Pharmacology GI
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:39 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
1
New cards
monogastric means
single stomach
2
New cards
what 4 compartments do ruminants have
rumen, reticulum, omasum, and abomasum
3
New cards
nonruminants consume a plant diet but do not have rumens
for example?
for example?
horses
4
New cards
functions or diseases related to the stomach uses the adjective
gastric
5
New cards
functions or diseases related to the small intestines would use the adejctive
enteric
6
New cards
functions or diseases related to the colon would use the adjective
colonic
7
New cards
carnivores are
opportunistic gorgers
8
New cards
what dosage forms are less likely to harm the dog
enteric coating and sustained release
9
New cards
equine GI tract
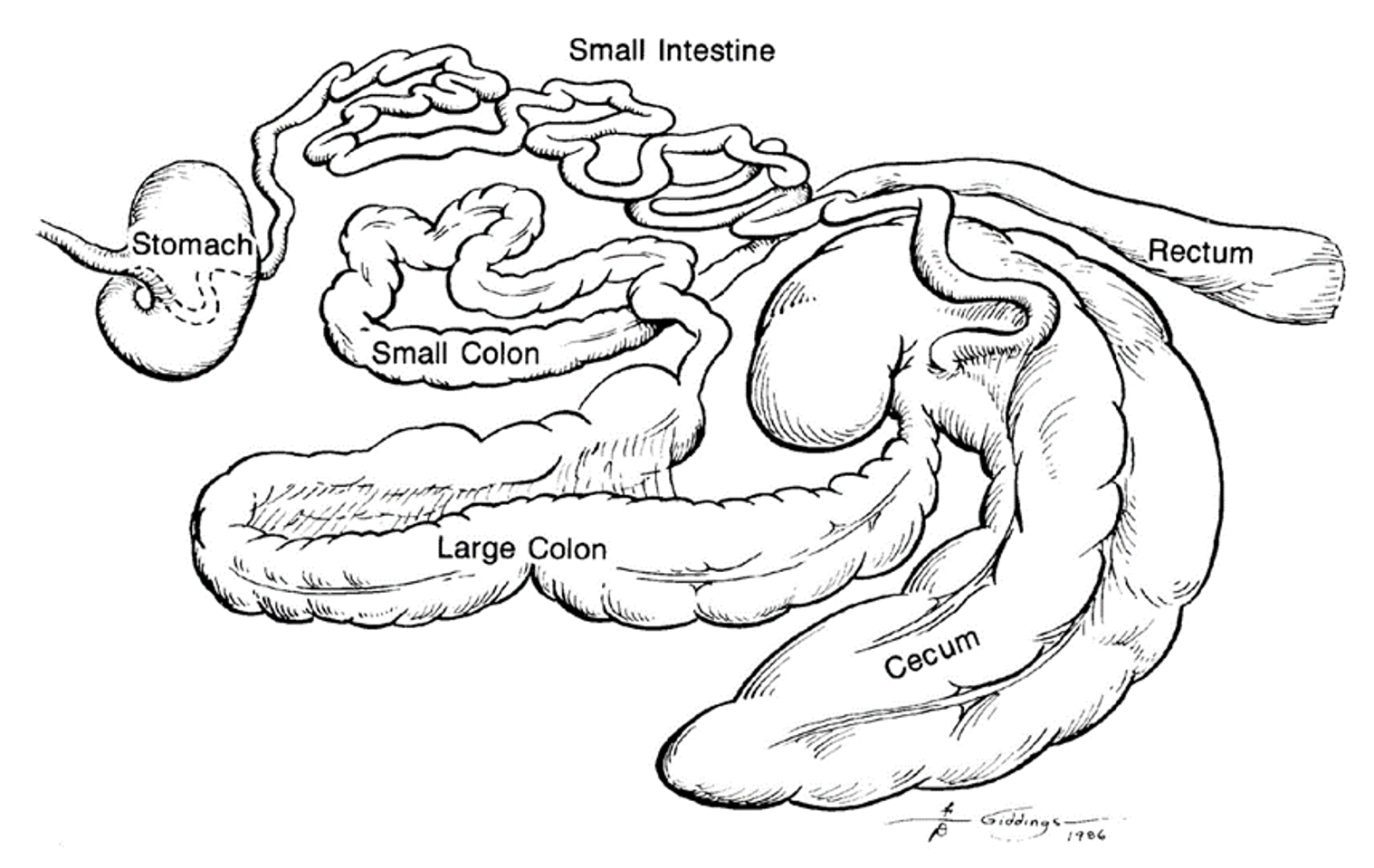
10
New cards
what is dangerous about an empty stomach for a horse
horses constantly secrete gastric acid so if there is no feed in their stomach it attacks the squamous cells instead and causes gastric ulcers
11
New cards
why should we be cautious of NSAIDs?
