biology - DNA, transcription, translation
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
chromosomes are made of
long coiled molecules of DNA wrapped around histones
DNA molecule contains four different bases
cytosine
adenine
thymine
guanine
base pairings for DNA
A-T
C-G
wrong bases paired together can lead to
apoptosis
programmed cell death
what does DNA control
production of proteins
what is DNA
the genetic material found in all living organisms
types of nucleic acid
DNA and RNA
where is DNA found in which cell
nucleus of eukaryotes
and plasmids of prokaryotes
where can DNA also be found
mitochondria
chloroplasts of plant cells
RNA is found in what forms
transfer RNA
messenger RNA
ribosomal RNA
genetic material of some viruses
what does DNA and RNA consist of
units called nucleotides
what does a nucleotide consist of
sugar, phosphate and one of the 4 bases
what does the nucleotide base component do
compromise the genetic code
condensation polymerisation
joining nucleotides together
how are nucleotides joined together
covalent bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the third carbon atom of the pentose sugar in the next nucleotide.
what does condensation polymerisation produce
an alternating backbone of sugar-phosphate-sugar along the polynucleotide chain.
DNA structure
double stranded (double helix)
sugar and phosphate on outside (backbone)
nitrogenous bases created "rungs" (held together by hydrogen bonds)
the two strands of helix run in opposite directions (anti parallel orientation)
hydrogen bonds are
VERY STRONG
the more bonds means
the larger the molecule
DNA strand
double
RNA strand
single
DNA sugar
deoxyribose
RNA sugar
ribose
bases for RNA
guanine
cytosine
uracil
adenine
role of DNA
storing and transferring genetic information
role of RNA
to directly code for amino acids and act as a messenger between DNA and ribosomes to make proteins.
nucleotide structure in more depth
nitrogenous base (A,T,C,G) or (A,U,C,G)
pentose sugar (will have 5 sides)
1 or more phosphate groups
carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1′ through 5′
the base is attached to the ribose's 1′ position, and the phosphate is attached to the 5′ position.
the 'prime' distinguishes
these residues from those in the base
the T base is replaced with what mRNA base
uracil
transcription definition
transcription involves the production of a piece of messenger RNA (mRNA) using the DNA template. Happens in the nucleus of cells.
transcription pairs with
mRNA
first step of transcription
initiation:
RNA polymerase binds with transcription factors within the promoter region. This signal weakens the hydrogen bonds in DNA to break it - unwind or unzip it. This allows RNA polymerase to start transcribing.
initiation of transcription (different answer)
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region on the DNA and begins to unzip the DNA into two strands.
second step of transcription
elongation:
RNA polymerase moves along the strand and brings "free" complementary RNA nucleotides. Producing a new single strand of pre-mRNA.
elongation of transcription (different answer)
RNA polymerase unzips the DNA and assembles RNA nucleotides using one strand of DNA as a template.
termination of transcription (different answer)
DNA zips up and mRNA leaves the nucleus
third step of transcription
termination:
transcription ends when RNA polymerase detaches, releasing the pre-mRNA - this allows the DNA to reform its original double helix (the pre-mRNA becomes mRNA).
steps of transcription
initiation, elongation, termination
RNA polymerase
an enzyme that builds RNA by reading the DNA
how to tell if its a copy
pairs are A-U not T
summarisation of transcription
-DNA unwinds/unzips
-RNA polymerase catalyses transcription
-nucleotides are joined by RNA polymerase
-transcription of DNA template strand to pre-mRNA
-pre-mRNA is complementary to DNA template strand
-in the pre-mRNA 'A' pairs with 'U' not 'T'
why can't DNA leave the nucleus
it is too big
sections of a gene
promoter, coding sequence, terminator
first section of a gene
promoter region (TATA box)
second section of a gene
coding sequence (transcribed gene) (transcription)
last section of a gene
terminator
the terminator sequence
post-transcriptional process means
after transcription has occurred
exons (simple)
the coding regions
introns (simple)
sequences that do not code for the protein
in eukaryotic cells a piece of what is produced as a result of transcription
pre-mRNA
what needs to be modified before translation
the piece of pre-mRNA
what does the piece of RNA produced contain
introns and exons
what is removed to leave only the part of mRNA that will be expressed
introns
what are the three processes that pre-mRNA will undergo before becoming mRNA and functional outside of the nucleus
addition of a methyl cap (5' capping)
addition of a poly A tail (3' polyadenylation)
RNA splicing (removing introns)
what happens at the end of post transcription
there is a piece of mRNA that can be translated into a protein
what does the three processes do
completes the molecule
coming out with nice ends
summarised post transcriptional process
pre-mRNA
remove excess info
3 processes
becomes mRNA
introns definition
introns in the DNA are long sequences of codons that have no protein-coding function.
