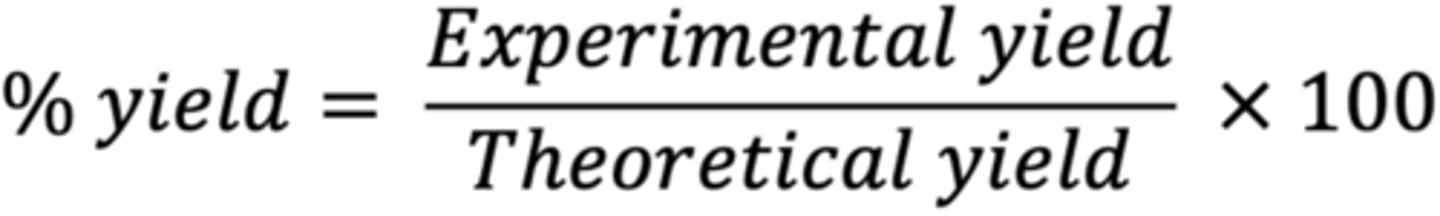Reduction
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
A: 4
B: 1
G: 4
H: 4
J: 1
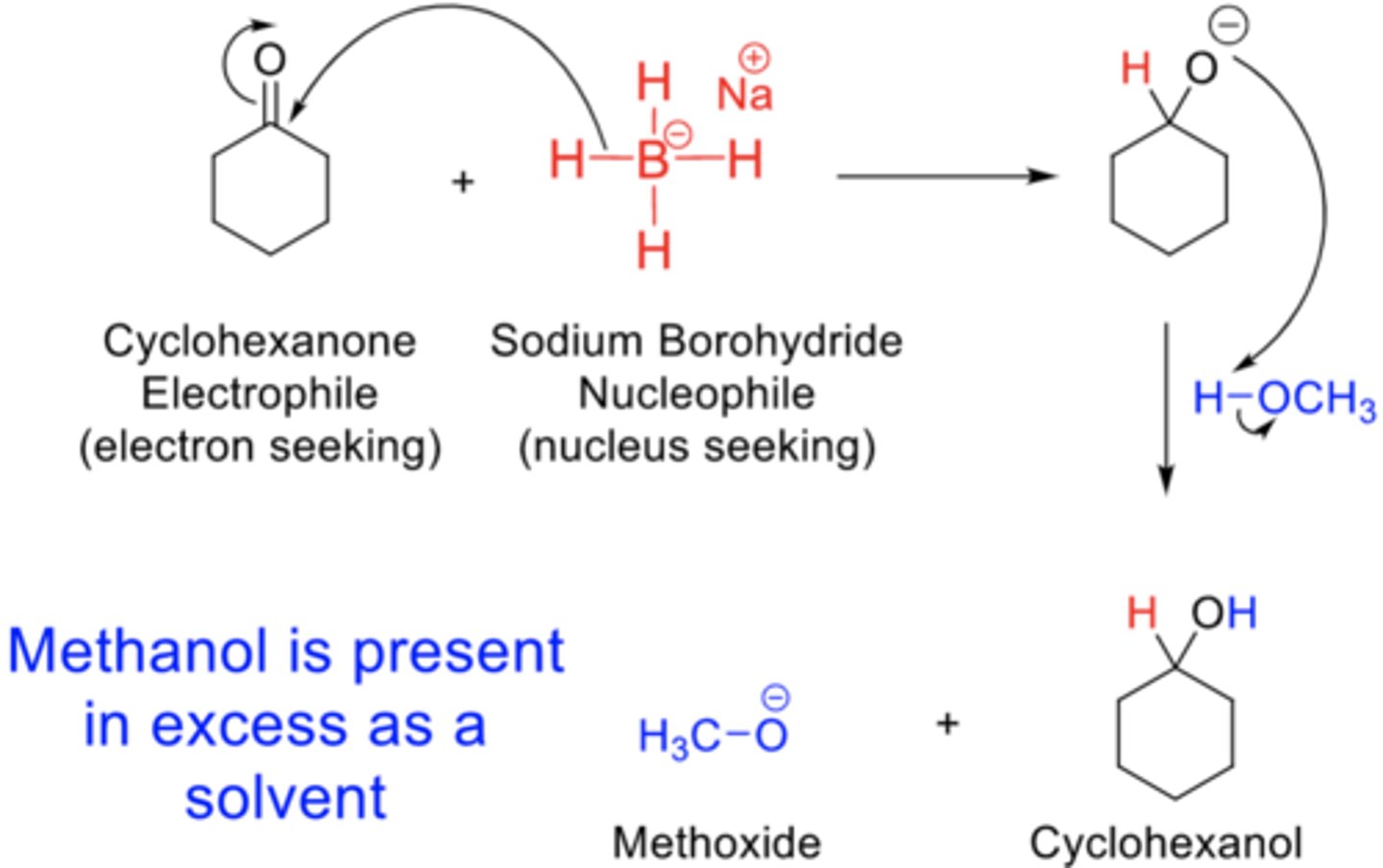
Based on the stoichiometric reaction equation for the reduction of cyclohexanone pictured above, balance the equation by matching the red letters A, B, G, H, and J.