they can cause gastric ulcers
12
New cards
why can’t horses vomit
they have a very oblique angle at the connection between the esophagus and the stomach
13
New cards
what other animal cannot vomit due to the oblique angle from the esophagus to the stomach?
rabbit
14
New cards
why should we not fast rabbits?
they can get hepatic lipidosis “fatty liver disease”
they can develop hypoglycemia
they can develop hypoglycemia
15
New cards
the nervous system regulates GI function by the
autonomic nervous system
16
New cards
what is the autonomic nervous system
regulates bodily functions without concious thought
17
New cards
what are the two components of the autonomic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
Sympathetic nervous system
18
New cards
what nerve is associated with the parasympathetic nervous system
vagus nerve X
cranial nerves and nerves in the caudal portion of the spinal cord
cranial nerves and nerves in the caudal portion of the spinal cord
19
New cards
what neurotransmitter is associated with parasympathetic nervous system
acetylcholine
20
New cards
what does the parasympathetic nervous system do to the body
decrease HR
constrict pupils
increase digestion
improve blood flow to GI tract
increase gut smooth muscle tone
increase motitility
OVERALL: increase digestion and absorption
constrict pupils
increase digestion
improve blood flow to GI tract
increase gut smooth muscle tone
increase motitility
OVERALL: increase digestion and absorption
21
New cards
what is a name for the parasympathetic system
rest and restore system
22
New cards
what nerves are involved with the sympathetic nervous system
synapse with the chain of ganglia
nerves emerge from the spinal cord at the thoracic and lumbar segments
nerves emerge from the spinal cord at the thoracic and lumbar segments
23
New cards
what is the neurotransmitter associated with the sympathetic nervous system
norepinephrine
24
New cards
the sympathetic nervous system does what to the body
increase heart rate
redirect blood flow from nonessential to essential
decreased perfusion of the intestinal tract
Increased blood pressure
reducing absorption of digested food
decrease gastric and enteric motility
decrease secretion of digestive juices
OVERALL: decreased digestion and absorption of substances
redirect blood flow from nonessential to essential
decreased perfusion of the intestinal tract
Increased blood pressure
reducing absorption of digested food
decrease gastric and enteric motility
decrease secretion of digestive juices
OVERALL: decreased digestion and absorption of substances
25
New cards
what is the term for the sympathetic nervous system
Fight or Flight system
26
New cards
Locally acting hormones and biologically active compounds
prostaglandins E and I
Histamine
H2 receptors
Oxyntic cells
Gastrin
Bacterial toxins
Histamine
H2 receptors
Oxyntic cells
Gastrin
Bacterial toxins
27
New cards
what are prostaglandins
compounds produced by different tissues in the body to exert change in that immediate area
28
New cards
what do prostaglandins E and prostaglandins I do
increase intestinal mucus and fluid production
decrease gastric hydrochloric acid production
increase intestinal motility
improves blood flow
increases bicarbonate buffers in the mucus layer that protects the stomach
decrease gastric hydrochloric acid production
increase intestinal motility
improves blood flow
increases bicarbonate buffers in the mucus layer that protects the stomach
29
New cards
drugs that can block prostaglandins are
anti-inflammatory drugs
30
New cards
what is histamine
released by basophils and mast cells throughout the body during inflammation or allergic reactions
31
New cards
what are H2 receptors
located on parietal cells (oxyntic cells)
produce hydrochloric acid in the stomach
increases gastric acidity
produce hydrochloric acid in the stomach
increases gastric acidity
32
New cards
what do overstimulation of H2 receptors do
produce hyperacidity syndrome
results in gastric or duodenal ulcers
results in gastric or duodenal ulcers
