Microbio Test 3 (2015,16,17)(S-last)
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
157 Terms
The production of viral antigens in a bacterium circumvents many problems associated with virus attenuation. Which of the following is not true of genetically engineered virus vaccines?
a) Cost following start-up is higher than with attenuated vaccines
b) No danger of causing an infection when product is used therapeutically
c) Large-scale production is possible in fermenters
d) Concentration of antigen can be manipulated to ensure optimal dosage
e) Time to market for synthetic antigens is generally quicker than with attenuated vaccines
Cost following start-up is higher
Synthesis of an oligonucleotide with a sequence deviating in at least one base from the wild-type gene followed by replacement of the wild-type gene with the synthetic sequence is known as:
Site-directed mutagenesis
The Sanger method relies on
ddNTP (limiting in the reaction)
DNA microarrays are used to perform which of the following analyses?
Determine which mRNA transcripts are present in a cell under defined conditions
The list below contains three methods used for the location or detection of a desired clone. Circle each of the three correct methods. Remaining methods are not used for this purpose.
a) Biochemical identification of the correct species used in a cloning procedure
b) Detection of protein function of the desired gene product
c) Antibody detection of an expressed protein on the surface of a desired cell
d) 16S rRNA sequencing to detect the correct bacterium
e) Detection of a particular gene sequence using a tagged nucleic acid probe
b) Detection of protein function of the desired gene product
c) Antibody detection of an expressed protein on the surface of a desired cell
e) Detection of a particular gene sequence using a tagged nucleic acid probe
What does FISH stand for?
Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization
FISH probes can be used to:
a) identify metabolic activity in environmental samples
b) differentiate taxonomic groups of Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
c) discriminate species within a mixed bacterial population
d) both a) and b)
e) both b) and c)
both b and c
Penicillin is produced by only a relatively small number of strains of microorganisms, is not essential for growth and reproduction, and its formation is dependent on the growth conditions and medium constituents of the culture. These characteristics indicate that penicillin is a ______ metabolite.
Secondary
Which of the following statements is true? (Assume bacterial genetics with no introns. Answer only one.)
a) It is generally possible to determine the exact genetic code for a protein if the primary sequence of the protein is known
b) It is generally possible to determine the exact primary sequence of a protein if the genetic code for the protein is known
c) The presence of post-translational modifications of proteins means that the primary sequence of a protein cannot be determined from the genetic code for the protein
d) In most cases, the sequence of a bacterial gene describes the structure of the protein it encodes
It is generally possible to determine the exact primary sequence of a protein if the genetic code for the protein is known
In Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2DPAGE), the identification of proteins is carried out by a process known as peptide mass fingerprinting. In this process how is the sequence of a protein determined?
By matching masses of theoretically digested predicted gene products from the genome with observed peptide masses of actual digested proteins
What is the definition of the term Isoelectric Point
pH at which the protein has a neutral charge of 0
Which of the following statements is false with respect to the basic strategy for cloning?
a) Source DNA is isolated and fragmented
b) DNA fragments are joined to a cloning vector using DNA ligase
c) Cloning vector is introduced and maintained in a host organism
d) Host organism chromosomal DNA is mutated by addition of chemical agent
e) Desired clone or recombinant DNA is amplified
Host organism chromosomal DNA is mutated by addition of chemical agent
In aerobic industrial microbial processes, one of the most difficult problems to solve is:
Providing adequate aeration
The principal evidence that supports the idea that RNA was the nucleic acid from which all life evolved includes all of the following except
It is a common genetic material of viruses
In the polymerase chain reaction, DNA is amplified following the rapid cycling of annealing, primer extension, and denaturation steps. Match the temperatures with the correct step:
Temperature options:
a) 35°C
b) 50°C
c) 70°C
d) 90°C
Denaturation : 90°C
Annealing: 50°C
Primer Extension: 70°C
As revealed by rRNA sequencing, the mitochondria are most closely related to:
Argobacterium and Rhyzobium species
For 5/6 of its history, the dominant life form on Earth has been unicellular.