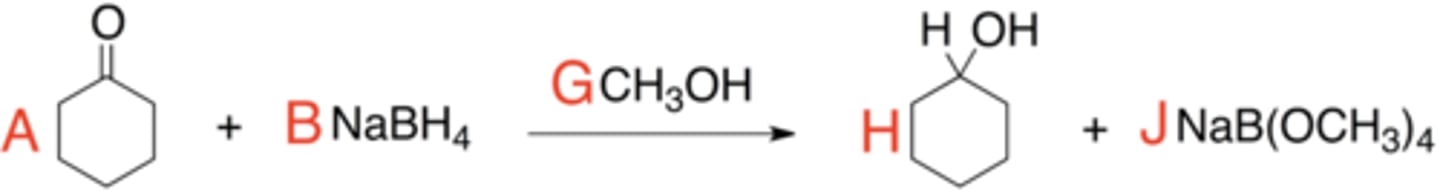
Electrophile: A
Nucleophile: B
Using the reaction equation, identify the nucleophile and electrophile by matching the correct red letter(s) below.
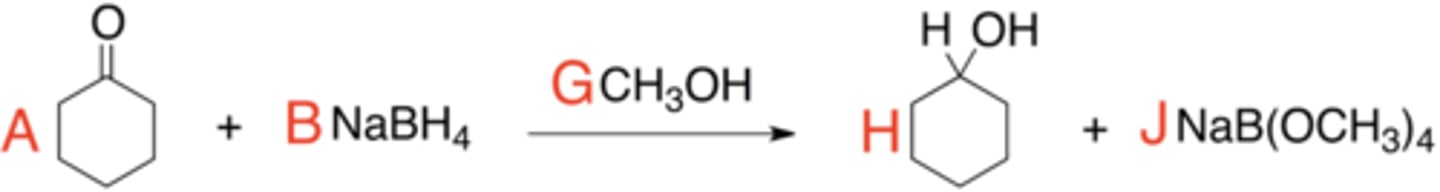
Cyclohexanone
What is the name of this structure?