introns may be remnants of now unused ancient genes
codons
a three-nucleotide sequence of DNA or mRNA that specifies a particular amino acid or termination signal; the basic unit of the genetic code.
what happens when the introns are removed
it leaves only the part of mRNA that will be expressed
what does the methyl cap and poly A tail do for the pre-mRNA
THESE PROTECT THE RNA FROM DEGRADATION
degradation
a decline to a lower condition, quality, or level
translation definition
translation is the process of building a polypeptide chain from amino acids, guided by the sequence of codons on the mRNA.
structures involved in translation
messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomes, amino acids
messenger RNA in translation
delivery service
molecules (mRNA) carries the code for the DNA that will be translated into an amino acid sequence
transfer RNA in translation
deliver truck - gets it to the right location
molecules (tRNA) transport amino acids to their correct position on the mRNA strand
ribosomes in translation
storage shed/facility
provide the environment for tRNA attachment and amino acid linkage
amino acids in translation
from which the polypeptides are constructed
what fits into the grooves of the ribosomes
mRNA strand and polypeptide chain
what is the ribosomal subunits constructed up of
protein and ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
when are the ribosomal subunits form a functional unit only
when they attach to a mRNA molecule
the job of the ribosome
sending information out
when they see a need they will act on it
like firefighters
tRNA molecule
anticodon
the site of the 3-base sequence that 'recognises' and matches up with the codon on the mRNA molecule
mRNA molecule
mRNA
anti
opposite to the codon
nuclear pore
in which the mRNA passes into the cytoplasm
exit point of the nucleus
anticodon