True
The Miller-Urey experiment was responsible for which of the following?
demonstrated that an electric spark when applied to a mixture of presumed early earth gasses could produce many of the organic molecules found in living cells
The characteristics of mitochondria and chloroplasts that link them phylogenetically to the bacteria have led scientists to theorize that early bacteria developed a relationship with proto-eukaryotes which has come to be known as the theory of ________.
Endosymbiosis
The evolutionary distance between two organisms can be measured by differences in the sequence of homologous genes isolated from them. Current evolution-based taxonomies used to establish evolutionary distance between prokaryotes are based (primarily) on what molecule?
16S rRNA
Two organisms having less than 97% homology in the sequence of the evolutionary chronometer referred to above indicates that they are separate species.
True
The types and proportions of fatty acids present in cytoplasmic membrane lipids and the outer membrane lipids of Gram-negative bacteria are major phenotypic traits of interest. The technique for identifying these fatty acids has been nicknamed: (Acronym is OK
FAME (Fatty Acid Methyl Ester analysis)
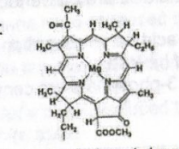
The structure shown to the right is
Chlorophyll
Two distinct reactions are involved in photoautotrophy. The light reaction is run primarily to produce ______, while the dark reaction is used to ______.
ATP, NADPH
Carbon fixation
Whether an organism is classified as a photoheterotroph or a photoautotroph depends on its:
Carbon source
When cyclic photophosphorylation occurs (using only Photosystem I), both ATP and NADPH are produced but no electrons are consumed.
False
In photosynthetic membranes, reaction center chlorophylls are surrounded by more numerous light-harvesting chlorophylls which function to absorb light and funnel its energy to the reaction center.
True
Cross-feeding in bacterial communities is known as:
Syntrophic consortia
In non-cyclic oxygenic photosynthesis, the primary electron donor is ________, the terminal electron acceptor (directly reduced by the electron transport system) is
H2O
NADP+
All of the following are true of phycobilins except:
a) They have long hydrocarbon chains arranged in a conjugated double bond system
b) They are usually red or blue
c) They typically act as the reaction center responsible for donating electrons to bacteriopheophytin
d) They transfer energy (via allophycocyanin) to the reaction center to be used in photophosphorylation
They typically act as the reaction center responsible for donating electrons to bacteriopheophytin
Phycobilins are just light-harvesting pigments, not the reaction center
In order to fix carbon using the Calvin Cycle, autotrophs require reducing power in the form of NAD(P)H + H⁺. This reducing power is necessary to:
reduce 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid to glyceraldehyde-3-P
Nitrification is an aerobic process.
True
The end product of carbon fixation pathways depends on the amount of energy input into the system, resulting in reduced carbon compounds of differing carbon chain length. Match each of the three carbon fixation pathways with the number of carbons in the skeleton of their final product.
Calvin Cycle
Hydroxypropionate pathway
Reverse citric acid cycle
Carbon numbers:
a) 2 carbons
b) 3 carbons
c) 4 carbons
d) 5 carbons
e) 6 carbons
Calvin Cycle → 6 carbons
Hydroxypropionate pathway → 2 carbons
Reverse citric acid cycle → 3 carbons
In the Calvin cycle which of the following is true?
a) 12 molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate are converted to 6 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid and one hexose
b) 5 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid are converted to 10 molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and 2 hexoses
c) 12 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid serve as carbon skeletons to form 6 new molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and 1 molecule of hexose
d) 10 molecules of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate are converted to 5 molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and one molecule of hexose
12 molecules of phophoglyceric acid serve as carbon skeletons to form 6 new molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and 1 molecule
Dentrification results in the production of
N₂O, NO, and N₂
The reduction potential of H₂ = –0.42 V. The reduction potential of NADH = –0.32 V. This information indicates that hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria:
Can reduce NAD⁺ directly with hydrogen
Which of the following electron donors yields the greatest amount of energy?