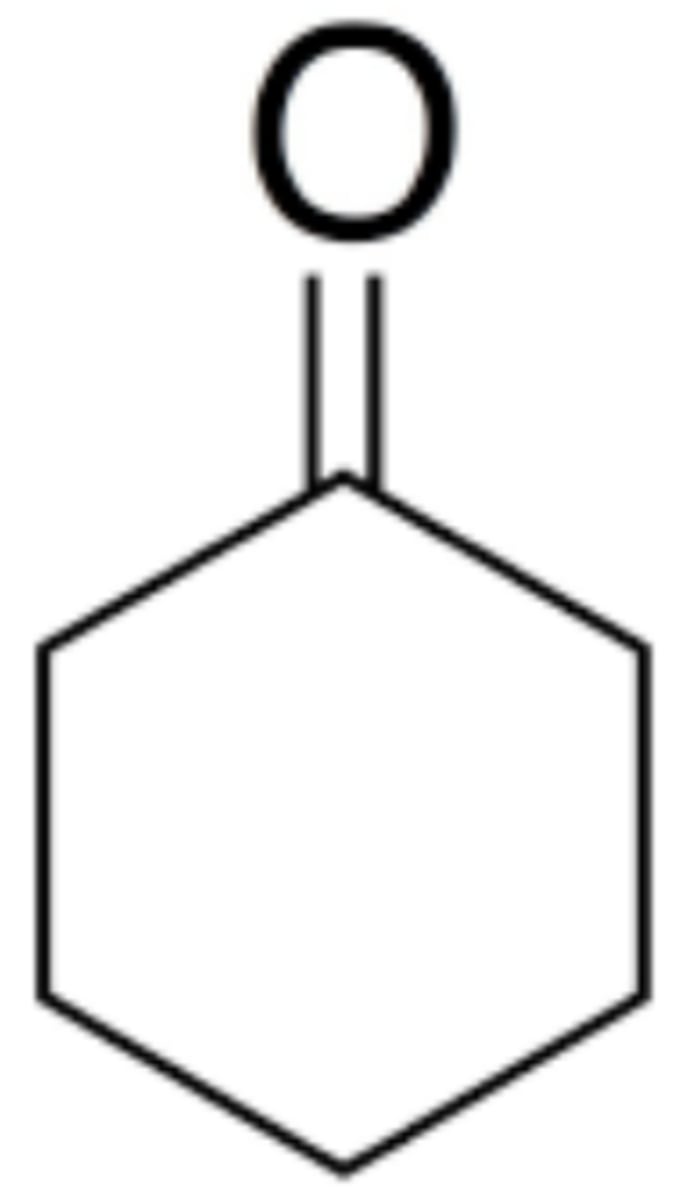
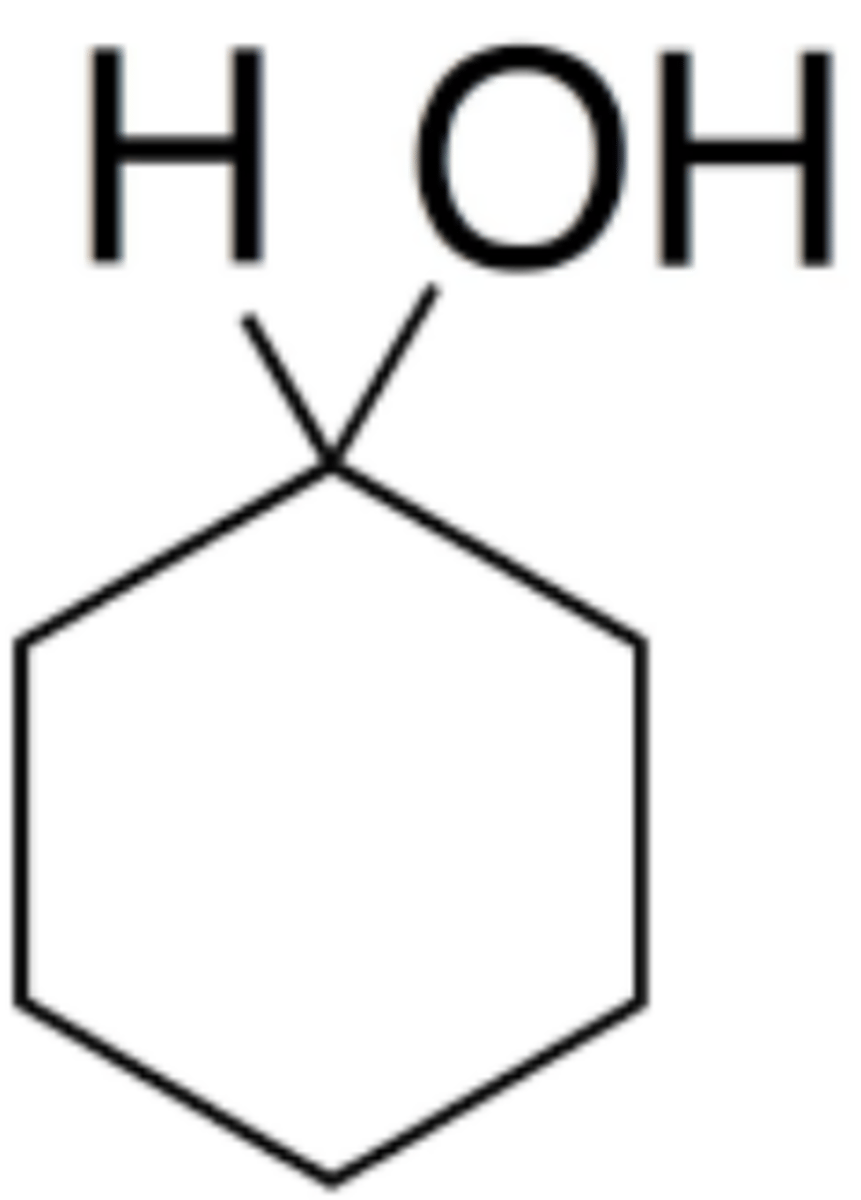
Cyclohexanol
What is the name of this structure?
1650-1725 cm-1
Identify the approximate frequencies in wavenumbers
C=O
2850-3000 cm-1
Identify the approximate frequencies in wavenumbers
sp3 C-H
3300-3600 cm-1
Identify the approximate frequencies in wavenumbers
O-H
1000-1250 cm-1
Identify the approximate frequencies in wavenumbers
