(19): introduction to biogeography
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
in koppen’s climate classification, what does A stand for?
tropical
in koppen’s climate classification, what does B stand for?
dry
in koppen’s climate classification, what does C stand for?
temperate
in koppen’s climate classification, what does D stand for?
continental
in koppen’s climate classification, what does E stand for?
polar
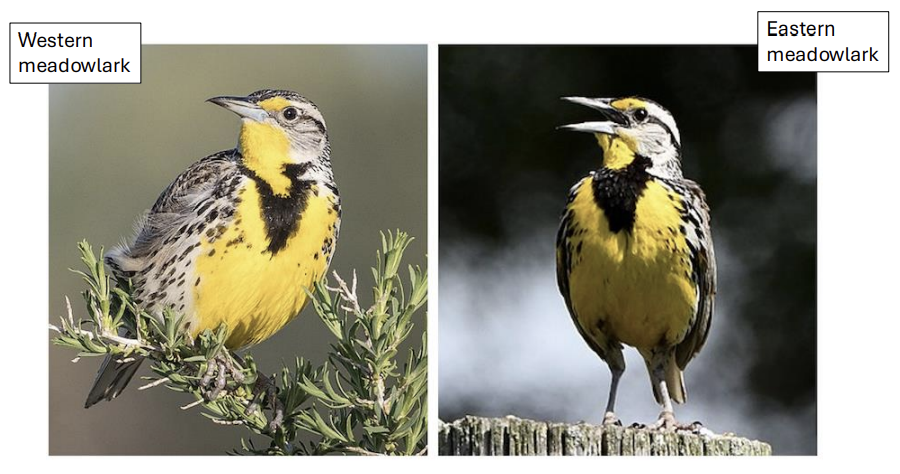

what is a biological concept?
compatibility based on the ability to reproduce
(eastern and western meadowlark)
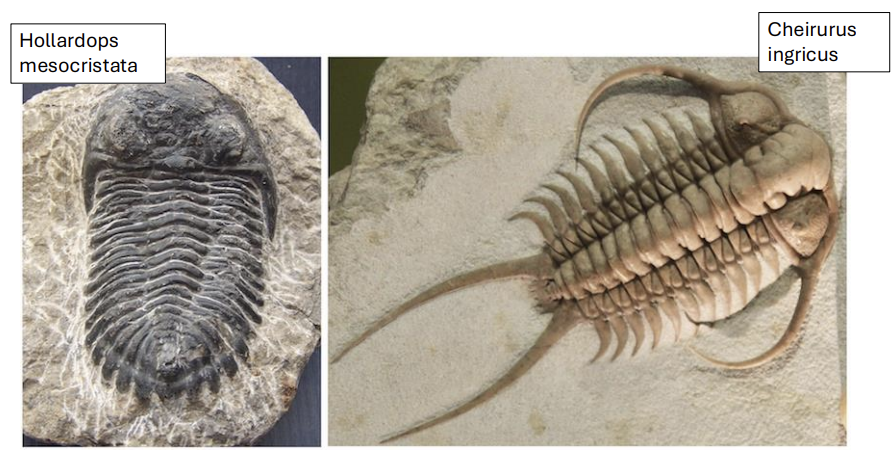

what is a morphological concept?
compatibility based on physical characteristics
(fossils)
what is a phylogenetic concept?
compatibility based on evolutionary relationships
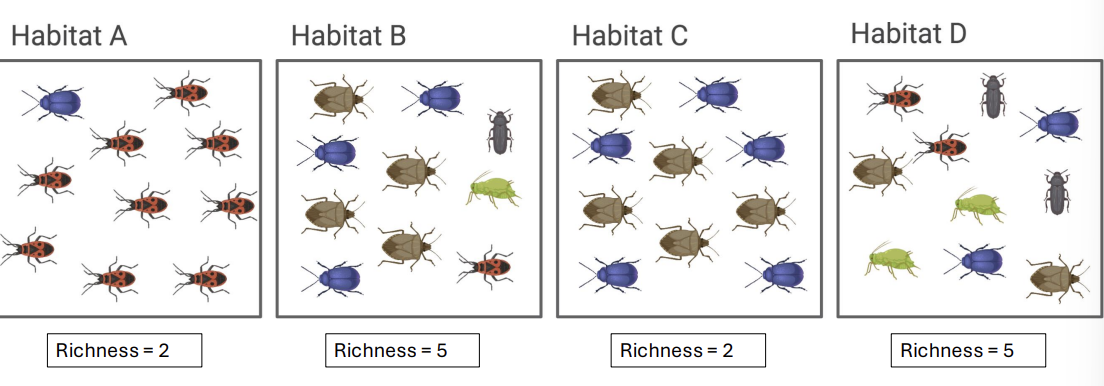
