Microbiology Chapter 17
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:35 AM on 4/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
what antigens does the humoral response identify
extra-cellular
2
New cards
what antigens does the cell-mediated response identify
intra-cellular
3
New cards
what cells are involved in humoral response
b-cells
4
New cards
what cells are involved in cell-mediated response
t-cells
5
New cards
what type of MHC cell is involved in the humoral response
MHC II
6
New cards
what type of MHC cell is involved in the cell-mediated response
MHC I
7
New cards
what is an antigen
substance that causes production of antibodies
8
New cards
all antigens have multiple …
epitopes
9
New cards
what is a hapten
antigens too small to provoke immune responses so they attach to a career molecule
10
New cards
hapten molecules and a carrier molecule combine to make a …
hapten-carrier conjugate
11
New cards
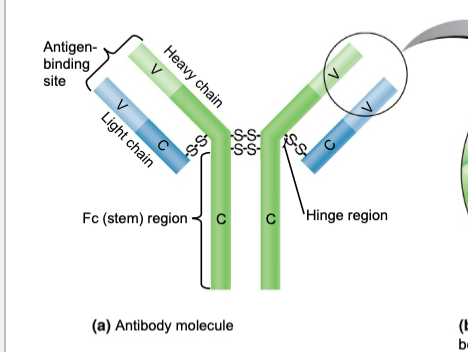
explain the structure of a typical antibody molecule
2 heavy chains held together by 2 disulfide bridges with light chains connected by 1 disulfide bridge
the heavy chains are known to be constant regions and activates complement
the light chains are the variable regions
the heavy chains are known to be constant regions and activates complement
the light chains are the variable regions
12
New cards
what are the five classes of antibodies
IgG
IgM
IgA
IgD
IgE
IgM
IgA
IgD
IgE
13
New cards
which of the 5 antibodies is most abundant
IgG
14
New cards
what is the shape of IgG
monomer

15
New cards
what is 2 known functions of IgG
placental barrier between mother and fetus in immune support
target bacteria and extracellular toxins
target bacteria and extracellular toxins
16
New cards
what shape is IgM
pentamer
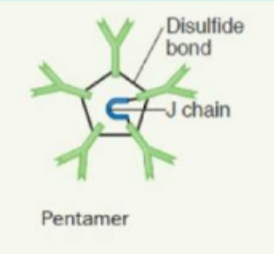
17
New cards
which antibody is first to be made in an immune response
IgM
18
New cards
what is the shape of IgA
dimer
19
New cards
where is IgA found
tears, salvia, mucus
20
New cards
what is the shape of both IgD and IgE
monomers
21
New cards
where are IgD antibodies found
present on surface of B-cells
22
New cards
where are IgE antibodies found
surface on mast cells and basophils
23
New cards
what two responses are IgE antibodies involved in
inflammatory response
anti-parasitic response
anti-parasitic response
24
New cards
what does MHC stand for
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
25
New cards
what are MHC
genes that encode molecules on the cell surface
26
New cards
where are class I MHC found
membranes of nucleated animal cells
27
New cards
what is the role of class I MHC