H2
B/c lightest energy
The uptake of an inorganic nutrient for use in biosynthesis is an example of:
Assimilative metabolism
Sulfate reduction leads to the formation of which toxic gas?
H₂S
A microbial Guild is:
A group of metabolically related bacterial populations
Why does Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, an iron-oxidizing bacterium, only grow in waters having an acidic pH?
Ferrous iron is spontaneously converted to ferric iron at neutral pH in the presence of oxygen
Which of the following statements is true of Acridine Orange?
Dead cells are green because very little single stranded DNA and almost no RNA is present in dead cells
In a Winogradsky column enriched for the presence of sulfur metabolizing organisms, it is noticed that large areas of black precipitate are present and an area of white precipitate is present surrounded by a patch of green (as discussed in class). This information indicates which of the following ecologies?
Aerobic sulfide oxidizing bacteria are present in the white zone and anaerobic sulfate-reducing bacteria are present in the black zone.
When fields fertilized with nitrate become waterlogged, they become anaerobic (due to oxygen consumption by heterotrophs). Why does this (i.e., the lack of oxygen) result in reduced agricultural productivity?
Anoxic soils promote denitrification resulting in the production of gaseous nitrogen compounds
Which of the following is not true of viable non-culturable organisms?
a) They are alive but can never be cultured
b) They do not grow in most standard media
c) They represent the majority of microorganisms isolated from the environment
d) They are most often detected by non-culture techniques
They are alive but can never be cultured
All of the following are benefits to living within a biofilm, except:
a) Biofilms trap nutrients for growth and help prevent detachment of cells in flowing systems
b) Biofilm cells are protected from attack by reactive chemicals (such as oxidizing biocides)
c) Biofilm cells experience reduced competition for nutrients compared to planktonic cells
d) Biofilm cells are protected from attack by grazing protists and by cells of the immune system
e) Biofilm cells are protected from the activity of antibiotics
f) Biofilm cells are buffered from changes in pH, temperature, water activity, salinity, etc.
Biofilm cells experience reduced competition for nutrients compared to planktonic cells
True or False (circle one).
Most nitrate-reducing bacteria are typically facultative and will grow on oxygen when present in the environment.
True
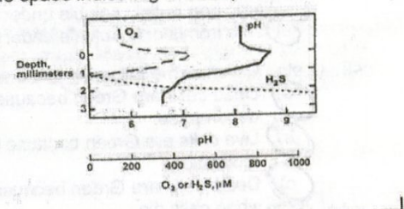
The figure below shows results from microelectrode measurements of a sediment sample (as discussed in class). From the information given in the graph, match the depth to the correct microorganism by placing the letter for each of the four organisms next to the space:
Organisms:
a) Chemoorganotroph
b) Oxygenic phototroph
c) Sulfate-reducing bacteria
d) Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria
Depth zones:
0 mm (surface) →
0 – 0.5 mm →
0.5 – 1 mm →
1 – 3 mm →
0 mm → Oxygenic phototroph
0-0.5 mm → Chemoorganotroph
0.5-1 mm → Sulfur-oxidizing bacteria
1-3 mm → Sulfur-reducing bacteria
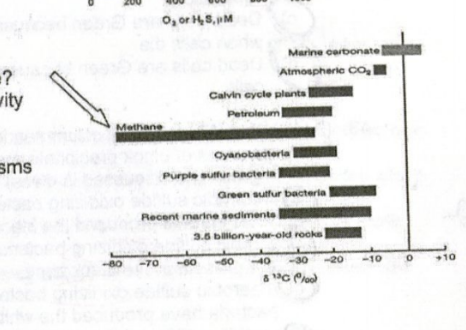
What does the chart at right indicate about methane?