C-O
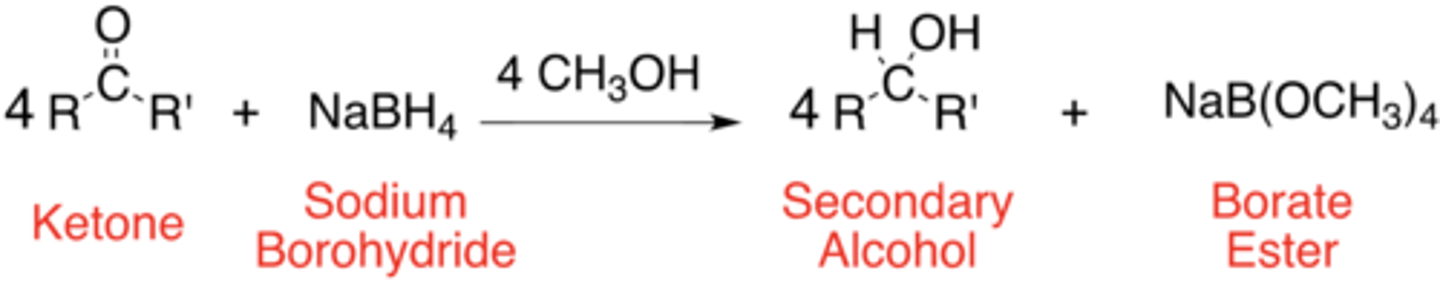
secondary alcohol
The product of reduction of a ketone using sodium borohydride is a ___________
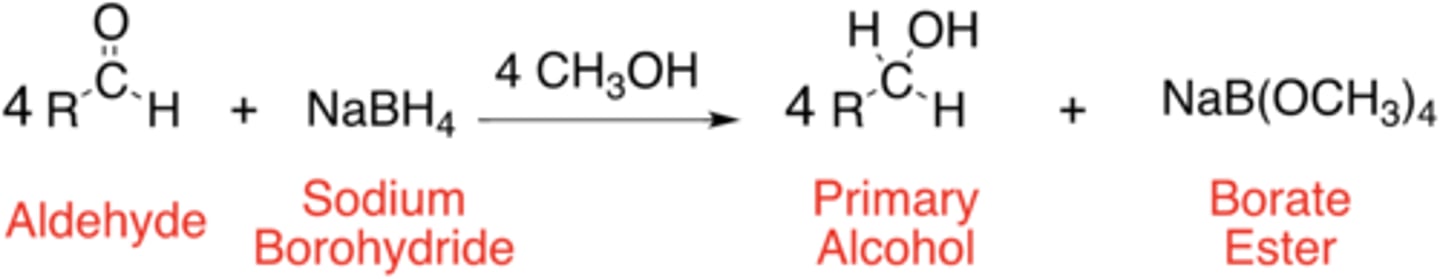
primary alcohol
The product of reduction of an aldehyde using sodium borohydride is a ___________
Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4)
In this experiment, which compound gets oxidized during the reaction?