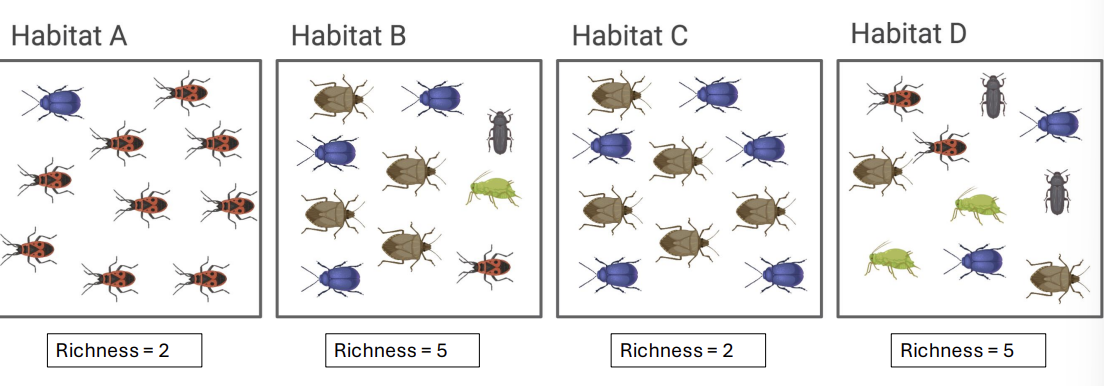
what is species richness?
the number of species present
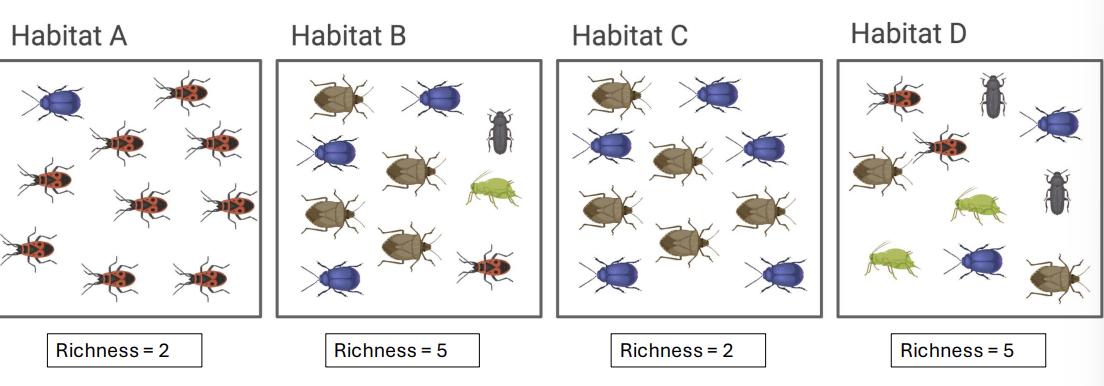
what is species evenness?
how equally abundant each species is (even)
what is species diversity?
the mathematical formulas that combine richness and evenness
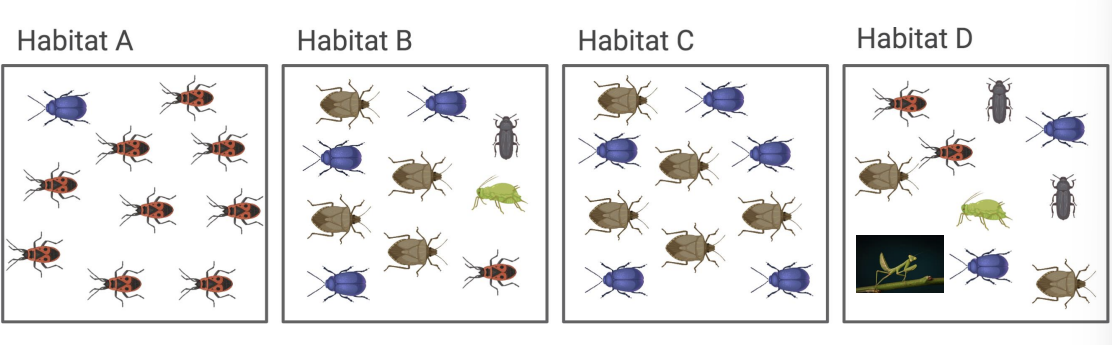
what is endemism?
a species found in only one place on earth (praying mantis)
what is a macroscope?
viewing patterns at a large geographic and temporal scale, the opposite of a microscope
which area of the earth is more rich in species?
the tropics, due to climate stability
which area of the earth has more unique species?
islands, due to isolation
biogeographic realms:
each realm has a characteristic fauna that evolved in relative isolation. (originally 6)
what is important about the Australian region?