33
New cards
what are oxyntic cells
receptors for neurotransmitter acetylcholine
increase stomach acidity
increase stomach acidity
34
New cards
what is the hormone gastrin
signals relaxation of the stomach
increases stomach acidity
increases stomach acidity
35
New cards
what do bacterial toxins do
stimulate sodium and chloride
causes perfuse diarrhea and dehydration
causes perfuse diarrhea and dehydration
36
New cards
things that influence vomiting reflex
stimulation of neurons from emetic center
stimulation of chemoreceptor trigger zone
inner ear/balance
distention or irritation of the pharynx, stomach, intestines, peritoneum, kidney, gallbladder, or uterus
emotional stimulus or intracranial pressure
stimulation of chemoreceptor trigger zone
inner ear/balance
distention or irritation of the pharynx, stomach, intestines, peritoneum, kidney, gallbladder, or uterus
emotional stimulus or intracranial pressure
37
New cards
stimulation of neurons from the emetic center
contain alpha adrenergic receptors and serotonin receptors
38
New cards
which animal vomits because they are sensitive to sympathetic nervous system stimulation of the alpha receptor
cats
39
New cards
CRTZ stimulation detects ______ in blood and cerebrospinal fluid
toxins
like renal failure, excessive ketones, bacterial toxemia
like renal failure, excessive ketones, bacterial toxemia
40
New cards
distention or irritation of GI organs causes what to the body
causes impulses to travel by vagus nerve to the emetic center
hydrogen peroxide is an example of an irritant
hydrogen peroxide is an example of an irritant
41
New cards
what nerve does inner ear/balance associated with
plays on the 8th cranial nerve, vestibulocochlear nerve
42
New cards
what is contradicted with emetic drugs
comatose and seizures
depressed pharyngeal reflexes
shock or dyspnea
strong acid, alkali, volatile liquids ingested
depressed pharyngeal reflexes
shock or dyspnea
strong acid, alkali, volatile liquids ingested
43
New cards
which animals are emetics not used in
rabbits, horses, and some rodents
44
New cards
how much of the stomach contents do we want emetics to remove
no more than 80%
usually 40-60%
usually 40-60%
45
New cards
what can we give to a dog that hasn’t eaten a lot before giving them hydrogen peroxide to prevent making them sicker
bread
46
New cards
centrally acting drugs
work on the emetic center and CRTZ
stimulates dopamine receptors
includes apomorphine and alpha 2 agonists such as xylazine
stimulates dopamine receptors
includes apomorphine and alpha 2 agonists such as xylazine
47
New cards
locally acting drugs
produce effect by irritating the GI tract
distend the stomach and cause parasympathetic stimulation of the emetic center
distend the stomach and cause parasympathetic stimulation of the emetic center
48
New cards
apomorphine is a ______ acting drug
centrally
49
New cards
apomorphine characteristics
opioid
used primarily to induce vomiting in dogs
stimulate dopamine receptors in CRTZ
poorly absorbed orally
must be compounded
not a DEA controlled substance
usually given SQ, IV, and conjuctival
used primarily to induce vomiting in dogs
stimulate dopamine receptors in CRTZ
poorly absorbed orally
must be compounded
not a DEA controlled substance
usually given SQ, IV, and conjuctival
50
New cards
what drug reverses the CNS depression and respiratory effects that are happen due to apomorphine
Naloxone
51
New cards
which drug stops vomiting
acepromazine
52
New cards
what animal is apomorphine not used in
cats
it causes morphine mania
it causes morphine mania
53
New cards
IV drug dose for apomorphine in the dog
0\.04 mg/kg
almost immediate response
almost immediate response
54
New cards
IM, SC drug dose for apomorphine
0\.08 mg/kg
5-10 min response
5-10 min response
55
New cards
conjunctival dose for apomorphine
0\.25 mg/kg
10-20 min response
10-20 min response
56
New cards
what is very important to know with apomorphine
wear gloves! because it can irritate your skin if it touches your skin
57
New cards
Xylazine is a ____ acting drug