identify “self”
28
New cards
where are class II MHC found
on the surface of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), including B cells
29
New cards
what is the 3 step process of activation of B cells to produce antibodies
1. recognition
2. communication
3. action
30
New cards
explain the activation of B cells to produce antibodies
B cell internalizes antigen and expresses on MHC II
T-helper cells recognizes antigen and produce cytokines
cytokines activate b-cells to plasma cells for antibody production
T-helper cells recognizes antigen and produce cytokines
cytokines activate b-cells to plasma cells for antibody production
31
New cards
what is a t-dependent antigen
antigen that requires on a t-helper cell to produce antibodies
32
New cards
what is a t-independent antigen
stimulate the B cell without the help of t cells
provoke a weak immune response, usually producing IgM
no memory cells generated
provoke a weak immune response, usually producing IgM
no memory cells generated
33
New cards
what is the result of antigen-antibody interaction
antigen-antibody complex
34
New cards
what does affinity mean
strength of bond
35
New cards
what does antigen-antibody complex protect
the host by tagging foreign molecules or cells for destruction
36
New cards
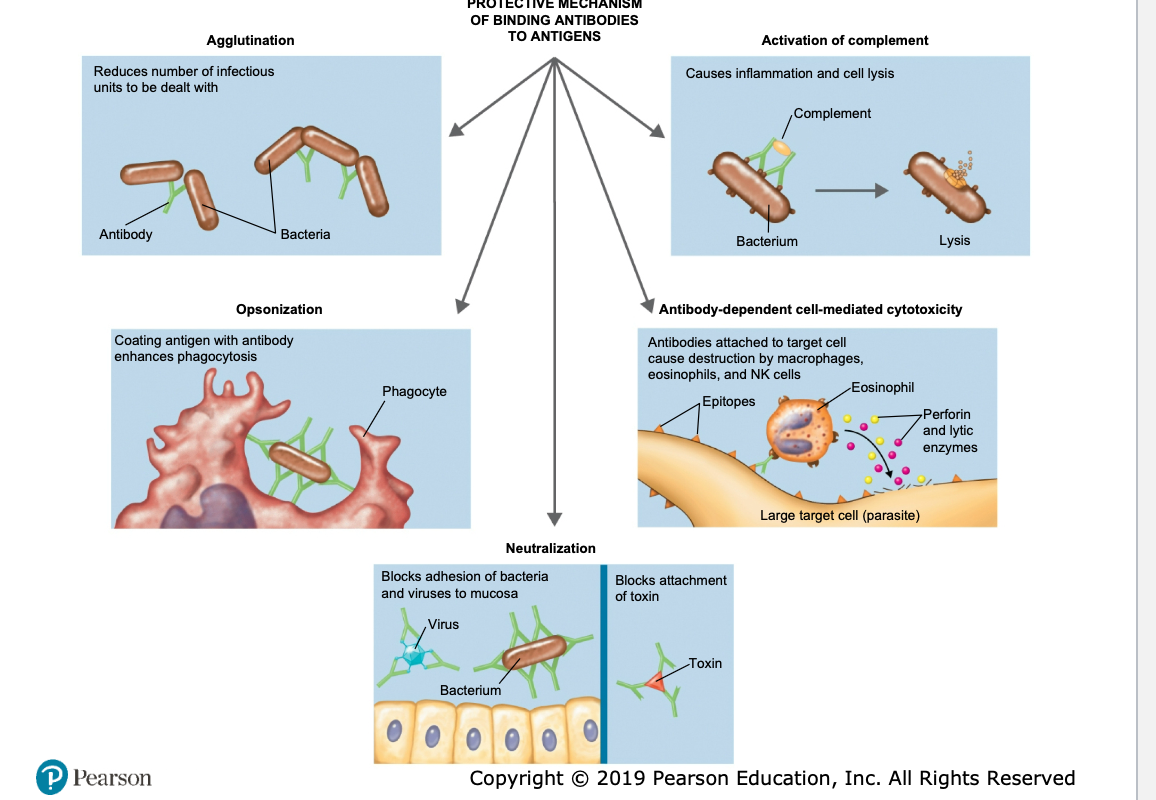
what are the 5 results of antigen-antibody complexes
agglutination
opsonization
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
neutralization
activation of complement system
opsonization
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
neutralization
activation of complement system
37
New cards
what is opsonization
coating antigen with antibody enhances phagocytosis
38
New cards
what is the purpose of neutralization
blocks adhesion
39
New cards
what is the result of activation of complement system
inflammation or cell lysis
40
New cards
pathogens entering the gastrointestinal tract pass through…
microfilm cells (M cells)
41
New cards
where are m cells located over
Peyer’s patches
42
New cards
what is the role of Peyer’s patches
transfer antigens to lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
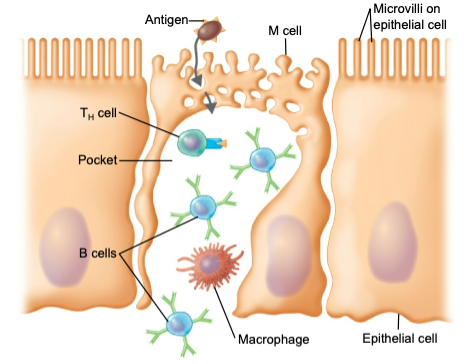
43
New cards
what are the two antigen-presenting cells
1. dendritic cells
2. macrophages
44
New cards
what is the role of dendritic cells
engulf and degrade microbes and display them to T cells
45
New cards
where are dendritic cells found
skin, genital tract, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, mucus membranes, and blood
46
New cards
what is the role of macrophages
activated by cytokines or the ingestion of antigenic material