a) That it is primarily produced as the result of biological activity
b) That it is primarily not produced by biological activity
c) That it is produced both biologically and abiotically
d) That its initial production pre-dates the rise of microorganisms
That it is primarily produced as the result of biological activity
Extra credit:
In the Blue-White screen typically used in cloning, a DNA fragment of interest is inserted into a multiple cloning site within a lacZ gene of a cloning vector, which is then transformed into E. coli. Upon screening of colonies that grow on plates containing X-gal, successful transformants (those containing the insert at the proper location) are indicated by which type of colonies? Circle the correct answer below.
a) Blue
b) White
White
The transfer of genetic information through mechanisms other than reproduction is called
horizontal gene transfer
Which of the following is not typically a method used for the detection of a host containing an original clone?
a) detection of gene product by antibody binding
b) detection of function of the product of inserted sequence
c) determination of altered phenotype by fatty acid profile
d) detection of inserted sequence by nucleic acid probe
determination of altered phenotype by fatty acid profile
Synthesis of an oligonucleotide with a sequence deviating in at least one base from the wild-type gene followed by replacement of the wild-type gene with the synthetic sequence is known as:
Site-directed mutagenesis
Which of the following is a definition of the term “Paralogs” as it relates to microbial genomics?
Two or more genes in the same cell whose similarity is the result of gene duplication within a chromosome
Which of the following statements is true? (Assume bacterial genetics with no introns — answer only one)
a) It is generally possible to determine the exact primary sequence of a protein if the genetic code for the protein is known
b) It is generally possible to determine the exact genetic code for a protein if the primary sequence of the protein is known
c) The presence of post-translational modifications of proteins means that the primary sequence of a protein cannot be determined from the genetic code for the protein
d) In most cases, the sequence of a bacterial gene describes the structure of the protein it encodes
It is generally possible to determine the exact primary sequence of a protein if the genetic code for the protein is known
In Two-Dimensional Gel Electrophoresis (2DPAGE), the identification of proteins is carried out by a process known as peptide mass fingerprinting. In this process how is the sequence of a protein determined?
By matching the gene sequences of theoretically digested gene products from the genome with predicted gene sequences from observed peptide masses of actual digested proteins
What is the definition of the term Isoelectric Point
pH at which the protein has a neutral charge of zero
Which of the following is not true of genetically engineered virus vaccines (compared to attenuated virus vaccines)?
a) No danger of disease if only the antigen is introduced into the patient
b) Large-scale production is possible in fermentors
c) Antigen when purified can be administered at higher concentration, resulting in better immune response
d) Time to market is generally quicker than classical techniques
e) Cost to manufacture following start-up is generally high but is compensated by higher market price for more effective vaccine
Cost to manufacture following start-up is generally high but is compensated by higher market price for more effective vaccine
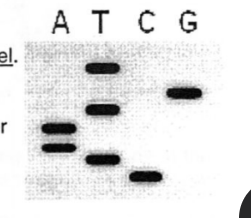
The image at right shows a sequencing gel run using the Sanger Method.
In the space provided, write the sequence of nucleotides indicated by the gel
Indicate the correct sequence of the target DNA used to perform the Sanger Sequencing Method (indicate 3’ and 5’ ends)
CTAATGT
Start from the lowest band
3’ GATTACA 5’
DNA microarrays are used to perform which of the following analyses
determine which mRNA transcripts are present in a cell under a defined set of conditions
Pyro-sequencing is a powerful technique for sequencing DNA. Which of the following characteristics is not true of pyro-sequencing
existing nucleotides at the 3’ end of the molecule are removed by heating
In aerobic industrial microbial processes, one of the most difficult problems to solve is
providing adequate aeration
The principal evidence that supports the idea that RNA was the nucleic acid from which all life evolved includes all of the following except:
it is a common genetic material of viruses
Antibiotics are produced by only a relatively small number of strains of microorganisms; they are not essential for growth and reproduction, and their formation is dependent on the growth conditions and medium constituents of the culture. These characteristics indicate that antibiotics are __________ metabolites.
secondary
Which of the following statements is false with respect to the basic strategy for cloning?