centrally
58
New cards
what is ylazines reversal drug
yohimbine
59
New cards
what is the dose rate for xylazine
0\.05 mg/kg
60
New cards
dexmedetomidine trade name is
Dexdomitor
61
New cards
dexmedetomidine is a ______ acting drug
centrally
62
New cards
characteristics of dexmedetomidine
alpha 2- adrenergic agonist
not classified as emetic
best used in cats not dogs
stimulates alpha 2 receptors in the CRTZ and vomiting center
Yohimbine, atipamezole, and tolazoline is a reversal for sedative effects not emetic
not classified as emetic
best used in cats not dogs
stimulates alpha 2 receptors in the CRTZ and vomiting center
Yohimbine, atipamezole, and tolazoline is a reversal for sedative effects not emetic
63
New cards
hydrogen peroxide is a ______ acting drug
locally
causes irritation of gastric mucosa leading to parasympathetic stimulation of emetic center
causes irritation of gastric mucosa leading to parasympathetic stimulation of emetic center
64
New cards
emetic
what percent hydrogen peroxide do we use
what percent hydrogen peroxide do we use
3%
65
New cards
Emetic drugs
apomorphine
xylazine
dexmedetomidine
hydrogen peroxide
sodium chloride
xylazine
dexmedetomidine
hydrogen peroxide
sodium chloride
66
New cards
emetic
what is the dose rate for hydrogen peroxide
what is the dose rate for hydrogen peroxide
cats and dogs: 1 ml per pound PO
67
New cards
1 tsp is equal to
5 mls
68
New cards
emetic
what is the max dose for hydrogen peroxide
what is the max dose for hydrogen peroxide
dogs: 45 mls
cats: 10 mls
cats: 10 mls
69
New cards
emetic
hydrogen peroxide can cause
hydrogen peroxide can cause
gastric hemorrhage
70
New cards
emetic
we do not use hydrogen peroxide in
we do not use hydrogen peroxide in
cats unless deemed necessary
71
New cards
emetic
sodium chloride may cause
sodium chloride may cause
gastric bleeding. failure to induce vomiting can cause hypernatremia, worsening toxic symptoms
rarely used
rarely used
72
New cards
antiemetic
phenothiazines are antiemetics that act on the
phenothiazines are antiemetics that act on the
dopamine antagonist in CRTZ and emetic center
73
New cards
antiemetic
phenothiazines are _____ antagonist
phenothiazines are _____ antagonist
alpha 1
they block compensatory vasoconstriction in peripheral blood vessels
they block compensatory vasoconstriction in peripheral blood vessels
74
New cards
antiemetic
Phenothiazines are good for ____ because they have an antihistamine effect
Phenothiazines are good for ____ because they have an antihistamine effect
motion sickness
75
New cards
antiemetic
what is important to know about phenothiazines
what is important to know about phenothiazines
antiemetic dose usually is not high enough to prevent vomiting by parasympathetic impulses for GI, peritoneal, visceral stimulation
antiemetic doses generally don’t produce tranquillization
lower seizure threshold in animals prone to seizures
antiemetic doses generally don’t produce tranquillization
lower seizure threshold in animals prone to seizures
76
New cards
antiemetic
phenothiazines: what are motion sickness drugs
phenothiazines: what are motion sickness drugs
acepromazine, chlorpromazine, and prochlorperazine
77
New cards
antiemetic
phenothiazines: acute gastroenteritis drug
phenothiazines: acute gastroenteritis drug
chlorpromazine
78
New cards
antiemetic
antihistamines decrease vestibular apparatus to the emetic center by blocking ________
antihistamines decrease vestibular apparatus to the emetic center by blocking ________
H1 receptors in the CRTZ
79
New cards
dogs have greater H1 receptors on the CRTZ than cats so ______
antihistamines are more effective in dogs
80
New cards
antihistamines are not very effective in vomiting caused by
parasympathetic stimulation
81
New cards
why are antihistamines not effective in cats
the vestibular signals bypass the CRTZ in cats and travel directly to the emetic center
82
New cards
what are the examples of the antihistamines
diphenhydramine and dimenhyrdrinate
83
New cards
antiemetic
anticholinergics: what do they do