migrate to the lymph tissue, presenting antigen to T cells
migrate to the lymph tissue, presenting antigen to T cells
47
New cards
what are the 4 classes of t-helper cells
TH1
TH17
TH2
T reg
TH17
TH2
T reg
48
New cards
what class of cytokine does TH1 cell release
Iγ
49
New cards
what class of cytokine does TH17 cell release
IL-17
50
New cards
what class of cytokine does TH2 cell release
IL-4
51
New cards
what is the role of TH1 cells
intracellular cell mediated immunity
52
New cards
what is the role of TH17 cells
extracellular pathogens (humoral)
53
New cards
what is the role of TH2 cells
parasitic immune responses
54
New cards
what is the role of T reg
regulate t-cell activity
55
New cards
what are the 3 stages of cell mediated immunity
1. presentation
2. communication
3. action
56
New cards
explain as a short answer question the stages of cell mediated immunity response
virus infected cell presents antigen on MHC I
TH cells recognizes antigen and releases cytokines
cytokines activate CLT cells which destroy infected cells
TH cells recognizes antigen and releases cytokines
cytokines activate CLT cells which destroy infected cells
57
New cards
what is programmed cell death called
apoptosis
58
New cards
what does apoptosis prevent
spread of infectious viruses into other cells
59
New cards
what two proteins does a CLT cell release
perforin
granzymes
granzymes
60
New cards
natural killer cells do not need what
stimulation by an antigen / t-helper cells releasing cytokines
61
New cards
what do natural killer cells do
kill virus-infected and tumor cells and attach parasites
62
New cards
what cells don’t express MHC class I self antigens
natural killer cells
63
New cards
when is antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity useful
when organisms such as parasites which are too large for ingestion by phagocytic cells must be attacked externally
64
New cards
what is the role of eosinophil
releases cytotoxic cytokines
lytic enzymes and perforin enzymes
lytic enzymes and perforin enzymes
65
New cards
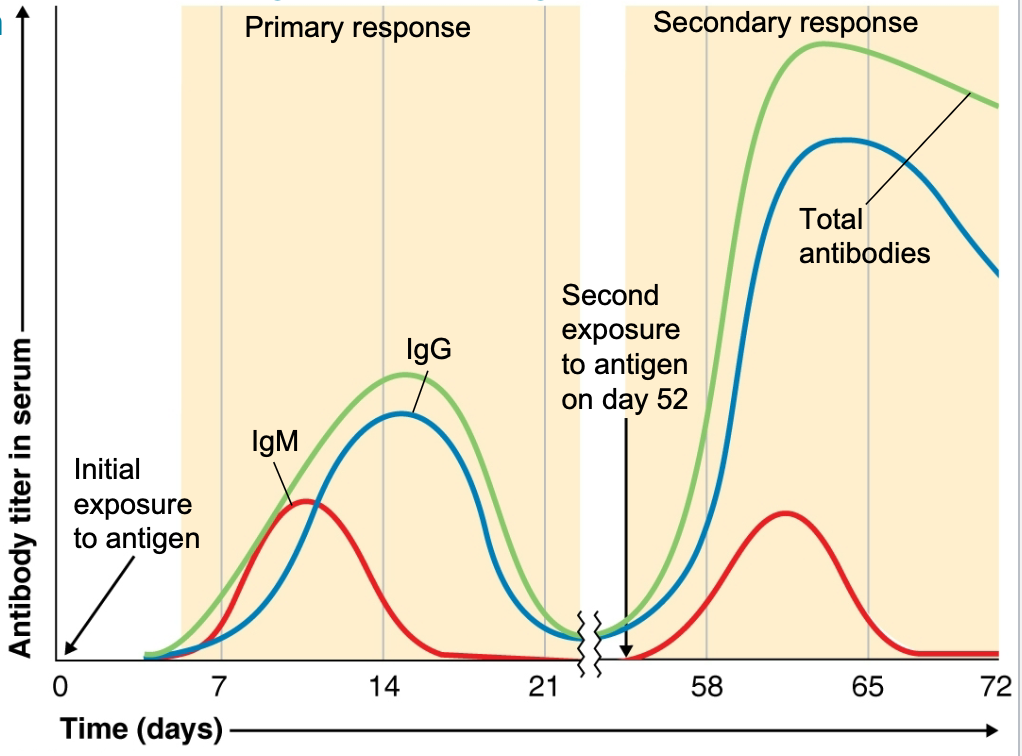
what is a a secondary response
occurs after second exposure to an antigen
66
New cards
what is class switching mean in a secondary response
where initial IgM response shifts to IgG, IgE or IgA occurs
67
New cards
what is naturally acquired active immunity
resulting from infection
68
New cards
what is naturally acquired passive immunity
transplacental or via colostrum
69
New cards
what is artificially acquired active immunity
injection of vaccination
70
New cards
what is artificially acquired passive immunity
injection of antibodies