a) Source DNA is isolated and fragmented
b) DNA fragments are joined to a cloning vector using DNA ligase
c) Cloning vector is introduced and maintained in a host organism
d) Host organism chromosomal DNA is mutated by addition of chemical agent
e) Desired clone is detected and purified
f) Desired clone or recombinant DNA is amplified
Host organism chromosomal DNA is mutated by addition of chemical agent
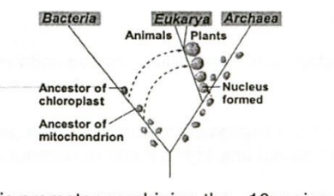
The picture at right diagrams the incorporation of bacteria into eukaryotic cells by a process that is known today as the theory of:
Endosymbiosis
The tac promoter is a chimeric promoter combining the −10 region of the lactose operon lac and the −35 region of the tryptophan operon trp.
True
For 5/6 of its history, the dominant life form on Earth has been unicellular.
(Assume the Earth is 4.567 billion years old.)
True
Two organisms having less than 97% homology in the sequence of the 16S rRNA molecule referred to above indicates that they are separate species.
True
Transposons and Insertion Sequences are both characterized by having inverted tandem repeats
True
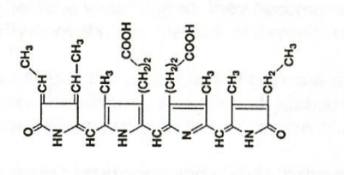
The structure shown at right is:
Phycobillin
Two distinct reactions are involved in photoautotrophy. The light reaction is primarily run to produce _____, while the dark reaction is used to ____
ATP and NADPH
Fix Carbon
In photosynthetic membranes, reaction center chlorophylls are surrounded by more numerous light-harvesting chlorophylls which function to absorb light and funnel its energy to the reaction center
True
Cross-feeding in bacterial communities is known as:
syntrophic consortia
In non-cyclic oxygenic photosynthesis, the primary electron donor is ______, the terminal electron acceptor (directly reduced by the electron transport system is) ______
H2O
NADP+
When Cyclic Photophosphorylation occurs (using only Photosystem I), both ATP and NADPH are produced but no electrons are consumed
False
In order to fix carbon using the Calvin Cycle, autotrophs require reducing power in the form of NAD(P)H + H⁺. This reducing power is necessary to:
reduce 1,3-bisphosphoglyceric acid to glyceraldehyde 3-P
The end product of carbon fixation pathways depends on the amount of energy input into the system, resulting in reduced carbon compounds of differing carbon chain length.
Match each of the three carbon fixation pathways with the number of carbons in the skeleton of their final product:
Calvin Cycle -
Hydroxypropionate pathway -
Reverse citric acid cycle
6
2
3
In the Calvin Cycle which of the following is true?
a) 12 molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate are converted to 6 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid and one hexose
b) 5 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid are converted to 10 molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and 2 hexoses
c) 12 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid serve as carbon skeletons to form 6 new molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and 1 molecule of hexose
d) 10 molecules of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate are converted to 5 molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and one molecule of hexose
12 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid serve as carbon skeletons to form 6 new molecules of ribulose bis-phosphate and 1 molecule of hexose
When fields fertilized with nitrate become waterlogged, they become anaerobic (due to oxygen consumption by heterotrophs). Why does this lack of oxygen result in reduced agricultural productivity?
anoxic soils promote denitrification resulting in the production of gaseous nitrogen compounds
The reduction potential of H₂ = –0.42 V. The reduction potential of NADH = –0.32 V. This information indicates that hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria:
Can reduce NAD+ directly with hydrogen
Which of the following electron donors yields the greatest amount of energy?