it consists of unique plants and animals that are not found anywhere else
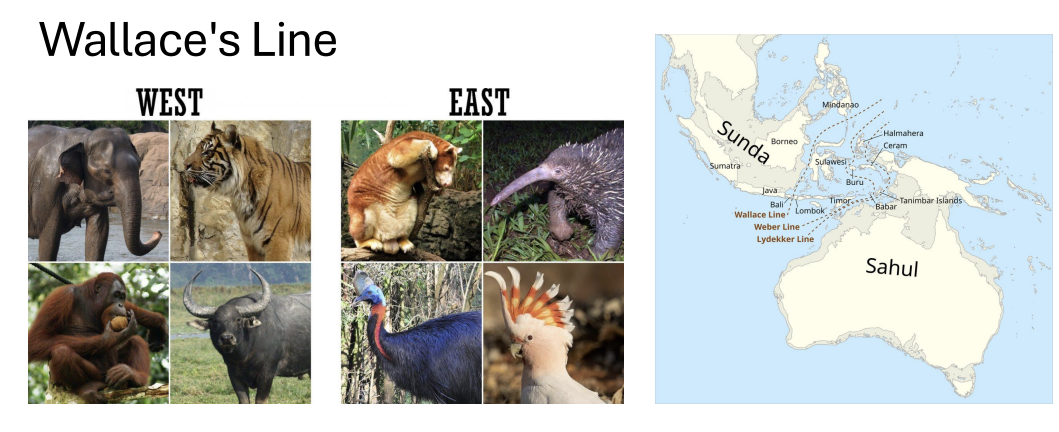
what is wallace’s line?
a sharp boundary that separates Asian fauna (west) from Australasian fauna (east)
runs between Bali and Lombok, then Borneo and Sulawesi
biodiversity = ?
speciation + dispersal - extinction
what is dispersal?
plants and animals moving across natural barriers (flying, wind, ocean, and river currents, ballooning, rafting, hitchhiking, etc.)
what is vicariance?
barriers that naturally change and split the landscape (pangea)
what is the difference between vicariance and dispersal?
vicariance = barrier forms and splits a population
dispersal = plants & animals move on their own and cross a barrier
if divergence (barriers diverging) dates match geological events, what has occurred?
vicariance
if multiple unrelated groups show the same distribution patterns, what has occurred?
vicariance
if a single lineage is in an unusual place, what has occurred?
dispersal
what is an example of vicariance?
the great American biotic interchange (GABI)
what factors promote biodiversity?
area, isolation, time (antiquity)
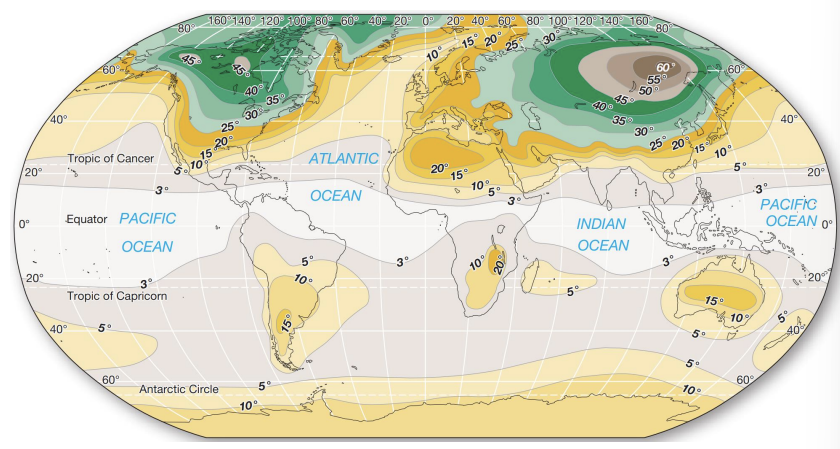
why are the tropics so diverse?
climate stability
how have the tropics been more climatically stable over long periods of time?
time stability (ice age)
how does the earth’s area affect the diversity of the tropics?
because the earth is a sphere, the tropics have a larger area
what are biotic interactions?
interactions between organisms, they promote specialization
what is the mountain diversity gradient?
diversity is generally highest in the middle mountains
what is the depth diversity gradient?
diversity is generally highest between the deep ocean and surface ocean
what are the five biogeographic rules?
species area relationship
rapoport’s rule
bergmann’s rule
allen’s rule
island rule
what is a species area relationship?
increasing area increases the number of species
what is rapoport’s rule?
species ranges increase towards the poles
what is bergmann’s rule?
body size increases with latitude (larger animals are in colder climates and smaller animals are in warmer climates)
what is allen’s rule?
appendage size (ears, tails, limbs) decreases with latitude due to rates of heat loss
what is the island rule?
island species show size changes toward intermediate sizes
(gigantism & dwarfism) (release from competition)