group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon
DNA polymerase
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of the DNA molecule.
helicase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix at the replication forks, separating the two parental strands and making them available as template strands.
gene expression
process by which a gene produces its product and the product carries out its function
differential gene expression
The expression of different sets of genes by cells with the same genome.
direction of transcription
5' to 3' direction
initiation of transcription
RNA polymerase attaches to the promoter region on the DNA and begins to unzip the DNA into two strands.
elongation of transcription
RNA polymerase unzips the DNA and assembles RNA nucleotides using one strand of DNA as a template.
structural gene
genes that code for polypeptides
regulatory gene
A gene that codes for a protein, such as a repressor, that controls the transcription of another gene or group of genes.
homeotic genes
Genes that determine basic features of where a body part is.
transcription factors
a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence.
sense strand
original
antisense strand
opposite
moves from 3' to 5' (opposite direction)
adenine base
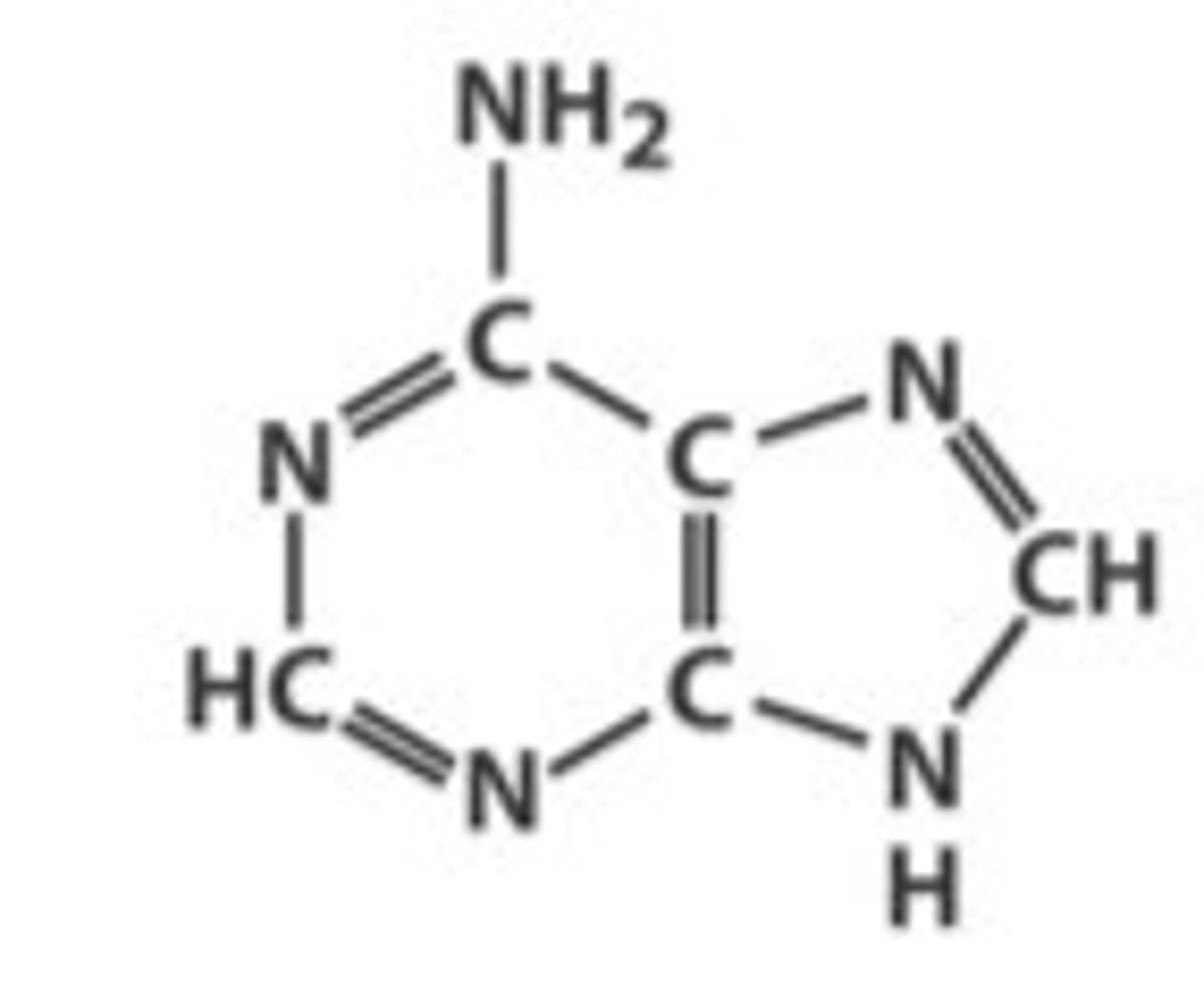
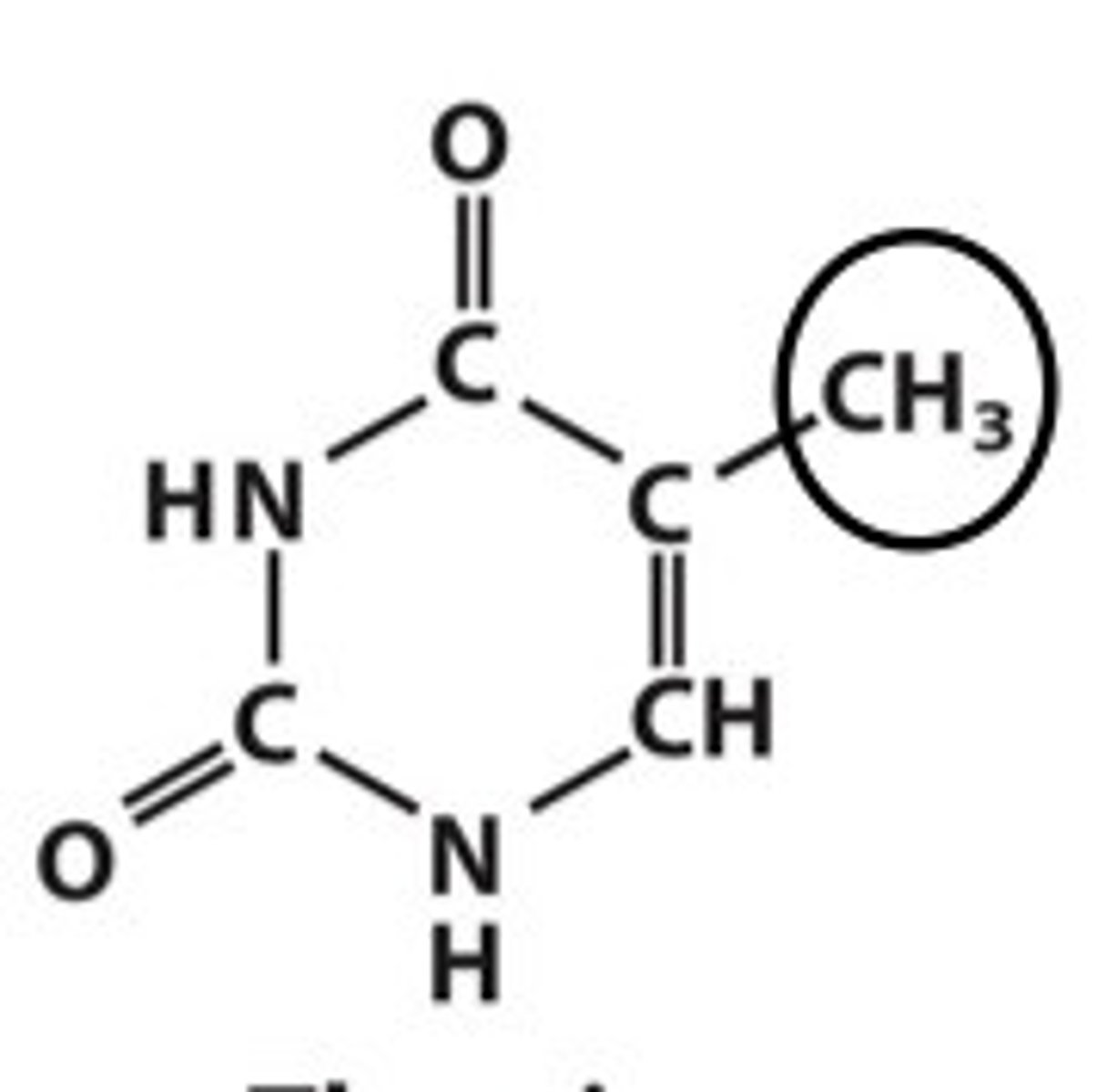
thymine base
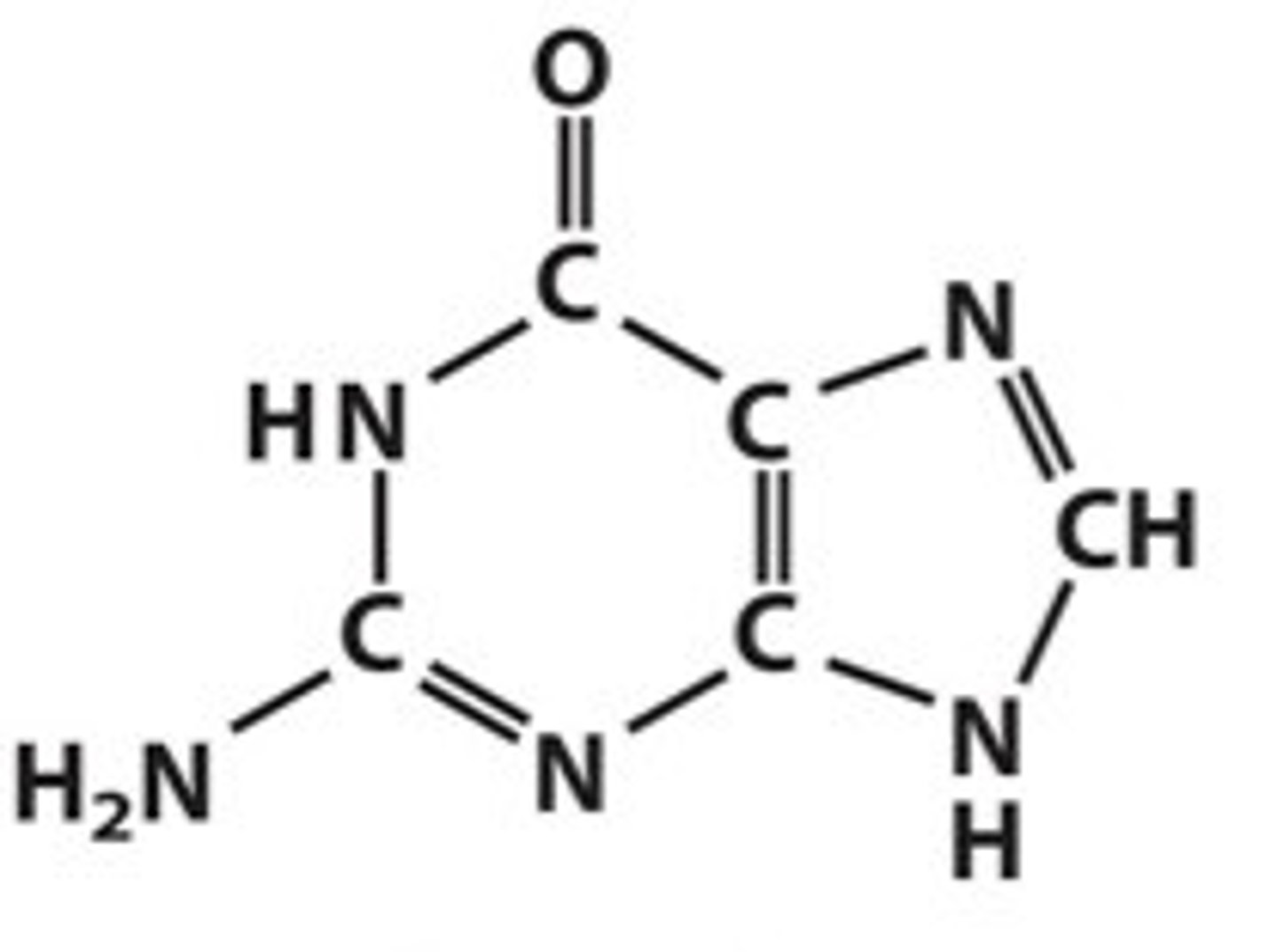
guanine base
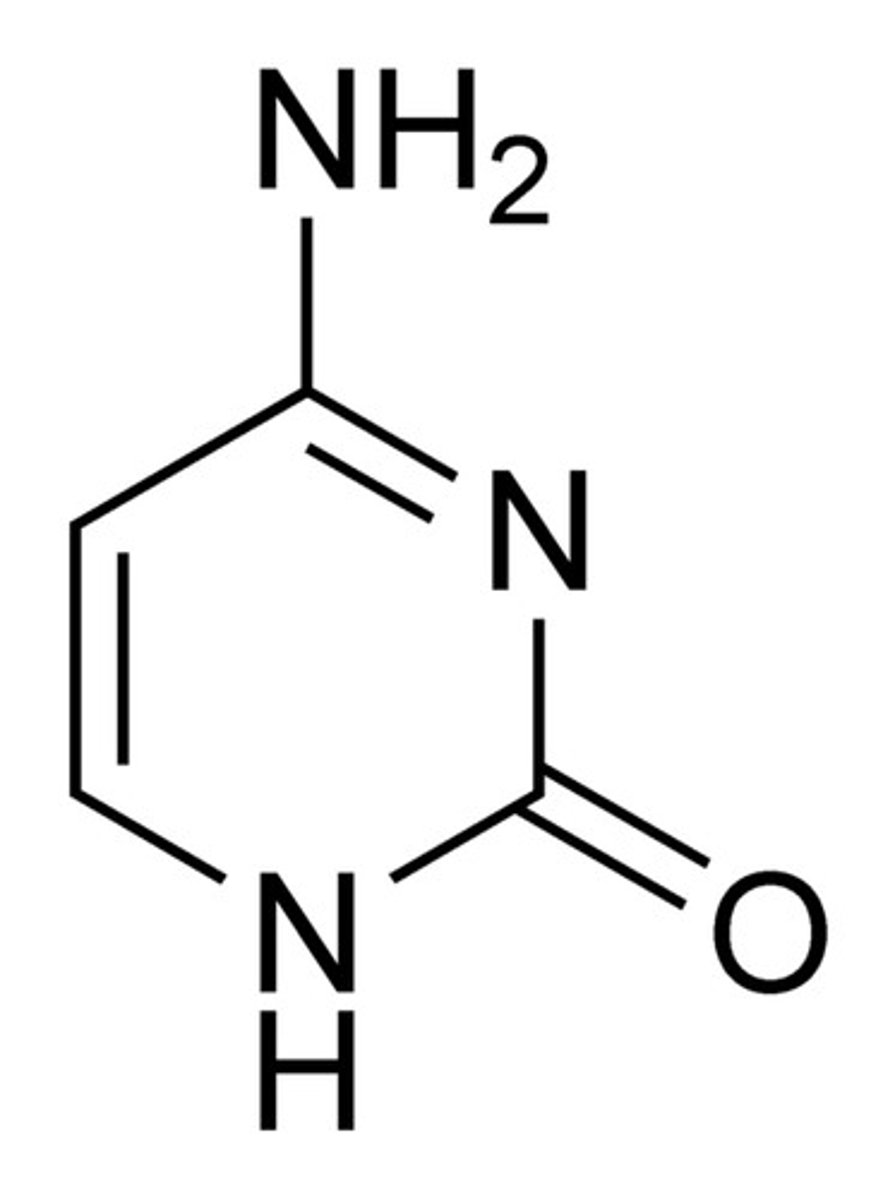
cytosine base
anti parallel
run in opposite directions
also paired with opposite pairs
dissociation
split in hydrogen bonds between bases in double helix
helpful in dna replication
polysome
assembly of ribosomes translating a piece of mRNA
genetic code
all living things on earth use the same code to turn DNA or RNA information into protein amino acid sequences.
degenerate
multiple things can code for the same amino acid