anticholinergics: what do they do
block the effect acetylchloline neurotransmitter
known as antiparasympathetic nervous system drugs
known as antiparasympathetic nervous system drugs
84
New cards
antiemetic
anticholinergic drugs: examples
anticholinergic drugs: examples
atropine
aminopentamide (Centrine)
isopropamide
hyoscine
aminopentamide (Centrine)
isopropamide
hyoscine
85
New cards
antiemetic
anticholinergics: it is not recommended for
anticholinergics: it is not recommended for
irritable bowel syndrome patients and excessive stimulation of parasympathetic nervous system patients
86
New cards
antiemetic drugs
metoclopramide: _______ __and__ _________ acting
metoclopramide: _______ __and__ _________ acting
centrally and locally
87
New cards
antiemetic
metoclopramide: what are the centrally acting drug effects
metoclopramide: what are the centrally acting drug effects
dopamine and serotonin receptor antagonist in CRTZ
88
New cards
Metoclopramide is more effective in
dogs
89
New cards
Antiemetic
Metoclopramide: useful in _______ patients
Metoclopramide: useful in _______ patients
chemotherapy-induced and other blood-borne vomiting stimulants
90
New cards
antiemetic
metoclopramide: what is important to know
metoclopramide: what is important to know
it has to be given in a light sensitive line and you should wrap the syringe
if you puncture the vial and you give it over a long period of time, the light can decrease the concentration
if you puncture the vial and you give it over a long period of time, the light can decrease the concentration
91
New cards
antiemetic
serotonin receptor antagonists: examples
serotonin receptor antagonists: examples
Ondansetron (Zofran)
Dolasetron (Anzemet)
Mirtazapine 5-HT3 and 5HT4 receptor antagonist
Dolasetron (Anzemet)
Mirtazapine 5-HT3 and 5HT4 receptor antagonist
92
New cards
antiemetic
serotonin receptor antagonists: Ondansetron (Zofran)
serotonin receptor antagonists: Ondansetron (Zofran)
available as injection and oral
thought to be more effective
few side effects more expensive
0\.5 to 1.0 mg/kg PO or 1.0 mg/kg IV
thought to be more effective
few side effects more expensive
0\.5 to 1.0 mg/kg PO or 1.0 mg/kg IV
93
New cards
Antiemetic
Serotonin receptor antagonists: Dolasetron (anzemet)
Serotonin receptor antagonists: Dolasetron (anzemet)
0\.6 - 1.0 mg/g IV, SC, PO
94
New cards
antiemetic
serotonin receptor antagonists: Mirtazapine effect
serotonin receptor antagonists: Mirtazapine effect
used more for appetite stimulant but also has antiemetic effect
95
New cards
Antiemetic
Cerenia (Maropitant) effect
Cerenia (Maropitant) effect
neurokinin (NK1) receptor antagonist antiemetic
blocks the action of substance P in the CNS
blocks the action of substance P in the CNS
96
New cards
antiemetic
Cerenia (Maropitant)
what is the difference between injections and tablets
Cerenia (Maropitant)
what is the difference between injections and tablets
injection: prevention and treatment of acute vomiting in dogs (extra label in cats)
tablets: prevention of acute vomiting and prevention of motion sickness vomiting in dogs (extra label in cats)
tablets: prevention of acute vomiting and prevention of motion sickness vomiting in dogs (extra label in cats)
97
New cards
antiemetic
Cerenia (Maropitant) technician note
Cerenia (Maropitant) technician note
can burn when given as an injection so anticipate this reaction
98
New cards
Antiemetic
Prokinetic: Cisapride definition
Prokinetic: Cisapride definition
used for GI stasis, reflux esophagitis, megacolon (cats)
must be compounded
must be compounded
99
New cards
Antiemetic
Prokinetic: Cisapride need to know
Prokinetic: Cisapride need to know
can cause cardiotoxicity when used concurrently why macrolide antibiotics and azole antifungals
100
New cards
Antidiarrheal
Intestinal motility modifiers examples
Intestinal motility modifiers examples
Anticholinergic drugs: Aminopentamide (centrine)
Narcotics: Diphenoxylate (Lomotil), Loperamide (Imodium)
Narcotics: Diphenoxylate (Lomotil), Loperamide (Imodium)