H₂
The uptake of an inorganic nutrient for use in biosynthesis is an example of
Assimilative metabolism
Nitrification is an aerobic process
True
Sulfate reduction leads to the formation of which toxic gas
H2S
A microbial guild is
A group of metabolically related bacterial populations
Why does Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, an iron-oxidizing bacterium, only grow in waters having an acidic pH?
ferrous iron is spontaneously converted to ferric iron at neutral pH in the presence of oxygen
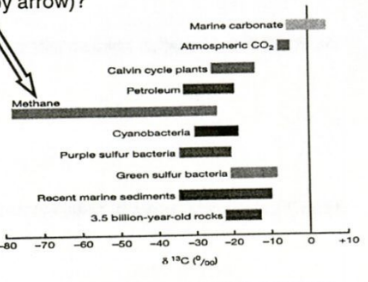
What does the chart at right indicate about methane (indicated by arrow)?
that it is primarily produced as the result of biological activity
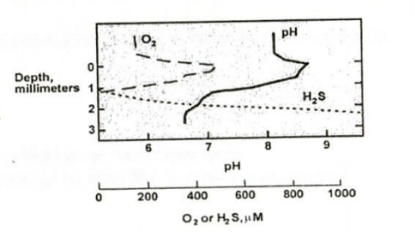
Match the depth to the correct microorganism based on microelectrode measurements of a sediment sample.
0 mm – 0.5 mm above ________
0 – 0.5 mm below ________
0.5 – 1 mm below ________
1 – 3 mm below ________
Organisms:
a) Chemoorganotroph
b) Oxygenic phototroph
c) Sulfur Oxidizing Bacteria
d) Sulfate Reducing Bacteria
0 mm – 0.5 mm above → Oxygenic Phototroph
0 – 0.5 mm below → Chemoorganotroph
0.5 – 1 mm below → Sulfur Oxidizing bacteria
1 – 3 mm below → Sulfate Reducing bacteria
Which of the following is not typically a reason why plasmids are useful for the manipulation of DNA?
Lack of restriction sites prevent unwanted cutting of plasmid by bacterial host
“Vehicles” by which DNA can be transported by the scientist/technician, and into which genes can be recombined and replicated
Cloning vectors
M13mp18 contains an intergenic region modified by insertion of a polylinker, encoding 18 amino acids and containing multiple restriction sites within a lacZ reporter. When used as a cloning vector, DNA successfully inserted into the polylinker has what effect on bacterial cultures harboring M13mp18 grown on medium containing X-gal?
colonies appear white

The image at right shows a sequencing gel run using the Sanger Method.
In the space provided, write the sequence of nucleotides indicated by the gel
For one extra point, indicate the correct sequence of the target DNA used to perform the Sanger sequencing method and label the 3’ and 5’ ends.
CTAATGT
3’GATTACA 5’
The list below contains three methods used for the location or detection of a desired clone. The remaining methods in the list are not generally used for this purpose.
Circle each of the three correct methods below for location or detection of a desired clone.
(No partial credit.)
a. Biochemical identification of the correct species used in a cloning procedure
b. Detection of protein function of the desired gene product
c. Antibody detection of an expressed protein on the surface of a desired cell
d. rRNA sequencing to detect the correct bacterium
e. Detection of a particular gene sequence using a tagged nucleic acid probe
b. Detection of protein function of the desired gene product
c. Antibody detection of an expressed protein on the surface of desired cell
e. Detection of a particular gene sequence using a tagged nucleic acid probe
In two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, separation of proteins is carried out in the first dimension based upon isoelectric point and in the second dimension based upon ___________.
size
The isoelectric point of a peptide is:
the pH at which the charge of the peptide is zero
When a gene cassette is inserted into a wild-type gene, the gene function is typically disrupted by a process known as gene disruption, creating a ________ mutation
knockout mutation
Which of the following is a definition of the “Orthologs” as it relates to microbial genomics
Genes found in one organism that are similar to those found in another, but may differ due to speciation
Pyro-sequencing is a powerful new technique for sequencing DNA.
Which of the following characteristics is true of pyro-sequencing?
detection of added bases is done by measuring light emitted following the incorporation of each new nucleotide
Synthesis of an oligonucleotide with a sequence deviating in at least one base from the wild-type gene followed by replacement of the wild-type gene with the synthetic sequence is known as:
Site-directed Mutagenesis