Influential Ethologists
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
31 matching/ multiple choice, 4 fill in the blank, 6 short answers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Who is the father of classical conditioning?
Ivan pavlov
Who conducted the little Albert experiment?
John B. Watson
Who did operant conditioning?
B.F Skinner
This ethologists work revolved around the study of animals as sentient beings.
Donald Griffen
Later findings revealed that prior education, training, and culture played an important role in the performance on standardized assessments
Robert Yerkes
Proved that fears may transfer to other similar objects/ scenarios by association.
John B. Watson
Able to understand/ “use” 92 words
Bunny/ Bunnys mom
studied memory retrival
karl lashley
Demonstrated how human intervention has changed the appearance/behavior of an animal.
Dimitri Belyaev
studied altruism
Edward O Wilson
Worked primarily with chimpanzees (and later, great apes)
Jane Goodall
Found that some species of bird have cognitive abilities on par with primates
Irene Pepperberg/ Alex
Studies involved domestication
Dimitri Belyaev
Who said “… The only reason that animal thinking was given consideration at all”
Donald Griffen
Chemical signs play a major role in communication and behavior.
Edward O Wilson
Made incisions into the cortex of rat brains
Karl Lashley
Demonstrated the importance of social bonding during the early stages of life
Harry Harlow
Developed a comparative analysis for studying the sociology and psychology of insects
William Morton Wheeler
Equus
Monty Roberts
Training began as a way to develop assistive technology for non- verbal children
Bunny/ Bunnys mom
Purposive behaviorism (example: you study for a test specifically for a good grade)
B.F Skinner
Father, lord, or king of the ants
Edward O Wilson
Thinks “like an animal” to improve processes in slaughterhouses and other facilities
Temple Grandin
worked on latent learning
Tolman
FatherS of ethology
Konrad Lorenz, Niko Tinbergen, and Karl Von Frisch
Trained a bird to differentiate between size, color, texture, make comparisons between two different things, etc
Irene Pepperberg/ Alex

Law of figure ground
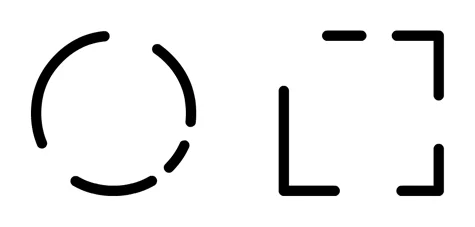
(not the exact same picture as on test)
Law of closure
(not the exact same picture as on test)
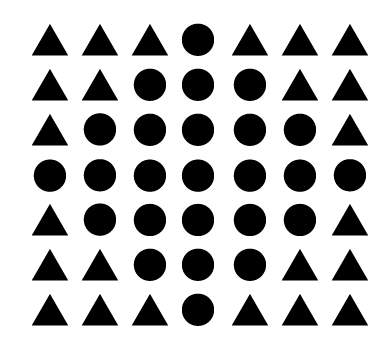
law of similarity
(not same pic as on the test)
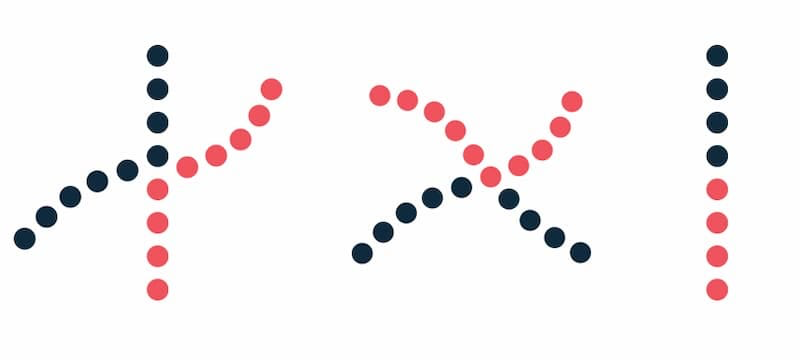
Law of continuity
Identify the stimulus in pavlov’s experiment.
foot steps/ bell ringing
Identify the dogs response in pavlov’s experiment.
salivation
another word for memories
engrams
Animals (including humans) put off chemical signals to communicate certain things. These are called…
pheromones
Describe why/how athletes might “choke” during the big game. Underline the proper name for this phenomenon in your explanation
The Yerkes- Dodson Theory explains that there is an “ideal” level of stress when performing any task for best performance. Too little stress, and you may be too relaxed to do well, and too much stress will cause you to “choke.”
Give an example OR definition of shaping a behavior.
Taking a natural/ pre-existing behavior and changing, or shaping it, to be something else (generally something we desire.) Ex: horses begging —> horses bowing
Give an example of latent learning.
Essentially subconsciously learning. Ex: the rat maze, or if you watch someone make a recipe enough times you may be able to do it without assistance as well.
What is meant by the “critical period”?
The period when an organism is very young and impressionable. During this period, it is critical that an organism experiences certain things in order to end up “typical.”
Why are many behavioral studies of the past ( and some of the present) considered controversial?
Because they are not humane to the animal, or in some cases, person. Little Albert was traumatized at a young age, and Karl Lashley caused permeant physical and mental damage to the rats.
Explain “join up” and why it works better/faster than older methods.
Join up is a method where a horse is asked to move its feet around a person I order to gain respect for the person, but isn’t forced to be near the person. Essentially the horse decides it is better to be with the trainer than to run. This method works because it causes for the trainer to become a safe space for the horse, building trust. Older methods force the horse to be near the trainer while the trainer does things that the horse perceives as scary. This causes for the horse to resist the person, making the older methods take longer than join up.