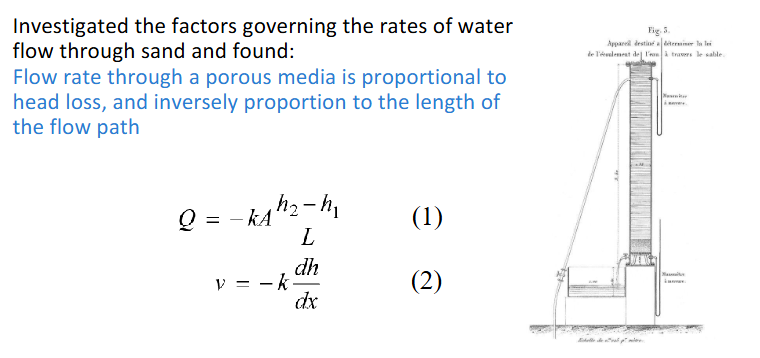
darcy’s law
k is the hydraulic conductivity in m/d
streer-phelps equation
predicts the dissolved oxygen changes in water over time after introduction of a biodegradable substance into an aquatic environment
t is the time for water to travel a distance x downstream (t=x/U river velocity)
if DO is taken as water quality parameter, streeter-phelps equation can provide relationship between water quality standards and effluent standards

deoxygenation coefficient k1
calculated to give the best fit to BOD data
characteristic of particular waste
affected by temperature
affects relative easy with which waste or waste water is degraded
affects the rate of oxygen demand, but not the ultimate demand
reaeration rate k2
characteristic of surface water
waters with swift movement and turbulence have higher k2
aral sea
saline lake - diverted to irrigate desert water level drop and salinity rose, soil eroison, dust storms.
what do engineers design for
robustness, adaptability, resilience
last for long term (sustainable) respond to threats (resilience)
main source of NOx in Ireland
traffic emissions
contributes to ground level ozone and acid rain
PM 10 & PM 2.5 in Ireland in relation to WHO guidelines
both above
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs)
can impact water quality
organic compounds from burning
the overall AQIH
highest of five pollutant indices (ozon, nitrogen, sulphur, PM 2.5, PM 10)
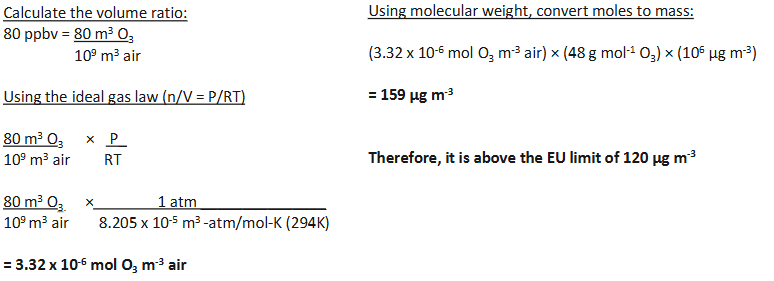
We know the hourly mean value (for the EU directive) for ozone (O3) is limited to a daily average of 120 μg/m3, but our sensor measures the concentration of O3 in ppb.
What is the concentration in μg/m3 for a concentration of O3 of 80 ppbv, assuming the temperature is 21oC and pressure is 1 atm.
Is it below the EU limit?
What is the concentration in μg/m3 for a concentration of O3 of 80 ppbv?
calculate volume ratio from concentration value oxygen to air
use ideal gas law to get n = V X (P/RT)
use molecular weight to convert moles to mass
EU limit is 120
advection
when molecules move in bulk with mean fluid flow
plug flow
dispersion
random motion within a fluid
eliminates dramatic concentration gradients
EU treaties
the objectives of the european union,
the rules for EU institutions, how decisions are made and
the relationship between the EU and its member countries.
stokes law
determines terminal velocity
darcy law
flow rate through porous media proportional to head loss and inversely proportional to length flow path
dh/dx is hydraulic gradient with dh as the loss of energy due to friction
available volume for flow, velocity, true velocity
water framework directive
BOD, chemical status, physico-chemical, hydromorphological
agreed by all EU member states in 2000
implemented as 6 yr cycle in 2009
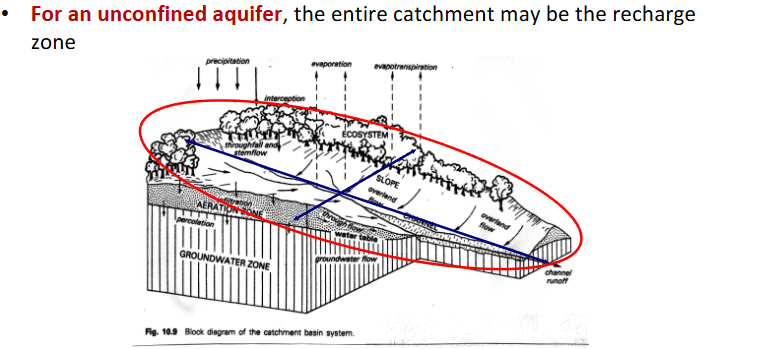
catchment for recharge zone in an unconfined aquifer
hyetograph
graph of intensity (mm/hr) vs time
depth-duration-frequency analyses
polluter pays principle
someone is financially responsible for elimination of pollution they cause
customers pay for their own bag or bring one
precautionary principle
must take a precautionary approach (policy makers) in situations of uncertain damage
proximity principle
waste should be managed as close to source of creation as possible
regulations
legal acts that apply automatically and uniformly to all eu countries as soon as they enter into force, without needing to be transposed into national law.
They are binding in their entirety on all EU countries.
directives
require EU countries to achieve a certain result, but leave them free to choose how to do so.
bathing water directive
must monitor at least two parameters of faecal bateria
must inform public about bathing quality
should
do every year
four samples per season
at the end of every season
prepare description
decisions
are binding to those whom which it is specified / addressed to (only).
recommendations
EU institutions to make their views known
to suggest a line of action without imposing any legal obligation on those to whom it is addressed.
They have no binding force.
opinions
allow institutions to make a statement, without imposing legal obligation.