Nucleophilic addition
What type of reaction is the reduction of cyclohexanone to cyclohexanol?
Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4)
The reducing agent in this lab is _________
Ethanol
What is the name of the organic product obtained in the reaction below?
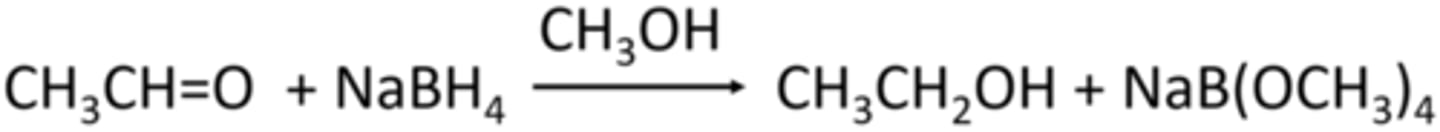
To neutralize the excess sodium borohydride
What is the purpose of adding hydrochloric acid during the workup of this experiment?
LiAlH4
What is a powerful reducing agent (NOT used in the experiment)?
4
How many moles of hydride ions (H:−) can one mole of NaBH4 provide?
The reduction of cyclohexanone requires heat. (T/F)
False
You will record boiling point in this experiment. (T/F)
False
Cyclohexanone
What is the limiting reagent?
In this experiment, reduction occurs when cyclohexanone is reduced by gaining electrons from sodium borohydride, the reducing agent. This serves as an important route for the synthesis of alcohols to occur.
What is reduction (as applied to this experiment)?
Hydride - a hydrogen atom with two electrons that possesses a negative charge (H-).
Proton - a hydrogen atom with no electron that possesses a positive charge (H+)
In the reaction mechanism, the hydride attached to carbon is introduced by the sodium borohydride reagent.
The proton attached to oxygen is introduced by methanol, the protic solvent.
What is the difference between a hydride and a proton?
1) Lithium aluminum hydride (powerful)
2) Sodium borohydride (mild; only works for aldehydes or ketones)
In this experiment, sodium borohydride was used because cyclohexanone contains a ketone functional group which allows it to be reduced by this mild reducing agent.
Name two common reducing agents and explain the benefits and drawbacks of each. Which one was used in this experiment?
Infrared Spectroscopy
Due to the individual structures that each compound possesses, every compound will produce a unique spectrum which can be used to identify them.
What method of analysis was used to determine the success of your reduction? How does that method help in identifying the functional groups in the product?
To neutralize any excess sodium borohydride in the solution
What was the purpose of adding HCl in this experiment?
Drying the organic layer
What is the purpose of using sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) column?
General Reaction of a Ketone -> Secondary Alcohol
General Reaction of a Aldehyde -> Primary Alcohol
Reaction Mechanism
C=O at ~1710 cm-1 (indicates unreacted starting material)
What peak should not be present in the final IR?
O-H at ~3300 cm-1
What peak should be present in the final IR?
Fingerprint Region
The region towards the right side of an IR spectrum, in the region 1500-500 cm-1 is known as the __________
3300cm-1
The peak due to O-H stretching in the IR spectrum of cyclohexanol would appear at ________
Percent Yield